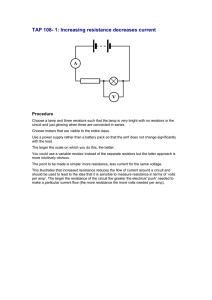
Wizard Test Maker - Physics 12
advertisement
1. What is the current in a circuit if 15 coulombs of electric charge move past a given point in 3 seconds? (1) 5 A (3) 18 A (2) 12 A (4) 45 A 11. A copper wire is part of a complete circuit through which current flows. Which graph best represents the relationship between the wire's length and its resistance? (1) 2. If 60. electrons pass a given point in a conductor in one second, the current in this conductor is (1) 9.6 × 10–18 A (2) 1.6 × 10–19 A (3) 1.6 × 10–20 A (4) 2.7 × 10–21 A 3. An ampere can be defined as one (1) coulomb per second (3) joule per coulomb (2) ohm per volt (4) Newton per coulomb (2) 4. The number of electrons that pass a certain point in a conductor in a given amount of time is defined as (1) potential difference (3) resistance (2) charge (4) electric current 5. An operating lamp draws a current of 0.50 ampere. The amount of charge passing through the lamp in 10. seconds is (1) 0.050 C (3) 5.0 C (2) 2.0 C (4) 20 C 6. A current of 3.0 amperes is flowing in a circuit. How much charge passes a given point in the circuit in 30. seconds? (1) 0.10 C (3) 33 C (2) 10. C (4) 90. C (3) (4) 7. A uniform copper wire has a resistance of 100 ohms. If the wire is cut into 10 equal lengths, the resistance of each piece will be (1) 1 Ω (3) 100 Ω (2) 10 Ω (4) 1,000 Ω 8. A piece of wire has a resistance of 8 ohms. A second piece of wire of the same composition, diameter, and temperature, but one-half as long as the first wire, has a resistance of (1) 8 Ω (3) 16 Ω (2) 2 Ω (4) 4 Ω 9. If the length of a copper wire is reduced by half, then the resistance of the wire will be (1) halved (3) quartered (2) doubled (4) quadrupled 10. To reduce the resistance of a metal conductor one should (1) cool the conductor to a low temperature (2) heat the conductor to a high temperature (3) coat the conductor with an insulator (4) wire the conductor in series with another resistor 12. A manufacturer recommends that the longer the extension cord used with an electric drill, the thicker (heavier gauge) the extension cord should be. This recommendation is made because the resistance of a wire varies (1) directly with length and inversely with cross-sectional area (2) inversely with length and directly with cross-sectional area (3) directly with both length and cross-sectional area (4) inversely with both length and cross-sectional area 13. As the temperature of a coil of copper wire increases, its electrical resistance (1) decreases (3) remains the same (2) increases 14. A copper wire of length L and cross-sectional area A has resistance R. A second copper wire at the same temperature has a length of 2L and a cross-sectional area of 12A. What is the resistance of the second copper wire? (1) R (2) 2R (3) 1 R 2 (4) 4R 15. When an incandescent light bulb is turned on, its thin wire filament heats up quickly. As the temperature of this wire filament increases, its electrical resistance (1) decreases (3) remains the same (2) increases 16. An incandescent light bulb is supplied with a constant potential difference of 120 volts. As the filament of the bulb heats up, its resistance (1) increases and the current through it decreases (2) increases and the current through it increases (3) decreases and the current through it decreases (4) decreases and the current through it increases 17. The diagram below represents a lamp, a 10-volt battery, and a length of nichrome wire connected in series. As the temperature of the nichrome is decreased, the brightness of the lamp will (1) decrease (3) remain the same (2) increase 18. If the cross-sectional area of a fixed length of wire were decreased, the resistance of the wire would (1) decrease (3) remain the same (2) increase 19. A copper wire has a resistance of 200 ohms. A second copper wire with twice the