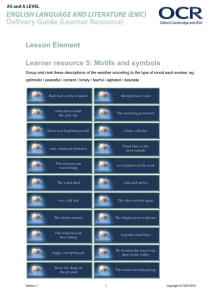
b5c5p5 past papers - Debden Park High School
advertisement

Units B5 C5 P5 th Exam date: 25 June - pm – Past exam questions H GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION A216/02 TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE A Unit 2 Modules B5 C5 P5 (Higher Tier) *CUP/T63225* Friday 23 January 2009 Morning Candidates answer on the question paper A calculator may be used for this paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Duration: 40 minutes Other Materials Required: • Pencil • Ruler (cm/mm) * A 2 1 6 0 2 * INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES • • • • • • Write your name clearly in capital letters, your Centre Number and Candidate Number in the boxes above. Use black ink. Pencil may be used for graphs and diagrams only. Read each question carefully and make sure that you know what you have to do before starting your answer. Answer all the questions. Do not write in the bar codes. Write your answer to each question in the space provided, however additional paper may be used if necessary. INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES • • • • • The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. The total number of marks for this paper is 42. A list of physics equations is printed on page 2. The Periodic Table is printed on the back page. This document consists of 20 pages. Any blank pages are indicated. © OCR 2009 [D/103/3775] SPA (NH/TC) T63225/3 FOR EXAMINER’S USE 1 4 2 5 3 5 4 5 5 4 6 5 7 4 8 4 9 3 10 3 TOTAL 42 OCR is an exempt Charity Turn over 2 TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE EQUATIONS Useful Relationships Explaining Motion speed = distance travelled time taken momentum = mass × velocity change of momentum = resultant force × time for which it acts work done by a force = force × distance moved by the force change in energy = work done change in GPE = weight × vertical height difference kinetic energy = 1 2 × mass × [velocity]2 Electric Circuits resistance = voltage current Vp Np = Vs Ns energy transferred = power × time power = potential difference × current efficiency = energy usefully transferred × 100% total energy supplied The Wave Model of Radiation wave speed = frequency × wavelength © OCR 2009 3 Answer all the questions. 1 Mary draws some chemical structures A, B, C, D and E. A B C D E (a) Which structure, A, B, C, D or E, is most likely to contain a chain of carbon atoms? answer ........................... [1] (b) Which structure, A, B, C, D or E, will have the lowest boiling point? answer ........................... [1] (c) Which structure, A, B, C, D or E, is part of a covalent giant structure? answer ........................... [1] (d) Which structure, A, B, C, D or E, is part of an ionic giant structure? answer ........................... [1] [Total: 4] © OCR 2009 Turn over 4 2 Henry draws a table of some of the elements that might be in his body. (a) Some of the elements in this table are very common in his body. Others are only present in smaller amounts. Put a tick (✓) in each row of the table to show how common each element is in his body. element very common smaller amounts carbon hydrogen nitrogen oxygen phosphorus sulfur [2] © OCR 2009 5 (b) One type of compound is called an amino acid. There are different ways of writing the formula of an amino acid. amino acid A B simplified structural formula CH3 | NH2—CH—COOH | NH2—CH—COOH C CH2SH | NH2—CH—COOH D CH2COOH | NH2—CH—COOH molecular formula C3H7O2N C2H5O2N C4H7O4N (i) Complete the simplified structural formula of acid B in its box. [1] (ii) Write the molecular formula of acid C in its box. [1] (iii) Rotting hair smells of hydrogen sulfide, the smell of bad eggs. The hydrogen sulfide comes from one of the amino acids A, B, C or D in the table. Which one? answer................... [1] [Total: 5] © OCR 2009 Turn over 6 3 Electric wires are usually made of copper because copper is a good electrical conductor. (a) How is electricity conducted through copper? Put a tick (✓) in the box next to the best answer. Anions move to the anode, cations to the cathode. Positive ions move through the lattice. Electrons move between ions in the lattice. Electrons move between atoms in the lattice. Atoms vibrate within the lattice. [1] (b) Copper is extracted from its ore using a blast furnace. The blast furnace melts all the reactants and allows them to react. One reaction that takes place is that of molten copper sulfide with molten copper oxide to produce molten copper and sulfur dioxide gas. Complete the reaction by putting state symbols into the brackets. Cu2S [......] + 2Cu2O [......] 6Cu [......] + SO2 [......] [1] (c) Another of the reactions that takes place is 2Cu2S + O2 Complete the boxes to balance the equation. © OCR 2009 Cu2O + SO2 [1] 7 (d) The cable connecting a TV to a DVD player sometimes has gold plated contacts. There are two different reasons why the gold is used for contacts. Put ticks (✓) in the boxes next to the two best reasons why gold is used for contacts. Gold bends easily. Gold is a very unreactive metal. Gold is the same colour as copper. Gold is a rare metal. Gold can be plated very thinly. Gold holds its outer electrons quite weakly. [2] [Total: 5] © OCR 2009 Turn over 8 4 Geoff builds this circuit. (a) The lamp only lights when the switch is closed. Put a tick (✓) in the box next to the correct reason. The open switch has a very low resistance. The switch is connected in parallel with the resistor. The closed switch allows the battery to make a voltage. The closed switch allows charge to flow through the lamp. [1] (b) Complete the sentences below. Choose words from this list. current moving oscillating power stationary voltage The lamp gets hotter when it has an electric .............................. passing through it. This is caused by collisions between .............................. electrons and .............................. atoms. [2] (c) Geoff’s circuit has a resistance of 3.0 Ω and a current of 1.5 A. How should Geoff calculate the voltage of the battery? Put a ring around the answer. 3.0 1.5 © OCR 2009 3.0 × 1.5 1.5 3.0 [1] 9 (d) Why is there a resistor in the circuit? Put a tick (✓) in the box next to the correct reason. The resistor keeps the current in the lamp at the correct value. The lamp needs more current than the battery can supply on its own. The battery doesn’t have a big enough voltage to make the lamp light. The resistor stops the voltage from reaching the switch, making it safe to touch. [1] [Total: 5] © OCR 2009 Turn over 10 5 Lucinda reads her electricity meter. 1000 amp / kWh (a) Why is the energy transfer measured in kilowatt-hours instead of joules? Put a tick (✓) in the box next to the best reason. The joule is a very small amount of energy. It tells you how much electricity is being used moment by moment. Each type of energy transfer has its own special unit of measurement. The meter design can’t be adapted to measure energy transfers in joules. [1] (b) Lucinda uses her 2.1 kW heater for 3 hours. Each kilowatt-hour costs 8p. (i) What is the correct way of calculating how many pence it costs to use the heater? Put a ring around the answer. 2.1 x 3 x 8 © OCR 2009 2.1 x 8 3 3 x8 2.1 [1] A216/02 Mark Scheme January 2009 A216/02 Modules B5, C5, P5 Higher Question 1 (a) (s) (d) (f) 2 Expected Answers Marks 1 1 1 1 Total 4 B (1) A (1) D (1) E (1) (a) element carbon hydrogen nitrogen oxygen phosphorus sulfur (b) very common smaller amounts 2 accept nitrogen in either column (so ignore nitrogen row) do not allow any other response which appears in both columns 9 9 9 9 remaining 5 rows correct = 2 marks 4 correct = 1 mark 3 or less correct scores = 0 marks 9 9 (i) 'H' approximately above the vertical line (1) 1 (ii) C 3 H 7 O 2 NS (1) 1 (iii) C (1) 1 Total Rationale if answer line blank, accept any clear indication of correct letter if answer line blank, accept any clear indication of correct letter if answer line blank, accept any clear indication of correct letter if answer line blank, accept any clear indication of correct 5 23 OR (ignoring Nitrogen line) no errors = 2 marks 1 error = 1 mark 2 or more errors = 0 marks the ‘H’ must be a capital letter allow ‘H1’ but not ‘H1’ do not allow alterations elsewhere in the formula numbers MUST be either smaller or subscripted allow elements in any order so long as their subscripts are correct accept C 3 H 7 O 2 N 1 S 1 (reject C 3 H 7 O 2 N1S1) the subscripts on N 1 and S 1 are not normally used, but are not incorrect, so the mark can be awarded accept any clear indication of box C A216/02 Mark Scheme Question 3 (a) Expected Answers Marks 1 January 2009 Rationale electrons move between ions 9 (1) in the lattice (b) [l], [l], [l], [g] 1 (c) (d) 3, 2, 2 1 2 Gold is less reactive than copper. 9 (1) Gold holds its outer electrons quite weakly. 9 (1) Total 5 24 accept upper case letters, do not accept words (eg “gas”, “liquid”, “liq”) boxes must contain numbers only if answer line blank, accept any clear indication of correct letter if only 2 responses given, and one or both is then crossed out, mark both responses A216/02 Mark Scheme Question 4 (a) Expected Answers The closed switch allows charge to flow through the lamp (b) (c) (d) current (1) moving Marks 1 stationary (1) 3.0 × 1.5 (1) 1 1 Total Rationale 9 (1) 2 the resistor keeps the current in the lamp at the correct value January 2009 9 (1) 5 25 first line correct = 1 mark second line correct = 1 mark allow oscillating instead of stationary A216/02 Mark Scheme Question 5 (a) Expected Answers The joule is a very small amount of energy (b) (c) (i) (ii) Marks 1 January 2009 Rationale 9 (1) 2.1 x 3 x 8 (1) Alan (1) 1 1 accept “50.4” if response not clear if answer line blank, accept any clear indication allow 6 x 100 instead of ‘Alan’ 2.1x3 charge (1) 1 if answer line blank, accept any clear indication of correct letter Total 4 26 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question 6 (a) (b) Expected Answers 0.36 W (1) decrease increase stays the same Marks 1 1 both rows correct = 1 mark Rationale 1 both lines correct = 1 mark 2 both ticks correct = 2 marks one correct = 1 mark 9 9 (c) (i) decrease increase stays the same 9 9 (ii) Both resistors have the same potential difference across them 9 (1) both resistors have the same current 9 (1) Total if more than two ticks: (6 rows correct = 2 marks) 5 rows correct = 1 mark 4 rows correct = 0 5 27 January 2009 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question 7 (a) Expected Answers Marks 2 mitosis meiosis A D E B C D C Total Rationale allow any order of responses within a column do not mark any letter which appears in both columns all correct = 2 marks 4 or 3 correct = 1 mark 1 or 2 correct = 0 marks 2 B January 2009 A 4 28 D anywhere before C = 1 mark C anywhere before A = 1 mark repeated letters apply strictly as above, e.g. ACA = 1 mark A216/02 Question 8 (a) Mark Scheme Expected Answers statement four bases order not important DNA in cytoplasm bases pair up differently copy of DNA into cytoplasm order of bases determines amino acid order true false 9 Rationale accept any unambiguous response 9 all correct =-3 marks 5 or 4 rows correct = 2 marks 3 or 2 rows correct = 1 mark 1 row correct = 0 marks 9 or 9 all correct = 3 marks 1 or 2 errors = 2 marks 3 or 4 errors = 1 mark 5 or 6 errors = 0 marks 9 9 1 (b) TAAGCCTGT Question 9 Marks 3 January 2009 9 (1) Total 4 Expected Answers Marks 3 meristems (1) auxins (1) clones (1) Total 3 29 Rationale must be in correct order A216/02 Question 10 Mark Scheme Expected Answers Marks 3 Up to the eight cell stage … 9 Specialised cells can … 9 Some genes in the nucleus … 9 Both embryonic and adult … Total 9 3 30 January 2009 Rationale 7 or 6 correct = 3 marks 5 or 4 correct = 2 marks 3 correct = 1 mark 2 or 1 correct = 0 marks H GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION A216/02 TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE A Unit 2: Modules B5 C5 P5 (Higher Tier) * O C E / 1 1 0 9 3 * Wednesday 24 June 2009 Morning Candidates answer on the question paper A calculator may be used for this paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Duration: 40 minutes Other Materials Required: • Pencil • Ruler (cm/mm) * A 2 1 6 0 2 * INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES • • • • • • Write your name clearly in capital letters, your Centre Number and Candidate Number in the boxes above. Use black ink. Pencil may be used for graphs and diagrams only. Read each question carefully and make sure that you know what you have to do before starting your answer. Answer all the questions. Do not write in the bar codes. Write your answer to each question in the space provided, however additional paper may be used if necessary. INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES • • • • • The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. The total number of marks for this paper is 42. A list of physics equations is printed on page 2. The Periodic Table is printed on the back page. This document consists of 20 pages. Any blank pages are indicated. © OCR 2009 [D/103/3775] DC (SJH/CGW) 11093/7 OCR is an exempt Charity Turn over 2 TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE EQUATIONS Useful Relationships Explaining Motion speed = distance travelled time taken momentum = mass × velocity change of momentum = resultant force × time for which it acts work done by a force = force × distance moved by the force change in energy = work done change in GPE = weight × vertical height difference 1 kinetic energy = 2 × mass × [velocity]2 Electric Circuits resistance = Vp Vs = voltage current Np Ns energy transferred = power × time power = potential difference × current efficiency = energy usefully transferred × 100% total energy supplied The Wave Model of Radiation wave speed = frequency × wavelength © OCR 2009 3 BLANK PAGE Question 1 starts on page 4. PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE © OCR 2009 Turn over 4 Answer all the questions. 