LEARNING MODULE DESCRIPTION (SYLLABUS) I. General
advertisement
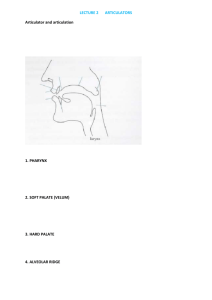
LEARNING MODULE DESCRIPTION (SYLLABUS) I. General information 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Module title: Experimental phonetics Module code: 09-EXPHON-22 Module type – compulsory or optional: optional Programme title st Cycle of studies (1st or 2nd cycle of studies or full master’s programme): 1 cycle Year of studies (where relevant) Terms in which taught (summer/winter term): summer & winter term Type of classes and the number of contact hours (e.g. lectures: 15 hours; practical classes: 30 hours): practical classes, 30 hours 9. Number of ECTS credits: 6 10.Name, surname, academic degree/title of the module lecturer/other teaching staff: Agnieszka Wagner, PhD, Katarzyna Klessa, PhD 11.Language of classes: English II. Detailed information 1. Module aim (aims): The aim of the course is to consolidate and broaden theoretical knowledge in general phonetics and phonology (with a focus on both Polish and English language) and to develop practical skills in the field of description and classification of speech sounds. The course will provide students with hands-on experience in methods of experimental phonetic research, including audio recording, speech database construction, recording and interpreting speech air flow and pressure and the design of perception tests. Additionally, the course will offer training in writing up experimental results for publication. 2. Pre-requisites in terms of knowledge, skills and social competences (where relevant): proficiency in English (at least B1 level) 3. Module learning outcomes in terms of knowledge, skills and social competences and their reference to programme learning outcomes Upon completion of the course, the student will: Reference to programme # learning outcomes 09-EXPHON-22_01 Identify and classify the main types of speech sounds on the basis of: sagittal slices of articulation, spectrograms of recorded speech signals displayed by a software for speech analysis K_W02, K_U04, K_U05 09-EXPHON-22_02 - Have knowledge of and be able to effectively apply standard tools and methods used in the field of experimental phonetics Know and will be able to explain relation between articulatory features of speech sounds and their spectrographic representation and be aware of differences between speech production and perception Transcribe a text phonetically (in Polish) K_W02, K_W05, K_W08, K_U06 - Be able to align and label speech files containing recorded utterances on the basis of their visual (spectrogram, oscillogram) and audio representation K_U05, K_U06 Learning outcomes symbol* 09-EXPHON-22_03 09-EXPHON-22_04 09-EXPHON-22_05 K_W02, K_U04 K_U04, K_U05 1 09-EXPHON-22_06 - have knowledge and skills necessary to K_W06, K_U05, K_U06, K_U09 carry out measurements of segmental and suprasegmental features of speech, to manipulate speech parameters (e.g. F0 smoothing, interpolation), to extract acoustic parameters and to create database for experiment 09-EXPHON-22_07 - know how to design and carry out a phonetic experiment K_U03, K_U04, 09-EXPHON-22_08 - Be able to create a simple recording scenario according to specific phoneticacoustic criteria and to carry out recordings based on this scenario and with cooperation with other persons K_U04, K_K05, K_K06, K_K07 09-EXPHON-22_09 - know how to plan and carry out a perception test with cooperation with other persons K_U04, K_K05, K_K06, K_K07 09-EXPHON-22_10 K_W05, K_W06, K_U06 - have the knowledge of and be able to make use of basic and more advanced statistical methods (T-test, ANOVA, nonparametric tests, CART, neural networks, linear/multiple regression) in order to test experimental hypotheses 09-EXPHON-22_11 - have the knowledge and skills necessary to represent experimental results (in forms of graphs, tables etc.) K_U06, K_U11, 09-EXPHON-22_12 Know the specialist terminology of the subject domains in English and in Polish and is aware of the main contemporary challenges for experimental phonetics (as an interdisciplinary field) in Poland and in other countries (as regards linguistic, social and cultural factors) K_W01, K_W02 * module code, e.g. KHT_01 (KHT – module code in USOS; stands for Polish “Kataliza Heterogeniczna” /Heterogeneous Catalysis/ ) # programme learning outcomes (e.g. K_W01, K_U01, … ); first K stands for programme title symbol in Polish, W for “wiedza” (knowledge) in Polish, U – for “umiejętności” (skills) in Polish, K – for “kompetencje społeczne” (social competences) in Polish 01, 02… - learning outcome number 4. Learning content Module title Learning content symbol* Learning content description Reference to module learning # outcomes TK_01 Phonetics as a scientific study of speech: of anatomy and physiology of the vocal tract, initiation of speech, airstream mechanisms and phonation types. Objectives and application domains of phonetics. 