cross-sectional area and the same length would have a resistance of (1) 50Ω (3) 200Ω (2) 100Ω (4) 400Ω 20. One watt is equivalent to one (1) N•m (3) J•s (2) N/m (4) J/s 21. If the diameter of a wire were to increase, its electrical resistance would (1) decrease (3) remain the same (2) increase 22. Which graph below best represents how the resistance (R) of a series of copper wires of uniform length and temperature varies with cross-sectional area (A)? (1) (3) (2) (4) 23. The diagram below shows a circuit in which a copper wire connects points A and B. The electrical resistance between points A and B can be decreased by (1) replacing the wire with a thicker copper wire of the same length (2) replacing the wire with a longer copper wire of the same thickness (3) increasing the temperature of the copper wire (4) increasing the potential difference supplied by the battery 24. If both the cross-sectional area and the length of a metallic conductor were doubled, the resistance of the conductor would be (1) halved (3) unchanged (2) doubled (4) quadrupled 25. A student needs to increase the resistance in a circuit. All that is available for this task is a wide variety of wires of different lengths and thicknesses. To obtain the maximum resistance, the student should replace the wire with one that is (1) shortest and thickest (3) longest and thickest (2) shortest and thinnest (4) longest and thinnest 26. In the diagrams below, l represents a unit length of copper wire and A represents a unit cross-sectional area. Which copper wire has the smallest resistance at room temperature? (1) (2) 30. Which changes would cause the greatest increase in the rate of flow of charge through a conducting wire? (1) increasing the applied potential difference and decreasing the length of wire (2) increasing the applied potential difference and increasing the length of wire (3) decreasing the applied potential difference and decreasing the length of wire (4) decreasing the applied potential difference and increasing the length of wire 31. A potential difference of 12 volts is applied across a circuit which has a 4.0-ohm resistance. What is the magnitude of the current in the circuit? (1) 0.33 A (3) 3.0 A (2) 48 A (4) 4.0 A (3) (4) 32. The ratio of the potential difference across a metallic conductor to the current in the conductor is known as (1) potential drop (3) resistance (2) conductivity (4) electromagnetic force 27. A metal wire has length L and cross-sectional area A. The resistance of the wire is directly proportional to (1) L A (2) L × A (3) A L (4) L + A 28. Which graph best represents the relationship between resistance and length of a copper wire of uniform crosssectional area at constant temperature? 33. The ratio of the potential difference across a conductor to the current in the conductor is called (1) conductivity (3) charge (2) resistance (4) power 34. A 20.-ohm resistor has 40. coulombs passing through it in 5.0 seconds. The potential difference across the resistor is (1) 8.0 V (3) 160 V (2) 100 V (4) 200 V 35. What is the current through a 25 ohm resistor connected to a 5.0 volt power supply? (1) 0.20 A (3) 25 A (2) 5.0 A (4) 30. A 36. In a simple electric circuit, a 110-volt electric heater draws 2.0 amperes of current. The resistance of the heater is (3) 55 Þ (1) 0.018 Þ (2) 28 Þ (4) 220 Þ (1) (3) 37. A 330.-ohm resistor is connected to a 5.00-volt battery. The current through the resistor is (1) 0.152 mA (3) 335 mA (2) 15.2 mA (4) 1650 mA (2) (4) 29. A lamp has a current of 2.0 amperes at 6.0 volts. The resistance of the lamp must be (1) 1.5 Ω (3) 3.0 Ω (2) 6.0 Ω (4) 12 Ω 38. A student needs a 4-ohm resistor to complete a circuit. Only a large quantity of 1-ohm resistors are available. Which of the following should be done to complete the circuit? (1) Connect four 1-ohm resistors in series. (2) Connect four 1-ohm resistors in parallel. (3) Connect two of the 1-ohm resistors in series and two in parallel. (4) Connect only two 1-ohm resistors in parallel. 