Dual/Quad, Low Power, High Speed
JFET Operational Amplifiers
OP282/OP482
Active filters
Fast amplifiers
Integrators
Supply current monitoring
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The OP282/OP482 dual and quad operational amplifiers feature
excellent speed at exceptionally low supply currents. The slew
rate is typically 9 V/μs with a supply current of less than 250 μA
per amplifier. These unity-gain stable amplifiers have a typical
gain bandwidth of 4 MHz.
The JFET input stage of the OP282/OP482 ensures that the bias
current is typically a few picoamps and is less than 500 pA over
the full temperature range. The offset voltage is less than 3 mV
for the dual amplifier and less than 4 mV for the quad amplifier.
With a wide output swing (within 1.5 V of each supply), low
power consumption, and high slew rate, the OP282/OP482 are
ideal for battery-powered systems or power-restricted applications. An input common-mode range that includes the positive
supply makes the OP282/OP482 an excellent choice for highside signal conditioning.
The OP282/OP482 are specified over the extended industrial
temperature range. The OP282 is available in the standard
8-lead, narrow SOIC and MSOP packages. The OP482 is
available in the PDIP and narrow SOIC packages, as well as
a 14-ball WLCSP.
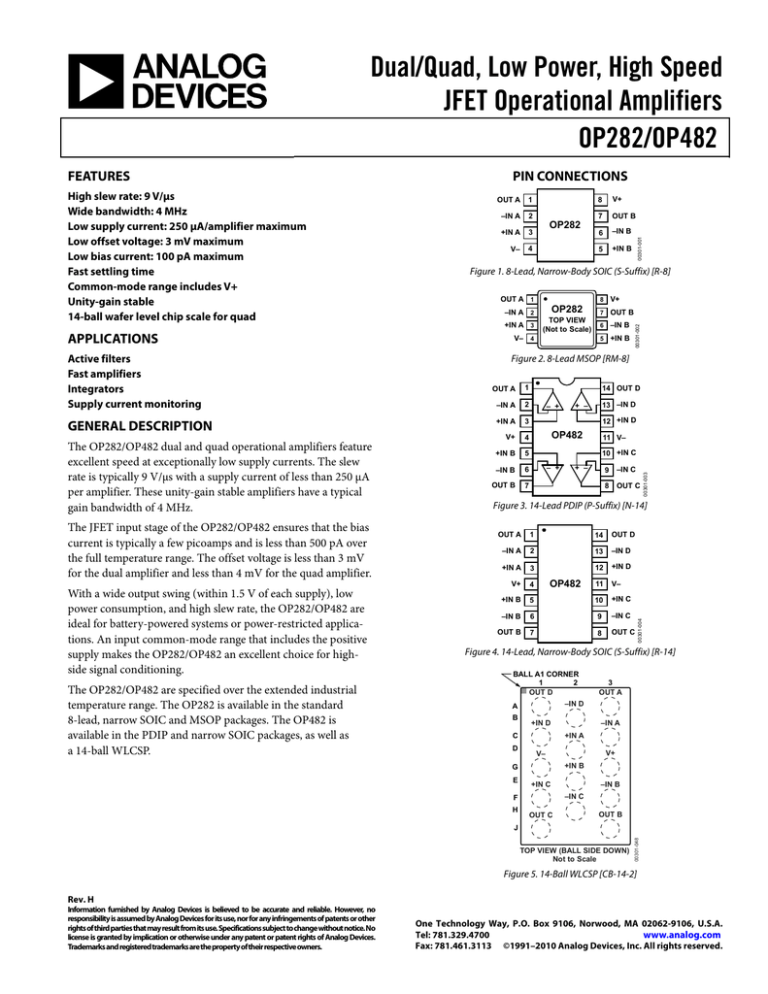
1
8
V+
–IN A
2
7
OUT B
+IN A
3
6
–IN B
V–
4
5
+IN B
OP282
OP-482
00301-001
OUT A
Figure 1. 8-Lead, Narrow-Body SOIC (S-Suffix) [R-8]
OUT A 1
–IN A 2
+IN A 3
OP282
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
V– 4
8
V+
7
OUT B
6
–IN B
5
+IN B
00301-002
APPLICATIONS
PIN CONNECTIONS
Figure 2. 8-Lead MSOP [RM-8]
OUT A
1
–IN A
2
+IN A
3
V+
4
+IN B
5
–IN B
6
OUT B
7
14 OUT D
– +
13 –IN D
+ –
12 +IN D
OP482
11 V–
10 +IN C
– +
+ –
9
–IN C
8
OUT C
00301-003
High slew rate: 9 V/μs
Wide bandwidth: 4 MHz
Low supply current: 250 μA/amplifier maximum
Low offset voltage: 3 mV maximum
Low bias current: 100 pA maximum
Fast settling time
Common-mode range includes V+
Unity-gain stable
14-ball wafer level chip scale for quad
Figure 3. 14-Lead PDIP (P-Suffix) [N-14]
OUT A
1
14
OUT D
–IN A
2
13
–IN D
+IN A
3
12
+IN D
11
V–
OP482
V+
4
+IN B
5
10
+IN C
–IN B
6
9
–IN C
OUT B
7
8
OUT C
00301-004
FEATURES
Figure 4. 14-Lead, Narrow-Body SOIC (S-Suffix) [R-14]
BALL A1 CORNER
2
1
OUT D
–IN D
A
B
+IN A
+IN B
–IN B
+IN C
–IN C
F
H
V+
V–
G
E
–IN A
+IN D
C
D
3
OUT A
OUT C
OUT B
TOP VIEW (BALL SIDE DOWN)
Not to Scale
00301-048
J
Figure 5. 14-Ball WLCSP [CB-14-2]
Rev. H
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©1991–2010 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
OP282/OP482
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1 ESD Caution...................................................................................4 Applications....................................................................................... 1 Typical Performance Characteristics ..............................................5 General Description ......................................................................... 1 Applications Information .............................................................. 12 Pin Connections ............................................................................... 1 High-Side Signal Conditioning ................................................ 12 Revision History ............................................................................... 2 Phase Inversion........................................................................... 12 Specifications..................................................................................... 3 Active Filters ............................................................................... 12 Electrical Characteristics............................................................. 3 Programmable State Variable Filter ......................................... 13 Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 4 Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 14 Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 4 Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 16 REVISION HISTORY
9/10—Rev. G to Rev. H
Added WLCSP ....................................................................Universal
Changes to Features Section............................................................ 1
