Application Specification
114-106118
POWER TRIPLE LOCK (PTL)
Connector System
24 AUG 16 Rev F
NOTE
All numerical values are in metric units [with U.S. customary units in brackets]. Dimensions are in millimeters. Unless
otherwise specified, dimensions have a tolerance of ±0.13 and angles have a tolerance of ±2°. Figures and illustrations are
for identification only and are not drawn to scale.
For an overview of the PTL connector system, view the video on www.te.com.
1. INTRODUCTION
This specification covers the requirements for application of POWER TRIPLE LOCK* connector system. The
connector system consists of a plug housing that accepts receptacle contacts and a cap housing that accepts
tab contacts. The housings are available in single, dual, and triple (matrix) rows with 2 to 15 positions having a
centerline spacing of 6 and row-to-row spacing of 8.1 for free-hanging and panel mount applications.
When corresponding with personnel, use the terminology provided in this specification to facilitate inquiries for
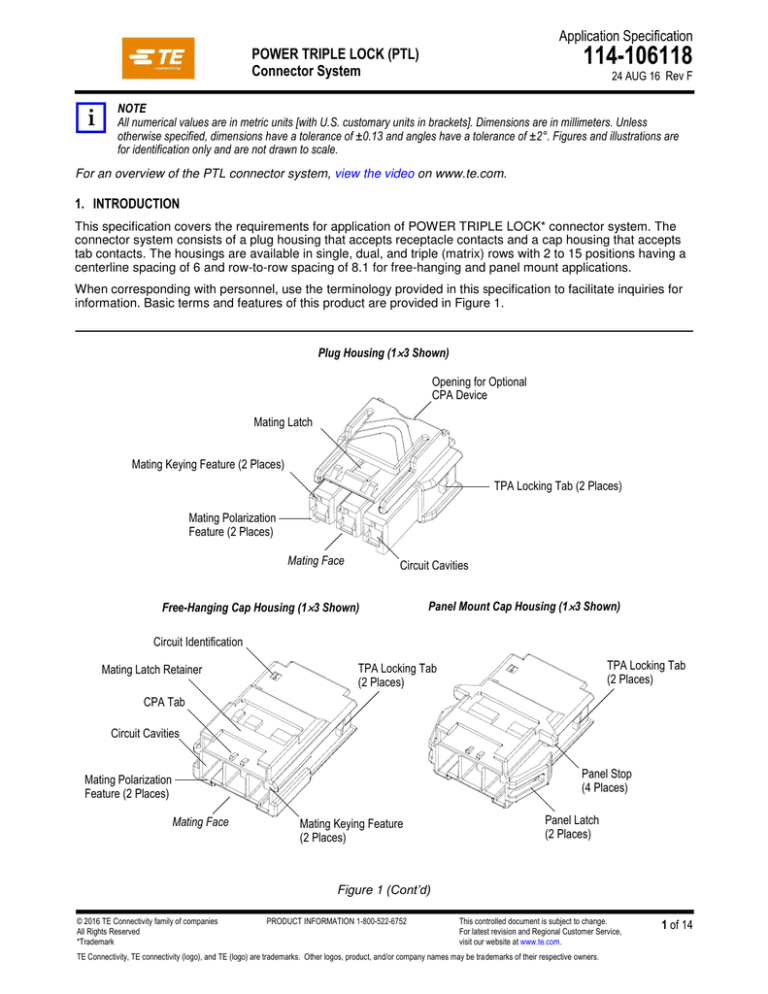
information. Basic terms and features of this product are provided in Figure 1.
Plug Housing (13 Shown)
Opening for Optional
CPA Device
Mating Latch
Mating Keying Feature (2 Places)
TPA Locking Tab (2 Places)
Mating Polarization
Feature (2 Places)
Mating Face
Circuit Cavities
Free-Hanging Cap Housing (13 Shown)
Panel Mount Cap Housing (13 Shown)
Circuit Identification
Mating Latch Retainer
TPA Locking Tab
(2 Places)
TPA Locking Tab
(2 Places)
CPA Tab
Circuit Cavities
Panel Stop
(4 Places)
Mating Polarization
Feature (2 Places)
Mating Face
Mating Keying Feature
(2 Places)
Panel Latch
(2 Places)
Figure 1 (Cont’d)
© 2016 TE Connectivity family of companies
All Rights Reserved
*Trademark
PRODUCT INFORMATION 1-800-522-6752
This controlled document is subject to change.
