Audit Energy Home - Saskatchewan Environmental Society

ENERGY AUDIT 8
HOME ENERGY AUDIT
BACKGROUND:
Whenever we use electricity there are two main costs. One is that the electricity costs us money, and the other is that there are CO2 emissions created during the production of electricity. (Remember that about 50% of Saskatchewan’s electricity is produced by burning coal.)
PROCEDURE:
1.
Use the appliance table to calculate the approximate cost per month to operate electrical devices/appliances in the home. Watts determine the amount of electricity an item uses. One kilowatt equals 1000 watts.
Kilowatt hours (kWh) are the units used by the electric meter to measure the electricity consumed. One kilowatt hour is the electricity taken from an electrical circuit for one hour.
To calculate monthly electrical consumption of electrical devices/appliances:
•
Determine the wattage of the device or appliance
•
Divide the wattage by 1000 to determine kilowatts
•
Estimate the daily usage in hours of the device or appliance
•
Multiply daily usage by 30 days to calculate monthly usage
•
Multiply monthly usage by kilowatts to calculate kWh per month
Saskatchewan Environmental Society ©2012 ENERGY Home Energy Audit
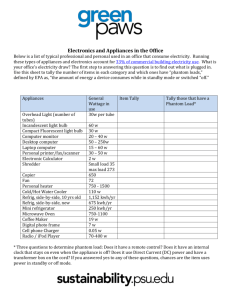
APPLIANCE TABLE
Appliances Wattage kW
(divide by 1000)
1420
700
87
47
140
70
1.42
.7
.087
.047
.14
.07
Use per day
24
1 kWh per month(kW x use per day x 30)
Cost per kWh
($.10)
.10
.10
.10
Cost per month
(kWh per month x
$.10)
Dishwasher
Standard
Energy star
Refrigerator
Standard
Energy star
TV
Standard
LCD 26”
Energy star
LCD 26”
Hair Dryer
Computer
CPU/Monitor
Standard
Energy star
Lap Top
Standard
Energy star
1000
119
51
19
9
1
.119
.051
.019
.009
0.1 .10
.10
.10
Video Game
System
Playstation
3tm
Nintendo
Wiitm
197
19
.197
.019
.10 click on “cost calculator”.
Information in this table was taken from the SaskPower web site.
To find more electrical devices/appliances, go to www.saskpower.com
and
Saskatchewan Environmental Society ©2012 ENERGY Home Energy Audit
2.
Are any of these appliances/devices energy star rated? Which ones? Are they turned off or unplugged when not in use?
3.
Using the KWh from each of your appliances, calculate how much CO2 each one is producing. Use this calculation:
KWh x .83 = kgCO2.
4.
Circle the types of lighting found in your home. (You can calculate the electricity used by looking at the wattage of each bulb. E.g. A 15W compact fluorescent bulb puts off as much light as a 60W incandescent bulb, but uses 1/4 of the electricity).
Compact Fluorescent Fluorescent Incandescent Halogen
5.
What was the most common type of lighting found in your home?
6.
What temperature is the furnace thermostat set to?
•
During winter months daylight hours?
•
During winter months night time hours?
7.
Does your family use timers for any electrical items or thermostats in your home?
8.
Are the furnace and hot water tank high efficiency?
Are hot water pipes wrapped in insulation?
9.
Can you feel drafts around doors and windows? Which ones?
10.
What could your family do to be more energy efficient?
Saskatchewan Environmental Society ©2012 ENERGY Home Energy Audit
CURRICULUM CONNECTIONS
Grade 4 Science: Outcome: LI4.3 Assess personal, societal, and environmental impacts of light-related technological innovations including optical devices.
Social Studies: Outcome: RW4.1 Analyze the strategies Saskatchewan people have developed to meet the challenges presented by the natural environment.
Grade 5 Social Studies: Outcome RW5.1 Explain the importance of sustainable management of the environment to Canada’s future.
English Language Arts:
Outcomes CC5.1 Compose and create a range of visual, multimedia, oral, and written texts that explore and express personal thoughts shaped through inquiry.
CC5.4 Use a writing process to experiment with and produce multi- paragraph narrative and persuasive compositions that clearly develop topic and provide transitions for the reader.
AR5.1 Identify strengths in viewing, listening, reading, speaking, writing, and other forms of representing.
AR5.2 Set goals to enhance the development and improvement of the skills and strategies in viewing, listening, reading, speaking, writing, and other forms of representing and take steps to achieve goals.
Grade 6 Science: Outcome: EL6.1
Assess personal, societal, economic, and environmental impacts of electricity use in Saskatchewan and propose action to reduce those impacts.
Grade 7 Science: Outcome: HT7.1
Assess the impact of past and current heating and cooling technologies related to food, clothing, and shelter on self, society, and the environment.
Grade 10 Science: Outcome: WD5 Identify consequences of global climate change
Grade 12 Physics: Electricity 5 Explain how the power rating on electrical appliances can assist a person in making wise decisions as a consumer.
Design-Housing 30: Module10 Students examine their own home, school or classroom to determine ways to make them more energy efficient.
Construct/Fabricate Module 19 To be aware of the economic and environmental advantages of a well insulated structure.
Saskatchewan Environmental Society ©2012 ENERGY Home Energy Audit