Information the Next Generation Science Standards
advertisement

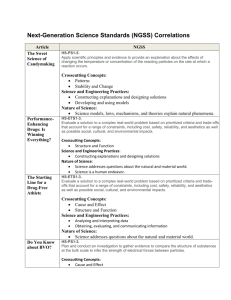
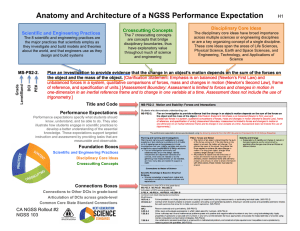
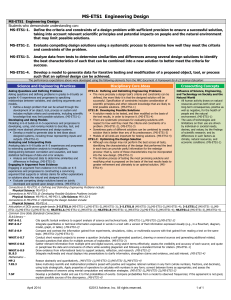
Transitioning to the NGSS New Jersey Department of Education Evolution of State Science Standards 1990s 1990s-2009 7/2010 – April 2013 1/2010 - 7/2011 How are they different? Characteristics of a Core Idea 1. Have broad importance across multiple sciences or engineering disciplines or be a key organizing principle of a single discipline. 2. Provide a key tool for understanding or investigating more complex ideas and solving problems. 3. Relate to the interests and life experiences of students or be connected to societal or personal concerns that require scientific or technological knowledge. 4. Be teachable and learnable over multiple grades at increasing levels of depth and sophistication. That is, the idea can be made accessible to younger students but is broad enough to sustain continued investigation over years. Core Ideas Physical Science • Matter & Its Interactions (PS1) • Motion and Stability: Forces & Interactions (PS2) • Energy (PS3) • Waves & Their Application in Technologies for Information Transfer (PS4) Earth & Space Science • Earth’s Place in the Universe (ESS1) • Earth’s Systems (ESS2) • Earth & Human Activity (ESS3) Life Science • From Molecules to Organisms: Structures & Processes (LS1) • Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics (LS2) • Heredity: Inheritance & Variation of Traits (LS3) • Biological Evolution: Unity & Diversity (LS4) Engineering Design • Defining and Delimiting Engineering Problems (ETS1.A) • Developing Possible Solutions (ETS1.B) • Optimizing the Design Solution (ETS1.3) Example: Cells Theory Essential functions of plant and animal cells are carried out by organelles. Is the Jell-O Model Sufficient? How does a cell help organisms survive? (States, 2012) NGSS Appendix E: Disciplinary Core Idea Progressions Coherence with Post-Secondary Scientific and Engineering Practices • Asking questions and defining problems • Developing and using models • Planning and carrying out investigations • Analyzing and interpreting data • Using mathematics, information and computer technology, and computational thinking • Constructing explanations and designing solutions • Engaging in argument from evidence • Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information Practices All NGSS standards are defined using science and engineering practices. learners build their understandings by posing questions, designing investigations, building explanations and models of findings, and engaging in argumentation to conduct principled comparisons of competing ideas and reach consensus Science and Engineering Practices Crosscutting Concepts 1. Patterns 2. Cause and effect 3. Scale, proportion, and quantity 4. Systems and system models 5. Energy and matter 6. Structure and function 7. Stability and change Crosscutting Concepts Describe how (_________) is observable in the image? 1. Systems and system models 2. Energy and matter 3. Structure and function Framework Crosscutting Concepts pp. 83-102 Next Generation Science Standards Foundation Boxes Appendix G: Crosscutting Concepts An Analogy between 3-Dimensional Learning and Cooking Basic Ingredients (Core Ideas) Kitchen Tools & Techniques (Practices) Preparing a Meal (Three dimensional Learning) Herbs, Spices, & Seasonings (Crosscutting Concepts)