For latest revision and Regional Customer Service,
visit our website at www.te.com.
TE Connectivity, TE connectivity (logo), and TE (logo) are trademarks. Other logos, product, and/or company names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
1 of 14
114-106118
Optional Connector Position Assurance (CPA) Device
Optional Terminal Position Assurance (TPA) Device
(13 Shown)
Receptacle Contact
Tab Contact
Contact Stabilizer
Contact Stabilizer
Wire Barrel
Wire Barrel
Insulation Barrel
Side Key
Center Key
Mating End
Insulation Barrel
Side Key
Latch Opening
(Not Shown)
Mating End
Latch Opening
(Not Shown)
Figure 1 (End)
The housing features contact cavities each having a keying feature, mating polarization feature, a mating latch
(plug) or mating latch retainer (cap) that provides positive mating. The ribs surrounding the mating latch prevent
wires from becoming caught underneath the latch. The polarization feature prevents mating housings of
different sizes and keying configuration. The housings have a mating keying feature available in 4 configurations
(A, B, C, and D) to prevent mis-mating. The housings are also color coded for 4 available housing materials:
standard, high temperature, glow wire, and hot wire. In addition, the panel mount cap housing features panel
stops and flexible panel latches. In use, the panel latches secure the housing to a panel without the use of
mounting hardware.
Optional connector position assurance (CPA) device and terminal position assurance (TPA) device (also called
locking plate) are available to install onto the housing. These devices provide added security to ensure that the
mated housings remain together and ensure proper contact insertion and retention in the circuit cavities. The
CPA device prevents the plug housing mating latch from being accidentally depressed.
Each contact features a wire barrel, insulation barrel, contact stabilizer, and center key (plug) or side keys (tab).
The underside at the mating end of the contact has a latch opening that engages the housing contact cavity
latch and secures the contact to the housing. The key(s) only allow the contact to be inserted into the
associated housing.
2. REFERENCE MATERIAL
2.1. Revision Summary
Revisions to this application specification include:
Revised Figure 1 drawings to include rectangular stabilizer and proper width after crimping wire
Revised Figure 3. Changed Crimp height for 2238066 and 2238067. Show 0.70mm² wire is #19 AWG.
Revised Figure 3. Changed Detail A dimensions for Rear Bellmouth.
Section 2.4 added a reference to 408-143020 Instruction Sheet
Rev F
2 of 14
114-106118
2.2. Customer Assistance
Reference Product Base Part Number 1971779 (receptacle contact) and 1971238 (tab contact) and Product
Code L755 are representative of PTL connector system. Use of these numbers will identify the product line and
help you to obtain product and tooling information, which can be obtained by visiting www.te.com or by calling
the number at the bottom of page 1.
2.3. Drawings
Customer drawings for product part numbers are available from www.te.com. Information contained in the
customer drawing takes priority. Also available for this product is:
1969744
PTL Receptacle Contact Continuity Test Fixture Design Guidelines
1969745
PTL Tab Contact Continuity Test Fixture Design Guidelines
2.4. Instructional Material
Instructional material that pertains to this product is:
408-10389 Ocean Side-Feed Applicators 2151741-1, 2151742-1, 2151743-1, 2151744-1, 2151745-1,
and 2151746-1
408-32082 SDE-SA Commercial Hand Tools 2217266-1 and 2217267-1
408-32083 SDE-SA Commercial Hand Tool 2217268-1
408-32084 SDE-SA Commercial Hand Tool 2217208-1
408-32184 Guidelines for PTL Receptacle Contact Continuity Test Fixture Design and Probing
408-32187 Guidelines for PTL Tab Contact Continuity Test Fixture Design and Probing
408-32206 Re-Work Procedure for Power Triple Lock (PTL) Connector System
408-143020 Procedure for Vertical Force Testing PTL Cap Housings
409-5128
AMP-O-LECTRIC* Model “K" Terminator Machine 1-471273-2
409-5842
AMP-O-LECTRIC Model “G” Terminating Machines 354500-[ ]
409-10047 AMP 3K* Terminating Machines 1725950-[ ] and AMP 5K* Terminating Machines 1725900-[ ]
409-10099 AMP 3K/40* Terminating Machines 2119683-[ ] and AMP 5K/40* Terminating Machines
2119684-[ ]
2.5. Specifications
Product Specification 108-106118 provides product performance requirements and test information. When
mating single row Caps with POWER TRIPLE LOCK* PC Board headers refer to specifications 108-32090 and
114-32136
3. REQUIREMENTS
3.1. Storage
A. Ultraviolet Light
Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light may deteriorate the chemical composition used in the product
material.