39. The diagram below represents a simple circuit consisting of a variable resistor, a battery, an ammeter, and a voltmeter. What is the effect of increasing the resistance of the variable resistor from 1000 Þ to 10000 Þ? [Assume constant temperature.] (1) The ammeter reading decreases. (2) The ammeter reading increases. (3) The voltmeter reading decreases. (4) The voltmeter reading increases. 40. The graph below shows the relationship between current and potential difference for four resistors A, B, C, and D. Which resistor has the greatest resistance? (1) A (3) C (2) B (4) D 41. The slope of the line on the graph at the right represents 42. The graph below represents the relationship between the potential difference across a metal conductor and the current through the conductor at a constant temperature. What is the resistance of the conductor? (1) 1 (3) 0.1 (2) 0.01 (4) 10 43. The graph below represents the relationship between the potential difference (V) across a resistor and the current (I) through the resistor. Through which entire interval does the resistor obey Ohm’s law? (1) AB (3) CD (2) BC (4) AD 44. Which circuit segment has an equivalent resistance of 6 ohms? (1) (1) (2) (3) (4) resistance of a material electric field intensity power dissipated in a resistor electrical energy (3) (2) (4) 45. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which represents an electric circuit consisting of four resistors and a 12volt battery. What is the current measured by ammeter A? (1) 0.50 A (2) 2.0 A Base your answers to questions 46 through 49 on the diagram below. The reading of voltmeter V1 is 26 volts, and the reading of ammeter A1 is 2 amperes. 46. What is the total resistance of the circuit? (1) 3/4 Ω (3) 10 Ω (2) 4/3 Ω (4) 13 Ω 47. The reading of ammeter A2 is (1) 6 A (3) 3 A (2) 2 A (4) 52 A 48. What is the reading of voltmeter V2? (1) 52 V (3) 13 V (2) 26 V (4) 8 V (3) 72 A (4) 4.0 A Base your answers to questions 51 and 52 on the diagram below which shows 3 resistors connected to a 15-volt source. 51. If resistor R3 is removed and replaced by a resistor of lower value, the resistance of the circuit will (1) decrease (3) remain the same (2) increase 52. The total power developed in the circuit is (1) 2.5 W (3) 7.5 W (2) 5.0 W (4) 10 W 53. The diagram below shows a circuit with three resistors. 49. If additional resistances are added in series and the applied voltage is kept constant, the reading of voltmeter V3 will (1) decrease (3) remain the same (2) increase 50. Which quantity must be the same for each component in any series circuit? (1) voltage (3) resistance (2) power (4) current What is the resistance of resistor R3? (1) 6.0 Ω (3) 12 Ω (2) 2.0 Ω (4) 4.0 Ω Base your answers to questions 54 and 55 on the diagram below. 54. What is the current in resistor R2? (1) 8.00 A (3) 16.0 A (2) 2.00 A (4) 4.00 A 55. The voltage drop across R1 is (1) 0 V (3) 12.0 V (2) 8.00 V (4) 24.0 V 56. A 5-ohm and a 10-ohm resistor are connected in series. The current in the 5-ohm resistor is 2 amperes. The current in the 10-ohm resistor is (1) 1 A (3) 0.5 A (2) 2 A (4) 8 A 59. The diagram below represents a simple electric circuit. How much charge passes through the resistor in 2.0 seconds? (1) 6.0 C (3) 8.0 C (2) 2.0 C (4) 4.0 C 60. The diagram below shows two resistors connected in series to a 20.-volt battery. 