Gateway Science - Kingsdown School
advertisement
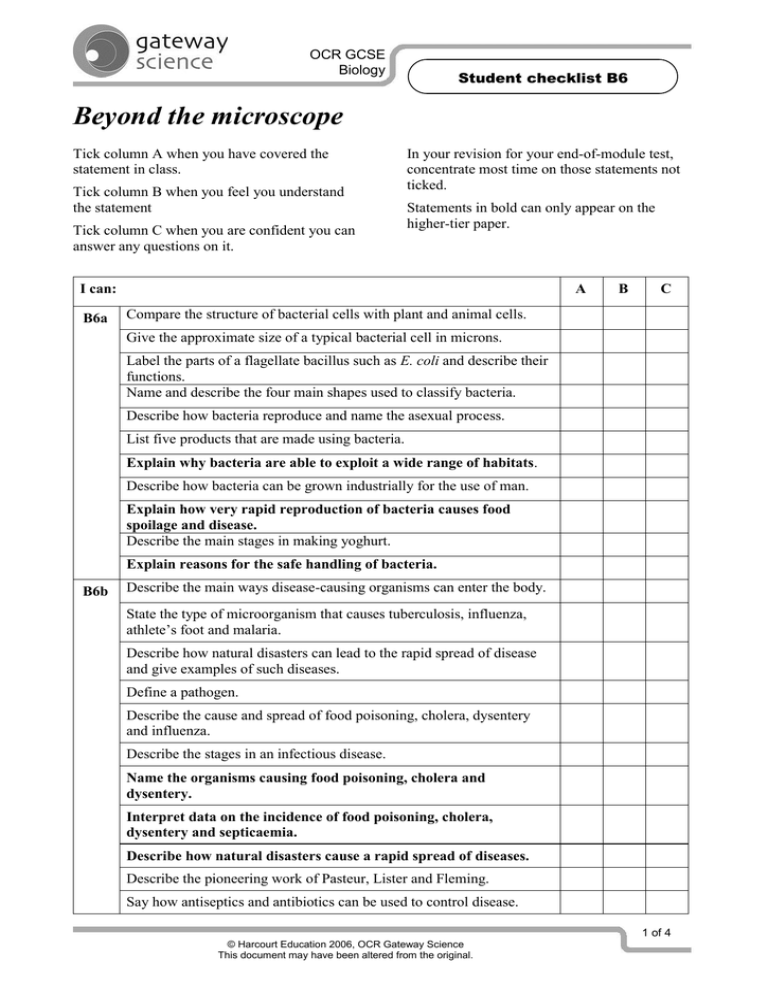
OCR GCSE Biology Student checklist B6 Beyond the microscope Tick column A when you have covered the statement in class. Tick column B when you feel you understand the statement Tick column C when you are confident you can answer any questions on it. In your revision for your end-of-module test, concentrate most time on those statements not ticked. Statements in bold can only appear on the higher-tier paper. I can: B6a A B C Compare the structure of bacterial cells with plant and animal cells. Give the approximate size of a typical bacterial cell in microns. Label the parts of a flagellate bacillus such as E. coli and describe their functions. Name and describe the four main shapes used to classify bacteria. Describe how bacteria reproduce and name the asexual process. List five products that are made using bacteria. Explain why bacteria are able to exploit a wide range of habitats. Describe how bacteria can be grown industrially for the use of man. Explain how very rapid reproduction of bacteria causes food spoilage and disease. Describe the main stages in making yoghurt. Explain reasons for the safe handling of bacteria. B6b Describe the main ways disease-causing organisms can enter the body. State the type of microorganism that causes tuberculosis, influenza, athlete’s foot and malaria. Describe how natural disasters can lead to the rapid spread of disease and give examples of such diseases. Define a pathogen. Describe the cause and spread of food poisoning, cholera, dysentery and influenza. Describe the stages in an infectious disease. Name the organisms causing food poisoning, cholera and dysentery. Interpret data on the incidence of food poisoning, cholera, dysentery and septicaemia. Describe how natural disasters cause a rapid spread of diseases. Describe the pioneering work of Pasteur, Lister and Fleming. Say how antiseptics and antibiotics can be used to control disease. 1 of 4 © Harcourt Education 2006, OCR Gateway Science This document may have been altered from the original. OCR GCSE Biology B6c Student checklist B6 Name the kingdom in which yeast is classified and describe how yeast can be stored. Identify and label parts of a yeast cell (nucleus, cytoplasm, wall, bud). Name the process by which yeast cells reproduce asexually. List three drinks made by fermentation and give the main ingredients. Describe and give the word equation for fermentation. State the balanced chemical equation for fermentation. List factors that can reduce the optimum rate of reproduction in yeast. Explain how yeast can be used to treat water contaminated by sugars. Give the quantitative relationship between yeast growth and temperature. Recognise that yeast can undergo aerobic or anaerobic respiration and the implications of this to the fermentation process. Interpret data on breakdown of sugar by yeast in different conditions such as changing temperature or oxygen availability. Describe the main stages in brewing beer or wine. Describe what is meant by the term pasteurisation and understand why this needs to be done in the case of bottled beers. Name the food used to produce rum, whiskey and vodka. Describe the process of distillation and know this needs a licence. Say what happens to yeast cells as the level of alcohol increases. B6d Explain how different strains of yeast are useful to brewers. Name the waste gas produced by rotting organic material. Name the type of organism that causes rotting. Describe what biogas is and how it can be produced on a large scale. Explain why biogas is used in certain remote parts of the world. Describe the dangers of methane being released from landfill sites. Describe how gasohol is made and used in countries such as Brazil. Give the chemical composition, three sources and three uses of biogas. State the percentage of methane that burns and that which is explosive. Describe how different types of bacteria are needed to break down organic material. Describe how methane can be produced on a large scale. Describe how biogas production is affected by temperature. State advantages and disadvantages of biogas versus diesel and petrol. Explain why biogas production is affected by temperature. 