The demand for many varieties of rechargeable batteries
advertisement
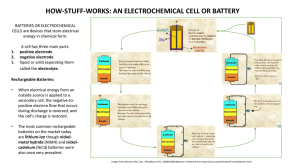
The demand for many varieties of rechargeable batteries is due to their lower cost and lower environmental impact. LEARNING OBJECTIVE [ edit ] Discuss the general characteristics of rechargeable batteries KEY POINTS [ edit ] Rechargeable batteries store energy through a reversiblechemical reaction, which allows charge to be stored again after the battery has been drained. Rechargeable batteries have lower total cost of use and environmental impact than disposable batteries, which might be why the U.S. demand for rechargeable batteries is growing much faster than is the demand for non-rechargeable batteries. Common types of rechargeable batteries are lead-acid, nickel-cadmium (NiCd), nickelmetal hydride (NiMH), lithium-ion (Li-ion), lithium-ion polymer (LiPo), and rechargeable alkalinebatteries. TERMS [ edit ] energy density The amount of energy that can be stored relative to the volume of the battery. secondary cell An electric cell that is rechargeable because it converts chemical energy into electrical energy by a reversible chemical reaction. Give us feedback on this content: FULL TEXT [edit ] Rechargeable Batteries A rechargeable battery is a type of electrical battery that is comprised of one or more electrochemical cells. It is known as asecondary cell because its electrochemical reactions are electrically reversible. In other words, after the stored charge has been drained, the battery's chemical reactions can occur again, in reverse, to store a new charge. The U.S. demand for rechargeable batteries is growing twice as fast as the demand for non-rechargeable batteries, in part because rechargeable batteries have lower environmental impact and total cost of use than do disposable Register for FREE to stop seeing ads batteries. Grid energy storage applications use rechargeable batteries for load-leveling. Load-leveling involves storing electric energy for use during peak load period. By charging batteries during periods of low electrical demand for use during periods of high demand, load-leveling helps eliminate the need for expensive peaking power plants and helps reduce the cost of generators over more hours of operation. Rechargeable Battery Construction As with all batteries, rechargeable batteries consist of an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte. During charging, the anode material is oxidized, producing electrons, and the cathode is reduced, consuming electrons. Current Charge Charger Positive Negative Separator Cathode Charging a battery Electrolyte Anode Diagram of charging a battery. These electrons constitute the current flow in the external circuit. The electrolyte may serve as a simple buffer for internal ion flow between the electrodes, as in lithium-ion and nickelcadmium cells, or it may be an active participant in the electrochemical reaction, as in leadacid cells. Types of Rechargeable Batteries Several different combinations of chemicals are commonly used in rechargeable batteries. Different types include lead-acid, nickel-cadmium (NiCd), nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), lithium-ion (Li-ion), lithium-ion polymer (LiPo), and rechargeable alkaline batteries. Lead-Acid Batteries Lead-acid batteries, invented in 1859 by French physicist Gaston Planté, are the oldest type of rechargeable battery. Their ability to supply high-surge currents means that the cells maintain a relatively large power-to-weight ratio. These features, along with their low cost, make them attractive for use in motor vehicles, which require high currents. Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries A nickel-metal hydride battery, abbreviated NiMH or Ni-MH, is very similar to the nickelcadmium cell (NiCd). NiMH batteries use positive electrodes of nickel oxyhydroxide (NiOOH), as does the NiCd, but the negative electrodes use a hydrogenabsorbingalloy instead of cadmium. A NiMH battery can have two to three times the capacity of a NiCd battery of equivalent size, and its energy density approaches that of a lithium-ion cell. Lithium-Ion Batteries The lithium-ion battery is a family of rechargeable batteries in which lithium ions move from the negative electrode to the positive electrode during discharge, and back when charging. The negative electrode of a conventional lithium-ion cell is made from carbon. The positive electrode is a metal oxide, and the electrolyte is a lithium salt in an organic solvent. They are one of the most popular types of rechargeable battery for portable electronics, with one of the best energy densities and only a slow loss of charge when not in use. Lithium ion batteries are more expensive than NiCd batteries but operate over a widertemperature range while being smaller and lighter. They are fragile and thus need a protective circuit to limit peak voltages. Lithium-Ion Polymer Batteries Lithium-ion polymer (LiPo) batteries are usually composed of several identical secondary cells in parallel to increase the discharge-current capability. They are often available in series "packs" to increase the total available voltage. Their primary distinction from lithium-ion batteries is that their lithium salt electrolyte is not held in an organic solvent. Instead, it is in asolid polymer composite, such as polyethylene oxide or polyacrylonitrile. The advantages of LiPo over the lithium-ion design include potentially lower cost of manufacture, adaptability to a wide variety of packaging shapes, reliability, and ruggedness. Their major disadvantage is that they hold less charge. Alkaline Batteries There are also rechargeable forms of alkaline batteries, which are a type of primary battery dependent upon the reaction between zinc (Zn) and manganese dioxide (MnO2). They are manufactured fully charged and have the ability to carry their charge for years, longer than most NiCd and NiMH batteries, which self-discharge. Rechargeable alkaline batteries can also have a high recharging efficiency and have less environmental impact than disposable cells.