chapter 19 test

CHAPTER 19 TEST
Directions: Show work on problems. Choose correct answer when available and place next to the question number.
Current Electricity 19:
I = Q/t V = W/Q E = VIt E = QV
USE THE ABOVE DIAGRAM FOR THIS QUESTION AND THE FOLLOWING 2
QUESTIONS.
1. What is the value of the current in the circuit?
A. 2.5 mA B. 3.0 mA C. 25 mA D. 250 mA
2.
3.
What does the symbol mA stand for?
A. mega-amperes B. milliamperes C. microamperes D. meteramperes
If you were not sure what current is in your circuit, which lead hookup would you use?
A. positive to 5, negative to +
B. positive to 50, negative to +
C. positive to +, negative to 50
D. positive to +, negative to 5
**********************************************************************
USE THE ABOVE DIAGRAM TO ANSWER THIS QUESTION AND THE
FOLLOWING 4 QUESTIONS.
4. What does this meter measure?
A. current C. charge
B. resistance D. electrical potential difference
5.
6.
What is the voltage across the resistor in the diagram?
A. 120 V B. 4.0 V C. 40 V D. 12.0 V
7.
If the negative lead were attached to the 5 V terminal, and the needle is in the same position, what is the correct reading?
A. 120 V B. 4.0 V C. 40 V D. 12.0 V
8.
If the negative lead were attached to the 50 V terminal, and the needle is in the same position, what is the correct reading?
A. 120 V B. 4.0 V C. 40 V D. 12.0 V
What would the meter reading be if the positive wire were hooked to the 5 terminal on the meter and the negative wire were hooked to the 150 terminal on the meter, and the needle is in the same position?
A. 145 V B. 0 V C. 30 V D. 1.0 V
**********************************************************************
USE THE ABOVE DIAGRAM TO ANSWER THIS QUESTION AND THE
FOLLOWING 3 QUESTIONS.
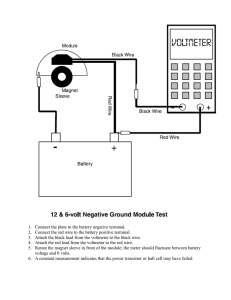
9. Where is the positive contact of the battery?
A. point A B. point B C. point C D. point D
10. Where is the negative contact of the battery?
A. point A B. point B C. point C D. point D
11. What is the direction of electron flow through the light bulb?
A. from the negative contact towards the positive contact
B. from the positive contact towards the negative contact
C. from point B to point D inside the battery
D. from point D to point B inside the battery
12. How does the electric current cause the bulb to light up?
A. Mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy.
B. Electrical energy is converted into nuclear energy.
C. Chemical energy is converted into electrical energy, which is then converted into heat and light.
D. The light bulb has no resistance.
13. Electric current is composed of
A. static electricity. C. electric potential.
B. moving electric charges. D. potential difference.
14. The particles that compose electric current in metals are
A. electrons. B. protons. C. neutrons. D. atoms.
15. Electric current is measured in
A. coulombs. B. amperes. C. volts. D. ohms.
16. An ampere is the amount of electric current that flows when
A. 3 m move through a conductor in 1 s.
B. 10 v/h are produced by parallel conductors.
C. 1 C of charge moves past a point in 1 s.
D. 10 electrons per millisecond move through a cylindrical wire.
17. What French scientist suggested that tiny electric currents existed in the atom long before the existence of the electron was proposed?
A. Ampere B. Coulomb C. Oersted D. Ohm
18. To measure electric current, which of the following is correct?
A. Only half of the current needs to travel through the ammeter.
B. Only a third of the current needs to travel through the ammeter.
C. All of the current must go through the ammeter.
D. The conductor does not have to be broken for the ammeter to work.
19. An ammeter should be connected so that
A. electrons enter through the positive terminal and leave by the negative terminal.
B. electrons enter through the negative terminal and leave by the positive terminal.
C. protons enter through the negative terminal and leave by the positive terminal.
D. Neutrons enter through the negative terminal and leave by the positive terminal.
20. Which color is used to indicate positive polarity on electrical instruments?
A. red B. black C. green D. white
21. Electric potential difference is
A. work per unit of charge. C. voltage per unit of time.
B. work per unit of current. D. work per unit of time.
22. Electric potential difference is measured in
A. amperes. B. ohms. C. volts. D. coulombs.
23. The electric energy lost or work done by a charge, Q, going through a potential difference is equal to
A. charge times potential difference.
B. charge divided by potential difference.
C. potential difference divided by charge.
D. charge raised to the power of potential difference.
24. To prevent more current from going through a conductor than it can handle, what device should be used?
A. a quartz crystal C. a dry cell
B. a circuit-breaker D. a copper penny
25. In which situation will a 15 A fuse "blow"?
A. when the current is less than 15 A
B. when the current is greater than 15 A
C. when the potential difference is 120 V
D. when a 6 gauge wire is used in the circuit
26. What is the temperature of the tungsten filament in an incandescent light bulb?
A. 25øC B. 100øC C. 1000øC D. 3000øC
27. In a neon light, electrons move through
A. a solid. B. a gas. C. a liquid. D. carbon.
28. What general term describes devices that use electric energy?
A. potential difference B. current C. loads D. sources
29. What general term describes devices that produce electric energy?
A. sources B. loads C. potential difference D. current
30. When electrons enter a motor, they pass through a coil of wire and use their energy to create
A. an electric field. C. a magnetic field.
B. a gravitational field. D. a force field.
31. How much current passes through an electric toaster if it takes 945 C of charge to toast two slices of bread in 2.0 min?
