Energy and Electric Potential Potential Difference (∆V)
advertisement
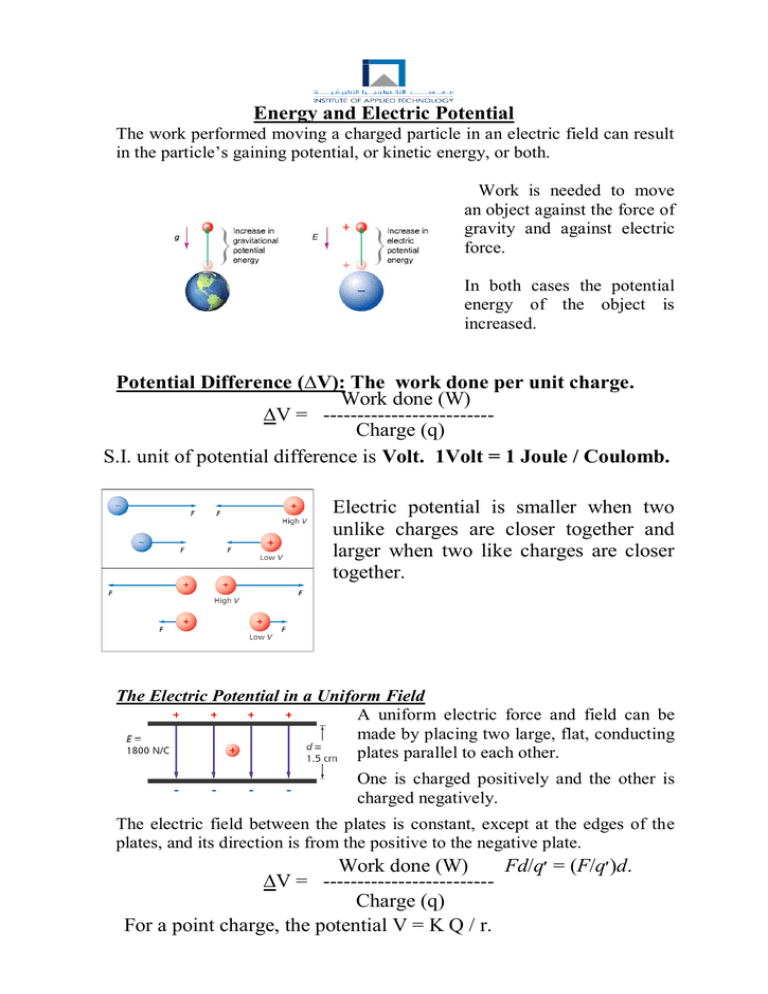
Energy and Electric Potential The work performed moving a charged particle in an electric field can result in the particle’s gaining potential, or kinetic energy, or both. Work is needed to move an object against the force of gravity and against electric force. In both cases the potential energy of the object is increased. Potential Difference (∆V): The work done per unit charge. Work done (W) ∆V = ------------------------Charge (q) S.I. unit of potential difference is Volt. 1Volt = 1 Joule / Coulomb. Electric potential is smaller when two unlike charges are closer together and larger when two like charges are closer together. The Electric Potential in a Uniform Field A uniform electric force and field can be made by placing two large, flat, conducting plates parallel to each other. One is charged positively and the other is charged negatively. The electric field between the plates is constant, except at the edges of the plates, and its direction is from the positive to the negative plate. Work done (W) Fd/q( = ׳F/q)׳d. ∆V = ------------------------Charge (q) For a point charge, the potential V = K Q / r. Electric Potential Difference in a Uniform Field, ΔV = Ed The electric potential increases in the direction opposite the electric field direction. That is, the electric potential is higher near the positively charged plate. The units of E and d are (N/C)(m). This is equivalent to one J/C, which is the definition of 1 V. Equipotential: Whenever the electric potential difference between two or more positions is zero, those positions are said to be at equipotential. Mllikan’s Oil drop Experiment Millikan’s experiment showed that Charge is quantized. It means that An object can have only a charge with magnitude that integral multiple of the charge of an electron. Q = + ne n =0,1,2,3….. e = 1.6 x 10 –19C. Sharing of charge : Charge transfer takes place from the point where the higher potential to the lower potential when they are in contact. In irregular shapes charges will be closest together at sharp points. Lightning rod is pointed so that the electric field will be strong near the end of the rod. As a result of the rod’s sharply pointed shape, charges in the clouds spark to the rod, rather than to a chimney or other high point on a house or other building. From the rod, a conductor takes the charges safely to the ground. Capacitor: Device used to store the charges. It is made up of two conductors of equal and opposite charges separated by an insulator. For a given shape and size of an object, the ratio of charge stored to electric potential difference is a constant called the capacitance, C. Capacitance is the ratio of charge on one plate to potential difference. C = q / ∆V. It is measured by the unit called Farad. 1 Farad is 1 Coulomb per 1 volt. 1Micro farad (1μF) = 10-6F. 1 Pico farad (1pF) = 10-12F. Capacitance depends only on the construction of the capacitor, not on the charge q. ******************************** N.Krishnan