57. When the circuit shown below is completed what will be the reading on the ammeter at B? If the current through the 5.0-ohm resistor is 1.0 ampere, the current through the 15.0-ohm resistor is (1) 1.0 A (3) 3.0 A (2) 0.33 A (4) 1.3 A 61. The diagram below represents an electric circuit. (1) less than the reading at A (2) greater than the reading at A (3) the same as the reading at A 58. The potential difference between points A and B in the electric circuit shown below is 10 volts. What is the voltage between points B and C? (1) 5 V (3) 20 V (2) 10 V (4) 30 V If the voltage between A and B is 10 volts, the voltage between B and C is (1) 5 V (3) 15 V (2) 10 V (4) 20 V Base your answers to questions 62 and 63 on the diagram below. 62. If the potential difference across R1 is V volts, the potential difference across R2 would equal (1) V volts (3) (60 – V) volts (2) ¡ (60 – V) volts (4) (60 + V) volts 63. If the potential difference of the source were decreased, the total heat developed in the circuit would (1) decrease (3) remain the same (2) increase 67. Base your answer to the following question on the circuit diagram below. The voltage drop at R1 will be (1) less than 10 volts (3) 20 volts (2) 10 volts (4) more than 20 volts 68. The diagram below shows three resistors, R1, R2, and R3, connected to a 12-volt battery. 64. As more resistors are added in series across a battery, the potential drop across each resistor (1) decreases (3) remains the same (2) increases 65. What is the voltage of the power supply shown on the below? If voltmeter V1 reads 3 volts and voltmeter V2 reads 4 volts, what is the potential drop across resistor R3? (1) 12 V (3) 0 V (2) 5 V (4) 4 V 69. What must be inserted between points A and B to establish a steady electric current in the incomplete circuit represented in the diagram below? (1) 0.5 volt (2) 10 volts (3) 15 volts (4) 50 volts 66. In the circuit shown below, how many coulombs of charge will pass through resistor R in 2.0 seconds? (1) (2) (3) (4) (1) 36 C (2) 6.0 C (3) 3.0 C (4) 4.0 C switch voltmeter magnetic field source source of potential difference 70. As the number of resistors connected in parallel to a constant voltage source is increased, the potential difference across each resistor (1) decreases (3) remains the same (2) increases 71. Base your answer to the following question on the circuit diagram below which represents a solenoid in series with a variable resistor and a voltage source. 75. A 6.0-ohm lamp requires 0.25 ampere of current to operate. In which circuit below would the lamp operate correctly when switch S is closed? (1) (2) The resistance of the circuit is (1) 72 Ω (3) 12 Ω (2) 24 Ω (4) 8.0 Ω (3) 72. Base your answer to the following question on the circuit diagram below. (4) If switch S1 is open, the reading of ammeter A is (1) 0.50 A (3) 1.5 A (2) 2.0 A (4) 6.0 A Base your answers to questions 76 and 77 on the diagram below which represents three resistors connected in parallel across a 24volt source. The ammeter reads 3.0 amperes. 73. The diagram below represents an electric circuit consisting of a 12-volt battery, a 3.0-ohm resistor, R1, and a variable resistor, R2. 76. The potential difference across R3 is (1) 8.0 V (3) 48 V (2) 24 V (4) 72 V At what value must the variable resistor be set to produce a current of 1.0 ampere through R1? (1) 6.0 Þ (3) 3.0 Þ (2) 9.0 Þ (4) 12 Þ 74. If a 15-ohm resistor is connected in parallel with a 30.-ohm resistor, the equivalent resistance is (1) 15 ohm (3) 10. ohm (2) 2.0 ohm (4) 45 ohm 77. The power supplied to the circuit is (1) 220 W (3) 72 W (2) 190 W (4) 24 W 78. Two identical resistors connected in series have a combined resistance of 8 ohms. When connected in parallel, the resistance of the combination will be (1) 8 Ω (3) 16 Ω (2) 2 Ω (4) 4 Ω Base your answers to questions 79 through 82 on the diagram of the circuit below. 85. In the diagram below, lamps L1 and L2 are connected to a constant voltage power supply. If lamp L1 burns out, the brightness of L2 will (1) decrease (3) remain the same (2) increase 79. If resistance R2 were removed, the potential difference across R1 would (1) decrease (3) remain the same (2) increase 86. In the circuit diagram below, what are the correct readings of voltmeters V1 and V2? 