A. 473 A B. 0.132 A C. 7.9 A D. 1890 A
32. A light bulb with a current of 0.955 A is lit for 5.00 min. How much electric charge passes through the filament of the bulb?
A. 287 C B. 4.78 C C. 0.191 C D. 5.24 C
33. An electric clothes dryer uses a current of 30.0 A for 12 min to dry a load of clothes. This process gives off 5184 kJ of heat energy. What is the potential difference across the dryer?
A. 240 V B. 120 V C. 12 V D. 14 V
34. What does the product of volts times amperes equal?
A. resistance B. watts C. joules/coulomb D. amperes/joules
35. What amount of energy does a hair dryer use if it has 785 C of charge passing through it with a potential difference of 120 V?
A. 6.54 J B. 1.52 kJ C. 0.152 J D. 94.2 kJ
36. What two materials would make good electrodes for a voltaic cell?
A. distilled water and gold
B. hydrogen gas and dilute sulfuric acid
C. copper and zinc
D. two strips of copper metal in distilled water
37. Which of the following is NOT an advantage that dry cells have over voltaic cells?
A. Dry cells are almost unbreakable.
B. Dry cells are easier to handle than voltaic cells.
C. Dry cells are easier to connect together.
D. Dry cells have more historic significance than voltaic cells.
38. When do we consider a dry cell to be "dead"?
A. when it can no longer separate charge and produce a potential difference
B. when a 1.5 V battery has a potential difference of only 1.4 V
C. when the dry cell can no longer produce neutrons
D. when the dry cell can no longer produce a magnetic field
39. Which one of the following devices would NOT be a good use of the piezoelectric effect?
A. compact disc player C. microphone
B. record player needle D. quartz crystal watches
40. Which one of the following devices would NOT be a good application of the photoelectric effect?
A. solar panels C. automatic door opener
B. car speaker D. on/off control switch for lights
41. Which of the following statements is false?
A. Solar cells are made from common conducting material.
B. Solar cells are made from thin wafers of semiconductors.
C. Solar cells must have a large area to produce enough potential difference to be useful.
D. Solar cells are used to power satellites and space probes.
42. What is a major cause of fires in many older homes?
A. Smoke detectors fail to work properly.
B. More solar cells are being used.
C. Older wiring can overheat due to current overload.
D. Copper wire is very flammable.
43. Which of the following can be used to produce electric potential energy?
A. the photoelectric effect C. an electromagnetic generator
B. the piezoelectric effect D. All of the above are correct.
44. Utilities sell electric energy in units of kilowatt hours (kWùh), while physicists measure energy in joules. How many joules does 1 kW • h equal?
A. 1000 J B. 3600 J C. 1 000 000 J D. 3 600 000 J
45. In an ordinary light bulb, the tiny wire filament becomes so hot that it glows.
Only about 15% of the electrical energy is converted into visible light. The rest is transformed into thermal energy. If a light bulb uses 75 J/s of electrical energy, how many joules of energy are given off as thermal energy each second?
A. 11 J B. 64 J C. 75 J D. 15 J
46. An increase in electric potential difference of a positive charge that is moved a given distance from a negative charge is similar to
A. the increase in gravitational potential energy of a ball raised a certain distance from the ground.
B. the increase of kinetic energy as a ball falls to the ground.
C. the movement of a boat in a river.
D. the change in velocity of an accelerating car.
47. Which product shows the work done to move a positive charge away from a negative charge?
A. V x I x t B. V x Q C. I x t D. W x Q
USE THE ABOVE GRAPHS TO ANSWER THIS QUESTION AND THE NEXT 2
QUESTIONS.
48. Which graph shows the correct relationship between wire gauge and the fuse required for that wire?
49. What is the relationship between wire gauge and wire thickness?
50. If a 12 gauge wire were added to a circuit with 6 gauge wire, would the circuit breaker need to be changed? Explain.
51. When 255 C of charge pass through a point in an electric wire in 0.100 min, what is the amperage?
52. How much charge goes through a motor used to start an air conditioner compressor if it takes 2.00 s to start the compressor and there is a current of 36
000 mA during that time?
53. The charge on an electron is 1.6 x 10 -19 C.
How many electrons pass from the negative terminal to the positive terminal of a car battery in 5 s when the battery is providing a current of 3 A?
54. A 6.0 V battery gives 5.3 C of charge to a portable cassette player. How much energy is used by the cassette player?
55. A charge of 3.0 C moves from one point to another in a stereo circuit. When this happens, it relases 45.0 J of electrical energy. What is the potential difference between the two points?
56. If a 12 V battery supplies a current of 2 A, how much work does the battery do in
10 s?
57. What is the energy of a proton accelerated through a potential difference of 6 x
10 5 V?
58. Why would you choose NOT to use a rechargeable Ni-Cad battery to power a smoke detector?
59. When you pay the electric company for the electricity you use, you are charged by the number of kilowatt-hours used. What are you paying for?
C USE THE FOLLOWING KEY TO ANSWER THIS QUESTION AND THE NEXT
QUESTIONS.
60. Which device is also called a storage cell?
61. Which device is no longer used very often but has great historical significance?
62. Which device works on the principle of electromagnetic induction?
USE THE FOLLOWING KEY TO ANSWER THIS QUESTION AND THE NEXT
QUESTIONS.
A. thermoelectricity
63. Which source of electric potential energy do solar cells use?
64. Which source of electric potential energy do phonograph needles and microphones use?
65. Which source of electric potential energy do thermocouples use?