Architecture Consistency
advertisement

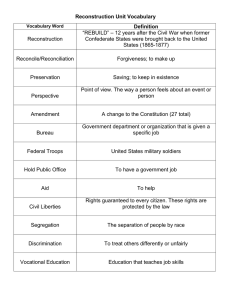
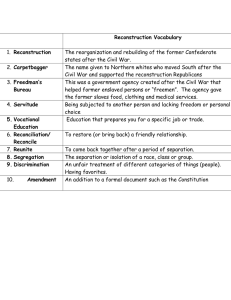
Detecting and Maintaining Architecture Consistency Dr Liam O’Brien, Geoscience Australia Personal Background 25 years experience in the IT area mainly as: • Researcher (21 years) • Reverse engineering, Reengineering, Software Architecture, Architecture Reconstruction, SOA, Cloud Computing • Solution Architect (past 4 years) • CSIRO – Chief Software Architect for eResearch – SOA, Cloud Computing, Scientific Workflow, Data Management Tools and Workflows • Geoscience Australia – SOA, Data services, Data Processing • CO2 Infrastructure Assessment (CIAP) • Sentinel – Bushfire Hotspots • National Offshore Petroleum Information Management System (NOPIMS) • National Flood Risk Information Platform (NFRIP) SAEroCon April 2014 Overview • Why is Architecture Important? • Architecture Consistency and Clarity • Architecture Inconsistencies • Detecting Architecture Inconsistency • Ensuring Architecture Consistency • Architecture Reconstruction • Examples of Architecture Reconstruction • Reflexion Modelling • Conclusion SAEroCon April 2014 Why is Architecture Important? Represents earliest design decisions First design artifact addressing Key to systematic reuse • hardest to change later • most critical to get right • communication vehicle among stakeholders • performance • modifiability • reliability • security • transferable, reusable abstraction The right architecture paves the way for system success. The wrong architecture usually spells some form of disaster. SAEroCon April 2014 Consistency and Clarity From: http://www.codingthearchitecture.com/pages/book/structure-and-guidelines-consistency-and-clarity.html SAEroCon April 2014 Architecture Conceptual Integrity “The goal of “conceptual integrity” or unity of design: The best programs and software systems exhibit a sense of consistency and elegance, as if they are shaped by a single creative mind, even when they are in fact the product of many. The fiendish problem is less how to create that sense in the first place than in how to preserve it against all the other pressures that come to bear throughout the process of writing software.” Frederick P Brooks Jr The Mythical Man-Month: Essays on Software Engineering SAEroCon April 2014 Architecture Inconsistencies • Differences between architectural documentation and implemented code • Name Inconsistencies – difficult to catch • Interface Inconsistencies – ill-defined interfaces • Behavioural inconsistencies - differences • Interaction Inconsistencies – protocol/sequence • Refinement Inconsistencies – high-level to low-level – adding or removing something, or violating (inter-layer bridging) SAEroCon April 2014 Causes of Architecture Inconsistencies • Differences between architecture views • Implementation does not follow the architecture • Uncontrolled evolution of code • Architecture documentation not kept up to date SAEroCon April 2014 Example of Architecture Inconsistency from CIAP SAEroCon April 2014 CIAP GUI SAEroCon April 2014 Example of Architecture Inconsistency from CIAP SAEroCon April 2014 Example of Architecture Inconsistency from CIAP SAEroCon April 2014 Example of Architecture Inconsistency from CIAP SAEroCon April 2014 Example of Architecture Inconsistency from CIAP SAEroCon April 2014 Ensuring Architecture Consistency From Implementation Perspective • Code Review From Architecture Perspective • Architecture Review • Other members of Architecture team • Architecture Committee (technical people from across Organisation) Enforcing Architecture Consistency • Disabling access to Databases • Logging and Auditing of the system SAEroCon April 2014 Reviews and Inspections of Code/Architecture Reviews and inspections of code and architecture involve several participants and activities Participants: Coders, Architects, Project Managers, Reviewers Activities: • Preparation for inspection of code and architecture material • Preparation of participants • Review/Analysis of code and architecture • Analysis of the review results and recommend actions • Follow-up and Finalisation SAEroCon April 2014 Architecture Reviews More thorough architecture reviews – ATAM, etc SAEroCon April 2014 Detecting Architecture Inconsistencies Detecting inconsistencies between the implemented system and the architecture can be done using: • Architecture Reconstruction • Reflexion Modelling SAEroCon April 2014 Architecture Reconstruction Architecture Reconstruction is the process of reconstructing or recovering the architecture of an implemented system. Also known as Architecture Recovery. Source Code, Documentation Extraction Fusion Source Extraction Source Model, Selected Architecture Views Reconstruction Architecture View Composition Architectural Views, Styles, Patterns, Drivers SAEroCon April 2014 Architecture Reconstruction • ARMIN – Architecture Reconstruction Tool Sources Sources extraction Extracted Extracted Sources Sources im port ARMIN Tool Project Manager definition of products and models Navigator product and model browsing Aggregator Architects creation of aggregation models creation of architecture views Interpreter ARL Experts Repository export Design Design Tools Tools Analysis Analysis Tools Tools SAEroCon April 2014 Architecture Consistency – Arch Recon Example 1 Embedded Automotive Control System Files C/c 61 Header 71 Total 132 KLOC 9 2 11 Functions 376 0 376 Macros 225 1055 1280 Variables 180 311 491 Types 5 56 61 Consistency/Conformance Exercise • Determine if the architecture as documented reflects the as-built system. • Layered system with three layers – ApplicationSW, Data and HardwareControl. • In the documentation the ApplicationSW and HardwareControl layers were only connected through the Data layer and were not directly connected. SAEroCon April 2014 Example – Highest-level System View – Layers SAEroCon April 2014 Exploring the Data Layer – 1 Data Accesses SAEroCon April 2014 Exploring the Data Layer – 2 Calls SAEroCon April 2014 Example 2 Automotive Infotainment System Code C/C++ Java Total Size Files Classes 2.58MLOC 6484 1018 1.78MLOC 9570 22542 4.36MLOC 16054 23560 Consistency of the Architecture • Determine if the Top Level Architecture as Documented reflects the as-built system • Produce views of several layers to determine consistency and if they conform to expectations SAEroCon April 2014 Another Example System – CMM Layer SAEroCon April 2014 MM_SERVICES - Dependencies SAEroCon April 2014 Reflexion Modelling for Architecture Consistency Checking SAEroCon April 2014 Conclusion • Architecture consistency not easy to enforce • Architecture inconsistencies will occur • Needs mechanisms to detect inconsistencies • Don’t want to make detection and enforcement too onerous on implementers or architects • Similar architecture inconsistencies happen in Infrastructure Architecture SAEroCon April 2014 Questions or requests for meetings for further information QUESTIONS? SAEroCon April 2014 References • Kazman, R., O’Brien, L., and Verhoef, C., Architecture Reconstruction Guidelines, CMU/SEI-2001-TR-026. • Van Deursen, et al, Symphony: view driven software architecture reconstruction, WICSA 2004. • Stoermer, C, O’Brien, L., Verhoef, C., Moving Towards Quality Attribute Driven Software Architecture Reconstruction, WCRE 2003. • Murphy, G, Notkin, D., Sullivan, K., Software reflexion models: bridging the gap between source and high-level models, SIGSOFT 1995. • Buckley, J., Mooney, S., Rosik, J., Ali, N., JITTAC: a just-intime tool for architectural consistency, ICSE 2013. SAEroCon April 2014