B. Shelf Life
Contacts are shipped on continuous reels and housings are supplied in plastic bags in cartons. The
product should remain in the shipping containers until ready for use to prevent deformation to components.
The product should be used on a first in, first out basis to avoid storage contamination that could
adversely affect performance.
Rev F
3 of 14
114-106118
C. Reels
When using reeled contacts, store coil wound reels horizontally. When storing partial reeled contacts, the
end of the strip should be secured to the flange using a wire tie or similar method.
D. Chemical Exposure
Product must not be stored near any chemical listed below as they may cause stress corrosion cracking in
the material.
Alkalies
Amines
Ammonia
Carbonates
Citrates
Nitrites
Phosphates Citrates
Sulfur Nitrites
Sulfur Compounds
Tartrates
NOTE
Contacts that contain brass must not be stored or used in environments where these chemicals exist.
3.2. Wire Selection and Preparation
The contacts accept 1 stranded copper wire sizes 0.34 to 3.30 mm2 [22 to 12 AWG] or 2 stranded copper wires
sizes 0.34 to 0.89 mm2 [22 to 18 AWG] with an insulation diameter range of 2.00 to 4.25.
Each wire must be stripped to the dimension given in Figure 2.
CAUTION
Care must be taken not to nick, scrape, or cut any part of the wire during the stripping operation.
Note: Not to Scale
4.5±0.3
Strip Length
Figure 2
3.3. Contact Crimp
A. Cutoff Tab and Burr
The cutoff tab is the remaining portion of the carrier strip after the contact is cut from the strip, and the
burr is the result from the cutoff tab shearing. The cutoff tab and burr must not exceed the dimension
given in Figure 3.
B. Wire Barrel Crimp
The crimp applied to the wire barrel portion of the contact is the most compressed area and is most critical
in ensuring optimum electrical and mechanical performance of the crimped contact. The crimp must be
centered on the closed wire barrel. The crimp must result in an “F” crimp where the wire barrel forms a
closed seam with no evidence of loose wire strands or wire strands visible in the seam. The crimp height
and width must be within the dimensions provided in Figure 3.
C. Insulation Barrel Crimp
The crimp applied to the insulation barrel of the contact must result in either an “F” crimp where the
insulation barrel forms a closed seam with no evidence of wire insulation in the seam or an overlap crimp
where the tips of the insulation barrel wraps overlap each other and wrap firmly around the wire insulation
without cutting into the wire insulation. The crimp height and width must be within the dimensions provided
in Figure 3.
Rev F
4 of 14
114-106118
D. Contact Stabilizer
The contact stabilizer must not be crimped or deformed in any way. The width of the stabilizer must be
within the dimension given in Figure 3. Otherwise, in addition to reducing the function of the stabilizer, a
deformed stabilizer will cause the TPA to be ineffective.
E. Wire Barrel Flash
Wire barrel flash is the formation that may appear on both sides of the wire barrel as the result of the
crimping process. It must not exceed the dimension provided in Figure 3.
F. Twist and Roll
There should be no twist or roll of the wire barrel or mating portion of the crimped contact that would
cause overstress or impair usage. See Figure 3.
G. Wire End Extrusion
The wire conductor ends must extend beyond the end of the wire barrel within the dimensions given in
Figure 3.
H. Bellmouths
The front bellmouth and rear bellmouth shall be evident and conform to the dimensions given in Figure 3.
