Electronic Circuits – EE359A Final project requirements
advertisement

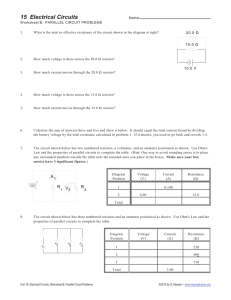
Electronic Circuits – EE359A Final project requirements • Write a report describing your design, including • Definition of the problem addressed by your design • Assumptions • Design goals (e.g., performance) • Component specifications, including tolerance and power dissipation • Presentation of design (including schematic) • Circuit analysis using concepts presented in course and textbook • Simulation results, including any models used • Tolerance of system design to system variation, e.g., component tolerances, supply voltage, temperature, etc. • Conclusions, observations • References Electronic Circuits – EE359A Final project requirements • The written report should be 8-10 pages, not including illustrations and simulation results. Each student will present a 5 minute verbal description of their project during the last two classes • A 1-2 paragraph project abstract will be due in 2 weeks describing the circuit you plan on designing Electronic Circuits – EE359A Sample projects • The following is a list of sample projects to illustrate the level of difficulty expected in your design project. You may choose one of these or propose your own problem of about the same complexity. Any of these circuits are available off-theshelf as IC modules, that is not what is required – you are to design the circuit out of discrete components (transistors, diodes, resistors, capacitors, etc.) • Just like Olympic high diving and acrobatic events, grading is based on performance as well as difficulty of task attempted. • Three transistor audio amplifier: input signal 10 mV P-P, output 2 watts into 8 ohm speaker. Frequency response: 50 Hz – 10 kHz ±1 dB. Operates with +12 V DC supply voltage. THD < .5% with maximum input level sine wave. • Transistorized oscillator: output signal up to 5 V P-P, level controlled to within .1 dB with +12±1 V DC supply voltage over an output frequency from 100 Hz to 10 kHz. THD < 1% for sine wave output. Extra credit for maintaining level to within .01 dB, extra credit for operation to 1 MHz, extra credit for generation of sine, triangle and square waves. • Regulated power supply: input voltage 90 – 130 VAC rms, output 12VDC ±1% with output current from 0 – 2A. Electronic Circuits – EE359A More sample projects • Audio filter with response from DC – 3000 Hz +/- 1 dB and at least 40 dB attenuation at 4000 Hz • “Color organ” – a device consisting of a set of filters that process an audio signal and drive a set of lamps or LEDs based on the energy present at individual ranges of frequencies (e.g., red for low frequencies, yellow for mid range, green for high frequencies) • LED sound level meter – one or more LEDs light up depending on sound level (on a logarithmatic scale corresponding to dB or Volume Units -VU) • DC motor speed H-bridge controller – a pulse width modulator controls the speed (and direction) of a DC motor based • Nonsense box – a series of LEDs or neon bulbs blink randomly based on operation of a series of relaxation oscillators • The Inebriated Lady Bug (a name used in Popular Electronics Magazine from ~1963) – a line following robot using only light sensors, transistors and DC motor controllers Electronic Circuits – EE359A Final project requirements • Do not over-specify components, e.g., a 2 Watt resistor where a ¼ watt will do, a 1% resistor where a 10% will do • Extra credit for experimentally verifying circuit operation