Changes to General Description Section ...................................... 1
Added Figure 5; Renumbered Sequentially .................................. 1
Changes to Large-Signal Voltage Gain Parameter, Table 1 ......... 3
Changes to Table 2, Thermal Resistance Section, and Table 3 ... 4
Change to Figure 30 ......................................................................... 9
Added Figure 53.............................................................................. 16
Changes to Ordering Guide .......................................................... 16
7/08—Rev. F to Rev. G
Changes to Phase Inversion Section ............................................ 12
Deleted Figure 45............................................................................ 12
Added Figure 45 and Figure 46..................................................... 12
Updated Outline Dimensions ....................................................... 14
Changes to Ordering Guide .......................................................... 16
10/04—Rev. E to Rev. F
Deleted 8-Lead PDIP .........................................................Universal
Added 8-Lead MSOP .........................................................Universal
Changes to Format and Layout.........................................Universal
Changes to Features.......................................................................... 1
Changes to Pin Configurations....................................................... 1
Changes to General Description .................................................... 1
Changes to Specifications ................................................................ 3
Changes to Absolute Maximum Ratings ....................................... 4
Changes to Table 3............................................................................ 4
Added Figure 5 through Figure 20; Renumbered
Successive Figures............................................................................. 5
Updated Figure 21 and Figure 22 ....................................................7
Updated Figure 23 and Figure 27 ....................................................8
Updated Figure 29 .............................................................................9
Updated Figure 35 and Figure 36 ................................................. 10
Updated Figure 43 .......................................................................... 11
Changes to Applications Information ......................................... 12
Changes to Figure 44...................................................................... 12
Deleted OP282/OP482 Spice Macro Model Section ....................9
Deleted Figure 4.................................................................................9
Deleted OP282 Spice Marco Model ............................................. 10
Updated Outline Dimensions....................................................... 14
Changes to Ordering Guide .......................................................... 14
10/02—Rev. D to Rev. E
Edits to 8-Lead Epoxy DIP (P-Suffix) Pin......................................1
Edits to Ordering Guide ...................................................................3
Edits to Outline Dimensions......................................................... 11
9/02—Rev. C to Rev. D
Edits to 14-Lead SOIC (S-Suffix) Pin .............................................1
Replaced 8-Lead SOIC (S-Suffix)................................................. 11
4/02—Rev. B to Rev. C
Wafer Test Limits Deleted ................................................................2
Edits to Absolute Maximum Ratings ..............................................3
Dice Characteristics Deleted............................................................3
Edits to Ordering Guide ...................................................................3
Edits to Figure 1.................................................................................7
Edits to Figure 3.................................................................................8
20-Position Chip Carrier (RC Suffix) Deleted ........................... 11
Rev. H | Page 2 of 16
OP282/OP482
SPECIFICATIONS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
At VS = ±15.0 V, TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted; applies to both A and G grades.
