CHAPTER 23 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL

CHAPTER 23
ELECTRIC POTENTIAL
BASIC CONCEPTS:
ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY
ELECTRIC POTENTIAL
ELECTRIC POTENTIAL GRADIENT –
POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE
1
POTENTIAL ENERGY
h
PE = U = mgh
PE KE
Or
U K
And U + K = total energy = constant
2
BOOK EXAMPLE
3
Charged Particle in Electric Field is similar
4
Consider a point charge q that sets up an electric field in space
5
Now a test charge q
0
is placed at position a a distance r a
from q
0 .
Then q
0
moves to position b a distance r b
from q
0
.
What is the change in potential energy?
The change in potential energy is the negative of the work done to move the test charge from a to b .
The force on the test charge is
6
The work done is force times distance.
But the force changes as q
0
moves away from q
Must integrate
Use
Then
7
The change in potential energy, is the negative of this work.
DEFINITION:
ELECTRICAL POTENTIAL IS POTENTIAL
ENERGY PER UNIT CHARGE
8
Therefore divide all terms by
Thus
9
Now consider the same situation
10
We have as we did at the beginning
The change in potential energy, is the negative of this work.
Therefore
In Chapter 21 we defined the Electric Field as the force per unit charge
11
And we have
Divide all terms by q
0
12
POTENTIAL AT A POINT
Once again look at this situation
We have
13
Just like in potential energy of the particle on a hill we can choose the potential energy and therefore the potential to be zero at any arbitrary point.
Choose infinity
In the figure
When
14
Then
From Chapter 21
Therefore
15
Choose where
16
The potential at any point in space a distance from a charge will be
POTENTIALS ADD (SCALERS)
Just as we did with the electric field we can add the potentials for many charges in an area.
17
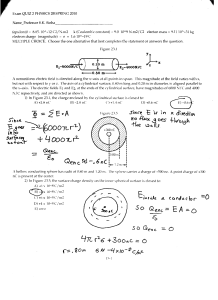
EXAMPLE
A
60cm
30cm
50µC ‐ 50 µC
What is the potential at A?
18
Example 23.11
Potential on axis of ring of charge.
Choose small segment of ring that has charge .
The segment is a distance form point P.
Then
19
Integrate to get V
Everything is constant except
20
Use the result to find potential on axis of disk of charge.
This is diagram for E but use it for finding potential at P
For ring of radius contribution to V is
21
Disk is made up of rings each with area
Charge density of disk is total charge divided by total area
Therefore
22
Integrate
23
For the disk
24
TWO MORE BASIC PIECES OF INFORMATION
If we know V we can find E
25
Example
In this chapter we found for ring of charge
In chapter 21 we found for ring of charge
Use equation above for V to find
26
27
ELECTRON VOLT
An electron volt is a unit for energy.
It is the work necessary to move an electron
(charge difference of 1 volt.
) a potential
1 Volt Batt
The work to move a charge across a potential difference is
28
Therefore
29