Standard Operating Procedures IN OPERATING DEEP WELL PUMP
advertisement

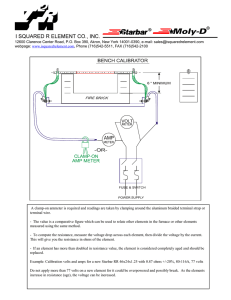
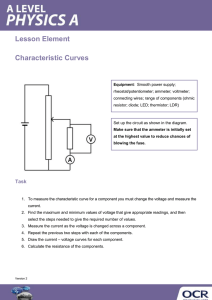
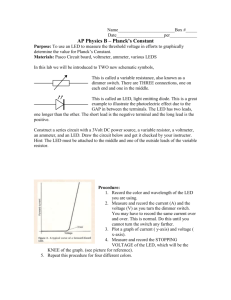
Standard Operating Procedures IN OPERATING DEEP WELL PUMP BEFORE YOU START • Make sure that you are properly oriented and knowledgeable to the location, functions and how to operate/manipulate the following: - Circuit breaker, switches, fuses, relays, reset button, autotransformer and ( VFD ) variable frequency drive of the motor control panel ( MCC ). - Metering devices and gauges like voltmeter, ammeter, pressure gauge and flow meter. - Discharge valve, blow-off valve, check valve and pressure transmitter. • Open the MCC with the circuit breaker OFF and check visually for its physical condition, signs of overheating, loosed or detached wires, burnt components particularly in the power circuit and ensure that they are in good condition. Report signs of deterioration to the maintenance personnel. • Always make it a point to go over the operation log book before powering up the motor and find out the important events that has transpired before your shift of duty. • Know the operating current and voltage of the submersible motor. Refer to the data on the logbook. Set the auto-man selector switch to OFF and then turn ON the main circuit breaker of the MCC. • Check if the supply line to line voltages are in accordance with the specified values or within safe operating range of the motor such as the following: - The supply line voltages should not exceed ± 10 % of the rated voltage of the motor. Example: Rated motor voltage Allowable voltage range 220 volts 198 – 242 volts 440 volts 396 – 482 volts - The difference between line to line voltages should not exceed 3%. To compute the percent (%) difference of line to line voltages, apply the formula; % difference = ( max. line to line voltage – average line to line voltage ) ÷ average line to line voltage x 100 Example: Voltmeter Reading 450 volts 445 volts 465 volts Average voltage = ( 450 + 445 + 465 ) ÷ 3 = 453.33 volts % Difference = ( 465 – 453.33 ) ÷ 453.33 x 100 = 2.57 % • Three line to line voltages must be able to read on the volt meter. Never attempt to start the pump with single phase electrical power supply. Some MCC however, are automatically inhibited from starting with abnormal power supply condition. • Close fully the discharge valve, open the blow-off valve at 1/3 opening and set the ammeter transfer switch to OFF position. STARTING THE PUMP UNIT • After satisfying the above requirements, start the submersible pump by setting the selector switch to manual mode, then press the start button. Should you want to operate in automatic mode, set the selector switch to automatic mode and no need to press the start button. • Once the motor control ( MCC ) have commenced starting sequence, observe its operation. If its controller is a reduce voltage ( RVAT ) will shift state from “starting” to “running” within 4 to 5 seconds, and if the motor control is a variable frequency drive ( VFD ) the output frequency will increases gradually until the set frequency is obtain. This time, fully open the blow-off valve, monitor the condition of water coming out of the blow-off header and also monitor the line current readings. • If in starting you have encountered trouble, determine the cause. If it is a minor one, fix it. If it is a major one and you cannot repair it, open the main circuit breaker and report immediately to the maintenance unit by a phone call. • Divert water output into the distribution pipe when the water coming out of the blow-off header is already clear in color. However, blow-off must be carried out not less than five minutes even if water is clear in the first time. After this, open fully the distribution valve, then gradually close fully the blow-off valve while observing the discharge pressure gauge as you do this. • Turn On the chlorine dosing pump and make sure that is working properly. DURING OPERATION • Always be vigilant and alert. Be sure to respond to an emergency in order to protect the equipment and facilities from serious and further damages. • Make frequent inspection of the volt meter, ammeter, discharge pressure gauge and flow meter to determine that the pump unit is functioning normally. • Record properly and correctly the line voltages, line currents, Kilowatt hour, discharge pressure, discharge flow and flow totalizer reading on the operation log sheet. Always analyze if these values are in accordance with the normal operation. • Record in the logbook all important informations and events relevant to the smooth and efficient operation to be passed to the incoming personnel. Make it a habit to go over the logbook every time you assume your tour of duty. Maintain a separate record for all repair and preventative maintenance done on pumping unit and facilities. • Always observe the schedule of operation. Never deviate from it unless approved by the office or due to an emergency. STOPPING THE PUMP UNIT - Stop the operation according to operation schedule. - Throttle the discharge valve at 1/3 opening, then press the stop button. - Fully close the discharge valve. - Record the time, hour-meter reading, flow totalizer reading and the kilowatt-hour reading when the pump is stopped. - Turn-Off the main circuit breaker at the MCC. Prepared and Submitted by: Approved by: Nathaniel P. Gueco Jorge P. Gumba OIC, Production Division General Manager Standard Operating Procedures IN OPERATING STANDBY GEN-SET Before starting the gen-set, check the following: • Cooling System - Check coolant level. Maintain level 13mm to the bottom of filler neck. • Engine Oil Level - Maintain oil level between the ADD and FULL marks of the oil level gauge. • Batteries - Clean top of batteries. Check electrolyte level. Check for loose connections and battery voltage. • Fuel System - Check fuel tank level. Check for leaks. • Belts - Inspect for worn, broken or looose belts. Adjust if necessary. • Gauges - Check the condition of all gauges. Repair or replace any broken gauge. • Control Panel - Visually inspect; check for loose, broken or damaged wiring components. • Generator - Check for moisture, dust, oil, greases. Clean as needed. • Walk-Around Inspection - Inspect engine, radiator and generator for debris, loose or broken fittings, hoses, or wires and guards. Repair as necessary. • If all of the above are in normal conditions, start the generator by pressing the Start Button. • Warm-up the gen-set for 5 minutes before loading. Check the following: - Frequency 60 Hz - RPM Refer to the name plate of the gen-set - Voltmeter reading Refer to the name plate of the gen-set - Ammeter reading Zero reading when no load - Engine oil pressure gauge Check for proper operating oil pressure - Engine jacket water temperature 70 to 90 ⁰C during normal operation - Fuel pressure gauge Check for proper operating fuel pressure. - Leaks and noises Check for leaks and unusual noises. • If all of the above are in normal conditions, shift the transfer switch from SFELAPCO power to Stand-by Gen-set power position. • Check the following before loading the gen-set: - Ammeter reading Voltmeter reading KW reading Frequency Power Factor • If all of the above are in normal conditions, start loading the Gen-set. ( Follow SOP in starting deepwell pump. ) • Make frequent inspection of the voltmeter, ammeter, frequency meter, KW meter, engine water temperature gauge and engine oil pressure gauge to determine if the gen-set is functioning normally. STOPPING THE GENSET • Stop the pump and all other electrical loads. ( Follow SOP in stopping deepwell pump. ) • Shift the transfer switch from stand-by gen-set power to SFELAPCO power position. • Allow standby gen-set to cool down at idle running for at least 10 minutes before stopping. • Stop the Gen-set by pressing the Stop Button. • Record the fuel tank level after stopping the stand-by genset. Prepared and Submitted by: Approved by: Nathaniel P. Gueco Jorge P. Gumba OIC, Production Division General Manager