Table 1.
Parameter
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Offset Voltage
Conditions
VOS
OP282
OP282, −40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C
OP482
OP482, −40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C
VCM = 0 V
VCM = 0 V 1
VCM = 0 V
VCM = 0 V1
Input Bias Current
IB
Input Offset Current
IOS
Input Voltage Range
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio
Large-Signal Voltage Gain
CMRR
AVO
Offset Voltage Drift
Bias Current Drift
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage High
Output Voltage Low
Short-Circuit Limit
Open-Loop Output Impedance
POWER SUPPLY
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
Supply Current/Amplifier
Supply Voltage Range
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Slew Rate
Full-Power Bandwidth
Settling Time
Gain Bandwidth Product
Phase Margin
NOISE PERFORMANCE
Voltage Noise
Voltage Noise Density
Current Noise Density
1
Symbol
−11 V ≤ VCM ≤ +15 V, −40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C
RL = 10 kΩ, VO = ±13.5 V
RL = 10 kΩ, −40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C
Min
ZOUT
Max
Unit
0.2
3
4.5
4
6
100
500
50
250
+15
mV
mV
mV
mV
pA
pA
pA
pA
V
dB
V/mV
V/mV
μV/°C
pA/°C
0.2
3
1
−11
70
20
15
ΔVOS/ΔT
ΔIB/ΔT
VOH
VOL
ISC
Typ
90
10
8
RL = 10 kΩ
RL = 10 kΩ
Source
Sink
f = 1 MHz
PSRR
ISY
VS
VS = ±4.5 V to ±18 V, −40°C ≤ TA ≤ +85°C
VO = 0 V, −40°C ≤ TA ≤ 85°C
SR
BWP
tS
GBP
ØM
RL = 10 kΩ
1% distortion
To 0.01%
en p-p
en
in
0.1 Hz to 10 Hz
f = 1 kHz
13.5
3
13.9
−13.9
10
−12
200
25
210
±4.5
7
−8
316
250
±18
V
V
mA
mA
Ω
μV/V
μA
V
9
125
1.6
4
55
V/μs
kHz
μs
MHz
Degrees
1.3
36
0.01
μV p-p
nV/√Hz
pA/√Hz
The input bias and offset currents are characterized at TA = TJ = 85°C. Bias and offset currents are guaranteed but not tested at −40°C.
Rev. H | Page 3 of 16
−13.5
OP282/OP482
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
THERMAL RESISTANCE
Table 2.
Parameter
Supply Voltage
Input Voltage
Differential Input Voltage1
Output Short-Circuit Duration
Storage Temperature Range
Operating Temperature Range
Junction Temperature Range
Lead Temperature (Soldering 60 sec)
1
Rating
±18 V
±18 V
36 V
Indefinite
−65°C to +150°C
−40°C to +85°C
−65°C to +150°C
300°C
For supply voltages less than ±18 V, the absolute maximum input voltage is
equal to the supply voltage.
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
θJA is specified for the worst-case conditions, that is, a device in
socket for PDIP. θJA is specified for a device soldered in the circuit
board for SOIC_N, MSOP, and WLCSP packages. This was
measured using a standard 4-layer board.
Table 3.
Package Type
8-Lead MSOP [RM]
8-Lead SOIC_N (S-Suffix) [R]
14-Lead PDIP (P-Suffix) [N]
14-Lead SOIC_N (S-Suffix) [R]
14-Ball WLCSP [CB]1, 2
1
2
θJA
142
120
83
112
70
Simulated thermal numbers per JESD51-9.
Junction-to-board thermal resistance.