1 Erupting volcanoes give out a mixture of gases. (a) Some of the gases from a volcano are sulfur compounds. Mary asks her friends if sulfur is in living things. Su Living things don’t contain sulfur. Jim Living things contain small amounts of sulfur. Mike Living things contain large amounts of sulfur. Kate Living things only contain sulfur if they have been poisoned. Who gives the best answer? answer ........................................................... [1] © OCR 2009 5 (b) Sulfur dioxide is just one of the sulfur compounds emitted by volcanoes. Sulfur dioxide is made of small SO2 molecules. Put a ring around each of the correct terms in this passage. The atoms in sulfur dioxide molecules are held together by bonding. These bonds are formed when electrons are atoms. shared ionic covalent metallic totally transferred between The bonds between the atoms in a sulfur dioxide molecule are Each nucleus is attracted to another nucleus strong weak. the electrons in between. [2] (c) Mary knows that sulfur compounds move between the atmosphere and the lithosphere in a cycle. She uses the information in the statements below to draw a sulfur cycle. A Sulfur compounds in sediments are taken up by plants. B Sulfur compounds get into the air from erupting volcanoes. C Sulfur compounds in acid rain end up in sediments, which form solid rock. D Sulfur compounds get into the air when we burn fuels such as wood or coal. E Sulfur compounds in the air dissolve in rainwater to make acid rain. sulfur compounds in air 1 2 5 acid rain 3 sulfur compounds in rocks and soil 4 sulfur compounds in plants Fill in the table below to show which statement letter fits which arrow number. arrow number 1 2 3 4 5 statement letter [2] © OCR 2009 Turn over 6 (d) Sulfur is present in two of the amino acids that make up proteins. These are cysteine and methionine. Cysteine contains a higher percentage of sulfur by mass than methionine. cysteine methionine C3H7NO2S C5H11NO2S 26.4% sulfur 21.5% sulfur Put a tick (✓) in the box next to the best reason. A molecule of cysteine contains more sulfur atoms than a molecule of methionine. The mass of sulfur atoms in a molecule of cysteine is greater than the mass of sulfur atoms in a molecule of methionine. The formula mass of cysteine is greater than the formula mass of methionine. A molecule of cysteine contains fewer carbon and hydrogen atoms than a molecule of methionine. [1] [Total: 6] © OCR 2009 7 2 Molten rock sometimes cools to form granite. feldspar biotite mica muscovite mica quartz (a) Granite contains crystals of different minerals. One of these minerals is mainly made of silicon dioxide. The other minerals are more complicated compounds of silicon. Put a ring around the one mineral that is mainly made of silicon dioxide. biotite mica feldspar muscovite mica quartz [1] (b) Here are some statements about silicon dioxide. Put a tick (✓) in the box next to each of the two correct statements. It is soft. It has a low boiling point. It has a high melting point. It does not dissolve in water. It conducts electricity when solid. [2] [Total: 3] © OCR 2009 Turn over 8 3 Mark knows that carbon will take the oxygen away from many metal oxides. (a) Put numbers in the boxes to balance the equation for the formation of zinc from zinc oxide. ZnO + C Zn + CO2 [1] (b) Mark finds that the reaction does not work for magnesium oxide. Put a tick (✓) in the box next to each of the two most likely reasons for this. He doesn’t heat the reactants enough to make the reaction start. Magnesium is too reactive to be extracted this way. Magnesium oxide is too reactive to be extracted this way. Magnesium has too high a melting point. Magnesium oxide has too low a melting point. The surface area of the magnesium oxide is too great. The magnesium oxide is too hot. Carbon is not reactive enough. [2] (c) He finds out that magnesium can be extracted by electrolysis. One way might be to electrolyse molten magnesium oxide. Choose terms from this list to complete the sentences. molecules ions atoms giant structures gain lose share The oxygen particles in the electrolyte are in the form of ....................................................... . They move to an electrode where they ......................................................... electrons to form neutral atoms. The neutral atoms then combine to form ......................................................... . [2] [Total: 5] © OCR 2009 9 4 Sylvia sets up this circuit. (a) Sylvia decides to measure the potential difference across the lamp. Draw on the circuit diagram to show how she connects a voltmeter. Use the correct symbol. [1] (b) The voltmeter across the lamp reads 4 V. Sylvia asks her friends what this means. Alan It tells you about the energy lost by charge on its way through the lamp. Bess It’s the rate at which charge passes through the lamp. Carlo It tells you how much energy there is in the battery. Davina It’s the amount of charge in the lamp. Who has the best answer? answer ........................................................... [1] © OCR 2009 Turn over 10 (c) (i) Sylvia adjusts the variable resistor. These four sentences explain why the brightness of the lamp changes. They are in the wrong order. A The lamp gets dimmer. B The power of the lamp decreases. C The current in the resistor decreases. D The resistance of the circuit increases. Put the sentences in the correct order. The last one has been done for you. A [1] (ii) Complete the sentences for the variable resistor. Choose words from this list. decreases increases stays the same Sylvia adjusts the variable resistor. The current in the variable resistor decreases. The voltage across the variable resistor ..................................................... . The voltage across the battery ........................................................ . [1] [Total: 4] © OCR 2009 11 5 Brian has an electric toothbrush. He connects it to the mains supply through a transformer. (a) Here is a description of a transformer. Put a ring around the correct word in each pair. A transformer has two coils of wire. The wire is made of copper iron and is coated with a layer of The wire is wound around a core made of copper The core should have the shape of a ring conductor insulator. iron. rod. [1] (b) The transformer reduces the 230 V mains supply to 4.6 V for the toothbrush. The primary coil has 460 turns of wire. How should Brian calculate the number of turns of wire in the secondary coil? Put a ring around the correct answer. 230 460 × 4.6 = 2 © OCR 2009 4.6 230 × 460 = 9 230 4.6 × 460 = 23 000 460 × 230 × 4.6 = 486 680 [1] Turn over 12 (c) The sentences below explain how a transformer works. They are in the wrong order. A There is a current in the toothbrush motor. B The current in the primary coil changes. C The magnetic field in the core changes. D The voltage across the primary coil changes. E A voltage is induced across the secondary coil. Put the sentences in the correct order. The last one has been done for you. A [2] (d) Here is the circuit diagram for Brian’s toothbrush. transformer M The table shows the current in some of the components when the switch is open and closed. Not all of the readings have been filled in. Complete the table to show the three missing readings. state of switch resistor current in amps open closed motor current in amps lamp current in amps 0.3 0.5 0.3 [1] [Total: 5] © OCR 2009 13 6 Joe tests a circuit from his computer. He needs to be careful. The chips in the circuit are easily damaged by static electricity. (a) Complete the sentences. Choose the best words from the list. atoms conductors electrons insulators particles placed pushed rubbed transformers Objects can become charged when they are ........................................... against each other. This allows .............................................. to be transferred from one to another. For this to happen, both objects must be ............................................... . [2] (b) When Joe walks across the floor to his circuit, he becomes negatively charged. Put a tick (✓) in the box next to each of the two correct statements. Joe is now a source of alternating voltage. The floor has become positively charged. Joe is now surrounded by a magnetic field. The floor must be made of a conducting material. Joe now repels other objects which are negatively charged. © OCR 2009 [1] Turn over 14 (c) Joe now touches his circuit and damages it. Use straight lines to connect each start of a sentence to its correct end. start The flow of charge from Joe is… end … a voltage in the circuit. … no electrons free to move. The insulators in the circuit have … … plastic coating around them. … lots of electrons free to move. The conductors in the circuit have … … an electric current in the circuit. [2] [Total: 5] © OCR 2009 15 7 (a) The cell cycle can be divided into cell growth and mitosis. Put a ring around the best word to complete each sentence. During cell growth, the number of The chromosomes nuclei proteins nuclei During mitosis, pairs of chromosomes Each cell forms two four organelles fuse eight cells increases. are copied. separate fragment. new cells. [3] (b) Meiosis is another way that cells can divide. Here are some statements about the results of mitosis and meiosis. Put one tick (✓) in each row in the correct box. statement true for mitosis true for meiosis true for both number of chromosomes in daughter cells decreases daughter cells are identical to parent cell can produce gametes the number of cells increases daughter cells are identical to each other [4] [Total: 7] © OCR 2009 Turn over 16 8 Cells contain the genetic code for making proteins. (a) Why does a hair cell produce the protein keratin but not the protein haemoglobin? Put a tick (✓) in the box next to the best explanation. The gene for haemoglobin has been destroyed. The gene for keratin is more dominant than the gene for haemoglobin. The gene for haemoglobin is not active. The cell does not contain the haemoglobin gene. [1] (b) DNA contains four different bases. These bases control which protein is made. Which three statements best explain this. A Each base reacts with an acid. B Each amino acid is coded for by three bases. C Proteins are coded for by three amino acids. D The protein made depends on the order of amino acids. E The bases make a copy of the protein and then reproduce it. F The order of the amino acids depends on the order of the bases. G The order of the bases can change depending on the conditions. H A DNA molecule changes its base order in order to make different proteins. statements ...................... and ....................... and ................... [2] [Total: 3] © OCR 2009 17 9 New plants can be grown from cuttings. (a) Complete the sentences to explain how this happens. Choose words from the list. auxins dormant enzymes fertilisers organ specialised tissue unspecialised xylem To grow a plant from a cutting the gardener first cuts off part of a plant shoot. The cut end of the shoot is dipped into hormones called .................................................. . The hormones act on ............................................... cells within the stem to make them develop into roots. Roots are just one type of .............................................. within a plant. [3] (b) The hormones can also control the direction of growth. This plant is receiving light from only one side. Which statement correctly explains why the shoot tip grows towards the light? Put a tick (✓) in the box next to the correct answer. The side nearest the light has more hormone so it grows slower. The side nearest the light has less hormone so it grows faster. The side furthest from the light has more hormone so it grows faster. The side furthest from the light has more hormone so it grows slower. [1] [Total: 4] END OF QUESTION PAPER © OCR 2009 18 BLANK PAGE PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE © OCR 2009 19 BLANK PAGE PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE Copyright Information OCR is committed to seeking permission to reproduce all third-party content that it uses in its assessment materials. OCR has attempted to identify and contact all copyright holders whose work is used in this paper. To avoid the issue of disclosure of answer-related information to candidates, all copyright acknowledgements are reproduced in the OCR Copyright Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations, is given to all schools that receive assessment material and is freely available to download from our public website (www.ocr.org.uk) after the live examination series. If OCR has unwittingly failed to correctly acknowledge or clear any third-party content in this assessment material, OCR will be happy to correct its mistake at the earliest possible opportunity. For queries or further information please contact the Copyright Team, First Floor, 9 Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 1PB. OCR is part of the Cambridge Assessment Group; Cambridge Assessment is the brand name of University of Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate (UCLES), which is itself a department of the University of Cambridge. © OCR 2009 © OCR 2009 89 actinium [227] Ac* 57 lanthanum 139 La* 39 yttrium 89 Y 21 scandium 45 Sc name 104 rutherfordium [261] Rf 72 hafnium 178 Hf 40 zirconium 91 Zr 22 titanium 48 Ti 105 106 seaborgium [266] Sg [262] Db dubnium 74 tungsten 184 W 42 molybdenum 96 Mo 24 chromium 52 Cr 73 tantalum 181 Ta 41 niobium 93 Nb 23 vanadium 51 V atomic (proton) number relative atomic mass atomic symbol Key 107 bohrium [264] Bh 75 rhenium 186 Re 43 108 hassium [277] Hs 76 osmium 190 Os 44 ruthenium 101 Ru [98] Tc technetium 26 iron 56 Fe 25 manganese 55 Mn cobalt 59 Co nickel 59 Ni copper 63.5 Cu zinc 65 Zn boron carbon nitrogen oxygen 16 O 6 fluorine 19 F 7 4 He 0 109 meitnerium [268] Mt 77 iridium 192 Ir 45 rhodium 103 Rh 27 110 darmstadtium [271] Ds 78 platinum 195 Pt 46 palladium 106 Pd 28 111 roentgenium [272] Rg 79 gold 197 Au 47 silver 108 Ag 29 The relative atomic masses of copper and chlorine have not been rounded to the nearest whole number. 81 thallium 204 Tl 49 indium 115 In 31 gallium tin 82 lead 207 Pb 50 119 Sn 32 germanium 73 Ge 14 silicon 28 Si 6 83 bismuth 209 Bi 51 antimony 122 Sb 33 arsenic 75 As 15 phosphorus 31 P 7 84 polonium [209] Po 52 tellurium 128 Te 34 selenium 79 Se 16 sulfur 32 S 8 85 astatine [210] At 53 iodine 127 I 35 bromine 80 Br 17 chlorine 35.5 Cl 9 86 radon [222] Rn 54 xenon 131 Xe 36 krypton 84 Kr 18 argon 40 Ar 10 neon Elements with atomic numbers 112-116 have been reported but not fully authenticated 80 mercury 201 Hg 48 cadmium 112 Cd 30 70 Ga 13 aluminium 27 Al 5 20 Ne 2 14 N 5 helium 12 C 4 1 11 B 3 hydrogen 1 H * The lanthanoids (atomic numbers 58-71) and the actinoids (atomic numbers 90-103) have been omitted. 