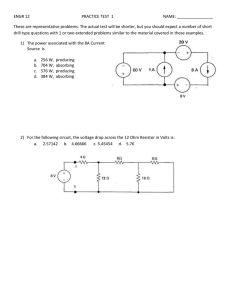
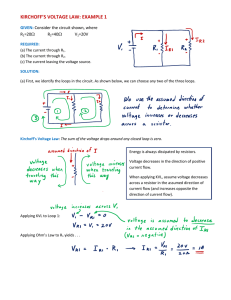
V - Dr. Ahmed ElShafee
advertisement

Lecture (01) Ohm’s and Kirchhoff’s laws Dr. Ahmed M. ElShafee 1 Ideal basic circuit element 1. Has only 2 terminal 2. Described mathematically in terms of voltage and current 3. It can’ t be divided. + i 1 v - 2 2 Passive sign convention theory • Passive sign convention: if the current reference direction is in the direction of the voltage lt d drop across the th element, l t +ev sign i in i any expression i relates voltage to the current, otherwise use a –ve sign. • Note: polarity reference is independent on function of the basic element, or its interconnection. + i 1 v - 3 2 Power and Energy • Power and energy calculations are so important in electric circuit analysis because 1 The 1. Th useful f l output t t off these th systems t often ft nonelectrical l ti l (heat, light, movement, ….). 2 All practical devices have limitations on the amount of 2. power that can handle. 4 Power and Energy (2) • Passive sign convention if the current flow is in the same direction of voltage drop, th then P=i×v dissipating, absorbing power if not P ‐i×v P= generating, losing power 5 Power and Energy (3) + i 1 v + 2 i 2 - P= vii P= -vii 1 v - i 1 v 2 + P= -vi 6 1 v - - i 2 + P= vi Power and Energy (4) • Example: in the following model if i = 4 A and v = ‐10V then P = ‐ (‐10)(4) = 40 W The element is absorbing (dissipating) 40 watts 7 Power and Energy (5) • Example: in the following model if i = ‐4 A and v = 10V then P = ‐ (10)(‐4) = 40 W The element is absorbing (dissipating) 40 watts 8 Example 01 Assume that a 10V drop occurs across an element from terminal 2 to terminal 1 and that a current of 4A enters terminal 2. a)) Specify S if th the values l off v and d i for f the th polarity l it references shown in figures. b) SState whether h h the h circuit i i iinside id the h box b is absorbing or delivering power. c)) How much power is the circuit absorbing? 9 Answer 01 • Start with sketching the circuit model • For the first model v= ‐20v i=‐4A; P=(‐20)x(‐40)=80W, absorbing • For the second model v= ‐20v i=4A; P=‐(‐20)x(4)=80W, absorbing 10 Answer 01(2) • For the 3rdd model v= 20v i=‐4A; P=‐(20)x(4)=80W, absorbing • For the 4th model v= 20v i=4A; P=(20)x(4)=80W, absorbing 11 Ohm’ss law Ohm The voltage v across a resistor is directly proportional to the current I flowing through the resistor. 1 Ohm h = 1 V/A / 12 Ohm’ss law (2) Ohm Passive sign convention: There are two possible reference choices for the current and voltage lt 13 Ohm’ss law (3) Ohm Conductance is the opposite of resistance: Symbol: G Units: Siemens (S) or mho ( 14 ) Ohm’ss law (4) Ohm Power dissipated by a resistor: 15 Example 09 For each figure, calculate; 1. V, and I. 2. Power. + 50V + 1A Vg - + 0.2S ‐ + ‐ 16 8Ω 1A Vg - 20Ω 50V 25Ω Answer 09 I = 1A V = I.R = 8V P = V2/R = 8W I = 1A V = ‐I.R = ‐20V P = V2/R = 20W 17 + 1A Vg - + 1A Vg - 8Ω 20Ω Answer 09 (2) V = 50V I = V.G = 10A P = I2/G = 8W V = 50V I = V/R = 2A P = I2.R = 100W + 0.2S 50V 25Ω ‐ + ‐ 18 50V Example 10 a. Vg=1KV, Ig=5mA, find