Current Electricity Lab –Series/Parallel Circuits Name ______
advertisement

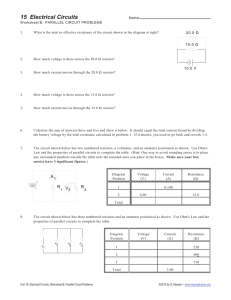
Current Electricity Lab –Series/Parallel Circuits Name ____________ Safety and Equipment Precautions! • • • • Plug in your power supply and use ONLY the D.C. terminals of the power source, NOT the A. C. terminals. DO NOT touch wires together when the power supply is on. DO NOT leave the circuit with the power supply on for long periods of time! The resistors get VERY hot and may fry! You must disconnect ALL wires from the resistor BEFORE you measure the Resistances of the resistors! R=V/I or Procedure Part 1 – “Creating Circuits” 1A. Using the SMALL wires, BULBS, and BATTERY, you and your electrician partner will build the following... 1. A circuit with two bulbs wired in Series. 2. A circuit with two bulbs wired in Parallel. * HAVE YOUR CIRCUIT CHECKED BY Mr. Putnam FOR REGENTS CREDIT! * Draw the circuits below that you have built making certain to use proper circuit symbols and labels! (Use your Reference Table for assistance with the symbols.) Series with 2 bulbs Parallel with 2 bulbs Part 2 – “Using Ohm’s Law in Series and Parallel Circuits” IMPORTANT! • • • • • • • Plug in your power supply and use ONLY the D.C. terminals of the power source, NOT the A. C. terminals. DO NOT touch wires together when the power supply is on. DO NOT leave the circuit with the power supply on for long periods of time! The resistors get VERY hot and may fry! You must disconnect ALL wires from the resistor BEFORE you measure the Resistances of the resistors! The Total Voltage ["Power Supply"] for both circuits must be set between 3 & 5 Volts. [Be certain to enter the ACTUAL voltage in the table.] You must disconnect the circuit BEFORE you measure the Resistances of the resistors! Have your Physics teacher check your circuit before you measure your values. SERIES CIRCUIT Create a SERIES circuit using Resistor #1 & Resistor #3. Check the power supply FIRST with your multimeter to be certain it is set between 3 & 5 Volts. Fill out the table below. Voltage Table-Series Circuit Measure the Voltage across… Resistor #1 Resistor #3 Total Voltage (R1 + R3) Voltage [V] TO TEST VOLTAGE… Measure ACROSS THE RESISTOR & set the Multi-meter to the 20V DC setting. Current Table-Series Circuit Measure the Current… BEFORE Resistor #1 AFTER Resistor #3 Total Current in circuit Current [I] TO TEST CURRENT… Set Multi-meter to the 10A setting with probe wires plugged in as in the above diagram. Using YOUR values for Total Voltage & Total Current in the above tables, CALCULATE the TOTAL RESISTANCE of the circuit using Ohm's Law. Calculated Total Resistance of your Series Circuit à __________________ WITH THE WIRES REMOVED FROM THE RESISTOR(S)… MEASURE RESISTANCE Measure with the Digital Multimeter... The Resistance of… Resistor #1 Resistor #3 CALCULATED Total Resistance of Circuit [Using Ohm’s Law] MEASURED Total Resistance of Circuit [Using the Multi-meter] PERCENT ERROR between the two Total Resistance values. Resistance [Ohms] TO TEST RESISTANCE… Set Multi-meter to the 200 Ω setting,. WITH THE WIRES REMOVED FROM THE RESISTORS BEFORE TESTING! PARALLEL CIRCUIT Create a PARALLEL circuit using Resistor #1 & Resistor #3. . Check the power supply to be certain it is set between 3 & 5 Volts. Fill out the table below. Voltage Table-Parallel Circuit Measure the Voltage across… Resistor #1 Resistor #3 Total Voltage [Power supply] Voltage [V] Current Table-Parallel Circuit Measure the Current… BEFORE Resistor #1 AFTER Resistor #3 Total Current TO TEST VOLTAGE… Measure ACROSS THE RESISTOR & set the Multi-meter to the 20V DC setting. Current [I] TO TEST CURRENT… Set Multi-meter to the 10A setting with probe wires plugged in as in the above diagram. Using YOUR values for Total Voltage & Total Current in the above tables, CALCULATE the TOTAL RESISTANCE of the circuit using Ohm's Law. Calculated Total Resistance of your Parallel Circuit à __________________ WITH THE WIRES REMOVED FROM THE RESISTOR(S)… MEASURE RESISTANCE Measure with the Digital Multimeter... The Resistance of… Resistor #1 Resistor #3 CALCULATED Total Resistance of Circuit [Using Ohm’s Law] MEASURED Total Resistance of Circuit [Using the Multi-meter] PERCENT ERROR between the two CALCULATED Total Resistance values. Resistance [Ohms] TO TEST RESISTANCE… Set Multi-meter to the 200 Ω setting WITH THE WIRES REMOVED FROM THE RESISTORS BEFORE TESTING! Conclusions Using your knowledge of electric circuits, answer the following… #1-3à For SERIES circuits… 1. A. What would happen to the Total Current of your circuit if you were to change from a two-bulb series circuit to a three-bulb series circuit? B. How could you tell from JUST LOOKING at the bulbs? 2. What would happen to the bulbs if one bulb blows out while doing the experiment? 3. What happens to the Total Resistance of your circuit if you added a bulb to the series circuit? #4-6à For PARALLEL circuits… 4. A. What would happen to the Total Current of your circuit if you change from a two-bulb parallel circuit to a three-bulb parallel circuit? B. How could you tell from JUST LOOKING at the bulbs? 5. What would happen to the bulbs if one bulb blows out while doing the experiment? 6. What happens to the Total Resistance of your circuit when you change from a two-bulb parallel circuit to a three-bulb parallel circuit? 7A. Why shouldn’t you wire your entire home ONLY in parallel? 7B. What would happen to the Total Current throughout the home? 7C. What would happen to the fuses or circuit breakers in your home? 8. For the Series Circuit, if R1 = 10Ω, R2 = 15Ω, Ammeter A = 2A & the Total Voltage is 60V, find… _______ = R3 _______ = Total Current _______ = Total Resistance _______ = Total Power A 9. For the Parallel Circuit, if R1 = 10Ω, R2 = 25Ω, the Voltage drop across R1 = 50V & the Ammeter A = 8A, find… _______ = R3 _______ = Total Potential Difference _______ = Total Resistance _______ = Total Power A