ESD CAUTION
Rev. H | Page 4 of 16
θJC
45
45
39
35
16
Unit
°C/W
°C/W
°C/W
°C/W
°C/W
OP282/OP482
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
70
180
90
20
45
0
0
40
30
AVCL = 100
AVCL = 10
20
10
0
AVCL = 1
–10
–45
00301-008
40
50
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
135
–20
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
60
PHASE (Degrees)
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
60
–20
100k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10k
–90
10M
1M
–30
1k
00301-005
–40
1k
Figure 6. OP282 Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs. Frequency
45
10k
100k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
30
10M
VS = ±15V
RL = 10kΩ
CL = 50pF
25
–SR
35
30
SLEW RATE (V/µs)
OPEN-LOOP GAIN (V/mV)
1M
Figure 9. OP282 Closed-Loop Gain vs. Frequency
VS = ±15V
RL = 10kΩ
40
25
20
15
20
15
10
+SR
10
00301-006
0
–75
–50
–25
0
25
50
75
100
0
–75
125
00301-009
5
5
–50
–25
TEMPERATURE (°C)
1000
+OS
50
–OS
30
20
00301-007
10
0
100
200
300
50
75
100
125
400
100
125
VS = ±15V
VCM = 0V
100
10
1
0.1
–75
500
LOAD CAPACITANCE (pF)
00301-010
INPUT BIAS CURRENT (pA)
VS = ±15V
RL = 2kΩ
70 V = 100mV p-p
IN
AVCL = 1
60 TA = 25°C
0
25
Figure 10. OP282 Slew Rate vs. Temperature
80
40
0
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 7. OP282 Open-Loop Gain vs. Temperature
OVERSHOOT (%)
OPEN-LOOP GAIN (dB)
80
–50
–25
0
25
50
75
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 8. OP282 Small-Signal Overshoot vs. Load Capacitance
Figure 11. OP282 Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
Rev. H | Page 5 of 16
OP282/OP482
20
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
100
10
1k
100
FREQUENCY (Hz)
0
–5
–10
VOL
00301-014
0
±5
±10
±15
±20
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
Figure 15. OP282 Output Voltage Swing vs. Supply Voltage
1000
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
100
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
100
OUTPUT IMPEDANCE (Ω)
INPUT BIAS CURRENT (pA)
5
–20
10k
Figure 12. OP282 Voltage Noise Density vs. Frequency
1000
VOH
10
–15
00301-011
1
10
TA = 25°C
RL = 10kΩ
15
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING (V)
VOLTAGE NOISE DENSITY (nV/√Hz)
1000
10
1
AVCL = 100
10
AVCL = 10
1
–10
–5
0
5
10
00301-015
0.1
–15
00301-012
AVCL = 1
0.1
100
15
1k
10k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE (V)
Figure 13. OP282 Input Bias Current vs. Common-Mode Voltage
480
480
TA = 25°C
475
SUPPLY CURRENT (µA)
470
465
460
470
465
460
0
±5
±10
±15
450
–50
±20
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
00301-016
455
455
00301-013
SUPPLY CURRENT (µA)
1M
Figure 16. OP282 Closed-Loop Output Impedance vs. Frequency
475
450
100k
–25
0
25
50
75
100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 14. OP282 Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage
Figure 17. OP282 Supply Current vs. Temperature
Rev. H | Page 6 of 16
125
OP282/OP482
10
VOH
8
6
4
2
0
100
1k
LOAD RESISTANCE (Ω)
25
20
15
10
5
0
100
10k
Figure 18. OP282 Absolute Output Voltage vs. Load Resistance
1k
10k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
140
VS = ±15V
120 TA = 25°C
1M
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
120
100
100
+PSRR
80
80
CMRR (dB)
60
40
20
–PSRR
60
40
20
0
–20
–20
00301-018
0
–40
–60
100
1k
10k
100k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
–40
–60
100
1M
Figure 19. OP282 PSRR vs. Frequency
14
1k
10k
100k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1M
Figure 22. OP282 CMRR vs. Frequency
200
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
300 × OP282
(600 OP AMPS)
12
160
SINK
10
120
UNITS
8
SOURCE
6
80
4
0
–50
–25
0
25
50
75
100
0
–2000
125
00301-022
40
2
00301-019
SHORT-CIRCUIT CURRENT (mA)
100k
Figure 21. OP282 Maximum Output Swing vs. Frequency
140
PSRR (dB)
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
RL = 10kΩ
AVCL = 1
00301-020
