University of Southern California
advertisement

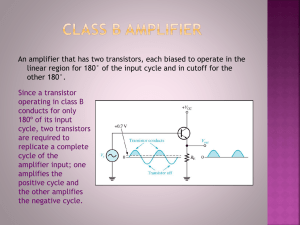
U niversity of S outhern C alifornia School Of Engineering Department Of Electrical Engineering EE 348L: #34056 MidTerm Exam #2: 3 pages, 4 questions,100 points Duration: 1.5 hours from 11:00 am to 12:30pm Spring 2005 Madhavan 1. This is Midterm 2 for EE348L. It is intended to test your understanding of material covered in class from February 8, 2005 to April 7, 2005. 2. This is an open text-book, open notes exam. 3. The weightage of each question is indicated in bold at the end of each question. 4. Questions are arranged in order of increasing difficulty. Questions toward the end of the exam have maximum weight. 5. If you are not sure of the answer, write down your best guess or the approach you will take to solve the problem. 6. Attempt as many questions as you can. Use your working paper for writing down the answers to the questions. 7. Write your name and student ID # on your answerbook. Useful Information: Impedance of a capacitor of value C is given by ZC(s) = 1/(sC) ; ZC(jω) = 1/(jωC); j = Sqrt(-1). Impedance of an inductor of value L is given by ZL(s) = sL ; ZL(jω) = jωL; j = Sqrt(-1). 1. Plot Vout versus Vin for the circuit in Figure P1, with Vin varying from –5 V to +5V. Assume D1 and D2 are ideal diodes. Clearly indicate which diodes are on and off in appropriate regions of your plot.…….Total: 10 points +2V D2 Vin 1 KΩ Vout D1 -2V Figure P1: Diode limiting circuit Vdd Iref M2 Vo M1 Figure P2: Circuit for Problem 2 Electronic Circuits I (EE 348L MidExam #1) University of Southern California Spring 2005 2. (MOSFETs). ………………………………………….……………………………………………. Total: 20 points For the circuit in Figure P2, µnCox = 40 µA/V2, µpCox = 10 µA/V2, Vtn = |Vtp| = 1 V, λ = 0, Ln = Lp = 10 µm, Wn = Wp = 20 µm. If Vdd = 3V, find the value of Vo and Iref. …………………………………………………………….…….. (15 points) Justify your choice of the operating region of M1 and M2…………...…………………………….…….. (5 points) 3. (MOSFETs, frequency response)…………………………………………………….……………Total: 32 points For the dc-coupled cascade of amplifier stages shown in Figure P3, vin is the input to the cascade, vo1 is the output of the first stage and vo2 is the output of the second stage. All MOSFETs have the same threshold voltage, Vt. Assume that the gate-to-source capacitance, Cgs, is significantly greater than Cgd, Cdb, and Csb for all MOSFETs. Vdd Vdd I I vo2 vo1 M1 vin M2 M3 M4 + - VGG Amplifier Stage 2 Amplifier Stage 1 Figure P3: DC-coupled amplifier cascade of two amplifier stages. vin is the input to the cascade, vo1 is the output of the first stage and vo2 is the output of the second stage. a) Draw the ac schematic of the amplifier stage highlighted in Figure P3..………………..………(4 points) b)Draw the small-signal circuit diagram of amplifier stage 1, taking care to account for the relevant capacitances that load the output of Amplifier stage 1. Include the drain to source resistance, rds1 and rds2 of MOSFETs M1 and M2, respectively. Assume that all MOSFETs are in saturation.…….…….(4 points) c) Assuming that the gain of the common-source amplifier is low enough that the miller multiplication of Cgd can be neglected, redraw the small-signal circuit diagram in (b) with appropriate transformation of Cgd to the input and output ports of your small-signal circuit diagram…..……….....…….………..…… (2 points) d) Assuming that Cgs >> Cgd, derive the general expression for the voltage gain of amplifier stage 1, Av(s)=vo1(s)/vin(s)…….…………………………………………………………………………………….(10 points) e) Assuming that all MOSFETs have the same gate length, and the same gate-to-source bias voltage VGS, and that Cgs >> Cgd, Make appropriate engineering assumptions to show that −G g , where G = m1 and ωT = gm1/Cgs1 = gm2/Cgs2.…..………………….……..….……(4 points) Av(s) = s(1 + G ) gm 2 1+ ωT f) What are the –3dB and unity-gain frequencies of the voltage gain, Av(s) ?……….………………(4 points) g) What condition must be satisfied to maximize the low-frequency gain and the unity-gain frequency of Av(s)?……………………………………………….………………………………………..…….….…..(4 points) 4. (MOSFETs). ………………………………………….……………………………………………..Total: 38 points For the modified common-gate amplifier shown in Figure P4 below, Note that Vin is the input to the amplifier, Vo is the output of the amplifier. Rin and Rout are respectively, the input and output resistance of the common-gate 1. Department of Electrical Engineering Page ii of 2 Bindu Madhavan Electronic Circuits I (EE 348L MidExam #1) University of Southern California Spring 2005 amplifier. Rs, the ac voltage-source resistance, is a small resistance. Iref is a precision reference current source supplied to you. The ac-coupling capacitor, Cc1, is a short circuit in the signal-frequency range of interest. All capacitances associated with the devices in the circuit are to be ignored for this question. Assume that all MOSFETs have the same threshold voltage i.e., Vtn = |Vtp| = |Vt |. Note that the bulk of transistor M2, is connected to the lowest potential of the circuit. An amplifier (called Amplifier A in Figure P4) with small-signal gain –G, where G>0, is connected across the gate-to-source terminals of transistor M2. You are to assume that the output of this amplifier provides the dc gate-to-source potential necessary to keep M2 in saturation. Vdd Rout M4 M3 Vo M2 Iref Cc1 -G Ibias RS + - Amplifier A Vin Rin Figure P4: Modified common-gate amplifier. Vin is the input to the amplifier, Vo is the output of the amplifier. Rin and Rout are respectively, the input and output resistances of the common-gate amplifier. Rs, the ac voltage-source resistance, is a small resistance. Ibias and Iref are bias current sources. a) What is the function of Iref, M4 and M3.……………...………………………………………………..(2 points) b) Draw the ac schematic of the amplifier stage in Figure P4……………………………………......(4 points) c) Draw the small-signal circuit diagram of the amplifier in Figure P4, assuming that all MOSFETs are in saturation. Ignore MOSFETs that are only used in biasing the amplifier stage and play no role in amplification. Include the relevant drain to source resistance, rds…………………………..….... (4 points) d) Derive the general expression for the voltage gain of the amplifier, Av=Vo/Vin………...……..…(10 points) e) Derive the general expression for the ac, small-signal input resistance, Rin, of the amplifier. Note that Cc1, is a short-circuit in the signal-frequency range of interest.. ………..….……………….……..…...(6 points) f) Derive the general expression for the ac, small-signal, output resistance, Rout, of the amplifier. Note that Cc1, is a short-circuit in the signal-frequency range of interest……………..……..………...….….(6 points) g)Justify the maximum voltage value that the output of the amplifier stage can take, such that the transistors in the amplifier stage remain in saturation……………………………………………………………(4 points) h) How has the amplifier block with small-signal gain -G modified the behavior of the amplifier in Figure P4 from that of a traditional common-gate amplifier, such as the one in your sample midterm exam 2 handed out in class?..………………………………………………………………………………...…….…....(2 points) 1. Department of Electrical Engineering Page iii of 3 Bindu Madhavan