80. The current in ammeter A is (1) 1.0 A (3) 6.0 A (2) 2.0 A (4) 8.0 A 81. If resistance R2 were removed, the current in ammeter A would (1) decrease (3) remain the same (2) increase (1) (2) (3) (4) V1 reads 2.0 V and V2 reads 4.0 V V1 reads 4.0 V and V2 reads 2.0 V V1 reads 3.0 V and V2 reads 3.0 V V1 reads 6.0 V and V2 reads 6.0 V 82. How much energy is used by the 12-ohm resistor in 2 hours? (1) 48 J (2) 3.456 × 105 J Base your answers to questions 87 and 88 on the circuit diagram below. (3) 3.6 × 103 J 4 (4) 1.1 × 10 J 83. Base your answer to the following question on the electric circuit below. The switch is in the open position. 87. If a third resistor is connected in parallel to the circuit, the total resistance will (1) decrease (3) remain the same (2) increase Compared to the potential drop across the 10.-ohm resistor, the potential drop across the 20.-ohm resistor is (1) less (3) the same (2) greater 84. Which is a unit of electrical energy? (1) ampere (3) volt (2) kilowatt-hour (4) watt 88. Compared to the current in ammeter A3, the sum of the currents in A1 and A2 is (1) greater (3) the same (2) less 89. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which represents an electric circuit. The voltmeter, V, reads 12 volts. 93. Which two of the resistor arrangements shown below have equal resistances? The resistance of the circuit is (1) less than 2 Ω (3) between 2 Ω and 6 Ω (2) 2 Ω (4) 6 Ω 90. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which represents an electrical circuit. (1) A and B (2) B and C The equivalent resistance of R1, R2, and R3 is approximately (1) 10 Ω (3) 20 Ω (2) 2 Ω (4) 7 Ω (3) C and D (4) D and A 94. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below. 91. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which represents an electrical circuit. If another resistance were added to the circuit in parallel, the equivalent resistance of the circuit (1) decrease (3) remain the same (2) increase 92. What is the total current in a circuit consisting of six operating 100-watt lamps connected in parallel to a 120volt source? (1) 5 A (3) 600 A (2) 20 A (4) 12 000 A The current reading of ammeter A is (1) 6.0 A (3) 8.0 A (2) 2.0 A (4) 12 A 95. A 10-ohm and a 20-ohm resistor are connected in parallel to a constant voltage source. If the current through the 10ohm resistor is 4 amperes, then the current through the 20ohm resistor is (1) 1 A (3) 8 A (2) 2 A (4) 4 A 96. A high resistance is connected in series with the internal coil of a galvanometer to make (1) a motor (3) a voltmeter (2) an ammeter (4) a generator 97. In which circuit would ammeter A show the greatest current? (3) (1) (2) (4) 98. Three ammeters are located near junction P in a direct current circuit as shown in the diagram below. 101. In the circuit represented below, which switches must be closed to produce a current in conductor AB? If ammeter Al reads 3 amperes and ammeter A2 reads 4 amperes, then what does ammeter A3 read? (1) 5 A (3) 3 A (2) 7 A (4) 8 A Base your answers to questions 99 and 100 on the information below. An electric heater rated at 4,800 watts is operated on 120 volts. 99. If another heater is connected in parallel with the first one and both operate at 120 volts, the current in the first heater will (1) decrease (3) remain the same (2) increase 100. What is the resistance of the heater? (1) 576,000 Ω (3) 3.0 Ω (2) 120 Ω (4) 40. Ω (1) 1 and 4 (2) 2 and 3 (3) 1, 2, and 3 (4) 2, 3, and 4 102. As the number of resistors in a parallel circuit is increased, what happens to the equivalent resistance of the circuit and total current in the circuit? (1) Both equivalent resistance and total current decrease. (2) Both equivalent resistance and total current increase. (3) Equivalent resistance decreases and total current increases. (4) Equivalent resistance increases and total current decreases. 