88 87 [226] Ra [223] Fr radium 56 francium barium 137 Ba 133 Cs 55 38 caesium strontium 88 Sr 85 Rb 37 20 rubidium calcium 40 Ca 39 K 19 12 potassium magnesium 24 Mg 23 Na 11 4 sodium beryllium 3 9 Be 7 Li lithium 2 1 The Periodic Table of the Elements 20 A216/02 Mark Scheme A216/02 Modules B5, C5, P5 Higher Tier Question Expected Answers Jim (1) 1 a covalent b shared strong the electrons in between c Marks Rationale 1 2 all four correct = 2 marks three correct = 1 mark less than three correct = 0 marks 2 B E C A D all five correct = 2 marks three or four correct = 1 mark 1 d a molecule of cysteine contains fewer … Total (1) 6 25 June 2009 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question Expected Answers quartz (1) 2 a b June 2009 Marks Rationale 1 accept any unambiguous indication 2 one mark for each correct tick if more than two ticks deduct one mark for each additional tick candidate cannot score less than 0 marks It has a high melting point. (1) It does not dissolve in water. (1) Total 3 26 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question 2 3 a 2 b Expected Answers Magnesium is too reactive to be … (1) (1) Carbon is not reactive enough. c Marks 1 both correct = 1 mark ions lose molecules Total June 2009 Rationale 2 one mark for each correct tick if more than two ticks deduct one mark for each additional tick candidate cannot score less than 0 marks 2 three correct = 2 marks two correct = 1 mark 1 correct = 0 marks 5 27 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question 4 a Expected Answers A B V C D Alan (1) b c i Marks Rationale 1 look for V in a circle with the two lines coming out of it connected to either side of the lamp (one line to join the circuit anywhere between points A & B one line to join the circuit anywhere between points C & D) the circle with a V can be to the left of the lamp look for clear intention of a voltmeter with leads coming out of it candidates should demonstrate an understanding of how to wire in a voltmeter rather than how to use the precise circuit symbols 1 D C B ii increases stays the same if the answer line is blank, look at the list in case the correct word is indicated 1 A 1 Total June 2009 both correct = 1 mark 4 28 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question copper 5 a insulator iron ring b Expected Answers Marks 1 all correct = 1 mark June 2009 Rationale 1 4.6 460 = 9 (1) 230 c D B C E A 2 all four correct = 2 marks two or three correct = 1 mark less than two correct = 0 marks 1 all three correct = 1 mark D immediately before B B immediately before C C immediately before E E immediately before A d open closed 0 0 0.5 Total 5 29 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question rubbed 6 a electrons ensulators b Expected Answers Marks Rationale 2 all three correct = 2 marks two correct = 1 mark one correct = 0 marks 1 all correct = 1 mark both ticks required for the mark The floor has become positively … Joe now repels other objects … 2 c The flow of … … a voltage in … lines from all three left hand boxes correct = 2 marks lines from two left hand boxes correct = 1 mark line from only one left hand box correct = 0 marks … no electrons … The insulators … … plastic … … lots of … The conductors … … an electric … Total 5 30 June 2009 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question Expected Answers organelles 7 a chromosomes separate two b true for true for true for statement mitosis meiosis both number of chromosomes … daughter cells … can produce gametes the number of cells increases daughter cells are identical … Marks 3 all four correct = 3 marks three correct = 2 marks two correct = 1 mark one correct = 0 marks 4 all 5 rows correct = 4 marks 4 rows correct = 3 marks 3 rows correct = 2 marks 2 rows correct = 1 mark 1 row correct = 0 marks Rationale if fourth row has a tick in right hand box, ignore other ticks in that row if fourth row has no tick in right hand box, accept ticks in both the other boxes for this row Total June 2009 7 31 A216/02 Question 8 a Mark Scheme Expected Answers Marks 1 June 2009 Rationale The gene for haemoglobin is not active. (1) b B, D, F in any order 2 Total 9 a all three correct = 2 marks 2 correct = 1 mark 1 correct = 0 marks accept any unambiguous indication of choice 3 3 auxins (1) unspecialised (1) organ (1) one mark for each correct answer 1 b The side furthest from the light has … Total (1) 4 32 H GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION A216/02 TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE A Unit 2: Modules B5 C5 P5 (Higher Tier) * O C E / 1 5 7 7 6 * Candidates answer on the Question Paper A calculator may be used for this paper Wednesday 27 January 2010 Afternoon OCR Supplied Materials: None Duration: 40 minutes Other Materials Required: • Pencil • Ruler (cm/mm) * A 2 1 6 0 2 * INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES • • • • • • Write your name clearly in capital letters, your Centre Number and Candidate Number in the boxes above. Use black ink. Pencil may be used for graphs and diagrams only. Read each question carefully and make sure that you know what you have to do before starting your answer. Answer all the questions. Do not write in the bar codes. Write your answer to each question in the space provided, however additional paper may be used if necessary. INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES • • • • • The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. The total number of marks for this paper is 42. A list of physics equations is printed on page 2. The Periodic Table is printed on the back page. This document consists of 20 pages. Any blank pages are indicated. © OCR 2010 [D/103/3775] DC (SHW 00377 12/08) 15776/5 OCR is an exempt Charity Turn over 2 TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE EQUATIONS Useful Relationships Explaining Motion speed = distance travelled time taken momentum = mass × velocity change of momentum = resultant force × time for which it acts work done by a force = force × distance moved by the force change in energy = work done change in GPE = weight × vertical height difference 1 kinetic energy = 2 × mass × [velocity]2 Electric Circuits resistance = voltage current voltage across primary coil number of turns in primary coil = voltage across secondary coil number of turns in secondary coil energy transferred = power × time power = potential difference × current efficiency = energy usefully transferred × 100% total energy supplied The Wave Model of Radiation wave speed = frequency × wavelength © OCR 2010 3 Answer all the questions. 1 We use millions of tonnes of iron every year. It is used to make an enormous number of things such as girders, chains and bridges. (a) Iron is important because it is comparatively cheap and its properties are useful. Draw straight lines to link each property to why it is useful. You should draw four lines. property why it is useful can be used to make roof supports good electrical conductor can be hammered into different shapes high melting point can be used to make lightning conductors malleable can be used to make barbecues strong can be used to make magnets © OCR 2010 Turn over [3] 4 (b) Iron is extracted from iron ore. Iron ore contains iron oxide. There are different types of iron oxide. Which of these formulae corresponds to the oxide with the highest proportion of iron atoms? Put a ring around the correct answer. FeO Fe2O3 Fe3O4 [1] (c) Iron is extracted from iron oxide in a blast furnace. Iron forms through a sequence of reactions. Here are the reactions, but they are not in the correct order. A 2C + O2 B FeO + CO C Fe3O4 + CO D 3Fe2O3 + CO 2CO Fe + CO2 3FeO + CO2 2Fe3O4 + CO2 Put the reactions into the correct order. The last one has been done for you. B start end [1] (d) Use the Periodic Table to find the relative atomic masses of iron and oxygen. What mass of iron is present in 72 g of FeO? Put a ring around the correct answer. 16 g 26 g 36 g 56 g [1] (e) Carbon monoxide is a gas at room temperature. What does this indicate about the structure and bonding of carbon monoxide? ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................ [2] © OCR 2010 5 (f) Iron is a metal. Solid metals have their own type of structure. Put a tick (✓) in the three boxes next to descriptions that are true for solid metals. contains electrons contains positive ions contains negative ions some of the ions are free to move some of the electrons are free to move contains no ions [2] (g) Some metals are extracted by electrolysis rather than in a blast furnace. electrodes electrolyte Electrolysis only works for some liquids. These are called electrolytes. Explain why electrolytes can conduct electricity. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................ [3] [Total: 13] © OCR 2010 Turn over 6 2 As the space shuttle re-enters the Earth’s atmosphere it gets intensely hot. A NAS (a) The skin of the space shuttle is covered with silicon dioxide tiles to protect it. Put ticks (✓) in the boxes next to the three properties of silicon dioxide that are most useful for withstanding re-entry. useful for re-entry chemically unreactive high melting point good thermal insulator good electrical insulator [1] (b) Silicon dioxide is held together by covalent bonds. Draw one line to link the type of interaction that holds the molecule together to the particles involved. type of interaction particles involved electrostatic attraction electrons or or magnetic attraction nuclei or or electrostatic repulsion electrons and nuclei [1] [Total: 2] © OCR 2010 7 3 A student investigates the effect of temperature change on a thermistor. The circuit diagram shows a battery and a thermistor. The circuit diagram is not finished. (a) A voltmeter and ammeter are missing from the diagram. Draw them in the correct places. Use the correct circuit symbols. [2] (b) Complete the sentence. Choose words from this list. decreases increases stays the same When the temperature of the thermistor is increased the resistance of the thermistor ………………………………………… and the reading of the ammeter ………………………………………… . [1] (c) Put a ring around the words that correctly complete the sentence. The ammeter measures the flow of in units of amperes / joules charge / / power in the thermistor volts. [1] [Total: 4] © OCR 2010 Turn over 8 4 The diagram shows a magnet close to a coil of wire. The magnet can spin on the shaft. coil magnet N shaft S terminals (a) Explain why there is an alternating voltage across the terminals when the magnet spins round. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................ [3] © OCR 2010 9 (b) A lamp is connected across the terminals of the coil. coil magnet N S shaft Put a ring around each term that correctly completes the sentences. The current in the lamp is a.c. / d.c. / p.c. The lamp filament heats up because atoms in the wire are hit by charges that are expanding / moving / spinning. [1] (c) The glowing filament has a resistance of 4 Ω. What is the current in the filament when the voltage across it is 2 V? Put a ring around the correct answer. 0.5 A 2A 6A 8A [1] [Total: 5] © OCR 2010 Turn over 10 5 A mains lamp connected to a 230 V supply has a power of 150 W. (a) Calculate the current in the lamp. Show your working. current = ..................................................... A [2] (b) The lamp is left on for 24 hours. 3.6 kWh of electrical energy is transferred to it. 0.18 kWh of light energy transfers out of the lamp in that time. What is the efficiency of the lamp? Put a ring around the correct answer. 0.05% 5% 20% 2000% [1] (c) The mains electricity supply is a.c., not d.c. Put ticks (✓) in the boxes next to the two correct reasons for this. d.c. heats up wires more than a.c. a.c. is easier to generate than d.c. d.c. can only be produced by batteries there is less risk of electric shock with a.c. a.c. can be distributed more efficiently than d.c. [1] © OCR 2010 11 (d) The 150 W lamp is replaced with one that has a power of only 60 W. Draw straight lines from each electrical property to how it changes when the lamp is replaced. electrical property how it changes current increases resistance decreases potential difference stays the same [1] [Total: 5] © OCR 2010 Turn over 12 6 Chloe analyses a sample of DNA. (a) Here is a short segment of DNA from the sample. Chloe knows that it contains four bases, A, C, G, and T, arranged like this. A T G C G C C G T A A T C G A T T A She finds the percentages of some of the bases in the whole DNA sample. Complete the table to suggest how much of the other two bases Chloe will find in her sample. base % present C 20 A 30 T G [1] © OCR 2010 13 (b) DNA controls the making of proteins. (i) Complete this sentence. Choose the answer from this list. amino acids carbohydrates enzymes fats sugars The sequence of bases in DNA determines the order of …………………………………… in the protein which is made. (ii) [1] Put ticks (✓) in the boxes next to the two correct statements. Proteins are made in the cytoplasm. Proteins are made in the nucleus. DNA takes the genetic code to the cytoplasm. A copy of the gene carries the genetic code to the cytoplasm. Proteins are made out of DNA. New DNA is made in the cytoplasm. [2] [Total: 4] © OCR 2010 Turn over 14 BLANK PAGE Question 7 starts on page 15. PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE © OCR 2010 15 7 (a) All cells in a plant originate from the same cell. Leaf cells contain chlorophyll, but root cells do not. Explain why leaf and root cells in the same plant can develop differently. Use ideas about genes in your answer. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................ [2] (b) New plants can be made by taking cuttings. Andrew takes a cutting of a plant stem. There are no roots on the cutting. State • • how to make a cutting produce roots which cells of the cutting develop into roots. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................ [2] [Total: 4] © OCR 2010 Turn over 16 8 This question is about how plant shoots respond to light. In an experiment, different parts of growing shoots are covered with metal foil. Light is shone from one side only. light = metal foil A B C D Some of the shoots bend towards the light. (a) Which shoot, A, B, C or D, does not bend towards the light? answer ........................................................ [1] (b) Some of the following statements can be used to explain how shoots grow towards the light. They are in the wrong order. Select the correct statements, and put them in the correct order. A B Auxin makes the shoot cells expand on this side. Auxin makes the shoot cells shrink on this side. C D Auxin moves down the stem from the tip. Auxin moves up the stem to the tip. E F Auxin concentration becomes highest on the dark side of the stem. Auxin concentration becomes highest on the light side of the stem. [2] © OCR 2010 17 (c) The growth of shoots towards the light can be an advantage to the plant. Some students were asked to explain why this is. Amelia Cary Phototropism helps the shoots gain the most light for photosynthesis. Geotropism helps the roots to spread out. Sam Growing towards the light increases the plant’s chances of survival. Martin Growing towards the light helps plants to gain more carbon dioxide. Jane Phototropism helps transport sugars in the phloem. Reena Growing towards the light helps plants to gain more water. Nicola Bending towards the light helps the plant keep low to the ground. Which two students gave the best reasons? answer ........................................................... and ........................................................... [2] [Total: 5] END OF QUESTION PAPER © OCR 2010 18 BLANK PAGE PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE © OCR 2010 19 PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE Copyright Information OCR is committed to seeking permission to reproduce all third-party content that it uses in its assessment materials. OCR has attempted to identify and contact all copyright holders whose work is used in this paper. To avoid the issue of disclosure of answer-related information to candidates, all copyright acknowledgements are reproduced in the OCR Copyright Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations, is given to all schools that receive assessment material and is freely available to download from our public website (www.ocr.org.uk) after the live examination series. If OCR has unwittingly failed to correctly acknowledge or clear any third-party content in this assessment material, OCR will be happy to correct its mistake at the earliest possible opportunity. For queries or further information please contact the Copyright Team, First Floor, 9 Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 1GE. OCR is part of the Cambridge Assessment Group; Cambridge Assessment is the brand name of University of Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate (UCLES), which is itself a department of the University of Cambridge. © OCR 2010 © OCR 2010 89 actinium [227] Ac* 57 lanthanum 139 La* 39 yttrium 89 Y 21 scandium 45 Sc name 104 rutherfordium [261] Rf 72 hafnium 178 Hf 40 zirconium 91 Zr 22 titanium 48 Ti 105 106 seaborgium [266] Sg [262] Db dubnium 74 tungsten 184 W 42 molybdenum 96 Mo 24 chromium 52 Cr 73 tantalum 181 Ta 41 niobium 93 Nb 23 vanadium 51 V atomic (proton) number relative atomic mass atomic symbol Key 107 bohrium [264] Bh 75 rhenium 186 Re 43 108 hassium [277] Hs 76 osmium 190 Os 44 ruthenium 101 Ru [98] Tc technetium 26 iron 56 Fe 25 manganese 55 Mn cobalt 59 Co nickel 59 Ni copper 63.5 Cu zinc 65 Zn boron carbon nitrogen oxygen 16 O 6 fluorine 19 F 7 4 He 0 109 meitnerium [268] Mt 77 iridium 192 Ir 45 rhodium 103 Rh 27 110 darmstadtium [271] Ds 78 platinum 195 Pt 46 palladium 106 Pd 28 111 roentgenium [272] Rg 79 gold 197 Au 47 silver 108 Ag 29 The relative atomic masses of copper and chlorine have not been rounded to the nearest whole number. 81 thallium 204 Tl 49 indium 115 In 31 gallium tin 82 lead 207 Pb 50 119 Sn 32 germanium 73 Ge 14 silicon 28 Si 6 83 bismuth 209 Bi 51 antimony 122 Sb 33 arsenic 75 As 15 phosphorus 31 P 7 84 polonium [209] Po 52 tellurium 128 Te 34 selenium 79 Se 16 sulfur 32 S 8 85 astatine [210] At 53 iodine 127 I 35 bromine 80 Br 17 chlorine 35.5 Cl 9 86 radon [222] Rn 54 xenon 131 Xe 36 krypton 84 Kr 18 argon 40 Ar 10 neon Elements with atomic numbers 112-116 have been reported but not fully authenticated 80 mercury 201 Hg 48 cadmium 112 Cd 30 70 Ga 13 aluminium 27 Al 5 20 Ne 2 14 N 5 helium 12 C 4 1 11 B 3 hydrogen 1 H * The lanthanoids (atomic numbers 58-71) and the actinoids (atomic numbers 90-103) have been omitted. 88 87 [226] Ra [223] Fr radium 56 francium barium 137 Ba 133 Cs 55 38 caesium strontium 88 Sr 85 Rb 37 20 rubidium calcium 40 Ca 39 K 19 12 potassium magnesium 24 Mg 23 Na 11 4 sodium beryllium 3 9 Be 7 Li lithium 2 1 The Periodic Table of the Elements 20 A216/02 Mark Scheme January 2010 A216/02 Modules B5, C5, P5 Higher Tier 1 Question a Expected Answers property why it is useful Marks [3] … roof supports … conductor … hammered … high melting … … conductor malleable … barbecues strong … magnets b c FeO (1) [1] [1] A d 56g (1) D C B (1) [1] 25 Additional Guidance all four property boxes have one line going to the correct place = 3 marks only three of the property boxes have one line going to the correct place = 2 marks only two of the property boxes have one line going to the correct place = 1 mark only one of the property boxes has one line going to the correct place = 0 marks A216/02 1 Mark Scheme Question e Expected Answers any two from: (small) molecules; (molecules/particles - not atoms) far apart; weak forces (implied between carbon monoxide molecules not between atoms); strong forces (implied inside carbon monoxide); ‘covalent’ used correctly; Marks [2] contains electrons contains positive ions ...electrons are free to move Additional Guidance accept bonds ‘loose’ [2] f January 2010 assume the candidate is discussing bonds holding atoms within the molecule unless stated otherwise one mark for each correct point which has not been contradicted ignore pairs of statements which are contradictory ignore incorrect statements which do not contradict a correct statement allow the word ‘bond’ for any interaction 3 correct = 2 marks 2 correct = 1 mark 1 correct = 0 marks if more than three ticks, each extra tick cancels out one correct marking point 26 A216/02 1 Question g Mark Scheme Expected Answers (electrolyte) is ionic / contains ions / charged particles(1) Marks [3] January 2010 Additional Guidance particles become charged = contradiction reject electrons/atoms/molecules/neutrons for first marking point only but allow ‘protons’ allow named examples eg sodium ions and chloride ions allow ‘contains positive ions’ or ‘contains negative ions’ movement (of particles mentioned above) (1) ignore attraction for the ‘movement’ marking point (attracted to/move) towards the electrodes (1) ignore incorrect directions eg ‘positive particles to anode’ ‘electrons move towards electrodes’ = 2 marks ‘ion free to move but stay in a regular pattern’ = 1 for ions contradiction for movement Total [13] 27 A216/02 2 Mark Scheme Question a Expected Answers chemically unreactive high melting point good thermal insulator b Marks [1] [1] electrostatic repulsion electrons and nuclei Total [2] 28 January 2010 Additional Guidance there must be the one correct line only A216/02 3 Mark Scheme Question a Expected Answers Marks [2] January 2010 Additional Guidance ammeter: correct symbol (capital A in circle) in correct place = 1 mark voltmeter: correct symbol (capital V in circle) in correct place = 1 mark b c decreases increases charge amperes [1] [1] Total [4] 29 both correct = 1 mark accept any unambiguous response both correct = 1 mark accept any unambiguous response A216/02 4 Mark Scheme Question a Expected Answers maximum of three marks made up of Marks [3] any two from: any important property of the magnet eg polarity / distance (from coil) / direction of movement (but not direction of spin); reference to movement of magnet / change in magnetism, including ‘spin’ of the magnet; effect of speed of movement; the current /voltage/electrons change direction; c a.c. moving 0.5 A (1) [1] Total Additional Guidance unspecified ‘it’ refers to the magnet ignore attraction and repulsion by or to the magnet ignore reference to the word ‘charge’ in connection with the magnet ignore reference to ‘ends’ of the magnet reject ‘the coil makes the magnet move’ (wrong causality) and any three from: explains reversal of current/voltage (not just change) / links reversal of current to each half turn of the magnet; use of high level term – ‘induction’; use of high level term - ‘(magnetic) field’ b January 2010 [1] [5] 30 examples: ‘different ends of the magnet have different charge’ = 0 marks ‘different ends of the magnet have different charged poles’ = 1 mark ‘moving magnet makes electric current’ = 1 mark ‘moving magnet makes electrons move backwards and forwards’ = 2 marks (reversal not explained) ‘as the magnet spins the coil of wire is attracted and repelled’ = 2 marks ‘as one pole of the magnet enters the coil, the direction of the current goes one way, as the opposite enters, the current is sent in the opposite direction’ = 3 marks ‘the current changes direction’ = 1 mark ‘the current changes direction for every half turn of the magnet’ = 2 marks accept any unambiguous response A216/02 5 Mark Scheme Question a Expected Answers 0.65 (2) if answer wrong look for working for maximum of 1 mark Marks [2] 150 (1) 230 b c Additional Guidance correct numerical answer with no working = 2 marks accept answers from 0.6 – 0.7 if no numerical working given acccept I=P/V (1) ignore P=IV 5% (1) [1] [1] a.c. is easier to generate than d.c. … distributed more efficiently … d [1] current increases resistance decreases potential difference stays the same Total [5] 31 January 2010 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question 6 a b Expected Answers i ii base % present C 20 A 30 T 30 G 20 Marks [1] amino acids (1) [1] [2] … are made in the cytoplasm. (1) A copy of the gene caries … Total (1) [4] 32 January 2010 Additional Guidance if answer not on dotted line, look for a ringed word if more than two ticks, each extra tick cancels out one correct marking point A216/02 7 Mark Scheme Question a b Expected Answers any two from: (all) cells have the same (set of) genes; idea that different genes do different jobs; idea that gene can be switched on/off; some (genes switched on); hormone/auxin/rooting powder (1) Marks [2] [2] meristem/unspecialised (cells) (1) Total 8 a b E c C A Amelia (1) Sam (1) Total Additional Guidance answer must refer to genes ignore ‘different cells have different genes’ ignore incorrect context eg ‘different cells have different genes which do different jobs’ = 1 mark for 2nd marking point ‘genes are switched on’ = 1 mark ‘some genes are switched on’ = 2 marks ‘some genes are switched off’ = 2 marks ‘the genes for making chlorophyll are switched on in the leaf not in the root’ = 2 marks accept plant it / put in a dish of compost/nutrient/water ignore unqualified ‘powder’ ignore ‘stem cells’ ignore ‘cut it down the middle’ [4] B (1) [1] [2] accept any unambiguous response ACE in incorrect order = 1 mark any letters incorrect = 0 marks [2] any order accept any unambiguous response accept ‘A’ and ‘S’ (2) [5] 33 January 2010 H GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION A216/02 TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE A Unit 2: Modules B5 C5 P5 (Higher Tier) * O C E / 1 5 3 5 4 * Monday 28 June 2010 Morning Candidates answer on the Question Paper A calculator may be used for this paper OCR Supplied Materials: None Duration: 40 minutes Other Materials Required: • Pencil • Ruler (cm/mm) * A 2 1 6 0 2 * INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES • • • • • • Write your name clearly in capital letters, your Centre Number and Candidate Number in the boxes above. Use black ink. Pencil may be used for graphs and diagrams only. Read each question carefully and make sure that you know what you have to do before starting your answer. Answer all the questions. Do not write in the bar codes. Write your answer to each question in the space provided. Additional paper may be used if necessary but you must clearly show your Candidate Number, Centre Number and question number(s). INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES • • • • • The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. The total number of marks for this paper is 42. A list of physics equations is printed on page 2. The Periodic Table is printed on the back page. This document consists of 20 pages. Any blank pages are indicated. © OCR 2010 [D/103/3775] DCA (LEO/CG) 15354/6 OCR is an exempt Charity Turn over 2 TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE EQUATIONS Useful Relationships Explaining Motion speed = distance travelled time taken momentum = mass × velocity change of momentum = resultant force × time for which it acts work done by a force = force × distance moved in the direction of the force change in energy = work done change in GPE = weight × vertical height difference 1 kinetic energy = 2 × mass × [velocity]2 Electric Circuits resistance = voltage current voltage across primary coil number of turns in primary coil = voltage across secondary coil number of turns in secondary coil energy transferred = power × time power = potential difference × current efficiency = energy usefully transferred × 100 % total energy supplied The Wave Model of Radiation wave speed = frequency × wavelength © OCR 2010 3 BLANK PAGE Question 1 starts on page 4 PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE © OCR 2010 Turn over 4 Answer all the questions. 1 Chemicals such as water are vital for life. Most of our planet is covered by water. (a) Sea water is too salty for us to use. The concentration of salt in the sea has increased over millions of years. The amount of sea water has not changed much over millions of years. condensation sun evaporation rain Use ideas from the diagram to explain how salt gets into the sea, and why the seas have become saltier. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... .............................................................................................................................................. [3] © OCR 2010 5 (b) Water easily evaporates into the air. What does this tell you about water? Draw one straight line to join the two correct boxes. water is made of forces between water particles small molecules strong forces of repulsion or or large molecules weak forces of repulsion or or a giant structure of ions strong forces of attraction or or a giant structure of atoms weak forces of attraction [2] (c) Astronomers look for signs of life on other planets. They look for water and also for other chemicals. Put a ring around the chemical most likely to show that life is present. Al 2O3 CH4 CaCl 2 NaCl SiO2 [1] [Total: 6] © OCR 2010 Turn over 6 2 The electric cables carried on pylons are made from aluminium. (a) Aluminium cables are good electrical conductors. Some students try to explain how a solid metal conducts electricity. Which two students make correct statements that are part of the true explanation? Carolyn Metals contain negative ions. Mary Metals don't contain ions. Judith Metals contain small molecules. Danielle Metals contain electrons. Alistair Heat can move through a metal. Andy Charge can move through a metal. Stan Nothing can move through a metal. Ryan Neutral particles can move through a metal. answer ................................. and ................................. [2] © OCR 2010 7 (b) The cables are suspended from tall pylons. The cables are made of aluminium rather than copper. Volume for volume, aluminium has 65 % of the electrical conductivity of copper. Weight for weight, aluminium has twice the electrical conductivity of copper. Use this information to explain why aluminium is used instead of copper. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................. [1] (c) The aluminium used to make the cables is extracted from aluminium oxide. Aluminium oxide is the mineral in aluminium ore. Some ores produce 2 tonnes of aluminium oxide from 5 tonnes of ore. Put a ring around the percentage of aluminium oxide in these ores. 10 % 20 % 25 % 40 % 50 % [1] (d) To make aluminium, melted aluminium oxide is electrolysed. Put a tick (✓) in the box next to the best description of electrolysis. using an electric current to melt a compound using an electric current to purify a compound using an electric current to make a compound using an electric current to decompose a compound © OCR 2010 [1] Turn over 8 (e) Carbon dioxide gas is produced when aluminium oxide is electrolysed. carbon electrode electrolyte of molten aluminium oxide carbon electrode Draw a straight line to link one statement from column 1 with one statement from column 2 to explain why carbon dioxide is produced. column 1 column 2 Oxygen is bubbled into the cell. Oxygen reacts with the electrolyte. or or Oxygen is not formed in the process. Oxygen reacts with the positive electrode. or or Oxygen is dissolved in the electrolyte. Oxygen reacts with the negative electrode. or or Oxygen is formed at the positive electrode. Electrolyte reacts with the positive electrode. or or Oxygen is formed at the negative electrode. Electrolyte reacts with the negative electrode. [2] © OCR 2010 9 (f) What is the electrode reaction that produces the aluminium? Put a tick (✓) in the box next to the correct answer. Al 3+ + e– Al Al 3+ + 3e– Al Al 3+ + 3e– 3Al Al 3+ + e3– 3Al [1] [Total: 8] © OCR 2010 Turn over 10 3 The circuit below contains a thermistor. A 4.5 V (a) Complete the sentence for a thermistor. Choose words from this list. current light level pressure resistance temperature voltage The .................................. of the thermistor increases with decreasing .................................. . [2] (b) When the switch is closed, the ammeter reads 0.5 A. Put a ring around the correct value for the thermistor resistance. 0.1 Ω 2.3 Ω 5Ω 9Ω [1] (c) A voltmeter can be used to measure the potential difference across the thermistor. Draw the voltmeter on the circuit diagram and show how it should be connected. [1] [Total: 4] © OCR 2010 11 4 Both resistors in this circuit have the same value. A 6Ω 6V 6Ω (a) Complete the sentences. Choose words from this list. charge current resistance voltage The energy transferred by each unit of charge as it goes around the circuit is equal to the .................................. of the battery. Closing the switch increases the battery ................................... . [2] (b) Complete the table. Choose numbers from the list. 0 0.5 state of the switch 1 2 ammeter reading in amps open closed [1] (c) The two resistors are now connected in series with the switch. A 6Ω 6V 6Ω Explain why the current in each resistor is 0.5 A when the switch is closed. Show a calculation in your answer. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... .............................................................................................................................................. [2] [Total: 5] © OCR 2010 Turn over 12 5 This transformer has two coils wound on a core. 230 coil volts a.c. lamp core The left-hand coil of the transformer is connected to the 230 V a.c. mains supply. (a) Explain why there is an a.c. voltage across the right-hand coil. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... .............................................................................................................................................. [3] (b) The left-hand coil has 180 turns and the right-hand coil has 90 turns. What is the voltage across the lamp? Put a ring around the correct answer. 90 V 115 V 230 V 460 V [1] (c) The lamp has a power of 0.1 kW. It is left on for a week. How much electrical energy does it use? Put a ring around the correct answer. 0.7 kWh 2.4 kWh 8.4 kWh 16.8 kWh [1] [Total: 5] © OCR 2010 13 6 Harry takes a cutting of a plant. He wants to know what happens to the cutting as it grows into a plant. (a) Explain how a new plant grows from a cutting. Your explanation should include these terms: clone hormone xylem cells unspecialised cells ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... .............................................................................................................................................. [3] (b) Harry’s new plant shows a positive phototropic response. How does this increase the plant’s chance of survival? ................................................................................................................................................... .............................................................................................................................................. [1] [Total: 4] © OCR 2010 Turn over 14 7 The cell cycle is made up of cell growth and mitosis. During mitosis a number of processes take place. (a) Put ticks (✓) in the boxes next to the two processes that occur only during mitosis. cells divide chromosomes are copied number of organelles increases number of nuclei stays the same copies of chromosomes separate [2] (b) Another type of cell division is meiosis. (i) What type of cell is formed by meiosis? ...................................................................................................................................... [1] (ii) The cells made in meiosis may not all be the same size. If one of the new cells is larger than another, what can you say about the number of chromosomes in each? Put a tick (✓) in the box next to the correct statement. The larger cell has more chromosomes. The smaller cell has more chromosomes. They have the same number of chromosomes. The first cell to form has more chromosomes. © OCR 2010 [1] 15 (c) Animal cells can now be made by cloning. Paul is a scientist working in a laboratory cloning rabbits. He removes the nucleus from an egg cell of one rabbit. He then inserts a nucleus from a donor cell taken from another rabbit. An embryo then develops. rabbit egg cell nucleus removed cloned cell developing embryo donor nucleus transferred donor cell (i) Which statement best describes what is happening to the genes from the donor cell in this process? Put a tick (✓) in the box next to the correct answer. All genes are activated. All genes are inactivated. All active genes are inactivated. Some inactive genes are reactivated. (ii) [1] In the early stages of embryo growth, only stem cells are present. How do these cells differ from normal body cells? Put a tick (✓) in the box next to the correct answer. Stem cells have twice the usual number of chromosomes. Stem cells are specialised. Stem cells are unspecialised. Stem cells have half the usual number of chromosomes. [1] [Total: 6] © OCR 2010 Turn over 16 8 A length of DNA is made up of two strands. (a) Some of the bases on the strands are shown. Complete the diagram to show the pairing of the bases. The first pair has been done for you. C G A C A G T [1] (b) Why is the pairing of the bases significant? Put ticks (✓) in the boxes next to the two best answers. to make all DNA molecules different to hold the strands of DNA together to allow exact copies of DNA to be made to allow proteins to join DNA in chromosomes to allow each base pair to code for a different amino acid © OCR 2010 [1] 17 (c) DNA contains the genetic code to make proteins. DNA molecules stay in one place, so a copy of the gene carries the information to where the protein is actually made. There are several stages in the process of making protein. Select the four correct statements from the list and place them in the correct order. One has been done for you. A A copy of the gene moves from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. B Fatty acid molecules join together. C A copy of the gene moves from the cytoplasm to the nucleus. D A copy of the information in the DNA base sequence is made. E Amino acid molecules join together. F The order of these determines the protein structure. F [2] [Total: 4] END OF QUESTION PAPER © OCR 2010 18 BLANK PAGE PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE © OCR 2010 19 PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE Copyright Information OCR is committed to seeking permission to reproduce all third-party content that it uses in its assessment materials. OCR has attempted to identify and contact all copyright holders whose work is used in this paper. To avoid the issue of disclosure of answer-related information to candidates, all copyright acknowledgements are reproduced in the OCR Copyright Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations, is given to all schools that receive assessment material and is freely available to download from our public website (www.ocr.org.uk) after the live examination series. If OCR has unwittingly failed to correctly acknowledge or clear any third-party content in this assessment material, OCR will be happy to correct its mistake at the earliest possible opportunity. For queries or further information please contact the Copyright Team, First Floor, 9 Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 1GE. OCR is part of the Cambridge Assessment Group; Cambridge Assessment is the brand name of University of Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate (UCLES), which is itself a department of the University of Cambridge. © OCR 2010 © OCR 2010 89 actinium [227] Ac* 57 lanthanum 139 La* 39 yttrium 89 Y 21 scandium 45 Sc name 104 rutherfordium [261] Rf 72 hafnium 178 Hf 40 zirconium 91 Zr 22 titanium 48 Ti 105 106 seaborgium [266] Sg [262] Db dubnium 74 tungsten 184 W 42 molybdenum 96 Mo 24 chromium 52 Cr 73 tantalum 181 Ta 41 niobium 93 Nb 23 vanadium 51 V atomic (proton) number relative atomic mass atomic symbol Key 107 bohrium [264] Bh 75 rhenium 186 Re 43 108 hassium [277] Hs 76 osmium 190 Os 44 ruthenium 101 Ru [98] Tc technetium 26 iron 56 Fe 25 manganese 55 Mn cobalt 59 Co nickel 59 Ni copper 63.5 Cu zinc 65 Zn boron carbon nitrogen oxygen 16 O 6 fluorine 19 F 7 4 He 0 109 meitnerium [268] Mt 77 iridium 192 Ir 45 rhodium 103 Rh 27 110 darmstadtium [271] Ds 78 platinum 195 Pt 46 palladium 106 Pd 28 111 roentgenium [272] Rg 79 gold 197 Au 47 silver 108 Ag 29 The relative atomic masses of copper and chlorine have not been rounded to the nearest whole number. 81 thallium 204 Tl 49 indium 115 In 31 gallium tin 82 lead 207 Pb 50 119 Sn 32 germanium 73 Ge 14 silicon 28 Si 6 83 bismuth 209 Bi 51 antimony 122 Sb 33 arsenic 75 As 15 phosphorus 31 P 7 84 polonium [209] Po 52 tellurium 128 Te 34 selenium 79 Se 16 sulfur 32 S 8 85 astatine [210] At 53 iodine 127 I 35 bromine 80 Br 17 chlorine 35.5 Cl 9 86 radon [222] Rn 54 xenon 131 Xe 36 krypton 84 Kr 18 argon 40 Ar 10 neon Elements with atomic numbers 112-116 have been reported but not fully authenticated 80 mercury 201 Hg 48 cadmium 112 Cd 30 70 Ga 13 aluminium 27 Al 5 20 Ne 2 14 N 5 helium 12 C 4 1 11 B 3 hydrogen 1 H * The lanthanoids (atomic numbers 58-71) and the actinoids (atomic numbers 90-103) have been omitted. 88 87 [226] Ra [223] Fr radium 56 francium barium 137 Ba 133 Cs 55 38 caesium strontium 88 Sr 85 Rb 37 20 rubidium calcium 40 Ca 39 K 19 12 potassium magnesium 24 Mg 23 Na 11 4 sodium beryllium 3 9 Be 7 Li lithium 2 1 The Periodic Table of the Elements 20 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question Expected Answers Where is the salt? 1 a Realises that the rocks/ mountains / ground / lithosphere contain the salt or salts or minerals (1) June 2010 Marks Additional Guidance [3] ‘Chemicals’ not enough for the ‘salt’ marking point. Must strongly infer that the salt is in the ground to start with. If ground not mentioned, allow any mention of salt in streams/rivers – assume from ground unless candidate contradicts that assumption. allow “Rivers pick up salt” for salt in ground. not “salt travels down rivers”, “rain picks up salt” - not enough How does [the salt] get into the water? Describes extraction of material from rocks by water e.g. salt dissolves / chemicals washed out of rocks (1) The extraction must be discussed, however briefly. “The water flows over salty ground”, “rains onto cliffs and picks up salts” both only get the first mark What happens to the sea? links evaporation to water or evaporation to salt left behind /salt doesn’t evaporate [any context must be suitable] (1) Any context must imply that water evaporates FROM the sea. ignore ‘Sea evaporates’ we are NOT looking for a description of the water cycle The second marking point will often include the first, and be worth two marks “salt washed out of rocks” = 2 “chemicals washed out of rocks” = 1 ie not ‘chemicals’ 1 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question 1 b Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance [2] mark each column separately, 1 mark for each correct column small molecules A column is correct if the correct box, and no other, is indicated, though it may have more than one line attached to it weak forces of attraction c June 2010 CH4 (1) Total [1] [6] 2 A216/02 2 Mark Scheme a b Danielle (1) Andy (1) realises the major factor is weight/mass [2] [1] June 2010 either order accept if marked on the diagram accept “Aluminium/cable is lighter” accept “twice the conductivity for the same weight” If the candidate gives several reasons, look where the emphasis lies. If in doubt, lighter should be the first in the list. So ignore “and it is lighter” c d 40% (1) [1] [1] ...to melt a compound ...to purify a compound ...to make a compound ... to decompose a compound (1) [2] e mark each column separately A column is correct if the correct box, and no other, is indicated, though it may have more than one line attached to it Oxygen...positive... ...formed...positive... 