2 of 4 © Harcourt Education 2006, OCR Gateway Science This document may have been altered from the original. OCR GCSE Biology B6e Student checklist B6 Explain the advantages of using biofuels instead of fossil fuels. Describe the main components of soil. State three main reasons why most plants rely on soil. Name the groups of living organisms that soil contains. Name four chemical elements that are recycled in soil and say why this is important. Describe a food web in a soil to include detritivores and carnivores. Give two factors that might limit soil organism populations. Explain why some life in soil depends on oxygen and water. Describe why aerating and draining will improve soils. Say why neutralising acid soils and mixing layers is important. Describe the importance of earthworms to soil structure and fertility. State Darwin’s ideas about earthworms in agriculture. Describe the role of different types of bacteria in nutrient cycles. B6f Explain the part played by named bacteria in the nitrogen cycle. Describe how pollution and acid rain affect aquatic microorganisms. Compare life in water with life on land and give advantages. Explain the difference between phytoplankton and zooplankton. State the main producers in aquatic food chains. Describe the seasonal variations shown in growth of plankton. Analyse data on water pollution to determine pollution source: • sewage, oil, PCBs; • fertilisers, pesticides and detergents. Explain the problems of water balance caused by osmosis. Describe the action of contractile vacuoles in amoeba. Give the problems of salmon of moving from salt to fresh water. Describe how seasonal changes cause algal blooms. Interpret data on marine food webs. Describe how sewage and fertiliser run-off can cause eutrophication. Say how some organisms are used as indicators for pH and oxygen. B6g Explain the effect of PCBs and DDT on whales. Give examples of everyday uses of enzymes. State the pH and temperature at which biological washing powders work best. Say how and why diabetics can test their urine for glucose. Explain what is meant by an immobilised enzyme. 3 of 4 © Harcourt Education 2006, OCR Gateway Science This document may have been altered from the original. OCR GCSE Biology Student checklist B6 Give an example of an immobilised enzyme in reagent sticks. Name three types of enzymes used in biological washing powders. Explain why biological washing powders may not work in acidic or alkaline tap water. Explain what the soluble products of amylase, lipase and protease activity are, and that these products will then wash out easily. Describe how sucrose can be broken down and compare the sweetness of the products with sucrose. Explain how foods can be sweetened to make low calorie foods. Describe advantages of immobilising enzymes. B6h Say how lactose-free milk is made and why such milk is useful. State where DNA is found and what is meant by the genetic code. Explain what is meant by genetic engineering and give some uses. Describe the main stages in genetic engineering. Give examples of genetically engineered crops and how they are better. Explain what a ‘transgenic organism’ is. Describe how bacteria can be used to produce human insulin. Describe how restriction enzymes cut open DNA and ligase enzymes rejoin DNA strands. Name methods used to check that a new gene has been transferred. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of genetic engineering. 4 of 4 © Harcourt Education 2006, OCR Gateway Science This document may have been altered from the original.