103. Which statement about ammeters and voltmeters is correct? (1) The internal resistance of both meters should be low. (2) Both meters should have a negligible effect on the circuit being measured. (3) The potential drop across both meters should be made as large as possible. (4) The scale range on both meters must be the same. 104. Which circuit shown below could be used to determine the total current and potential difference of a parallel circuit? (1) 109. Which circuit shows the correct use of meters? (A-ammeter, V-voltmeter) (1) (3) (2) (2) (4) 105. Compared to the resistance of the circuit being measured, the internal resistance of a voltmeter is designed to be very high so that the meter will draw (1) no current from the circuit (2) little current from the circuit (3) most of the current from the circuit (4) all the current from the circuit 106. A student uses a voltmeter to measure the potential difference across a circuit resistor. To obtain a correct reading, the student must connect the voltmeter (1) in parallel with the circuit resistor (2) in series with the circuit resistor (3) before connecting the other circuit components (4) after connecting the other circuit components 107. In simple electrical circuits, connecting wires are assumed to have a resistance of (1) one ohm (3) less than zero ohms (2) greater than one ohm (4) zero ohms 108. What quantities may be directly measured by the arrangement of meters shown in the diagram below? (3) (4) 110. A 120-volt toaster is rated at 600 watts. Under normal conditions, the current in the toaster is (1) 0.20 A (3) 10. A (2) 5.0 A (4) 25 A 111. Three resistors of 10 ohms, 20 ohms, and 30 ohms are connected in series to a 120-volt source. The power developed is (1) greatest in the 10 Ω (2) greatest in the 20 Ω resistor (3) greatest in the 30 Ω resistor (4) the same in all three resistors 112. If energy is used in an electric circuit at the rate of 20 joules per second, then the power supplied to the circuit is (1) 5 watts (3) 25 watts (2) 20 watts (4) 100 watts (1) (2) (3) (4) voltage drop across R2 and current through R2 current through R1 and R2 current through R1 and voltage drop across R2 the resistance of Rl and R2 113. To increase the brightness of a desk lamp, a student replaces a 60-watt light bulb with a 100-watt bulb. Compared to the 60-watt bulb, the 100-watt bulb has (1) less resistance and draws more current (2) less resistance and draws less current (3) more resistance and draws more current (4) more resistance and draws less current 114. Which circuit diagram below correctly shows the connection of ammeter A and voltmeter V to measure the current through and potential difference across resistor R? (1) (2) (3) (4) 115. A lamp and an ammeter are connected to a source as shown. What is the electrical energy expended in the lamp in 3.0 seconds? (1) 50. J (3) 50. W (2) 150 J (4) 150 W 116. An electric motor draws 150 amperes of current while operating at 240 volts. What is the power rating of this motor? (1) 1.6 W (2) 3.8 × 102 W (3) 3.6 × 104 W (4) 5.4 × 106 W 117. While operating at 120 volts, an electric toaster has a resistance of 15 ohms. The power used by the toaster is (1) 8.0 W (3) 960 W (2) 120 W (4) 1,800 W 118. A lamp operates at 10 volts and draws a current of .5 ampere for 60 seconds. What power is developed by the lamp? (1) 5 watts (3) 300 watts (2) 30 watts (4) 600 watts 119. An air conditioner is designed to operate at 110 volts and is rated at 2,400 watts. Is it possible to use the air conditioner in a circuit which has a 15-ampere circuit breaker (or fuse) on a 110-volt line? (1) Yes, because the current needed is less than 15 amperes. (2) No, because the voltage required is too high. (3) Yes, because the voltage is lower than that needed. (4) No, because the current needed is greater than 15 amperes. 