3 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question 2 f Expected Answers Al3+ + 3e− Al a b c resistance (1) temperature (1) 9 Ω (1) A Additional Guidance Total 3 Marks [1] June 2010 [8] [2] [1] [1] B look for V in a circle [not a square] with lines to either end of thermistor [accept the ‘V’ on its side] one end connected anywhere between A and B the other end connect anywhere between C and D The voltmeter maybe ‘inside’ the circuit accept diagram at bottom of page If there is an answer in both positions, neither crossed out, mark the top one only. C Candidates answer should be on the printed diagram. IF NOT, they may have drawn another diagram which can score the marks. D Total [4] 4 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question Expected Answers voltage (1) … current (1) [in that order] 4 a b switch ammeter reading open 1 closed 2 c 5 a b c First marking point Calculation, independent of reasoning 6/12=0.5 , 6/0.5=12, 12x0.5=6 OR 3/6 = 0.5, 3/0.5 = 6, 6x0.5 = 3 No other calculations are acceptable June 2010 Marks Additional Guidance [2] allow resistance for the second answer [1] beware –BOTH responses needed for the mark [2] accept the calculation in words “6 is half of 12, so it’s 0.5” Second marking point [mark independently] Any one of the following Correct equation written in symbol or word form I=V/R V=IR R=V/I any statement about current being split or shared between resistors cannot get the second marking point. [in series], current must be same through both resistors [components] / voltage split across the resistors in series, so charge must be same through both resistors BOD indicates that “12” is a measure of [total] resistance or that the pd across one resistor is 3 [volts] Total accept any reference to “12Ω”, “resistors add up to 12”, discusses magnetic field (1) which is changing (1) uses the term 'induces' or shows causal link between changing magnetic field and voltage (1) 115 V (1) 16.8 kWh (1) Total [5] [3] accept any reference to magnetism e.g. ‘electromagnet’ ignore ‘because transformers don’t work on dc’ [1] [1] [5] 5 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question Expected Answers 6 a any three from the following: June 2010 Marks Additional Guidance [3] IGNORE ANY INCORRECT STATEMENTS, unless they actually contradict a correct statement. Clone - the new plant/cutting/it is a clone Eg ignore ‘cutting is a clone of the DNA’ ignore “They clone cells that are needed” Hormone - Links hormone/auxin to growth or development [of any part of the plant] ignore ‘the hormones in the plant’, “the cutting gives off a hormone”, “hormone stimulates plant” ‘auxin is a hormone’ – not enough for a mark the hormone auxin helps the plant respond to light. BOD for growth unspecialised cells - infers that these are the cells which actually develop/ change/ specialise/ differentiate [into something else] accept ‘unspecialised cells grow into any cell’ ignore ‘unspecialised cells grow’ ignore “all plant cells are unspecialised” ignore ‘the unspecialised cells in the cutting means it can grow into something else” ignore ‘meristem’ xylem cells – infers that these develop from the unspecialised cells b mentions light/photosynthesis Total “unspecialised cells develop into xylem cells” = 2 “[meristem cells] develop into xylem cells” = 1 [1] [4] 6 ignore any mention of ‘Sun’, but accept ‘sunlight’ reject incorrect statements, e.g.Plant gets its food from the sunlight A216/02 Mark Scheme Question 7 a Expected Answers cells divide (1) (1) June 2010 Marks Additional Guidance [2] If more than two boxes ticked deduct a mark for each incorrect response. Candidates may not score less than zero. chromosomes are copied number of organelles increases number of nuclei stays the same copies of chromosomes separate b i gametes (1) [1] accept sex cells, egg (cell), sperm (cell), haploid, reproductive cells reject zygote, embryo If more than one answer – mark the first one [1] ii The larger cell has more... The smaller cell has more... They have the same number... (1) The first cell to form has more... c [1] i All genes are activated. All genes are inactivated. All active genes are inactivated. Some inactive genes are reactivated. (1) 7 A216/02 Question 7 c ii Mark Scheme Expected Answers Marks [1] Stem cells have twice... Stem cells are specialised. Stem cells are unspecialised. (1) Stem cells have half... Total [6] 8 June 2010 Additional Guidance A216/02 Mark Scheme Question T 8 a G T C A b Expected Answers Marks [1] [1] to make...different to hold the strands...together to allow exact copies... to allow proteins to join... ...code for a different amino acid [2] c D A E F uses D, A, E in any order = 1 mark order correct = 1 mark Total [4] 9 June 2010 Additional Guidance beware – one mark for BOTH answers H GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION A216/02 TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE A Unit 2: Modules B5 C5 P5 (Higher Tier) * O C E / 2 5 6 3 5 * Candidates answer on the question paper. A calculator may be used for this paper. Monday 24 January 2011 Afternoon OCR supplied materials: None Duration: 40 minutes Other materials required: • Pencil • Ruler (cm/mm) * A 2 1 6 0 2 * INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES • • • • • • Write your name, centre number and candidate number in the boxes above. Please write clearly and in capital letters. Use black ink. Pencil may be used for graphs and diagrams only. Read each question carefully. Make sure you know what you have to do before starting your answer. Write your answer to each question in the space provided. Additional paper may be used if necessary but you must clearly show your candidate number, centre number and question number(s). Answer all the questions. Do not write in the bar codes. INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES • • • • • The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. The total number of marks for this paper is 42. A list of physics equations is printed on page 2. The Periodic Table is printed on the back page. This document consists of 20 pages. Any blank pages are indicated. © OCR 2011 [D/103/3775] DC (SHW 00562 12/09) 25635/4 OCR is an exempt Charity Turn over 2 TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE EQUATIONS Useful Relationships Explaining Motion speed = distance travelled time taken momentum = mass × velocity change of momentum = resultant force × time for which it acts work done by a force = force × distance moved by the force change in energy = work done change in GPE = weight × vertical height difference 1 kinetic energy = 2 × mass × [velocity]2 Electric Circuits resistance = voltage current voltage across primary coil number of turns in primary coil = voltage across secondary coil number of turns in secondary coil energy transferred = power × time power = potential difference × current efficiency = energy usefully transferred × 100% total energy supplied The Wave Model of Radiation wave speed = frequency × wavelength © OCR 2011 3 Answer all the questions. 1 Air is a mixture of different gases. Each year we extract thousands of tonnes of gases from the air. Many of these gases are very useful. (a) We extract each gas by cooling the air until the gas turns into a liquid. Different gases turn into liquids at different temperatures. Here is some information about the gases. gas melting point in K boiling point in K argon 84 87 nitrogen 63 77 oxygen 55 90 water vapour 273 373 Which gas turns from a gas into a liquid at the lowest temperature? answer ......................................................... [1] (b) Oxygen is made of molecules. Liquid oxygen turns into a gas at extremely low temperatures. Explain why. Use your understanding of forces and molecules in your answer. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................ [3] [Total: 4] © OCR 2011 Turn over 4 2 We have extracted iron since the Iron Age. We still use the same method. We extract the iron by heating iron oxide with carbon in a furnace. Different reactions take place in the furnace. (a) In one reaction, carbon takes the oxygen away from iron oxide. (i) Fill in the boxes to write a word equation for this reaction. + + [2] (ii) combined Use words from this list to complete the sentences below. electrolysed melted oxidised precipitated reduced When carbon gains oxygen we say that the carbon has been ………………………… . When a metal oxide loses oxygen we say that the metal has been ………………………… . [1] (iii) Another reaction for making iron is between iron oxide and carbon monoxide gas. Put numbers in the boxes to balance the equation for this reaction. Fe2O3 + © OCR 2011 CO Fe + 3CO2 [2] 5 (b) Not all metals are extracted by heating their ores with carbon. Some metals are extracted by electrolysis. metal lead magnesium aluminium calcium cobalt iron extracted by heating with carbon electrolysis electrolysis electrolysis heating with carbon heating with carbon melting point of the metal in K 601 922 933 1112 1768 1808 Use the table to decide which three metals are likely to be more reactive than the others. answer .................................... and .................................... and ..................................... [1] [Total: 6] © OCR 2011 Turn over 6 3 Scientists are worried about the increasing amounts of carbon in our atmosphere. Look at the diagram of the carbon cycle. The numbers show how many gigatonnes of carbon move in each direction every year. atmosphere 102 102 5 land life 90 92 fossil fuels 36 40 oceans ocean life (a) The amount of carbon in the atmosphere is increasing. By how many gigatonnes does it increase every year? Put a ring around the correct answer. 2 3 5 90 102 [1] (b) Most of the carbon in the atmosphere is in the form of carbon dioxide. The diagram shows that 92 gigatonnes of carbon dissolve in the oceans every year. How many gigatonnes of carbon dioxide does this represent? Put a ring around the answer. 12 × 92 44 12 × 92 32 32 × 92 12 44 × 92 12 [1] (c) Carbon dioxide dissolves in seawater. Carbon dioxide in solution reacts with water to form ions. (i) Put state symbols in the boxes to complete the equation for this reaction. CO2(aq) + H2O (ii) H+ + HCO3– [1] Mary wants to see if sea water really is an ionic solution. What could she measure to show that it contains ions? .................................................................................................................................... [1] [Total: 4] © OCR 2011 7 4 Mains electricity is produced by generators in power stations. Each generator contains a magnet and a coil of wire. (a) Describe how the magnet and the coil of wire are used to make electricity. Include the name of the process. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................ [2] (b) State two ways that you could increase the voltage of the electricity produced by a generator. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................ [2] [Total: 4] © OCR 2011 Turn over 8 5 Charles puts this circuit together. lamp (a) The lamp glows. Here are some statements about the circuit. Which two statements, when taken together, explain why the lamp glows? Put ticks (✓) in the boxes next to the two statements required. The wires have some resistance. The current in the lamp heats it up. The battery pushes charges through the lamp. The wires have charges that are free to move. Only the lamp has charges that are free to move. [2] © OCR 2011 9 (b) Charles adds an ammeter to measure the current in the lamp. A 6V The lamp has a power of 3 W. What does the ammeter read? Put a ring around the correct answer. 0.5 A 2.0 A 6.0 A 18 A [1] (c) There is not enough current in the circuit to make the lamp glow brightly. Charles adds another battery and the lamp glows brightly. Complete the sentences. Choose words from this list. decreases increases parallel series Charles adds the second battery in ………………………… to the first one. This ………………………… the potential difference across the lamp. [1] [Total: 4] © OCR 2011 Turn over 10 6 Fleur assembles this circuit. A (a) The resistor, ammeter and lamp are in series. Explain why all three components have exactly the same current. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................ [2] (b) Fleur wants to add a voltmeter to measure the potential difference across the resistor. (i) Draw on this circuit diagram to show how Fleur should connect the voltmeter. A [1] © OCR 2011 11 (ii) Fleur finds that the potential difference across the resistor is 6 V. The potential difference across the battery is 9 V. The ammeter reads 0.5 A. What is the resistance of the lamp? Put a ring around the correct answer. 