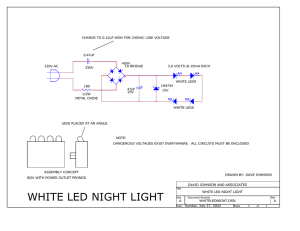
An Less Expensive LED Activity
advertisement

LED – Band gap Module Background Attended a TI uController development event where they demonstrated a uC using an LED as a light detector to control its own brightness. Use this frequently in electronics class One day a student wanted to really get some signal so they aimed a red laser pointer into a blue led – no signal I used this as an opportunity to explain how the photons had to have and energy > band gap to excite a voltage. Seemed like a way to demonstrate some quantum phenomena tied to everyday objects. Interesting Property of LEDs LED Usually LEDs are thought of as light sources LEDs are also light detectors We use this property to investigate the band gap structure of LEDs Use inexpensive LEDs and digital meter More advanced version have been developed http://laser.physics.sunysb.ed u/~tanya/report2/ Meter Objectives Primary Explain how quantum behavior of light and matter interact Band gaps Photons Identify LEDs as an example of nano-scale structures Three challenges in designing LEDs Efficiently producing light Thin film (nano-scale) Efficiently extracting light deposition techniques Selection of semiconductor Wide range of colors materials/dopants Objectives Secondary Instrumentation Technology Moving from manual to automated instrumentation “Beyond Moore” – semiconductor devices integrating more and more functionality Design and fabrication Basic soldering skills Board layout and design project Overview of Lab Use LEDs in pairs, one an illuminating LED, one a detecting LED. Fill in a table, also use an intense red source (laser pointer) as an illuminator: Overview of Lab Use LEDs in pairs, one an illuminating LED, one a detecting LED. Fill in a table, also use an intense red source (laser pointer) as an Detector illuminator: Energy Color Illuminator Energy IR RED YELLOW GREEN Blue Color IR RED YELLOW GREEN Blue Laser Ptr Observations (voltage difference with/without illuminator) Overview of Lab Use LEDs in pairs, one an illuminating LED, one a detecting LED. Fill in a table, also use an intense red source (laser pointer) as an Detector illuminator: Energy Color Illuminator Energy IR RED YELLOW GREEN Blue Color IR RED YELLOW GREEN Blue Laser Ptr Observations (voltage difference with/without illuminator) Review of Prior Knowledge Photons – wavelength, color and energy Color Wavelength Photon Energy E=hc/λ 3.1 eV 2.5eV 2.1eV 1.8eV Review of Prior Knowledge Single energy well (single atom) – discrete energy levels Several energy wells (molecule) – Each atomic levels splits to closely spaced levels separated by gaps Infinite array (crystal) – levels merge into bands separated by gaps . . . http://www.falstad.com/qm1d/ Prior Knowledge Number of good sources for review of semiconductor diodes and related topics: nanoHUB.org http://nanohub.org/ MRSEC http://mrsec.org/ Excellent YouTube overview Video at http://powerofthesun.ucs b.edu/ Working With LEDs LEDs as diodes – (Long lead = +) Show need for current limiting resistor (sacrifice an LED) Options for using LEDs Simply twist leads of LED and resistor Solder LED and resistor Simple soldering skills project Design & build a small board Working With LEDs Use LEDs with clear plastic cases Color cases add a confounding filtering effect √ X Lab – Color, Wavelength, Energy ~470Ω V Illumination Detection Use of a section Of drinking straw or other tubing helps direct the light and exclude ambient light Results Detector Energy Color Illuminator Energy IR RED YELLOW GREEN BLUE IR .3V 0 0 0 0 RED .2V .4V o 0 0 YELLOW .2V .2V .2V .1V???* 0 GREEN .4V .3V .2V .4V 0 BLUE .2V .5V .3V .3V .6V Laser Ptr .8V .6V 0 0 0 Color *Green and Yellow LED emission spectra overlap Explanation Egap Photon For an LED with a given band gap energy, illuminating photon has to be greater than this energy to excite a signal. Although green light is higher energy than yellow, we see a yellow LED does excite some signal in the green LED – LED colors are not sharp lines but bands, they yellow and green spectrum overlap. Extensions Automation Use uController with ADC to automate measurements For students in courses where they are already familiar with uC Design and fabrication LED boards are available for http://ice.chem.wisc.edu/ but students can build their own Simple soldering project Design a simple board with software such as EagleSoft (free education version) Extensions Male vs. Female color perception - who can match colors to a color chart best White and pink LEDs – view spectrum in a diffraction grating (or use a CD/DVD) and explain the use of phosphors. Economic/Environmental impact of LED lighting Candle vs. incandescent vs. CFL vs. LED Mercury emissions Coal fired electricity- Incandescent CFL – trace mercury