Chapter Summary
advertisement
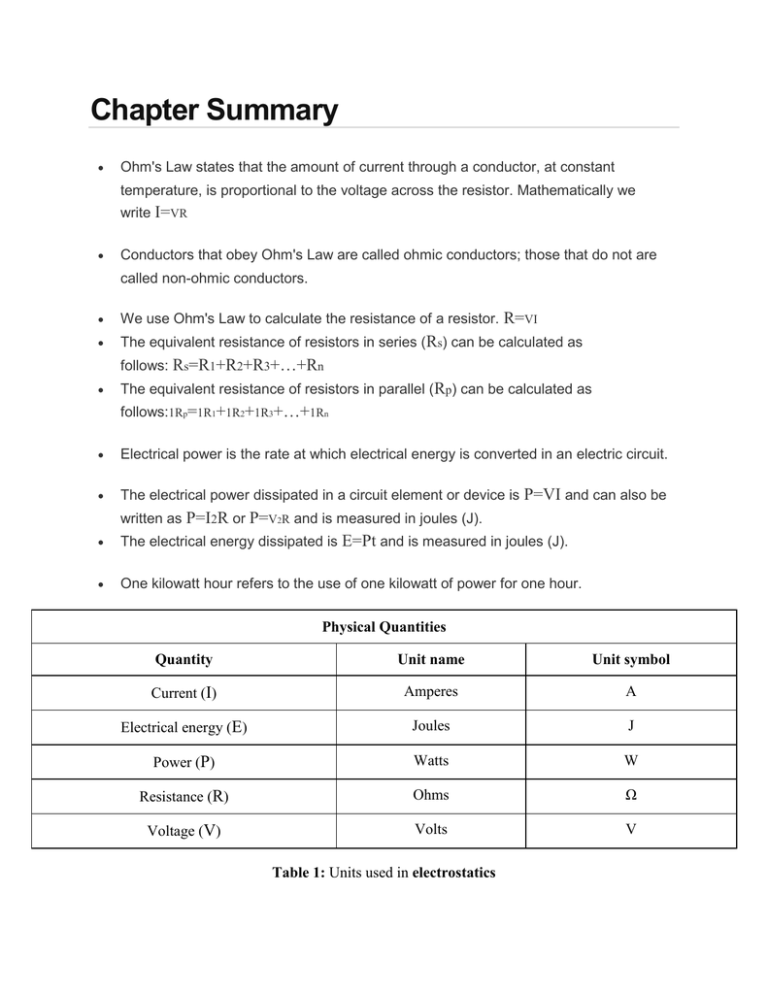
Chapter Summary Ohm's Law states that the amount of current through a conductor, at constant temperature, is proportional to the voltage across the resistor. Mathematically we write I=VR Conductors that obey Ohm's Law are called ohmic conductors; those that do not are called non-ohmic conductors. We use Ohm's Law to calculate the resistance of a resistor. R=VI The equivalent resistance of resistors in series (Rs) can be calculated as follows: Rs=R1+R2+R3+…+Rn The equivalent resistance of resistors in parallel (Rp) can be calculated as follows:1Rp=1R1+1R2+1R3+…+1Rn Electrical power is the rate at which electrical energy is converted in an electric circuit. The electrical power dissipated in a circuit element or device is P=VI and can also be written as P=I2R or P=V2R and is measured in joules (J). The electrical energy dissipated is E=Pt and is measured in joules (J). One kilowatt hour refers to the use of one kilowatt of power for one hour. Physical Quantities Quantity Unit name Unit symbol Current (I) Amperes A Electrical energy (E) Joules J Power (P) Watts W Resistance (R) Ohms Ω Voltage (V) Volts V Table 1: Units used in electrostatics