Integrated High Frequency Power Conversion using GaAs pHEMTs
advertisement
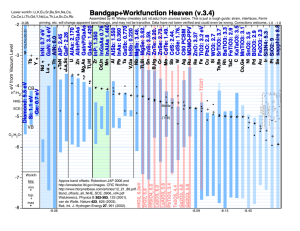
Integrated High Frequency Power Conversion using GaAs pHEMTs T. Paul Chow, Mona Hella, Vipindas Pala, Han Peng Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, NY Power Converters for Portable Electronics • • • • Battery Capacity IC Voltage Scaling Miniaturization Integration System Trends Page 2 Efficient POL Power Conversion • Bandwidth + • Efficiency + • Footprint SMPS Switch Power Losses for Hard Switched Converters Time Gate capacitance charging loss and output switching loss limit the switch gate width Product of RON and QG still determines minimum switch power loss 2 𝑃𝐶𝑂𝑁 = 𝐼𝐷𝑆 𝑅𝐷𝑆,𝑂𝑁 1 𝑉 𝐼 𝑡 + 𝑡𝑂𝐹𝐹 × 𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞 2 𝐵𝑎𝑡𝑡 𝐷𝑆 𝑂𝑁 𝑄𝐺 𝑉𝐵𝑎𝑡𝑡 𝐼𝐷𝑆 𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞 𝐼𝐺 𝑃𝑆𝑊 = I 1 PMin 2 I L2 RON ,SP Df L QG ,SPVBatt QG ,SPVDD QDS ,SPVBatt I 2 G 𝑃𝐺𝐷 = 𝑄𝐺 𝑉𝐺𝑆,𝑂𝑁 𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞 𝑃𝑂𝑆𝑆 = Page 3 1 𝑄 𝑉 𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞 2 𝐷𝑆1 𝐵𝑎𝑡𝑡 𝐹𝑂𝑀 = 𝑅𝑂𝑁 × 𝑄𝐺 FOM : Low-Voltage High Frequency Switches 𝐹𝑂𝑀 = 𝑅𝑂𝑁 × 𝑄𝐺 𝑅𝐶𝐻 + 𝑅𝐷 + 𝑅𝐸𝑋𝑇 ∗ 𝑄𝐶𝐻 + 𝑄𝐷 = 𝑅𝐸𝑋𝑇 + 𝐿𝐶𝐻 𝐿𝐷 + × 𝑄𝐶𝐻 𝐿𝐶𝐻 𝑊 + 𝑄𝐷 𝐿𝐷 𝑊 𝑊𝜇𝐶𝐻 𝑄𝐶𝐻 𝑊𝜇𝐷 𝑄𝐷 Channel Scaling to improve these • REXT : Contact, Access, Metallization resistance become critical Wide Bandgap Advantage limited to these two terms only Page 4 Comparison of Device Technologies HEMT : Higher mobility, NMOS : Smaller access resistance GaAs : Higher channel and drift mobility compared to GaN, Si GaN : Higher voltage supporting capability, but for low voltages, the drift region contribution is small, so other resistance components dominate Device HEMT Lateral NMOS RMETAL Source Gate LCH LD RCS Structure Page 5 RMETAL RMETAL Source Drain RCD RS RCH RD LD RCS RCS RAS RAS RMETAL Drain Gate LCH RCH RD RAD Material AlGaAs/InGaAs/ AlGaAs GaN Silicon µCH (cm2V-1s-1) µD (cm2V-1s-1) 6000 6000 1500 1500 500 1200 EC,Lat = BV/ LD Contact + Access Res. 25V/µm 150V/µm 15V/µm 0.2 .mm 0.2 .mm 0.1 .mm RAD Power Device for High Frequency Switching Silicon approach : – – – – Migrate to Nanometer gate lengths to reduce capacitance Below 5V : Cascoded nm-CMOS Below 20V : LDD NMOS Above 20-30V: LDMOS Our approach : Schottky gated AlGaAs/InGaAs/AlGaAs pHEMTs on GaAs substrates – Bandgap + Mobility Advantage – Low FOM without small feature size processes Page 6 First Order Comparison of FOM 0.1um Feature Size 0.5um Feature Size 1000 FOM (mOhm.nC) FOM (mOhm.nC) 1000 100 10 100 10 Silicon LDMOS GaAs pHEMT GaN HEMT Silicon LDMOS GaAs pHEMT GaN HEMT 1 1 0 20 40 60 80 Breakdown Voltage (V) 100 0 20 40 60 80 Breakdown Voltage (V) Mobility and Bandgap advantage for GaAs pHEMTs Best for under 20V Page 7 100 0.5µm E-Mode GaAs pHEMT Switch Source Gate 0.5µm 0.5µm 0.5µm Drain n+ GaAs n- AlGaAs Si Doping U.I.D InGaAs Si Doping U.I.D AlGaAs S.L Buffer S.I GaAs pHEMTs ubiquitous in RF MMICs Mature Process technology Double recessed commercially available E-pHEMT process (TriQuint TQPED) – For RF switches and front ends : Not-optimized for power