motors and generators - The University of Sydney
advertisement

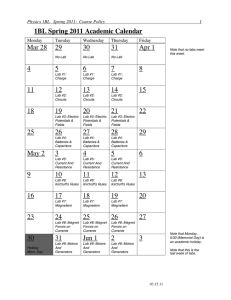
MOTORS AND GENERATORS HSC KICKSTART PHYSICS WORKSHOP LIST OF EXPERIMENTS 1. The Motor Effect 2. Electromagnetic Induction and Lenz’s Law 3. Generators 4. Transformers 5. AC Induction Motors Name:_____________________________ Kickstart would like to acknowledge and pay respect to the traditional owners of the land– the Gadigal people of the Eora Nation. It is upon their ancestral lands that the University of Sydney is built. As we share our own knowledge, teaching, learning, and research practices within this University may we also pay respect to the knowledge embedded forever within the Aboriginal Custodianship of Country. The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators The Motor Effect An electric charge experiences a force when it moves in a magnetic field. Thus, a current-carrying conductor feels a force from a magnetic field. This is the motor effect. B field into page force path of positively charged particle velocity A Working Motor Label the parts of the motor on the pictures below. Are these DC motors or AC? Or both? How can you tell? The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators Galvanometer Features: Characteristics: Describe the application of the motor effect in a galvanometer. Loudspeaker Features: Characteristics: Describe the application of the motor effect in a loudspeaker. The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators Electromagnetic Induction and Lenz’s Law Using the Predict, Observe, Explain model of scientific enquiry, examine these 5 experiments to synthesise the information into a description of Lenz’s Law. Magnet and coil The wire coil is connected to a galvanometer that measures small amounts of current. Move the magnet near the coil and notice the current induced. What happens when you move the magnet faster? What happens when you use the weaker (smaller) magnet? When you bring the magnet’s north pole towards the coil, can you tell which way the induced current flows in the coil? How? Explain using a diagram. Predict Observe Explain The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators Falling magnets You have a very strong magnet — a neodymium magnet — and some tubes. Drop the magnet down the tubes and observe how long it takes for the magnet to reach the bottom of each tube. The magnet falls slower in the copper tube than in the PVC pipe. Why? Predict Observe Explain Jumping rings Why do the rings jump into the air? Which ones don’t work and why? Predict Observe Explain The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators Pendulum Three different pendulums can be swung between the poles of the permanent magnet. Try each one in turn and observe how long they swing before stopping. Where is the stopping force coming from? How can this be used in electromagnetic braking? Predict Observe Explain Arago’s Disk Turn the magnets past the disk. The disk will move too. What is the disk made of? Is it magnetic? Why does the disk spin? (This phenomenon is used in AC induction motors). Predict Observe Explain Lenz’s Law There are 4 parts to Lenz’s Law. 1. A __________________________________________ induces a 2. ____________________________________________ that produces an 3. ____________________________________________ force that 4. ____________________________________________ the original force. The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators Generators AC/DC Generator How can you tell if the generator is producing AC or DC electricity? Draw the output of the generator as viewed on the CRO screen for both AC and DC V t V t The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators Twelve-phase generator What kind of commutator does the twelve-phase generator have? Predict and draw what you think the output of the generator would look like on the CRO: V t The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators Transformers Risk Analysis A very important part of any experimentation in physics is the identification of any risks, and the subsequent mitigation of those risks. As you can imagine, scientists use some very cool, and technical pieces of apparatus and equipment. High voltage falls into this category. Before we begin, identify three risks associated with high voltage. Once these risks have been identified, you must identify what might happen if the risks were to eventuate, and of course, what we can do to mitigate against the risks. These would be our safety rules. Assign a number to each of your risks using the table to the left. Risk Consequence Precaution Transformers use the ideas of electromagnetic induction to transform one voltage into another. The number of turns in the primary and secondary coils is the crucial point here, since the ratio of the primary voltage to the secondary voltage is Vp/Vs = np/ns That is, if the number of turns in the secondary coil is increased, the voltage output of the secondary coil is increased. The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators DIY transformer Primary np = ____________ Secondary ns = ____________ Vp = ____________ So we should get Vs = ____________ Compare your prediction to the actual value by using a multimeter: Vs = Does the predicted value match the measured value? What reasons can you give as to why our measurement might be different to the calculated value? Explain how this effect is used for transmission of electricity from power stations t our homes. Cause: • • • Relationship between • • • Why/How • • • Effect: • • • The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators AC Induction Motors The parts of the squirrel-cage rotor are: Constuct from the parts provided, a working AC induction motor. Different types of motors Different types of motors have different components. Fill in the table below for each type of motor. Component Rotor Stator Commutator Power supply Physics concept behind motor Applications/ Examples DC motor Description Universal Motor AC Induction motor The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators Generate some motor-vation If you listen closely throughout the workshop, the demonstrators might let some of this info slip, but if not, just ask them. What does your demonstrator do here at the School of Physics? or random fact from your demonstrator Can you list some safety measures in the lab? Find and list the 4 famous scientists in the lab. Careers with Motors and Generators Your demonstrator might be able to help with this What sort of career do you think you could get if you studied this topic at the University of Sydney? Industry Research Public service • • • • • • • • • The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators Physics Kickstart 2012 student survey School Name_____________________ Demonstrator’s name________________ 1 (a) Have you done this topic in class already? Yes No 1 (b) What did you learn from the workshops that you couldn’t get from your class? 2 (a) Why did you choose HSC Physics? 2 (b) How do you think Kickstart will help with your HSC? 2 (c) How has Kickstart influenced your ideas about physics? 2 (d) Are you now more likely to do Physics at the University of Sydney? No 3 (a) How would you rate Kickstart Physics overall? ________ out of 10 3 (b) What part of the workshop made most sense to you? 3 (c) Any other comments, like how could the workshops be improved? Yes