MAXIMUM OUTPUT SWING (V p-p)
VOL
12
00301-017
ABSOLUTE OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
14
30
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
00301-021
16
–1200
–400
0
400
1200
2000
VOS (µV)
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 20. OP282 Short-Circuit Current vs. Temperature
Figure 23. OP282 VOS Distribution, SOIC_N Package
Rev. H | Page 7 of 16
OP282/OP482
400
70
VS = ±15V
300 × OP282
(600 OP AMPS)
360
320
50
OVERSHOOT (%)
280
240
UNITS
AVCL = 1
NEGATIVE EDGE
VS = ±15V
RL = 2kΩ
VIN = 100mV p-p
60
200
160
120
AVCL = 1
POSITIVE EDGE
40
30
20
80
0
0
4
8
12
16
20
24
28
32
00301-026
10
00301-023
40
0
36
0
100
TCVOS (µV/°C)
Figure 24. OP282 TCVOS Distribution, SOIC_N Package
80
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
60
0
AVCL = 100
CLOSED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
PHASE (Degrees)
135
180
0
500
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
50
90
20
400
Figure 27. OP482 Small-Signal Overshoot vs. Load Capacitance
45
40
40
30
AVCL = 10
20
10
AVCL = 1
0
10k
100k
1M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10M
–20
00301-024
1k
100M
00301-027
–10
1k
10k
100k
1M
10M
100M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 25. OP482 Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs. Frequency
Figure 28. OP482 Closed-Loop Gain vs. Frequency
35
25
–SR
VS = ±15V
RL = 10kΩ
30
20
VS = ±15V
RL = 10kΩ
CL = 50pF
SLEW RATE (V/µs)
25
20
15
10
15
10
+SR
0
–75
–50
–25
0
25
50
75
100
0
–75
125
TEMPERATURE (°C)
00301-028
5
5
00301-025
OPEN-LOOP GAIN (V/mV)
OPEN-LOOP GAIN (dB)
60
300
200
LOAD CAPACITANCE (pF)
–50
–25
0
25
50
75
100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 26. OP482 Open-Loop Gain vs. Temperature
Figure 29. OP482 Slew Rate vs. Temperature
Rev. H | Page 8 of 16
125
OP282/OP482
1000
1000
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
10
1.0
0.1
–75
–50
–25
0
25
75
50
100
100
10
1
0.1
–15
125
00301-032
INPUT BIAS CURRENT (pA)
100
00301-029
INPUT BIAS CURRENT (pA)
VS = ±15V
VCM = 0V
–10
TEMPERATURE (°C)
0
25
50
TEMPERATURE (°C)
75
100
3.0
125
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING (V)
30
20
±5
±10
±20
±15
RL = 10kΩ
TA = 25°C
10
5
0
–5
–10
–15
00301-031
1k
0.90
15
40
100
0.95
20
50
0
10
1.00
Figure 34. OP482 Relative Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage
60
10
1.05
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
70
1.10
0
Figure 31. OP482 Phase Margin and Gain Bandwidth Product vs.
Temperature
80
TA = 25°C
0.85
00301-030
–25
15
00301-033
4.0
3.5
–50
10
00301-034
ØM
RELATIVE SUPPLY CURRENT (I SY)
GAIN BANDWIDTH PRODUCT (MHz)
4.5
GBW
40
–75
5
1.15
5.0
VS = ±15V
RL = 10kΩ
45
VOLTAGE NOISE DENSITY (nV/√Hz)
PHASE MARGIN (Degrees)
60
50
0
Figure 33. OP482 Input Bias Current vs. Common-Mode Voltage
Figure 30. OP482 Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
55
–5
COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE (V)
–20
0
10k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
±5
±10
±15
±20
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
Figure 32. OP482 Voltage Noise Density vs. Frequency
Figure 35. OP482 Output Voltage Swing vs. Supply Voltage
Rev. H | Page 9 of 16
OP282/OP482
100
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
500
80
400
60
300
–PSRR
40
20
200
AVCL = 10
100
0
0
100
1k
10k
00301-035
AVCL = 1
100k
00301-038
AVCL = 100
20
100
1M
1k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
20
SHORT-CIRCUIT CURRENT (mA)
1.05
1.00
0.95
0.90
0.85
00301-036
RELATIVE SUPPLY CURRENT (ISY)
1.10
0
25
50
75
100
15
10
SOURCE
5
0
125
–75
TEMPERATURE (°C)
–25
0
25
50
30
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
POSITIVE
SWING
8
NEGATIVE
SWING
6
4
0
100
00301-037
2
1k
125
20
15
10
5
0
10k
LOAD RESISTANCE (Ω)
00301-040
10
100
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
AVCL = 1
RL = 10kΩ
25
12
75