09-EXPHON-22_03, 09EXPHON-22_12 Description of articulatory and acoustic features of vowels and consonants 09-EXPHON-22_01, 09EXPHON-22_03, 09-EXPHON22_05, 09-EXPHON-22_06 The most important rules of grapheme-to-phoneme 09-EXPHON-22_04, 09- TK_02 TK_03 2 conversion (on the example of Polish) EXPHON-22_05 TK_04 09-EXPHON-22_01, 09Phonetic alignment of continuous speech recordings EXPHON-22_02, 09-EXPHON22_03, 09-EXPHON-22_04, 09(using computer tools) EXPHON-22_05, TK_05 Speech production and perception 09-EXPHON-22_03 Spectrographic analysis of speech using speech analysis software 09-EXPHON-22_01, 09EXPHON-22_02, 09-EXPHON22_03, 09-EXPHON-22_11 TK_06 TK_07 TK_08 TK_09 TK_10 TK_11 TK_12 Measurements, extraction, manipulation and graphical representation of selected speech parameters Design of a phonetic experiment: methodological and practical issues. Creation and selection of linguistic material and recordings of speech database for experiment. Design and realization of a perception test. Statistical testing of experimental hypotheses. Representation of the experimental results. 09-EXPHON-22_06, 09EXPHON-22_11 09-EXPHON-22_07 09-EXPHON-22_07, EXPHON-22_08 09-EXPHON-22_07, EXPHON-22_09 09-EXPHON-22_07, EXPHON-22_10 09-EXPHON-22_07, EXPHON-22_11 09090909- * e.g. TK_01, TK_02, … (TK stands for “treści kształcenia” /learning content/ in Polish) # e.g. KHT_01 – module code as in Table in II.3 5. Reading list Phonetics in general: Clark, J. and Yallop, C. (1995) An introduction to phonetics and phonology. 2nd edition. Oxford: Blackwell Davenport, M., Hannahs, S.J. (1998). Introducing phonetics & phonology. London, Arnold. Ladefoged, P. (1962) Elements of acoustic phonetics. Oliver and Boyd, Edinburgh and London Ladefoged, P. (2001) Vowels and Consonants. An introduction to the sounds of languages. Blackwell Publishers Laver, J. (1994). Principles of phonetics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Lieberman, P., Blumstein, S. (1988). Speech physiology, speech perception and acoustic phonetics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Polish phonetics and phonology: Dukiewicz, L. (1995). Fonetyka. [In:] H. Wróbel (ed.), Gramatyka współczesnego języka polskiego. Kraków: Instytut Języka Polskiego. Jassem, W. (1973) Podstawy fonetyki akustycznej. Warszawa: Państwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe Madelska, L., Witaszek-Samborska, M. (1997). Zapis fonetyczny. Zbiór ćwiczeń. Poznań: Wydawnictwo Naukowe UAM. Ostaszewska, D., Tambor, J. (2001). Fonetyka i fonologia współczesnego języka polskiego. Warszawa: Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN. Web resources: http://audite-vocem.coli.uni-saarland.de/ http://www.bmc.med.utoronto.ca/anatomia/intro.swf http://encyclopedia.vbxml.net/Head_and_neck_anatomy http://www.phonetics.ucla.edu/vowels/contents.html http://www.phonetics.ucla.edu/course/contents.html http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/International_Phonetic_Alphabet http://www.langsci.ucl.ac.uk/ipa/ipachart.html 6. Information on the use of blended-learning (if relevant) 3 7. Information on where to find course materials For each class a handout containing all necessary information (theory, tasks and instructions) will be provided. All course materials including the handouts will be published on the course website. III. Additional information 1. Reference of learning outcomes and learning content to teaching and learning methods and assessment methods Module title Symbol of module learning outcome* 09-EXPHON-22_01 Symbol of module learning content# TK_02, TK_04, TK_06 09-EXPHON-22_02 TK_04, TK_06 09-EXPHON-22_03 TK_01, TK_02, TK_04, TK_05, TK_06 09-EXPHON-22_04 TK_03, TK_04 