Electrostatics.Notes
advertisement
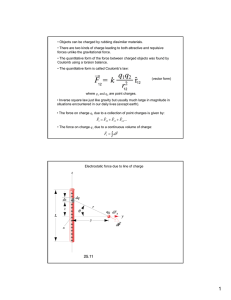
Unit 12 – Electrostatics.Notes Chapter 32. Understand charge & charged particles A particle is charged if it is not neutral/ Electrons are added or removed/ or moving define & examples like charges repel/ opposites attract Atomically, proton (+) is positive/neutron (0) is neutral/electron (-) is negative Conservation of charge When an electron (-) is added to a molecule, the entire molecule feels a net effect, meaning, the molecule is now negatively charged. When an electron (-) is removed, the entire molecule is now positively charged. define & examples Potassium, K (+), needs an electron. Chlorine (-) has an electron to donate. The molecule KCL is neutral because of the sharing of the electron. Coulomb [C] & Coulomb’s Law discuss Coulomb & define A Coulomb is the unit of charge a particle has, [ C ] Particle are far apart and very small, so this force must be strong to have such an influence F = k q q / d2 1 2 concept & formula 2 k = 9 x 10 -9N m2 /C , a constant q = charges on two particles [C] 1q 2 d = distance between particles [m] The force is strong and can be repulsive or attractive! electric force how it is generated by atoms electrostatics define electricity without motion or current conductor & insulator define Conductor: a material that conducts electricity, allows for electron movement, an example is a lightning rod, or your fingertip! There is no electric field inside a conductor Insulator: a bad conductor Induction: charge by proximity grounding define Electrons moving off of or on to a conductor Chapter 33. Understand electric field Cloud of interaction define & draw examples of Lines of force/ from (+) to (-)/can extend forever or onto the closest charge/You must draw at least 6 lines from the point charge On single point charges, the lines go towards (-) or away from the charge Two opposite/attracting charges Two like/repulsive charges Charges between plates, like a battery Electric field strength: E = F (force of the field) / q (a test charge placed in the field) = [N]/[C] = [V]/[m] electric potential analogous to potential energy define, no calculations EP = electrical energy [J] / charge [C] ⇒ measured in Volts/voltage volt & voltage define briefly, as intro to next unit of current Stored energy in the capacitor 1 volt = 1 Joule/1 Coulomb Volta capacitor define How electrical energy is stored. The energy comes from the work required to charge the capacitor. It takes high voltage & has high charge storage.