the temperate forest pdf
advertisement

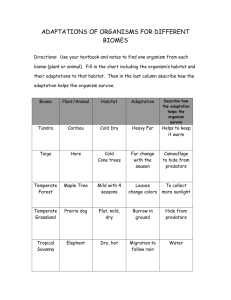
American Beech Shelter: Beech trees live in shady to sunny places. Food: They make their food from sunlight. This process is called photosynthesis. Size: 18–24 meters (60–80 feet) tall Kind of Organism: Plant Habitat: Temperate forest Predators: Birds, squirrels, deer, skunks, bears Adaptation: Beech trees have many leaves to catch the sunlight. Interesting Facts: Wood from the beech tree is almost white. It is used to make toys and furniture. 1 of 8 Temperate Forest Photos: © John Sohlden/Visuals Unlimited; © Patti Murray/Earth Scenes (inset) FOSS® Habitat Organism Cards Copyright © The Regents of the University of California Black Bear Shelter: Black bears live in a cave or a hole in a tree or the ground. Food: They eat fruit, nuts, berries, insects, fish, eggs, honey, turtles, and small mammals. Size: Males 90–105 centimeters (36–42 inches feet) tall; females smaller Kind of Organism: Mammal Habitat: Temperate Forest Predators: Brown bears, wolves Adaptation: Black bears are mostly active at night. They can swim and climb trees. Interesting Facts A mother black bear gives birth to two cubs in her winter den. 2 of 8 Temperate Forest Photo: © Art Explosion FOSS® Habitat Organism Cards Copyright © The Regents of the University of California Cicada Shelter: Adult cicadas live on leaves and branches. Cicada babies and young live underground. Food: The babies and young eat roots underground. The adults suck tree sap. Size: 2–5 centimeters (1–2 inches) long Kind of Organism: Insect Habitat: Temperate forest, grassland, desert Predators: Rattlesnakes, birds, foxes, skunks Adaptation: After hatching, baby cicada dig underground, where they live for three or more years. Interesting Facs: Adult cicadas come out of the ground in June. They and feed on the plants by sucking the sap and juices. 3 of 8 Temperate Forest Photo: © Harrison Shull/shullphoto.com FOSS® Habitat Organism Cards Copyright © The Regents of the University of California Earthworm Shelter: Earthworms live in the upper layers of the soil. Food: They eat plants and animals that have died. Size: 1–10 centimeters (0.4–3.9 inches) long Kind of Organism: Annelid Habitat: Temperate forest, wetland, grassland, rain forest Predators: Birds, frogs, lizards, salamanders, raccoons, turtles Adaptation: Earthworms can tunnel in the soil to find food, and to hide from predators. Interesting Fact: People add earthworms to gardens to help break up soil, and to add nutrients. 4 of 8 Temperate Forest Photo: Carol Sevilla/Lawrence Hall of Science FOSS® Habitat Organism Cards Copyright © The Regents of the University of California Robin Shelter: Robins live in trees, bushes, gardens, and towns. Food: They eat fruits, nuts, insects, and earthworms. Size: 23–28 centimeters (9–11 inches) long Kind of Organism: Bird Habitat: Temperate forest, grassland Predators: Foxes, skunks, raccoons, hawks, bobcats Adaptation: Robins build a nest in trees made of mud, grass, and twigs. They line it with soft grass. Interesting Fact: Robins lay hree to five blue-green eggs twice a year. 5 of 8 Temperate Forest Photo: © Art Explosion FOSS® Habitat Organism Cards Copyright © The Regents of the University of California Striped Skunk Shelter: Striped skunks live in burrows or dens that other animals have left. Food: They eat mice, insects, bird eggs, grass, leaves, seeds, and fruits. Size: 52–80 centimeters (20–31 inches) long Kind of Organism: Mammal Habitat: Temperate forest, grassland Predators: Bobcats, foxes, golden eagles, coyotes Adaptation: The black and white stripes of the skunk are a warning to predators. A skunk will lift its tail and spray a bad smell to defend itself. Interesting Fact: The spray of skunks is not poisonous, but it can make you feel sick, and sting your eyes. 6 of 8 Temperate Forest Photo: © Renee Lynn/Photo Researchers, Inc. FOSS® Habitat Organism Cards Copyright © The Regents of the University of California Sundew Shelter: Sundew grows best in moist places where it is sunny. Food: They make their food from sunlight. This process is called photosynthesis. They also catch insects. Size: 10–25 centimeters (4–10 inches) tall Kind of Organism: Plant Habitat: Temperate forest, wetland Adaptation: The leaves of a sundew have tiny, sticky hairs. Insects stick to the hairs, and the plants are digested by them. Interesting Facts: The sundew can grow in wet places where the soil has few nutrients. 7 of 8 Temperate Forest Photo: © Stephen P. Parker/Photo Researchers, Inc. FOSS® Habitat Organism Cards Copyright © The Regents of the University of California White-Tailed Deer Shelter: White-tailed deer sleep at dawn in places hidden under bushes and trees. Food: They eat grass, fruits, nuts, leaves, and mushrooms. Size: 68–114 centimeters (27–45 inches) tall Kind of Organism: Mammal Habitat: Temperate forest, grassland Predators: Coyotes, wolves, bobcats, bears Adaptation: White-tailed deer are active at night. They can run fast or hide to escape predators. Interesting Fact: Mother deer give birth to one to three fawns in the spring or summer. 8 of 8 Temperate Forest Photo: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service FOSS® Habitat Organism Cards Copyright © The Regents of the University of California