swtiching Page 8 InGaAs 2DEG Channel Threshold Voltage = +0.36V, Maximum VG,ON=0.8V Semi-insulating substrate : High side operation Device Characteristics Device A Output Characteristics Device A Transfer Characteristics 250 60 Output Characteristics Transfer Characteristics 50 200 IDS (mA/mm) IDS (mA/mm) V GS = 0-0.9 V 150 100 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 0 0.2 0.4 VDS (V) Threshold Voltage = +0.36V, Maximum VG,ON=0.8V – Low Leakage at VG=0V, VDS=5V : 20nA/mm – No negative voltage generator required in standby mode – PON / POFF = 105 Breakdown Voltage 11V (at VGS=0V) (10uA/mm) – Limited by leakage – Avalanche breakdown only at ~25-30V 1 2.5 Breakdown Characteristics 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 0 5 10 VDS (V) Page 9 0.8 Device A Breakdown Voltage IDS (mA/mm) 0.6 VGS (V) 15 20 Intrinsic FET Characteristics TLM Measurements : Single Finger FET (100um) Intrinsic Specific RON (Measured on single Finger 100µm wide FET= 1.48 Ohm.mm – Dominated by Contact and Access – Intrinsic Specific RON (Measured on single Finger 100µm wide FET= 1.48 Ohm.mm Specific Gate Charge (From Capacitance Models) : 3.1pC/mm Intrinsic FOM : 4.6 m.nC Page 10 Metallization and Packaging Effects Three Level Interconnect + Flip Chip 0.8 0.7 Cu Bump D D S Cu Bump S 5 m/□ 15 m/□ S 95 m/□ D VG (V) 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 G 0 0 2.5 5 QG (pC/mm) Metallization resistance further degrades resistance for multi-fingered devices 10mm gate width: RON = 1.75m, QG = 70pC FOM=12 m.nC – Compared to 27.5 m.nC for Silicon 0.5um, 11V LDMOS (GWS24N07) Page 11 7.5 Key Technologies for High Frequency Power Conversion Devices Passives Efficiency Bandwidth Power density Packaging Device is only part of the story !! Page 12 Passive Technology : Thick Cu Inductors on GaAs Air core inductors for switching above 100 MHz Thick Cu (65µm tall) spirals with spacing of 30-45µm Solder bumps on top, flip chipped to laminate Bump height (25um) prevents Eddy current losses to laminate interconnect Copper Copper 65um 65um 25um Page 13 Passives for DC-DC Conversion Tall Cu : Low DCR, High Q Page 14 Inductor Coupling for Multiphase Converters Can use smaller inductors for same ripple : improved efficiency, bandwidth Optimal Coupling Factor kopt Page 15 2 1 D D 1 1 for D 0.5 D 1 D 2 D 1 D 1 1 for D > 0.5 1 D D Coupling : Ripple and Bandwidth enhancement Current Ripple Reduction with Duty Ratio Page 16 Bandwidth enhancement with negatively coupled spirals Coupling : Ripple and Bandwidth enhancement Coupled Thick Cu Inductors on GaAs Coupling Factor : -0.4 for 65% conversion Ratio Page 17 Packaging : Multi-chip Module Use best technology for each component : – GaAs pHEMT– High Frequency Switch + Drivers – Inductor Chip– Thick Cu on bare semi-insulating GaAs / SMD – CMOS – Control and Logic GaAs Die Switches+Drivers Inductor Chip CIN CMOS Input Capacitor Page 18 CMOS Die Control Output Capacitor CBS CBS GaAs Buck Inductor COUT Flip Chip Bonding Solder on Copper bumps Can place bumps on active FET area : spreading resistance reduced No bondwire parasitics : lower wire