South African Junior College School
advertisement
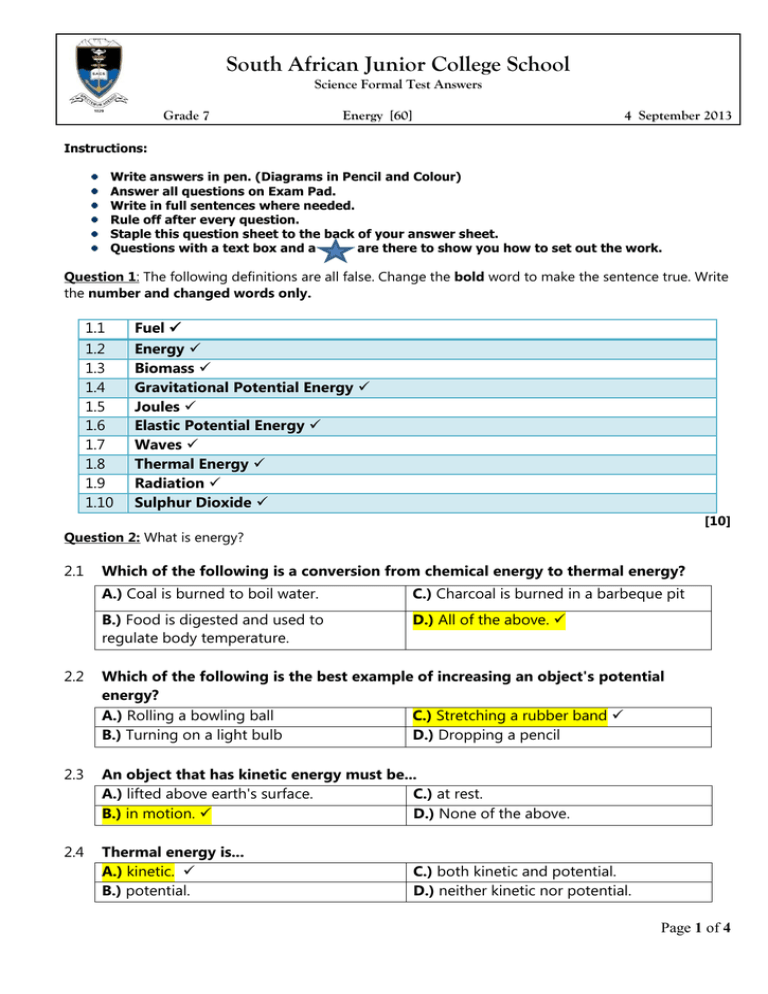
South African Junior College School Science Formal Test Answers Grade 7 Energy [60] 4 September 2013 Instructions: Write answers in pen. (Diagrams in Pencil and Colour) Answer all questions on Exam Pad. Write in full sentences where needed. Rule off after every question. Staple this question sheet to the back of your answer sheet. Questions with a text box and a are there to show you how to set out the work. Question 1: The following definitions are all false. Change the bold word to make the sentence true. Write the number and changed words only. 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1.9 1.10 Fuel Energy Biomass Gravitational Potential Energy Joules Elastic Potential Energy Waves Thermal Energy Radiation Sulphur Dioxide [10] Question 2: What is energy? 2.1 Which of the following is a conversion from chemical energy to thermal energy? A.) Coal is burned to boil water. C.) Charcoal is burned in a barbeque pit B.) Food is digested and used to regulate body temperature. D.) All of the above. 2.2 Which of the following is the best example of increasing an object's potential energy? A.) Rolling a bowling ball C.) Stretching a rubber band B.) Turning on a light bulb D.) Dropping a pencil 2.3 An object that has kinetic energy must be... A.) lifted above earth's surface. C.) at rest. B.) in motion. D.) None of the above. 2.4 Thermal energy is... A.) kinetic. B.) potential. C.) both kinetic and potential. D.) neither kinetic nor potential. Page 1 of 4 2.5 Sound energy is... A.) the energy of a compound that changes as its atoms are rearranged to form new compounds. B.) the total energy of the particles that make up an object. C.) the energy caused by an object's vibrations. D.) the energy of motion. 2.6 What device converts chemical energy to mechanical energy? A.) Human C.) Jet ski B.) Car D.) All of the above. 2.7 As height increases, so does... A.) thermal energy. C.) kinetic energy. B.) mechanical energy. D.) potential energy. 2.8 The law of _________________ of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed. A.) transformation B.) absorption C.) conservation D.) stability 2.9 According to the law of conservation of energy, in theory, a bouncy ball should never stop bouncing. However, we know that it eventually stops. Where does the energy go? A.) Some gets converted into sound B.) Some gets converted into thermal energy and escapes into the surroundings. energy and escapes into the surroundings. C.) Both A and B 2.10 Energy is the measure of something’s ability to do work. Which of the following has the most thermal energy? A.) A dead battery C.) Cup of coffee B.) A melting Wakaberry™ D.) Swimming pool [10] Question 3: Energy sources (answers may vary, use discretion) Nuclear Energy a) This energy is used in nuclear power stations to convert water into steam. The steam is used to drive turbines to generate electricity. This is done by splitting atoms with Uranium. b) Advantages: Clean Generates lots of power Disadvantages: Non-Renewable can be dangerous to dispose of. Any one Biomass a) These sources can be eaten and energy is passed though as food. These sources can be burned to produce heat. These sources may be converted into other forms before they are used. Some are fermented into alcohol that is uses in some petrol forms. any two b) Advantages: Renewable, Cheap Disadvantages: Takes up space, smells Page 2 of 4 Tidal Energy a) A dam is built across the place where a river meets the sea. The dam fills up at high tide and then empties at low tide. The movement of the water into and out of the dam turns turbines to make electricity. b) Advantages: Renewable, Efficient Disadvantages: Expensive Solar Energy (water) a) Using solar panels that contain water. This water is heated up by the sun and then it can be used by the people in the house. b) Advantages: Renewable, Efficient Disadvantages: Expensive to set up [10] Question 4: Energy Transfers and Forms of Energy 4.1 Teacher check. Any two moving objects that are increasing in height 4.2 Many options here are some suggestions. Any one of these or others: (2) Light Energy - Gararge light, camera, cellphone, police torch Kinetic – Lasoo, tree being pushed Sound – Man on phone, reporter Thermal – any light source Gravitational PE – Man in camera chair, boys on fence Chemical PE – Fuel in car, food, huge doughnut Elastic PE – Trampoline Biomass – Tree Electrical – Cellphone, camera Solar – sun is out (10 x ½ = 5 ) 4.3.1 Teacher check if relevant. Make sure that they stated an independent and dependent variable as well as how to keep it a fair test. (5) 4.3.2 Teacher check (3) [15] Question 5: Energy Transfer Diagrams 5.1 As the inventor moves his spoon, it triggers a dice to fly and hit a parrot. The parrot will fly away allowing a powder to be filled into a glass. As the glass gets heavier it pulls a string which lights a match. The match sets off a rocket that cuts a rope. This allow the napkin to fall on his face. (4) 5.2 5.3 Chemical Energy (Match) Heat Energy (Rochet fuse) Kinetic Energy (Rocket and knife) Any picture that represents the sequence. half a mark each change Kinetic Energy (Napkin) (2) [10] Page 3 of 4 Question 6: Heat Transfer 6.1 Conduction – heat through metal rod Convection – Heat warms air and makes a current Radiation - travels through waves [5] [Total Marks: 60] Page 4 of 4