6X 12 X 18 X 30 X [1] [Total: 4] © OCR 2011 Turn over 12 7 Zara does an experiment with a pair of balloons on strings. She rubs each balloon against her clothing. Zara then holds the balloons up by their strings. Complete this explanation of why the balloons hang like this. Choose the best words from the list. atoms shield attract negative different neutral electrons positive identical protons repel The rubbing transfers some …………………… from each balloon to Zara’s clothing so, this leaves each balloon with a …………………… charge. The reason the balloons …………………… each other is because they have …………………… kinds of charge. [2] [Total: 2] © OCR 2011 13 8 Martin is studying mayflies. He looks at an adult mayfly and a mayfly nymph. adult mayfly (a) (i) mayfly nymph The adult mayfly lays eggs in the water. The eggs hatch into nymphs. The nymphs grow bigger. adult P nymph gamete gamete from another adult Q fertilised egg Complete the sentences. The type of cell division at P is …………………… , which makes cells that have …………………… number of chromosomes as the adult cells. The type of cell division at Q is …………………… , which makes cells that have …………………… number of chromosomes as the fertilised egg. © OCR 2011 [2] Turn over 14 (ii) The statements A to D are about processes of the cell cycle. Put the letters A, B, C and D in the correct column of the table to show whether the processes occur during cell growth or cell division. A the numbers of organelles increase B copies of the chromosomes separate C new strands of DNA form D strands of each DNA molecule separate cell growth cell division [2] © OCR 2011 15 (b) Once a nymph grows into an adult, it has different specialised tissues. Five people are asked to explain this. Jeremy All of the genes are switched on and become active. Teresa Some of the genes are lost from the cells. Vick Some of the active genes are switched off. Cassie Andrew Some genes are added to the cells. Some of the inactive genes are activated. Which two people give the best explanations? answer ........................................................... and ........................................................... [1] [Total: 5] © OCR 2011 Turn over 16 9 Susie sees a plant she likes in a friend’s garden. She asks if she can take a cutting. (a) Which part of her friend’s plant should Susie use to grow an identical plant? Put a ring around the correct answer. flower fruit seed stem [1] (b) Susie dips the bottom of her cutting in some rooting powder. She then puts the cutting into a pot of soil. What does the rooting powder contain that helps the cutting grow roots? ............................................................................................................................................ [1] (c) Susie’s cutting grows into a new plant. Which statements explain how this is possible? Put ticks (✓) in the boxes next to the two correct answers. Some unspecialised cells develop into other tissues. Some unspecialised cells develop into organs. Some xylem cells become phloem cells. Some plant cells become unspecialised. Some leaf cells become root cells. [2] © OCR 2011 17 (d) Susie keeps her new plant in a pot near a window. The shoot grows towards the light. Draw one line to join the effect of light on the distribution of auxin to its effect on the cells in the shoot. effect of light effect on the cells more auxin on lit side makes these cells grow more slowly or or more auxin on shaded side makes these cells grow more quickly [1] [Total: 5] © OCR 2011 Turn over 18 10 DNA carries genetic information. (a) What is the name given to the shape of DNA? ........................................................................................................................................... [1] (b) DNA in one part of the cell codes for the production of molecules in another part of the cell. Explain how this happens. In your answer write about • • • the code in DNA different sites in the cell the type of molecule produced. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................ [3] [Total: 4] END OF QUESTION PAPER © OCR 2011 19 PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE Copyright Information OCR is committed to seeking permission to reproduce all third-party content that it uses in its assessment materials. OCR has attempted to identify and contact all copyright holders whose work is used in this paper. To avoid the issue of disclosure of answer-related information to candidates, all copyright acknowledgements are reproduced in the OCR Copyright Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations and is freely available to download from our public website (www.ocr.org.uk) after the live examination series. If OCR has unwittingly failed to correctly acknowledge or clear any third-party content in this assessment material, OCR will be happy to correct its mistake at the earliest possible opportunity. For queries or further information please contact the Copyright Team, First Floor, 9 Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 1GE. OCR is part of the Cambridge Assessment Group; Cambridge Assessment is the brand name of University of Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate (UCLES), which is itself a department of the University of Cambridge. © OCR 2011 © OCR 2011 89 actinium [227] Ac* 57 lanthanum 139 La* 39 yttrium 89 Y 21 scandium 45 Sc name 104 rutherfordium [261] Rf 72 hafnium 178 Hf 40 zirconium 91 Zr 22 titanium 48 Ti 105 106 seaborgium [266] Sg [262] Db dubnium 74 tungsten 184 W 42 molybdenum 96 Mo 24 chromium 52 Cr 73 tantalum 181 Ta 41 niobium 93 Nb 23 vanadium 51 V atomic (proton) number relative atomic mass atomic symbol Key 107 bohrium [264] Bh 75 rhenium 186 Re 43 108 hassium [277] Hs 76 osmium 190 Os 44 ruthenium 101 Ru [98] Tc technetium 26 iron 56 Fe 25 manganese 55 Mn cobalt 59 Co nickel 59 Ni copper 63.5 Cu zinc 65 Zn boron carbon nitrogen oxygen 16 O 6 fluorine 19 F 7 4 He 0 109 meitnerium [268] Mt 77 iridium 192 Ir 45 rhodium 103 Rh 27 110 darmstadtium [271] Ds 78 platinum 195 Pt 46 palladium 106 Pd 28 111 roentgenium [272] Rg 79 gold 197 Au 47 silver 108 Ag 29 The relative atomic masses of copper and chlorine have not been rounded to the nearest whole number. 81 thallium 204 Tl 49 indium 115 In 31 gallium tin 82 lead 207 Pb 50 119 Sn 32 germanium 73 Ge 14 silicon 28 Si 6 83 bismuth 209 Bi 51 antimony 122 Sb 33 arsenic 75 As 15 phosphorus 31 P 7 84 polonium [209] Po 52 tellurium 128 Te 34 selenium 79 Se 16 sulfur 32 S 8 85 astatine [210] At 53 iodine 127 I 35 bromine 80 Br 17 chlorine 35.5 Cl 9 86 radon [222] Rn 54 xenon 131 Xe 36 krypton 84 Kr 18 argon 40 Ar 10 neon Elements with atomic numbers 112-116 have been reported but not fully authenticated 80 mercury 201 Hg 48 cadmium 112 Cd 30 70 Ga 13 aluminium 27 Al 5 20 Ne 2 14 N 5 helium 12 C 4 1 11 B 3 hydrogen 1 H * The lanthanoids (atomic numbers 58-71) and the actinoids (atomic numbers 90-103) have been omitted. 88 87 [226] Ra [223] Fr radium 56 francium barium 137 Ba 133 Cs 55 38 caesium strontium 88 Sr 85 Rb 37 20 rubidium calcium 40 Ca 39 K 19 12 potassium magnesium 24 Mg 23 Na 11 4 sodium beryllium 3 9 Be 7 Li lithium 2 1 The Periodic Table of the Elements 20 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question 1 (a) (b) 2 (a) Expected Answers nitrogen (1) Any three from: forces between molecules are weak (1); molecules are small (1); (molecules) easy to separate/break bonds/ overcome forces between/ move apart (1); gives a reason for condensation at low temperature – eg less energy, slower speed of molecular movement (1) Total (i) iron oxide + carbon carbon dioxide (b) 3 [4] [2] [1] (iii) 3 (1) 2 (1) magnesium, aluminium, calcium (1) [2] Additional Guidance Left hand side iron oxide and carbon in either order. Right hand side iron and carbon dioxide in either order. All four boxes correct = 2 marks Any two or three boxes correct = 1 mark Allow carbon monoxide or carbon oxide as alternatives to carbon dioxide. Reject chemical symbols. Both must be correct for one mark. Accept other forms of the verbs, eg oxidisation, oxidising if clear. + (ii) oxidised reduced Accept in any order. If lead, cobalt or iron is one of the three, then no marks. [1] Total [6] [1] [1] l aq aq (ii) (electrical) conductivity (1) Total [1] All correct for one mark; allow upper case letters L, AQ. Ignore any brackets. [1] [4] Ignore pH, electrolysis. 3 (1) (a) (b) (c) iron Marks [1] [3] January 2011 44 92 (1) 12 (i) 4 A216/02 Question 4 (a) (b) Mark Scheme Expected Answers Marks Additional Guidance the magnet spins/rotates/turns inside the coil (1) Not moving the magnet in and out of the coil. [2] called (electromagnetic) induction (1) Accept induced, but not electromagnetic on its own. Accept coil spinning as alternative to magnet spinning. Apply list principle if more than two suggestions given (General [2] guidance point 8). Any two from: Accept spin/move coil faster as alternative to spin the magnet spin the magnet faster (1); faster. use a stronger magnet (1); Not bigger magnet, more magnets. more (turns of) wire in the coil (1); Accept larger coil. put iron inside the coil (1) Total 5 [4] [2] (a) (b) (c) January 2011 The current in the lamp heats it up. (1) The battery pushes charges... (1) 0.5 A (1) series increases [1] [1] Total Both correct = 1 mark [4] 5 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question 6 (a) (b) Expected Answers current is (rate of) flow of charge/electrons/all parts of circuit have mobile charges (1); only one path for charge/current or charges/electrons are not used up as they enter and leave components (1) Marks Additional Guidance First marking point is realising that current is due to charges [2] moving. Second marking point is either realising that charges do not get used up or lost, or that there are no branches/parallel circuits for them to go elsewhere Look for a correct symbol (circle with V inside), connected to either side of the resistor only. [1] (i) January 2011 One lead must connect between points A and B. The other lead must connect between points C and D. The voltmeter may be drawn either inside or outside the circuit (ii) 6 (1) Total 7 electrons positive repel identical Total [1] [4] [2] All four correct = 2 marks Any two or three correct = 1 mark [2] 6 A216/02 Mark Scheme Question 8 (a) (i) Expected Answers meiosis, half the/23 mitosis, the same/46 Marks Additional Guidance All four correct = 2 marks [2] Two or three correct = 1 mark One correct = 0 marks All four correct = 2 marks [2] Two or three correct = 1 mark One correct = 0 marks (ii) Cell growth A C D (b) Cell division B Vick and Andrew (1) 9 (a) (b) (c) Both names correct in either order = 1 mark [1] [5] [1] [1] [2] Total stem (1) (plant/growth ) hormone (1) Some unspecialised cells...tissues. (1) Some unspecialised cells...organs. (1) Accept auxin Correct pattern for [2] One mistake for [1] A mistake is an extra tick a missing tick a tick in the wrong place 7 January 2011 A216/02 Question (d) Mark Scheme Expected Answers more auxin on shaded side Marks Additional Guidance If more than the one correct link is drawn, no marks. [1] makes these cells grow more quickly Total 10 January 2011 (a) double helix (1) (b) Any three from: links DNA code to order of bases (1); (DNA stays where it is and) the code carried by a copy (of the gene)/RNA (1) sites – to the cytoplasm/ribosomes (1) type – amino acids/protein is made (1) Total [5] [1] Do not accept “helix” or ‘spiral helix’: must be double helix owtte Neutral – DNA is in the nucleus. May list A,T/U,C,G or may state that pairs match for this mark. [3] [4] 8 H GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION A216/02 TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE ADDITIONAL SCIENCE A Unit 2: Modules B5 C5 P5 (Higher Tier) * O C E / 3 3 0 3 2 * Tuesday 28 June 2011 Morning Candidates answer on the question paper. A calculator may be used for this paper. OCR supplied materials: None Duration: 40 minutes Other materials required: • Pencil • Ruler (cm/mm) * A 2 1 6 0 2 * INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES • • • • • • Write your name, centre number and candidate number in the boxes above. Please write clearly and in capital letters. Use black ink. Pencil may be used for graphs and diagrams only. Read each question carefully. Make sure you know what you have to do before starting your answer. Write your answer to each question in the space provided. Additional paper may be used if necessary but you must clearly show your candidate number, centre number and question number(s). Answer all the questions. Do not write in the bar codes. INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES • • • • • The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. The total number of marks for this paper is 42. A list of physics equations is printed on page 2. The Periodic Table is printed on the back page. This document consists of 20 pages. Any blank pages are indicated. © OCR 2011 [D/103/3775] DC (SHW 00621 4/10) 33032/3 OCR is an exempt Charity Turn over 2 TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE EQUATIONS Useful Relationships Explaining Motion speed = distance travelled time taken momentum = mass × velocity change of momentum = resultant force × time for which it acts work done by a force = force × distance moved in the direction of the force change in energy = work done change in GPE = weight × vertical height difference 1 kinetic energy = 2 × mass × [velocity]2 Electric Circuits resistance = voltage current voltage across primary coil number of turns in primary coil = voltage across secondary coil number of turns in secondary coil energy transferred = power × time power = potential difference × current efficiency = energy usefully transferred × 100% total energy supplied The Wave Model of Radiation wave speed = frequency × wavelength © OCR 2011 3 Answer all the questions. 1 When the Romans came to Britain they extracted lead from mines in Somerset. Lead ore contains lead sulfide. (a) The first stage in extracting the lead is to heat the lead sulfide with oxygen. Fill in the boxes to balance the equation for this reaction. 2PbS + O2 PbO + SO2 [2] (b) The relative atomic mass of lead is 207. The relative atomic mass of sulfur is 32. Use this information to calculate the mass of lead that can be obtained from 71.7 tonnes of pure lead sulfide, PbS. mass = ................................ tonnes [2] (c) The Romans could extract 10 tonnes of lead from 100 tonnes of ore. A modern mine can only extract 3 tonnes of lead from 100 tonnes of ore. Suggest why modern mines get less lead from their ore than the Romans did. Puts ticks (✓) in the boxes next to the two statements that best explain why. Roman ores were easier to get at. Romans mined higher quality ores. Romans were more skilled at getting the lead from the ore. There are no easily mined ores left which have high quantities of lead. We no longer need to get so much lead out of the ore. Roman ores did not contain impurities. [1] © OCR 2011 Turn over 4 (d) Some substances are left over after the lead is extracted. One of these is silicon dioxide – silicon dioxide is a solid. Sulfur dioxide is also produced – sulfur dioxide is a gas. Complete the table about solid silicon dioxide and sulfur dioxide gas. For each description put one tick (✓) in the correct column to show whether it is true for silicon dioxide only, sulfur dioxide only, both or neither description silicon dioxide only sulfur dioxide only both neither has a high melting point has a low melting point has covalent bonds has ionic bonds is a giant structure is a simple molecular compound has weak forces between molecules [4] © OCR 2011 5 (e) The chart shows the main uses of lead. pigments & chemicals 12 % lead sheet for roofing 7 % other uses 10 % lead electrodes in car batteries 71 % About 8500 million tonnes of lead are used every year. Only 4000 million tonnes of this lead are produced from ore every year. Suggest where the remaining lead comes from. Explain your reasoning. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................ [2] (f) Lead conducts electricity. Which of the diagrams, A, B, C or D, best shows the structure of lead? ‘sea’ of ions ‘sea’ of electrons + + + + + + + + A + – – – + + + + – + + – – – B + – – – – – – – – – C – – + – – + – + – – D answer ........................ [1] © OCR 2011 Turn over 6 (g) Lead bromide, PbBr2, is an ionic compound. Sarah passes an electric current through melted lead bromide. It breaks down into bromine gas and molten lead. (i) The symbol for a lead ion is Pb2+. Write the symbol for a bromide ion. answer ........................ [1] (ii) Draw labelled arrows on the diagram to show • • the movement of a lead ion the movement of a bromide ion. positive electrode negative electrode bromide ion lead ion [1] [Total: 14] © OCR 2011 7 2 Pete pushes a magnet into a tube. wire N tube S magnet A (a) There is a coil of wire around the tube. Complete the sentences. Choose from these words. charge current voltage power As the magnet moves into the tube, a …………………… is induced across the ends of the coil. This results in a …………………… in the ammeter. [2] (b) Here are some ways of changing the reading of the ammeter. Put ticks (✓) in the boxes next to the two ways which would increase the reading. Increase the length of the tube. Decrease the length of the tube. Move the magnet more slowly into the tube. Move the magnet more quickly into the tube. Increase the number of turns of wire in the coil. Decrease the number of turns of wire in the coil. [2] [Total: 4] © OCR 2011 Turn over 8 3 This circuit has three identical resistors, A, B and C, in series with a battery. A 12 V B C (a) Here are some statements about the circuit. Put a tick (✓) in the box next to the correct statement. Resistor C has 0 V across it. Resistor B has 12 V across it. Resistor A has a greater current than the other resistors. All three resistors have the same current. [1] (b) Resistors A, B and C get hot. Explain why. Use these words in your answer. atoms electrons energy ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................ [3] © OCR 2011 9 (c) The three identical resistors are now connected in parallel to the battery. A 12 V A B C The ammeter in the circuit reads 6 A. What is the heating power of resistor C? Put a ring around the correct answer. 2W 6W 8W 24 W 72 W [1] [Total: 5] © OCR 2011 Turn over 10 4 Jo builds a circuit with a battery, a lamp and a switch in series. (a) Complete the circuit diagram. Use the correct symbols for the lamp and the switch. [1] (b) Complete the sentences by putting a ring around the correct words in bold. Before Jo closes the switch, it has a very high charge / current / power / resistance. Closing the switch allows the battery / lamp / switch / wires the circuit. to push charge around This movement of charge in the wires is called a current / power / resistance / voltage. [3] (c) The lamp does not light up when the switch is open. Put a tick (✓) in the box next to the correct reason why. There is only charge in the switch when it is closed. Charge is not able to flow through part of the open switch. The charge gets used up as it passes through the open switch. The potential difference across the open switch is reduced to zero. [1] [Total: 5] © OCR 2011 11 BLANK PAGE Question 5 starts on page 12 PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE © OCR 2011 Turn over 12 5 Labradors and poodles are breeds of dog. A labrador mates with a poodle and produces a puppy. The puppy has chromosomes from both the labrador and the poodle. (a) The labrador has 78 chromosomes in each body cell. The table shows chromosome numbers in each body cell of the labrador, the poodle and the puppy. chromosomes in labrador chromosomes in poodle chromosomes in puppy A 78 78 156 B 78 78 78 C 78 46 46 D 78 39 39 Which row, A, B, C or D, is correct? answer ........................ [1] © OCR 2011 13 (b) The puppy cells have chromosomes from both parents. Explain why the cells have chromosomes from both parents. Include in your answer • • • what type of cell division produces gametes what happens to the chromosome number when a gamete is formed what happens when the gametes fuse. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................ [3] [Total: 4] © OCR 2011 Turn over 14 6 The snowshoe hare lives in forests which have a lot of snow in winter. (a) The cells of the snowshoe hare contain the genetic code. The genetic code controls the formation of proteins in each cell. Complete the sentences. The genetic code is found in the cell ....................................................... . Proteins are formed in the cell ....................................................... . The genetic code is found on DNA. The number of strands in a DNA molecule is ....................................................... . The number of different bases in DNA is ....................................................... . [2] (b) In the summer the snowshoe hare has a dark coat, which is due to certain proteins being produced by hair-producing cells. In winter it grows a white coat with different proteins colouring the hair. Explain how the same animal can produce different colours of coat at different times of the year. In your answer use ideas about genes and proteins. ................................................................................................................................................... ................................................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................................ [2] © OCR 2011 15 (c) A scientist tests a sample of snowshoe hare DNA. She finds these proportions of two of the bases. base C base A 23 % 27 % What proportion of the bases will she find to be base T? Put a ring around the correct answer. 23 % 25 % 27 % 46 % 50 % [1] [Total: 5] © OCR 2011 Turn over 16 7 Harry does an experiment with some plant tips. He cuts the tip from a shoot and places it on a block of agar for several hours. He then throws away the tip. He places the agar block over part of the end of the shoot where the tip was cut from. tip agar block shoot shoot with tip removed (a) The shoot is left to grow. Which way will it grow? Choose from A, B, C and D. A B C D tall and straight tall and to the left tall and to the right short and stumpy answer ........................ [1] © OCR 2011 17 (b) What is the correct explanation for this result? Put ticks (✓) in the boxes next to the two correct answers. Agar stopped all of the light to one side of the tip. Auxin diffused from the cut tip into the agar. Auxin diffused from the cut shoot into the agar. The side of the shoot with most auxin grew more. The side of the shoot with most auxin grew less. Auxin made no difference to the growth of the shoot. Auxin absorbed more light under the agar. [2] (c) When growing shoots receive light from one side only, they grow towards the light. This is called phototropism. Phototropism increases a plant’s chance of survival. Complete the sentence. Use a word from the list. meiosis photosynthesis pollination reproduction The increased chance of survival is due to the increased rate of ..................................................... . [1] © OCR 2011 Turn over 18 (d) Harry’s shoots grow into full sized plants. A group of students were asked how plants grow. Reuben Zarah Plants keep on growing by meiosis. Plants’ meristems fuse and stop growing. Wendy Plants keep on growing in height by mitosis. David Plants stop all mitosis when they are fully grown. Which student gave the correct answer? answer ........................................................ [1] [Total: 5] END OF QUESTION PAPER © OCR 2011 19 PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS PAGE Copyright Information OCR is committed to seeking permission to reproduce all third-party content that it uses in its assessment materials. OCR has attempted to identify and contact all copyright holders whose work is used in this paper. To avoid the issue of disclosure of answer-related information to candidates, all copyright acknowledgements are reproduced in the OCR Copyright Acknowledgements Booklet. This is produced for each series of examinations and is freely available to download from our public website (www.ocr.org.uk) after the live examination series. If OCR has unwittingly failed to correctly acknowledge or clear any third-party content in this assessment material, OCR will be happy to correct its mistake at the earliest possible opportunity. For queries or further information please contact the Copyright Team, First Floor, 9 Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 1GE. OCR is part of the Cambridge Assessment Group; Cambridge Assessment is the brand name of University of Cambridge Local Examinations Syndicate (UCLES), which is itself a department of the University of Cambridge. © OCR 2011 © OCR 2011 89 actinium [227] Ac* 57 lanthanum 139 La* 39 yttrium 89 Y 21 scandium 45 Sc name 104 rutherfordium [261] Rf 72 hafnium 178 Hf 40 zirconium 91 Zr 22 titanium 48 Ti 105 106 seaborgium [266] Sg [262] Db dubnium 74 tungsten 184 W 42 molybdenum 96 Mo 24 chromium 52 Cr 73 tantalum 181 Ta 41 niobium 93 Nb 23 vanadium 51 V atomic (proton) number relative atomic mass atomic symbol Key 107 bohrium [264] Bh 75 rhenium 186 Re 43 108 hassium [277] Hs 76 osmium 190 Os 44 ruthenium 101 Ru [98] Tc technetium 26 iron 56 Fe 25 manganese 55 Mn cobalt 59 Co nickel 59 Ni copper 63.5 Cu zinc 65 Zn boron carbon nitrogen oxygen 16 O 6 fluorine 19 F 7 4 He 0 109 meitnerium [268] Mt 77 iridium 192 Ir 45 rhodium 103 Rh 27 110 darmstadtium [271] Ds 78 platinum 195 Pt 46 palladium 106 Pd 28 111 roentgenium [272] Rg 79 gold 197 Au 47 silver 108 Ag 29 The relative atomic masses of copper and chlorine have not been rounded to the nearest whole number. 81 thallium 204 Tl 49 indium 115 In 31 gallium tin 82 lead 207 Pb 50 119 Sn 32 germanium 73 Ge 14 silicon 28 Si 6 83 bismuth 209 Bi 51 antimony 122 Sb 33 arsenic 75 As 15 phosphorus 31 P 7 84 polonium [209] Po 52 tellurium 128 Te 34 selenium 79 Se 16 sulfur 32 S 8 85 astatine [210] At 53 iodine 127 I 35 bromine 80 Br 17 chlorine 35.5 Cl 9 86 radon [222] Rn 54 xenon 131 Xe 36 krypton 84 Kr 18 argon 40 Ar 10 neon Elements with atomic numbers 112-116 have been reported but not fully authenticated 80 mercury 201 Hg 48 cadmium 112 Cd 30 70 Ga 13 aluminium 27 Al 5 20 Ne 2 14 N 5 helium 12 C 4 1 11 B 3 hydrogen 1 H * The lanthanoids (atomic numbers 58-71) and the actinoids (atomic numbers 90-103) have been omitted. 88 87 [226] Ra [223] Fr radium 56 francium barium 137 Ba 133 Cs 55 38 caesium strontium 88 Sr 85 Rb 37 20 rubidium calcium 40 Ca 39 K 19 12 potassium magnesium 24 Mg 23 Na 11 4 sodium beryllium 3 9 Be 7 Li lithium 2 1 The Periodic Table of the Elements 20 A216/01 Mark Scheme Answer Question 1 a Pbs PBs PbS Mark 1 Guidance PbSO4 2 b ignore references to the amount of lead, the answer must be in terms of amount of impurities idea of more impurities (in modern ores) ORA ; if refers to modern ores accept have less lead sulfide not have less lead idea of the good / Roman / high grade ores have been used up ORA ; gives a reason for the lack of high grade ore suggests what the other impurities might be 1 c lead oxide + lead sulfide lead + sulfur dioxide d June 2011 description high melting point low melting point silicon dioxide only sulfur dioxide only 4 ionic bonds simple molecular compound weak forces between neither covalent bonds giant structure both reactants in either order products in either order 1 7 ticks correct = 4 6 or 5 ticks correct = 3 4 or 3 ticks correct = 2 2 ticks correct = 1 1 tick = 0 A216/01 Mark Scheme Question e f Answer use property line water troughs lead has a low melting point heavy weights lead is dense filling gaps in stones lead is malleable i Mark all three lines correct = 2 2 2 or 1 lines correct = 1 June 2011 Guidance 1 2.125% 47% 50% 53% 3 ii any three from: bubbles / fizzes / red-brown / smell; ties bromine OR lead formation to electrodes; accept bromine formed at anode / positive electrode = 2 OR accept lead formed at cathode / negative electrode = 2 to the correct electrode; lead collects at the bottom; Total [14] 2 A216/01 Mark Scheme Answer Question 2 a b c Mark 1 2 lamp pushes charge... switch heats up battery changes resistance any two from: (closed switch) allows charge to move AW; this may be implied b c d accept AW for delivering e.g. taking / giving [5] 1 a voltage (1) i 6 (V) (1) ii 18 (W) (1) power (1) Total all three lines correct = 2 2 or 1 lines correct = 1 accept electrons instead of charge not electricity instead of charge delivering energy (from the battery to the lamp); Total All three resistors have the same ... Guidance 2 (the charge moves) around the circuit AW; 3 June 2011 (1) 1 1 1 1 [5] 3 A216/01 Mark Scheme Answer Question 4 a Mark 2 June 2011 Guidance voltage (1) current (1) 2 b Move the magnet more quickly into ... (1) (1) Increase the number of turns ... Total 5 [4] 2 a two (1) four (1) b i 1 nucleus (1) accept mitochondria / chromosomes / genes 1 ii accept ribosome cytoplasm (1) Total [4] 4 A216/01 Mark Scheme Question B (1) 6 a b any three from: Answer June 2011 Mark Guidance if no answer given, check the table 1 NB ‘Gametes fuse’ is in the stem 3 meiosis (1) accept mis-spelling of meiosis [ie but not if a ‘T’ is present!] accept ‘reduction division’ instead of meiosis unless stated otherwise, assume that the candidate is referring to gametes as the product of cell division idea that [gametes have] 39 chromosomes / haploid / half the chromosomes (1) this mark not available if candidate implies chromosomes come from both parents ignore ‘cells / chromosomes split in half’ allow ‘half the genetic information’ links [gamete fusion] to zygote / embryo (1) [gametes fuse] to give full number / diploid / double the number of chromosomes (1) ‘gametes fuse and double the number of chromosomes’ = 1 ignore ‘gametes double the number of chromosomes’ ignore ‘half the chromosomes from each parent’ in the context of this marking point references to fusing and to halving must be in the correct context Total [4] 5 A216/01 Mark Scheme Question Answer (plant) hormone (1) 7 a Mark accept auxins 2 to help roots to form/grow (1) 2 b tissue phloem property can develop into different types of cells meristem cannot develop into different types of cells xylem 1 c … some cells… mitosis (1) 1 d Chromosomes separate (1) Total [6] Paper Total [42] 6 June 2011 Guidance allow ‘rooting powder’ as a 1 mark answer 3 correct lines = 2 marks 1 or 2 correct lines = 1 mark