R&Presistor. b. Ig=75mA, Psource=‐3W, find Vg, R, Presistor. c. R=300Ω, Presistor=480mW, find Ig, Vg. + ‐ 19 Vg R Answer 10 a) Vg=1KV, Ig=5mA. find R&Presistor. + R= Vg/Ig = 103/5x10‐3 = 0.2x106= 200KΩ. P= V.I = 5W. b) Ig=75mA, Psource=‐3W. find f d Vg, R, Presistor. Vg=‐P/Ig = ‐( ‐3/(75x10‐3)) = 40V. R=Vg/Ig= 40/(75x10‐3)=533.33Ω. Presistor = 3W. 20 ‐ Vg R Answer 10 (2) R=300Ω, Presistor=480mW, find Ig, Vg. + Ig=(P/R)0.5=((480x10‐3)/300)0.5= 0.04A = 40mA. Vg=(PxR)0.5=((480x10‐3)x300) 0.5=12V. 21 ‐ Vg R Kirchhoff’ss laws Kirchhoff • Simple circuit – Voltage – Current – Power + + Vs R ‐ - Kirchhoff’ss laws (2) Kirchhoff • More Complex circuit, circuit – Circuit contains 2 loops 1, 2. – bd branch shared between the two loops. V1 – Nodes b, d are shared between the two loops. a R1 b R3 + c + R2 ‐ ‐ 1st loop 2nd loop d V2 Kirchhoff’ss laws (3) Kirchhoff Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL): “The algebraic sum of all voltage drops around any closed loop is zero”” M: number b off voltages l in the h loop l Vm: mth element voltage. – Satisfied around all loops of a circuit. – The law is about energy conservation Kirchhoff’ss laws (4) Kirchhoff • KVL example: • 1st loop: ‐Vg1 + V1 + V2 = 0 • 2nd loop: ‐Vg2 + V3 + V2 = 0 a b R1 + + ++ + Vg1 - - c R3 + R2 ‐ 1st loop ‐ - - 2nd loop • Passive sign convention: d Voltage get +ve if the current flow in side component is in the same direction of voltage drop, otherwise voltage get –ve sign. Vg2 Kirchhoff’ss laws (5) Kirchhoff • Kirchhoff's current Law (KCL): “The algebraic sum of currents around a node is zero” N: number of branches connected to the node in: h current entering the node – Satisfied at all nodes of a circuit – The law is about charge conservation Kirchhoff’ss laws (6) Kirchhoff • KCL example: node a: ‐Ig1+I1 = 0 Node b: ‐I1‐I3+I2=0 Node c: ‐Ig2+I3=0 Node d: ‐I2+Ig1+Ig2=0 So: I2=Ig1+Ig2. R1 a + - - c + ++ + Vg1 R3 b + R2 ‐ 1st loop ‐ - - 2nd loop d • Passive sign convention: Current gets +ve if the current leave the node is while gets –ve sign if the current entering the node. Vg2 Example 3 use KL and Ohm’s law to 1. find Io 2. Verify that total dissipated power – total generated power 10Ω + 120V ‐ Io 50Ω 6A Example 3 solution KCL: ‐Io‐6+I50=0 I50= Io+6 ………………..(1) KVL: ‐120 120 + (10xIo)+ (50xI50) =0 0 ……….…………………………(2) Submit 2 in 1 (10xIo)+ (50x(Io+6))=120 Io=‐3A 10Ω + + + 120V ‐- Io a - + 50Ω - 6A Example 3 solution (2) I50 = 3A P10=(io)2x10=9x10=90W P50=9x50=450W P120V=‐ 120 x –i120V =360W Total dissipated power= 360+90+450= 900W V50=50x3=150V P6A=‐V50x6=‐150x6=‐900W (generated) 10Ω + + + 120V ‐- Io a - + 50Ω - 6A Example 4 For the shown circuit; Find Is. V3. V2. V7 Power delivered by source. Example 4 solution KVL: ‐24 + 3xIs + 7xIs + 2xIs = 0 12xIs = 24 Is = 2A ‐‐‐> Ohm: V3Ω = Is x 3 = 6v V7Ω = Is x 7 = 14v V2Ω = Is x 2 = 4V Ps = ‐Vs x Is = ‐24 x 2 = ‐48V (generated) 32 Example 5 Find R Example 5 solution KVL@1: ‐200 + VR + 120 =0 VR = 80V KVL@2: ‐120 + 8xI8 =0 I8 = 120/8 = 15A Ohm: I24 = 120/24 = 5A KCL: IR = I24 + I8 IR = 20A 34 Example 5 solution (2) Ohm: R = VR / IR = 80/20 = 4Ω Thanks,… See you next week (ISA),… 36