electromag review
advertisement

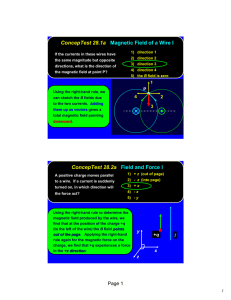
Test Review - Electromagnetism Magnetism A magnetic field is created by the movement of charged particles. permanent magnet - field created by spin of electrons. electromagnet - field created by current (flow of electrons) through a wire. Magnetic field lines travel N to S outside magnet, and S to N inside magnet. compass needle aligns with its N pole in direction of field lines. magnetic field = B (unit is the Tesla. 1 T = 1 N/Am) Current bearing wire produces a magnetic field tangent galvanometer electromagnet strength increases with current, # of coils, and an iron core. conventional current flows opposite direction as electron flow does. Right hand rule #1 “magnetic field around a current bearing wire” thumb = direction of conventional current fingers wrap around wire in direction of magnetic field. Right hand rule #2 “polarity of an electromagnetic coil” thumb = direction of conventional current fingers wrap around coil and point towards the N pole. Force on a current bearing wire in a magnetic field. F = BIlsinø Fmax = BIl electric motor - armature spins in magnetic field. Right hand rule #3 “direction of force acting on a current bearing wire” thumb = direction of conventional current fingers = direction of magnetic field palm points in direction that wire is forced. Force on an electric charge traveling in a magnetic field. Fmax = Bqv Bqv = mv2/r (when charge is traveling perpendicular to the field.) Right hand rule #4 “direction of force acting on a moving positive charge” thumb = direction of motion fingers = direction of magnetic field palm points in direction that charge is forced (reverse direction if the charge is negative). Electromagnetic Induction An induced emf is produced by a changing magnetic field (flux). emf = induced voltage or electromotive force. emf = Blv Generator Induces a current in a wire that is moving through a magnetic field. alternating current (sine wave) Right hand rule #5 “direction of induced current in a generator” thumb = direction wire is moved fingers = direction of magnetic field palm points in direction that current is induced Lenz’s Law back emf counter torque Transformers Used to change voltages through electromagnetic induction. Require alternating current. ratio of primary and secondary coils (step-up and step-down transformers) Vs/Vp = Ns/Np Is/Ip = Np/Ns power into a transformer equals power out of transformer (if 100% efficient) power transmission systems 1. Explain how power is transmitted to prevent excessive heat loss. 2. How can you differentiate between an electron and a proton traveling perpendicular to a magnetic field? 3. What is the force on an 18 cm length of wire that is perpendicular to a magnetic field of 0.005 T if the current in the wire is 0.025 A? What is the force if the wire makes a 45 degree angle with the field? 4. A magnetic field runs right to left. A current bearing wire runs into the page. What direction is the wire forced? 5. Why will a magnetic field acting perpendicular to the motion of a charged particle change the direction but not velocity of the particle? What are the Northern/Southern Lights and how are they related to this phenomenon? 6. A transformer is used to step 120 volts up to 60 Kv. What is the ratio of secondary to primary coils? What happens to the current in the secondary coil? The power? 7. Use Lenz’s law to explain how magnetic dampening works on a triple beam balance (a piece of metal at the end of the beam passes through a magnetic field).