Figure 40. OP482 Short-Circuit Current vs. Temperature
MAXIMUM OUTPUT SWING (V)
ABSOLUTE OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
–50
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 37. OP482 Relative Supply Current vs. Temperature
14
VS = ±15V
SINK
1.15
–25
1M
Figure 39. OP482 Power Supply Rejection Ratio (PSRR) vs. Frequency
VS = ±15V
–50
100k
00301-039
1.20
0.80
–75
10k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 36. OP482 Closed-Loop Output Impedance vs. Frequency
16
VS = ±15V
∆V = 100mV
TA = 25°C
+PSRR
PSRR (dB)
IMPEDANCE (Ω)
600
1k
10k
100k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 41. OP482 Maximum Output Swing vs. Frequency
Figure 38. OP482 Maximum Output Voltage vs. Load Resistance
Rev. H | Page 10 of 16
1M
OP282/OP482
320
100
280
80
240
200
UNITS
CMRR (dB)
60
40
160
120
20
80
–20
100
1k
40
10k
100k
0
1M
Figure 42. OP482 Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR) vs. Frequency
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
300 × OP482
(1200 OP AMPS)
600
400
300
200
100
00301-045
UNITS
500
0
0
400
–2000 –1600 –1200 –800 –400
VOS (µV)
0
4
8
12
16
20
24
28
TCVOS (µV/°C)
FREQUENCY (Hz)
700
00301-043
VS = ±15V
TA = 25°C
VCM = 100mV
00301-041
0
800
1200 1600 2000
Figure 43. OP482 VOS Distribution, PDIP Package
Rev. H | Page 11 of 16
Figure 44. OP482 TCVOS Distribution, PDIP Package
32
OP282/OP482
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
amp against phase reversal. R1, D2, and D3 limit the input
current when the input exceeds the supply rail. The resistor
should be selected to limit the amount of input current below
the absolute maximum rating.
V+
VIN
HIGH-SIDE SIGNAL CONDITIONING
D2
IN5711
R1
10kΩ
D1
IN5711
V–
Figure 46. Phase Reversal Solution Circuit
One application where such sensing is commonly used is in the
sensing of power supply currents. Therefore, the OP282/OP482
can be used in current sensing applications, such as the partial
circuit shown in Figure 45. In this circuit, the voltage drop across
a low value resistor, such as the 0.1 Ω shown here, is amplified
and compared to 7.5 V. The output can then be used for current
limiting.
VOLTAGE (5V/DIV)
VS = ±15V
0.1Ω
500kΩ
RL
2
VOUT
100k Ω
1/2
OP282
VIN
00301-044
100kΩ
VOUT
D3
IN5711
Many applications require the sensing of signals near the positive
rail. OP282 and OP482 were tested and are guaranteed over a
common-mode range (−11 V ≤ VCM ≤ +15 V) that includes the
positive supply.
15V
V+
V–
OP282/
OP482
00301-042
The OP282 and OP482 are dual and quad JFET op amps that
are optimized for high speed at low power. This combination
makes these amplifiers excellent choices for battery-powered or
low power applications that require above average performance.
Applications benefiting from this performance combination
include telecommunications, geophysical exploration, portable
medical equipment, and navigational instrumentation.
TIME (200µs/DIV)
00301-046
500kΩ
Figure 45. High-Side Signal Conditioning
PHASE INVERSION
Most JFET input amplifiers invert the phase of the input signal
if either input exceeds the input common-mode range. For the
OP282/OP482, a negative signal in excess of 11 V causes phase
inversion. This is caused by saturation of the input stage, leading
to the forward-biasing of a gate-drain diode. Phase reversal in
the OP282/OP482 can be prevented by using Schottky diodes to
clamp the input terminals to each other and to the supplies. In
the simple buffer circuit shown in Figure 46, D1 protects the op
Figure 47. No Phase Reversal
ACTIVE FILTERS
The wide bandwidth and high slew rates of the OP282/OP482
make either one an excellent choice for many filter applications.
There are many active filter configurations, but the four most
popular configurations are Butterworth, elliptic, Bessel, and
Chebyshev. Each type has a response that is optimized for a
given characteristic, as shown in Table 4.