Rev F
5 of 14
114-106118
Wire Barrel Seam (“F” Crimp) Closed with No Wire Strands Showing
Wire Conductors and Insulation
Visible Within This Area
0.1-1.5
Wire End Extrusion
Insulation Barrel
Width (See Table)
No Damage or Distortion
to Mating End
Wire Barrel Crimp Centered
on Closed Wire Barrel
Front Bellmouth 0.3 Max
(Except #22 AWG 0.5 Max)
X
Insulation Barrel Seam
(“F” Crimp Shown) (Refer to Table)
Stabilizer Width at Top:
4.50-5.20
See Detail A
Y
Insulation Barrel Height
(See Table)
X
See Detail B
Stabilizer Must Not Be Crimped
5.0 REF
Y
Detail A
SECTION Y-Y
Detail B
Rear Bellmouth
Wire Size Range (AWG)
0.2 - 0.5 Max
22-12 (1 wire)
0.2 - 0.6 Max
22-18 (2 Wires)
0.13 Max
Burr
0.51 Max
Cutoff Tab
Section X-X
Wire Barrel Crimp Width
(See Table below)
Avoid Twist and Roll
5° Max
0.13 Max
Wire Barrel Flash
Front of Contact
5° Max
Wire Barrel Crimp Height
(See Table)
Wire Barrel
Figure 3 (Cont’d)
Rev F
6 of 14
114-106118
CONTACT CRIMP (“F” Crimp Except Where Indicated OV—Overlap Crimp)
WIRE
USING HAND TOOL
Wire Barrel
NO. OF
SIZE
CONDUCTORS mm² [AWG]
0.34 [22]
0.56 [20]
0.70 [19]
1
0.80 [18]
INSULATION
DIAMETER
RANGE
Width
1.14-2.70
1.40
1.14-2.70
2.00-3.30
2.65-2.95
USING APPLICATOR
Insulation Barrel
Wire Barrel
Height
(Ref)
Width
Height
0.98
2.79
+0.03/-0.06
2.2
1.40
0.98±0.03
2.79
2.2
1.40
1.05±0.03
2.5
1.40
1.05±0.03
2.79
2.5
2.03
1.08
3.56 OV
+0.04/-0.08
2.5
2.03
1.08±0.04
3.56 OV
2.5
2.03
1.21
3.56 OV
+0.04/-0.08
2.7
2.03
1.21±0.04
3.56 OV
3.2
3.56
2.7
‡—‡
Height
‡—‡
Width
2.79
‡—‡
‡—‡
3.56
3.6
1.63±0.05
4.06
3.3
3.05
1.87±0.05
4.83
4.2
—
2.03
1.07±0.04
3.56 OV
4.0
4.7
2.03
1.28±0.04
3.05
4.7
2.29
1.48±0.05
3.3
1.37
3.56 OV
+0.04/-0.08
3.2
2.03
1.37±0.04
2.10 [14]
3.40-3.70
2.29
1.52
+0.05/-0.1
4.06
3.3
2.29
3.30 [12]
3.85-4.25
3.05
1.87
+0.05/-0.1
4.83
4.2
0.34 [22]
2.03 Max
—
—
0.56 [20]
2.40-2.70
2.03
1.28
3.05
+0.04/-0.08
2.29
1.40±0.10
0.80 [18]
2.69-2.99
(0.84 Thickness)
‡ 2.7 ‡
3.2
2.03
2.65-2.95
(0.76 Thickness)
Height
(Ref)
3.56 OV
3.00-3.30
—
Width
‡ 2.03 ‡ ‡ 0.99±0.03 ‡ 3.56 OV ‡
1.27 [16]
2
Insulation Barrel
4.9
3.3
4.9
5.0
5.0
For contacts 1971783 and 1971784. Refer to product customer drawing for minimum cross-sectional area (CMA).
‡ For contacts 2238066 and 2238067. Crimp Height shown applies to all wire types except #18 UL3071, UL3173 and UL3252 which are to
have a Crimp Height =1.07+/-0.05.
Figure 3 (End)
I. Mating End
There must be no damage or distortion to the mating end of the contact. See Figure 3.
J. Wire Location
All conductors must be held firmly inside the wire barrel. No strands can be folded back over the wire
insulation. The wire insulation must be inside the insulation barrel, but must not enter the wire barrel.
The wire conductors and insulation must be visible within the area between the wire barrel and insulation
barrel as shown in Figure 3.
K. Contact Length
The contact length measured from the front of mating end to the back of the contact stabilizer (not
including the carrier strip cutoff tab) must be within the dimensions given in Figure 4.
NOTE
Exceeding the contact length given may prevent the TPA from engaging the housing.