inductance, resistance Eliminates the need for ON-chip de-coupling High throughput, low assembly cost 5x5mm Module Die Page 19 Design Example A 150 MHz 2 Phase Interleaved Buck with Coupled Inductors Switches + Drivers on GaAs pHEMT 4.5V Input : 1.5-3.3V Output, 0.5A per Phase Page 20 Measurements Page 21 Design Example B ~100MHz DC-DC Converter for Power Amplifiers Single Phase , GaAs pHEMT Output Stage + 0402 Air Core inductors from Coilcraft GaAs pHEMT “Dummy CMOS” Chip Page 22 Power Converter Module Design Example B : GaAs Output Stage Synchronous Buck Converter High Side Bootstrapped driver for N-type device 100MHz switching frequency at full power (switching frequency varies with load) GaAs Buck Circuit + Bootstrapped Gate Driver High side gate driver Vdd Q13 D1 D2 D3 VBS D4 Q12 Vdd Q10 Q8 Q10 CBS Q4 Q1 Q11 Q9 Q7 Q5 VP,HS L Low side gate driver Vdd Q22 Q23 Q21 Q18 Q16 Q14 Q2 Q20 VP,LS Page 23 Q19 Q17 Q15 Q3 Chip Photograph Single Phase Used Measurements Efficiency Efficiency : 88% at 4.5V input, 3.375V output, 1A Efficiency degradation at low power due to GaAs gate driver power loss 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% VOUT = 3.375V VOUT = 2.25V VOUT = 1.125V 15 Page 24 20 25 30 POUT (dBm) 35 40 Simulated Power Loss Components At low power, GaAs gate driver loss degrades efficiency considerably GaAs has no PMOS like device, hard switched drivers are lossier than CMOS Page 25 High Side Rectifier Switch 0.0% 0.1% 0.8% 1.5% 1.6% Gate Drive 5.2% 11.9% 9.5% 12.3% 12.6% 17.4% Inductor 5.2% 6.4% 20% 18% 16% 14% 12% 10% 8% 6% 4% 2% 0% 0.4% 1.8% % Of Total Power Loss Vout=3.375, Efficiency=87% Vout=2.25, Efficiency=75.4% Vout=1.125, Efficiency=50.9% Other 00 Transient Response and Bandwidth 5 2.5 4 2 3 2 3.5 1.5 2.5 1 Amplitude1.5Response 0.5 1 200 400 600 800 -0.5 1.98 1000 Time (ns) 2.5 4.5 3.5 1.5 2.5 1 0.5 1.5 0 0.5 -0.5 1.98 1000 1.99 2 Time (ms) 2.01 -0.5 2.02 VIN (V) VOUT (V) 2 0.5 6 1.99 VOUT/VIN (dB) 0 Page 26 8 0 0 VIN (V) VOUT (V) VOUT (V) 4.5 2 4 (ms) Time 2.01 -0.5 2.02 2 0 -2 -4 0.1 1 Frequency (MHz) 10 Summary GaAs Technology platform for high frequency switching – Device : • E-pHEMTs with superior FOM, Breakdown and Ruggedness • 3 Layer Interconnect • Thick Cu Air core planar inductors for integration – Passive • Thick Cu high Q air core planar inductors on GaAs • Coupling to achieve bandwidth + efficiency improvement – Packaging • Flip Chip Interconnects : Low parasitic inductances, reduced de-coupling, integration • Multi-chip modules : pHEMT Power + GaAs Passive + CMOS Control Design Examples – 150MHz interleaved Converter with coupled inductors, 84% Efficient – 100 MHz Single Phase, 1A output – 88% Efficient, 3dB bandwidth – 14.5 MHz Page 27 Future Work Output Stage : – 0.25µm GaAs E-pHEMT process : Gate Charge Advantage – Resonant drivers : Reduce driver loss, improve switching time and thus reduce switching loss Adding CMOS based controller for PA power supply modulation up to 10-15 MHz E-Mode power pHEMT processes for higher voltages : 20V, 30V rated devices Page 28 chowt@rpi.edu palav@rpi.edu hellam@ecse.rpi.edu pengh2@rpi.edu Page 29