Table 4. Active Filter Configurations
Type
Butterworth
Chebyshev
Elliptic
Bessel (Thompson)
Selectivity
Moderate
Good
Best
Poor
Overshoot
Good
Moderate
Poor
Best
Phase
Nonlinear
Amplitude (Pass Band)
Maximum flat
Equal ripple
Equal ripple
Linear
Rev. H | Page 12 of 16
Amplitude (Stop Band)
Equal ripple
OP282/OP482
This cutoff frequency can now be expressed as
PROGRAMMABLE STATE VARIABLE FILTER
The circuit shown in Figure 48 can be used to accurately
program the Q, the cutoff frequency (fC), and the gain of a twopole state variable filter. OP482 devices have been used in this
design because of their high bandwidths, low power, and low
noise. This circuit takes only three packages to build because of
the quad configuration of the op amps and DACs.
fC =
1
⎛ D1 ⎞
⎜
⎟
2πR1C1 ⎝ 256 ⎠
where D1 is the digital code for the DAC.
The gain of this circuit is set by adjusting D3. The gain equation is
Gain =
The DACs shown are used in the voltage mode; therefore, many
values are dependent on the accuracy of the DAC only and not
on the absolute values of the DAC’s resistive ladders. This
makes this circuit unusually accurate for a programmable filter.
R4 ⎛ D3 ⎞
⎜
⎟
R5 ⎝ 256 ⎠
DAC 2 is used to set the Q of the circuit. Adjusting this DAC
controls the amount of feedback from the band-pass node to
the input summing node. Note that the digital value of the
DAC is in the numerator; therefore, zero code is not a valid
operating point.
Adjusting DAC 1 changes the signal amplitude across R1; therefore,
the DAC attenuation times R1 determines the amount of signal
current that charges the integrating capacitor, C1.
Q=
R2 ⎛ 256 ⎞
⎜
⎟
R3 ⎝ D2 ⎠
R7
2kΩ
R4
2kΩ
1/4
DAC8408
1/4
OP482
C1
1000pF
R5
2kΩ
1/4
OP482
1/4
1/4
OP482
DAC8408
C1
1000pF
R1
2kΩ
1/4
OP482
1/4
DAC8408
1/4
OP482
R1
2kΩ
1/4
OP482
HIGH PASS
LOW
PASS
BAND PASS
R6
2kΩ
R3
2kΩ
R2
2kΩ
1/4
1/4
OP482
1/4
DAC8408
OP482
00301-047
VIN
Figure 48. Programmable State Variable Filter
Rev. H | Page 13 of 16
OP282/OP482
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
3.20
3.00
2.80
8
3.20
3.00
2.80
5.15
4.90
4.65
5
1
4
PIN 1
0.65 BSC
0.95
0.85
0.75
1.10 MAX
0.15
0.00
0.38
0.22
COPLANARITY
0.10
0.80
0.60
0.40
8°
0°
0.23
0.08
SEATING
PLANE
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-187-AA
Figure 49. 8-Lead Mini Small Outline Package [MSOP]
(RM-8)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
5.00 (0.1968)
4.80 (0.1890)
8
1
5
4
1.27 (0.0500)
BSC
0.25 (0.0098)
0.10 (0.0040)
COPLANARITY
0.10
SEATING
PLANE
6.20 (0.2441)
5.80 (0.2284)
1.75 (0.0688)
1.35 (0.0532)
0.51 (0.0201)
0.31 (0.0122)
0.50 (0.0196)
0.25 (0.0099)
45°
8°
0°
0.25 (0.0098)
0.17 (0.0067)
1.27 (0.0500)
0.40 (0.0157)
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-012-A A
CONTROLLING DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS; INCH DIMENSIONS
(IN PARENTHESES) ARE ROUNDED-OFF MILLIMETER EQUIVALENTS FOR
REFERENCE ONLY AND ARE NOT APPROPRIATE FOR USE IN DESIGN.
Figure 50. 8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_N]
Narrow Body
S-Suffix (R-8)
Dimensions shown in millimeters and (inches)
Rev. H | Page 14 of 16
012407-A
4.00 (0.1574)
3.80 (0.1497)
OP282/OP482
0.775 (19.69)
0.750 (19.05)
0.735 (18.67)
14
8
1
0.280 (7.11)
0.250 (6.35)
0.240 (6.10)
7
0.325 (8.26)
0.310 (7.87)
0.300 (7.62)
0.100 (2.54)
BSC
0.060 (1.52)
MAX
0.210 (5.33)
MAX
0.015
(0.38)
MIN
0.150 (3.81)
0.130 (3.30)
0.110 (2.79)
SEATING
PLANE
0.022 (0.56)
0.018 (0.46)
0.014 (0.36)
0.195 (4.95)
0.130 (3.30)
0.115 (2.92)
0.015 (0.38)
GAUGE
PLANE
0.430 (10.92)
MAX
0.005 (0.13)
MIN
0.014 (0.36)
0.010 (0.25)
0.008 (0.20)
0.070 (1.78)
0.050 (1.27)
0.045 (1.14)
070606-A
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-001
CONTROLLING DIMENSIONS ARE IN INCHES; MILLIMETER DIMENSIONS
(IN PARENTHESES) ARE ROUNDED-OFF INCH EQUIVALENTS FOR
REFERENCE ONLY AND ARE NOT APPROPRIATE FOR USE IN DESIGN.