Rev F
7 of 14
114-106118
Contact Length (After Crimping)
16.80+0.50/-0.10
Contact Stabilizer
Receptacle Contact
Datum Line
0.80±0.10 Ref
12.00+0.50/-0.10
Tab Contact
Contact Stabilizer
Datum Line
0.80±0.10 Ref
Figure 4
L. Bend Allowance
The bend allowance between the wire barrel and cable is acceptable within the limits given in Figure 5.
Side-to-Side Bend Allowance
3° Max
Datum Line
Ref
3° Max
Up-and-Down Bend Allowance
1.5° Max
Datum Line
(Bottom of Wire Barrel)
1.5° Max
Ref
Figure 5
3.4. Keying
A. Contact Keying
The key(s) of the contact must match the contact keying feature of the circuit cavity to allow insertion into
the associated housing.
B. Housing Mating Keying Feature
Only plug housings and cap housings with identical keying configuration will mate; for example, key A will
only mate with key A, etc. The TE Connectivity customer drawing provides keying configurations.
Rev F
8 of 14
114-106118
3.5. Contact Insertion and Extraction
A. Insertion
Each contact must be aligned with the appropriate circuit cavity from the wire end of the housing so that
the contact key(s) faces the housing mating latch (plug housing) or latch retainer (cap housing) for the first
and third rows, and for the second row, the contacts must be inverted. The orientation of the contacts
must alternate from row to row. Refer to Figure 6.
The contact must be inserted into the circuit cavity until the contact internal latch locks onto the circuit
cavity locking finger. See Figure 7.
NOTE
Gently pulling on the wire after the contact has been inserted will ensure that the contact is locked.
Note: For clarity, the optional TPA device and contacts
are shown outside of the housing.
Wire End of
Plug Housing
(23 Shown)
Mating Face of
Panel Mount
Cap Housing
(23 Shown)
Circuit
Identification
Side Keys of
Tab Contact
Latch Retainer
Mating
Latch
Optional
CPA
Locking Latch
(2 Places)
Center Key of
Receptacle Contact
Panel Stop
(4 Places)
Circuit
Identification
Optional
TPA
Optional
TPA
Locking Latch
(2 Places)
Panel Latch
(2 Places)
Keying Feature
(2 Places)
TPA Locking
Tab (2 Places)
TPA Locking Tab
(2 Places)
Polarizing Feature
(2 Places)
Figure 6
Cross-Section of Contact Insertion
Contact Internal Latch Locked onto
Circuit Cavity Locking Finger (Ref)
Contact Cavity
Housing Row 1
Wire
Housing Row 2
Note: Contacts in Row 2 are inverted
as compared to rows 1 and 3
Housing Row 3
Figure 7
Rev F
9 of 14
114-106118
B. Extraction
If the optional TPA device is used, the contacts cannot be removed until the TPA is removed from the
housing. Contacts must be removed individually from the housing using the extraction tool given in
Paragraph 5.4 and the instructions for removing a contact given in 408-32206. After extraction, the
contact must be inspected for damage or deformation; if evident, the contact must be replaced.
NOTE
If the contact has been pushed or pulled out of the housing, the rework procedure given in 408-32206 must be followed.
3.6. Optional TPA and CPA Devices
An optional TPA device is available for the plug housing and cap housing, and an optional CPA device is
available for the cap housing.
The following requirements apply for installation (refer to Figure 6):
NOTE
All contacts must be inserted before the devices can be installed into the housing.
— The CPA device must be fully inserted into the opening at the top of the wire end of the plug housing
until the latch engages the plug housing. There should be an audible click. After installation, the tips of the
legs must be visible at the top of the mating face of the plug housing.
— The TPA device must be installed onto the wire end of the housing so that the latches are secure to the
housing TPA locking tabs. There should be an audible click. If the latches do not reach the locking tabs,
this indicates that one or more contacts has not been fully inserted or the contact internal latch has not
locked onto the circuit cavity.
The following requirements apply for removal (refer to Figure 6):
— The CPA device must be removed by depressing the tips of the legs, and sliding the CPA device out of
the housing.
— The TPA device must be removed by lifting each latch so that it clears the housing TPA locking tab,
and pulling the TPA device straight from the housing.
3.7. Continuity Testing
For continuity testing of the housing, design guidelines for the test fixture and pogo pin (probe) must be
considered (refer to Paragraphs 2.3 and 2.4); otherwise damage to the contacts may occur.
All contacts must be inserted and locked into the housing prior to placing the housing into the test fixture.