120. A light bulb operating at 120 volts draws a current of 0.50 ampere for 240 seconds. The power rating of the light bulb is (1) 30. W (3) 75 W (2) 60. W (4) 120 W 121. The potential difference across a 100.-ohm resistor is 4.0 volts. What is the power dissipated in the resistor? (1) 0.16 W (2) 25 W (3) 4.0 × 102 W (4) 4.0 W 122. The same potential difference is applied to two lamps, A and B. The resistance of lamp A is twice the resistance of lamp B. Compared to the power developed by lamp B, the power developed by lamp A is (1) less (3) the same (2) greater 123. As the resistance of a lamp operating at a constant voltage increases, the power dissipated by the lamp (1) decreases (3) remains the same (2) increases 124. As the resistance of a constant-voltage circuit is increased, the power developed in the circuit (1) decreases (3) remains the same (2) increases 125. An electric circuit contains a variable resistor connected to a source of constant voltage. As the resistance of the variable resistor is increased, the power dissipated in the circuit (1) decreases (3) remains the same (2) increases 126. How long must a 100-watt light bulb be used in order to dissipate 1,000 joules of electrical energy? (1) 10 s (3) 1,000 s (2) 100 s (4) 100,000 s 127. The potential difference applied to a circuit element remains constant as the resistance of the element is varied. Which graph best represents the relationship between power (P) and resistance (R) of this element? (1) 130. In the circuit diagram below, two 4.0-ohm resistors are connected to a 16-volt battery as shown. (3) The rate at which electrical energy is expended in this circuit is (1) 8.0 W (3) 32 W (2) 16 W (4) 64 W (2) (4) 131. 128. Identical resistors (R) are connected across the same 12-volt battery. Which circuit uses the greatest power? (1) (2) (3) (4) 129. What is the approximate amount of electrical energy needed to operate a 1,600-watt toaster for 60. seconds? (1) 27 J (3) 1,700 J (2) 1,500 J (4) 96,000 J The circuit represented in the diagram above is a series circuit. The electrical energy expended in resistor R in 2.0 seconds is (1) 20. J (3) 80. J (2) 40. J (4) 120 J 132. A clothes dryer connected to a 240-volt line draws 30. amperes of current for 20. minutes. Approximately how much electrical energy is consumed by the dryer? (1) 4.8 × 103 J (2) 7.2 × 103 J (3) 1.4 × 105 J (4) 8.6 × 106 J 133. An iron has a current of 10. amperes when 120 volts of potential difference is applied for 60. seconds. The total energy dissipated during the 60. seconds is (1) 10. J (3) 1,200 J (2) 20. J (4) 72,000 J 134. An operating 75-watt lamp is connected to a 120-volt outlet. How much electrical energy is used by the lamp in 60. minutes? (1) 4.5 × 103 J (2) 2.7 × 105 J (3) 5.4 × 105 J (4) 3.2 × 107 J 135. How long will it take the immersion heater shown in the diagram below to deliver 1000 joules of heat to the water? (1) 0.2 sec (2) 2 sec (3) 20 sec (4) 200 sec Answer Key [New Exam] 1. 1 31. 3 61. 4 91. 1 2. 1 32. 3 62. 3 92. 1 3. 1 33. 2 63. 1 93. 2 4. 4 34. 3 64. 1 94. 3 5. 3 35. 1 65. 3 95. 2 6. 4 36. 3 66. 2 96. 3 7. 2 37. 2 67. 1 97. 4 8. 4 38. 1 68. 2 98. 2 9. 1 39. 1 69. 4 99. 3 10. 1 40. 1 70. 3 100. 4 11. 2 41. 1 71. 4 101. 1 12. 1 42. 4 72. 2 102. 3 13. 2 43. 2 73. 2 103. 2 14. 4 44. 3 74. 3 104. 4 15. 2 45. 2 75. 4 105. 2 16. 1 46. 4 76. 2 106. 1 17. 2 47. 2 77. 3 107. 4 18. 2 48. 4 78. 2 108. 3 19. 2 49. 1 79. 3 109. 4 20. 4 50. 4 80. 4 110. 2 21. 1 51. 1 81. 1 111. 3 22. 3 52. 3 82. 2 112. 2 23. 1 53. 2 83. 3 113. 1 24. 3 54. 1 84. 2 114. 4 25. 4 55. 2 85. 3 115. 2 26. 3 56. 2 86. 4 116. 3 27. 1 57. 3 87. 1 117. 3 28. 3 58. 3 88. 3 118. 1 29. 3 59. 3 89. 1 119. 4 30. 1 60. 1 90. 2 120. 2 Answer Key [New Exam] 121. 1 122. 1 123. 1 124. 1 125. 1 126. 1 127. 2 128. 4 129. 4 130. 3 131. 3 132. 4 133. 4 134. 2 135. 3