CORNER LEADS MAY BE CONFIGURED AS WHOLE OR HALF LEADS.
Figure 51. 14-Lead Plastic Dual In-Line Package [PDIP]
P-Suffix (N-14)
Dimension shown in inches and (millimeters)
8.75 (0.3445)
8.55 (0.3366)
8
14
1
7
1.27 (0.0500)
BSC
0.25 (0.0098)
0.10 (0.0039)
COPLANARITY
0.10
0.51 (0.0201)
0.31 (0.0122)
6.20 (0.2441)
5.80 (0.2283)
0.50 (0.0197)
0.25 (0.0098)
1.75 (0.0689)
1.35 (0.0531)
SEATING
PLANE
45°
8°
0°
0.25 (0.0098)
0.17 (0.0067)
1.27 (0.0500)
0.40 (0.0157)
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-012-AB
CONTROLLING DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS; INCH DIMENSIONS
(IN PARENTHESES) ARE ROUNDED-OFF MILLIMETER EQUIVALENTS FOR
REFERENCE ONLY AND ARE NOT APPROPRIATE FOR USE IN DESIGN.
Figure 52. 14-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_N]
Narrow Body
S-Suffix (R-14)
Dimensions shown in millimeters and (inches)
Rev. H | Page 15 of 16
060606-A
4.00 (0.1575)
3.80 (0.1496)
OP282/OP482
0.645
0.600
0.555
1.165
1.128
1.090
0.3465
BSC
SEATING
PLANE
0.3465
BSC
3
BALL A1
IDENTIFIER
2
1
A
B
0.20
BSC
2.160
2.123
2.085
0.287
0.267
0.247
C
D
1.60
BSC
E
F
G
H
J
0.415
0.400
0.385
0.05
COPLANARITY
0.230
0.200
0.170
BOTTOM VIEW
(BALL SIDE UP)
0.693
BSC
032509-A
TOP VIEW
(BALL SIDE DOWN)
0.40
BSC
Figure 53. 14-Ball Wafer Level Chip Scale Package [WLCSP]
CB-14-2
Controlling dimensions are millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model 1
OP282ARMZ
OP282ARMZ-REEL
OP282GS
OP282GS-REEL
OP282GS-REEL7
OP282GSZ
OP282GSZ-REEL
OP282GSZ-REEL7
OP482ACBZ-RL
OP482ACBZ-R7
OP482GP
OP482GPZ
OP482GS
OP482GS-REEL
OP482GS-REEL7
OP482GSZ
OP482GSZ-REEL
OP482GSZ-REEL7
1
Temperature Range
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
−40°C to +85°C
Package Description
8-Lead MSOP
8-Lead MSOP
8-Lead SOIC_N
8-Lead SOIC_N
8-Lead SOIC_N
8-Lead SOIC_N
8-Lead SOIC_N
8-Lead SOIC_N
14-Ball WLCSP
14-Ball WLCSP
14-Lead PDIP
14-Lead PDIP
14-Lead SOIC_N
14-Lead SOIC_N
14-Lead SOIC_N
14-Lead SOIC_N
14-Lead SOIC_N
14-Lead SOIC_N
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
©1991–2010 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D00301-0-9/10(H)
Rev. H | Page 16 of 16
Package Option
RM-8
RM-8
S-Suffix (R-8)
S-Suffix (R-8)
S-Suffix (R-8)
S-Suffix (R-8)
S-Suffix (R-8)
S-Suffix (R-8)
CB-14-2
CB-14-2
P-Suffix (N-14)
P-Suffix (N-14)
S-Suffix (R-14)
S-Suffix (R-14)
S-Suffix (R-14)
S-Suffix (R-14)
S-Suffix (R-14)
S-Suffix (R-14)
Branding
A0B
A0B
A2J
A2J