09-EXPHON-22_05 TK_02, TK_03, TK_04 09-EXPHON-22_06 TK_02, TK_07 09-EXPHON-22_07 TK_08, TK_09, TK_10, TK_11, TK_12 09-EXPHON-22_08 TK_09 09-EXPHON-22_09 TK_10 09-EXPHON-22_10 TK_11 Methods of teaching and learning Analysis of sagittal slices, oscillograms and spectrograms – identification of phonemes Presentation of speech analysis tools and methods used in experimental phonetics, discussion and training in the class, student’s individual training Individual reading and writing, classroom discussion Individual training and training in pairs (text transcription, verification of partner’s transcription) Exercises on segmentation and labeling of speech recordings from different speakers and using speech analysis tools; student’s individual work and work performed in duty hours Assessment methods of LO & achievement student's activity in the class, final exam student's activity in the class, final exam final exam assessment of the transcription prepared by the student assessment of the segmentation and labeling Performance of measurements and creation of database for experiment – individual work and teamwork (in the class and outside duty hours) assessment of the measurements and the database Presentation of methodology and design of a phonetic experiment; discussion in the class, teamwork using laboratory & experimental methods student's activity in the class, final exam Exercises on the creation and selection of scenario for recordings; teamwork during the class student's activity in the class, final exam Exercises on the design of a perception test; teamwork during the class student's activity in the class, final exam Presentation of selected statistical methods and practical exercises using statistical software student's activity in the class, final exam 4 09-EXPHON-22_11 TK_06, TK_07, TK_12 09-EXPHON-22_12 Exercises on the creation of graphs, figures and tables using computer software, preparation of the final report on the experiment results; teamwork and student’s individual work Individual reading and writing, classroom discussion. TK_01 Assessment of student’s final report student's activity in the class, final exam * e.g. KHT_01 – module code as in Table in II.3 and II.4 # e.g. TK_01 – learning content symbol as in II.4 & Please include both formative (F) and summative (S) assessment It is advisable to include assessment tasks (questions). 2. Student workload (ECTS credits) Module title: Activity types Mean number of hours* spent on each activity type Contact hours with the teacher as specified in the programme 30 h Independent study 40 h Total hours Total ECTS credits for the module 70 h 6 * Class hours – 1 hour means 45 minutes # Independent study – examples of activity types: (1) preparation for classes, (2) data analysis, (3) librarybased work, (4)writing a class report, (5) exam preparation, etc. 3. Assessment criteria Final grade will be based on: 1. student’s activity in the class (all exercises and tasks have to be performed and delivered), 2. attendance (1/3) and 3. the results of final exam (1/3). Score 100-90 89-70 69-50 49-30 Under 30 grade 5/A 4/B 3/C 2/D pass 1/F fail 4. Titles of classes Syllabus: Week 1 Phonetics and a scientific study of speech: objectives, methods and applications. Week 2 Description of articulatory and acoustic features of vowels and consonants. Week 3 Grapheme-to-phoneme conversion: theory and practice. Week 4 Speech production and perception. 5 Week 5 Introduction to speech analysis tools. Week 6 Visual representation of speech sounds: spectrograms and oscillograms. Week 7 Segmentation (phonetic alignment) of continuous speech using audio and visual (spectrographic) representation. Week 8 Acoustic measurements of distinctive features of speech segments. Week 9 Measurements of suprasegmental features. Week 10 Designing and planning of a phonetic experiment. Formulating experimental hypotheses. Week 11 Creation/selection of recording scenarios and realization of recordings. Week 12 Annotation of speech recordings for use in the phonetic experiment. Week 13 Extraction of speech parameters and creation of a database. Week 14 Testing experimental hypotheses: selection and application of basic and more advanced statistical methods. Week 15 Presentation of the experimental results – preparation of the report. 6