To avoid deformation to the contact, it is extremely important to ensure specific probe location. See Figure 8.
Plug Housing
Cap Housing
See
Detail
See
Detail
Detail
Circuit
Cavity
Circuit
Cavity
Mating
Face
Mating
Face
Receptacle
Contact
Probe Location:
Bottom Edge of
Receptacle Contact
Probe Location:
Top Edge or
Bottom Edge
of Tab Contact
Tab
Contact
Figure 8
Rev F
10 of 14
114-106118
3.8. Panel Mounting
Recommended panel cutout dimensions are provided on the customer drawing for the specific cap housing.
The cap housing must be inserted through the panel in the same direction that the cutout was punched until the
panel stops sit against the panel so that the flexible panel latches engage the panel. No hardware is required.
See Figure 9.
To remove the cap housing from the panel, both latches must be simultaneously depressed, then the cap
housing must be gently pulled straight out of the panel. If there is no damage to the cap housing, the cap
housing can be re-mounted.
Direction of Punch of Cutout
Panel Cutout
Wire (Ref)
Panel Latch (2 Places) Engaged to Panel
Panel Stop (4 Places) Against Panel
Cap Housing
Figure 9
3.9. Mating and Unmating
The mating face of the cap housing must align with the mating face of the plug housing, then the housing must
be pushed together until the mating latch is secured to the latch retainer. There should be an audible click.
Refer to Figure 6.
To unmate the housings, if used, the CPA device must be withdrawn (but not removed). The plug housing
mating latch must be depressed until it is released from the latch retainer, then the housings can be pulled
straight apart.
CAUTION
These housings are not intended to be used as an electrical interruption device. To avoid degradation to the contacts, there
must be no current flow when unmating.
3.10. Strain Relief and Wire Dress
Wires can be bundled together and supported using cable ties or electrical tape. The wires must remain
perpendicular to the housing and avoid an excessively sharp bend radius. The wire bundle must be at least 76
[3.0] from the back of the housing before bending in any direction. Do not bend unsupported wires as this may
cause strain on the contacts.
3.11. Replacement and Repair
Damaged or defective product must not be used. The housings, contacts, CPA device, and TPA device are not
repairable.
A contact can be removed using the extraction tool given in Paragraph 5.4. The contact can be re-inserted into
the housing provided there has been no deformation or damage to the contact latch opening or housing
internal latch. Refer to Paragraph 3.5.B for contact extraction and insertion information. If the contact has been
pushed or pulled out of the housing, the rework procedure given in 408-32206 must be followed.
4. QUALIFICATION
The POWER TRIPLE LOCK* connector system is Recognized by Underwriters Laboratories Inc. (UL) in File
E28476.
Rev F
11 of 14
114-106118
5. TOOLING
Tooling part numbers and instructional material packaged with the tooling are given in Figure 10.
5.1. Machine (Power Unit)
The machine provides the force required to drive an applicator for crimping the contacts. These machines can
be set up to automatically measure, cut, strip, and terminate the wire.
5.2. Applicator
The applicators are designed to crimp tape-mounted contacts onto pre-stripped wire. The applicators accept
interchangeable die assemblies and must be installed onto a power unit.
