13.1 Electrical Current
13.1
Electrical Current
Electric Current
Electric current is the flow of
electric charge
.
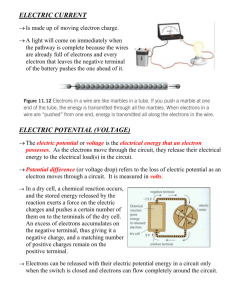
In solid conductors, electrons carry the charge through the circuit because they are
free to move
.
Electric Current
Measuring Current
Electric current is measured in amperes , symbol A .
An ampere is the flow of 1 coulomb of charge per second .
When the flow of charge past any cross section is 1 coulomb
( 6.25 x 10 18 electrons ) per second, the current is 1 ampere.
Electric Current
Formula:
Current = (charge / time)
I = Q / t
I = Current (amps)
Q = amount of charge (coulombs) t = time (seconds)
Units:
Amperes or Amps
Electric Current
Most small currents are expressed in: milli-amperes (mA): 1 mA = 1 x 10 -3 A micro-amperes (µA): 1 µA = 1 x 10 -6 A
Voltage Sources
Voltage Sources
Charges do not flow unless there is a potential difference .
Something that provides a potential difference is known as a voltage source .
Batteries and generators are examples of voltage sources that are capable of maintaining a continuous flow of electrons.
Voltage Sources
Steady Voltage Sources
In a battery, a chemical reaction releases electrical energy.
Generators—such as the alternators in automobiles—convert mechanical energy to electrical energy.
The electrical potential energy produced is available at the terminals of the battery or generator.
Voltage Sources
The potential energy per coulomb of charge available to electrons moving between terminals is the voltage .
The voltage provides the “ electric pressure ” to move electrons between the terminals in an electric circuit .
Voltage Sources
Low
Potential
High
Potential
Electron
Pump
When the potentials are equal, the current stops flowing .
To increase the potential of the electrons, an electron pump must convert (do work) another form of energy into electrical potential energy.
Voltage Sources
Distinguishing Between Current and Voltage
There is often some confusion between charge flowing through a circuit and voltage being impressed across a circuit.
Consider a long pipe filled with water:
• Water will flow through the pipe if there is a difference in pressure across the pipe or between its ends.
• Water flows from high pressure to low pressure.
What are two voltage sources used to provide the energy that allows charges to move steadily?
Batteries and Generators
Types of Current
There are two types of current:
1.
DC Current
2.
AC Current
Types of Current
DC Current
By DC , we mean direct current , which refers to a flow of charge that always flows in one direction .
• A battery produces direct current in a circuit because the terminals of the battery always have the same sign of charge.
• Electrons always move through the circuit from the negative terminal toward the positive terminal .
Types of Current
AC Current
Alternating current (AC), as the name implies, is electric current that repeatedly reverses direction .
• Electrons in the circuit move first in one direction and then in the opposite direction.
• They alternate back and forth about relatively fixed positions.
Which way does current flow?
Conventional Current
Flow of current from positive terminal to the negative terminal.
Electron Current
Flow of current from the negative terminal to the positive terminal.
Direction of Current:
Direction of Current
Current in Electric Circuits
For current to flow, an electric circuit needs to be a closed loop .
Basic electric circuits consist of three things:
• Electron pump (Battery)
• Device (User)
• Conducting connection (Wires)
What affects current flow?
1. Voltage
2. Resistance (Slowing or reduction of the flow of current )
Assessment Questions
Example #1
A charge of 30 Coulombs passes through a 24 Ω resistor in 6 seconds. What is the current through the resistor?
Assessment Questions
Example #2
Charge flowing at a rate of 2.5 x 10 6 elementary charges per second is equivalent to a current of:
Assessment Questions
Example #3
The current though a light bulb is 2 amps. How many coulombs of electric charge pass through the light bulb in one minute?
Assessment Questions
Example #4
The current going from the cathode to the screen in the television picture tube is 5 μ A . How many electrons strike the screen in 5 seconds?
Assessment Questions
Example #5
A current of 5 A flowed in a copper wire for 20 seconds. a. How many coulombs of charge passed through the wire at this time? b. How many electrons flowed through this wire at this time?
Assessment Questions
Example #6
Electric charge will flow in an electric circuit when: a. electrical resistance is low enough. b. a potential difference exists. c. the circuit is grounded. d. electrical devices in the circuit are not defective.
Assessment Questions
Example #7
The electric current in a copper wire is normally composed of: a. electrons b. protons c. ions d. amperes