SDE-SA Commercial Hand Tools
2217266-1 and 2217267-1 (408-32082)
2217268-1 (408-32083)
2217208-1 (408-32084)
AMP-O-LECTRIC Model “K"
Terminator Machine
1-471273-2 (409-5128)
AMP 3K/40 Terminating Machines
2119683-[ ] and AMP 5K/40
Terminating Machines 2119684-[ ]
(409-10099)
Ocean Side-Feed Applicators
(Atlantic Style and Pacific Style) 2151741-1,
2151742-1, 2151743-1, 2151744-1,
2151745-1, and 2151746-1 (408-10389)
AMP-O-LECTRIC Model “G”
Terminating Machines
354500-[ ] (409-5842)
Extraction Tool 2217301-1
(408-32206)
HDE Applicators
1552992-2, 1552993-2, 1552994-2,
1552995-2, 1552996-2, and 1552511-2
(No Document Available)
Model “T” Terminating Units
694620-[ ] (409-5207) or
458000-4 (409-5289)
PTL Receptacle Contact
Continuity Test Fixture
(Customer Supplied)
(408-32184)
(Design Guidelines
Drawing 1969744)
AMP 3K Terminating Machines
1725950-[ ] and AMP 5K
Terminating Machines
1725900-[ ] (409-10047)
PTL Tab Contact
Continuity Test Fixture
(Customer Supplied)
(408-32187)
(Design Guidelines
Drawing 1969745)
Figure 10 (Cont’d)
Rev F
12 of 14
114-106118
WIRE
NO. OF
CONDUCTORS
APPLICATOR
OCEAN (US/EMEA Only)
HAND TOOL
Pacific Style
HDE
(AP Only)
2151744-1
2-2151744-1
1552995-2
2217267-1
2151744-1
2-2151744-1
1552995-2
2217267-1
SIZE
(mm² [AWG])
INSULATION
DIAMETER RANGE
Atlantic Style
0.34 [22]
1.14-2.70
2.40-2.70
0.56 [20]
0.70 [19]
1
2151743-1
2.00-2.70
2151743-1
2-2151743-1 1552994-2
2-2151743-1 1552994-2
2217208-1
2217208-1
0.80 [18]
2.65-2.95
1.27 [16]
3.00-3.30
2.10 [14]
3.40-3.70
2151742-1
2-2151742-1
1552993-2
2217266-1
3.30 [12]
3.85-4.25
2151741-1
1552992-2
2217268-1
0.34 [22]
2.03 Max
2151743-1
2-2151741-1
0.56 [20]
2.40-2.70
2151746-1
2-2151746-1
1552511-2
2217267-1
2151745-1
2-2151745-1
1552996-2
2217266-1
2
0.80 [18]
2.65-2.95
(0.76 Thickness)
2.69-2.99
(0.84 Thickness)
2-2151743-1 1552994-2
—
For contacts 1971783 and 1971784. Refer to product customer drawing for minimum cross-sectional area (CMA).
This applicator will produce an overlap (OV) crimp on the contact insulation barrel.
Figure 10 (End)
5.3. Hand Tool
The hand tool consists of a tool frame and die assembly that has two crimping chambers. The tool features a
ratchet (crimp height) adjustment wheel and locator.
5.4. Extraction Tool
The extraction tool must be used to remove a contact from the housing. The extraction tool is designed to lift
the contact latch opening from the housing internal latch without causing deformation or damage. Refer to
Paragraph 3.5.B for contact extraction information.
5.5. Test Fixture
The test fixture is used for continuity testing of the housing. The design guidelines drawing provides geometry
and instruction of component assembly. Models are available upon request. For information concerning
continuity testing of the housing, call the number at the bottom of page 1.
Rev F
13 of 14
114-106118
6. VISUAL AID
The illustration below shows a typical application of PTL connector system. This illustration should be used by
production personnel to ensure a correctly applied product. Applications which do not appear correct should be
inspected using the information in the preceding pages of this specification and in the instructional material
shipped with the product or tooling.
FREE-HANGING APPLICATION
PLUG HOUSING LATCH
MUST BE SECURE UNDER
CAP HOUSING RETAINER
THERE MUST BE NO
DAMAGE TO HOUSINGS
IF USED, TIPS OF LEGS OF
CPA MUST BE VISIBLE
WIRES MUST NOT BE
DAMAGED IN ANY WAY
IF USED, CPA MUST BE
FULLY INSERTED INTO
PLUG HOUSING
WIRE CONDUCTORS
MUST NOT BE VISIBLE
WIRE CONDUCTORS
MUST NOT BE VISIBLE
HOUSINGS MUST BE
FULLY SEATED AGAINST
EACH OTHER
IF USED, EACH TPA LATCH
(2 PLACES) MUST BE ENGAGED
WITH TPA LOCKING TAB
IF USED, EACH TPA LATCH (2
PLACES) MUST BE ENGAGED WITH
TPA LOCKING TAB
REQUIREMENTS ABOVE
ALSO APPLY
PANEL-MOUNT APPLICATION
DIRECTION OF
PUNCH OF
CUTOUT
CAP HOUSING MUST BE
MOUNTED IN SAME
DIRECTION AS PUNCH
OF CUTOUT
EACH CAP HOUSING PANEL LATCH
MUST BE ENGAGED TO PANEL
EACH CAP HOUSING PANEL STOP
(4 PLACES) MUST SIT AGAINST PANEL
FIGURE 11. VISUAL AID
Rev F
14 of 14



