Guidance sheet 2: Dangerous Goods Classification System
advertisement

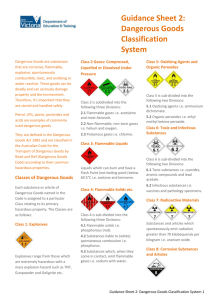
Guidance sheet 2: Dangerous Goods Classification System Dangerous Goods are substances that are corrosive, flammable, explosive, spontaneously combustible, toxic, oxidising or water reactive. Petrol, LPG, paints, pesticides and acids are examples of commonly used dangerous goods. They are defined in the Dangerous Goods Act 1985 and are classified in the Australian Code for the Transport of Dangerous Goods by Road and Rail (Dangerous Goods Code) according to their common hazardous properties. Classes of Dangerous Goods Each substance or article of Dangerous Goods named in the Code is assigned to a particular Class relating to its primary hazardous property. The Classes are as follows: Class 1 Explosives Class 3 Flammable Liquids Class 7 Radioactive Materials Liquids which can burn and have a Flash Point (not boiling point) below 60.5°C e.g. acetone and kerosene. Substances and articles which spontaneously emit radiation greater than 70 kilobequerals per kilogram e.g. uranium oxide. Class 4 Flammable Solids etc. Class 8 Corrosive Substances and Articles Class 4 is sub-divided into the following three Divisions: 4.1 Flammable solids e.g. phosphorous (red). 4.2 Substances liable to (white) spontaneous combustion e.g. phosphorus. 4.3 Substances which, when they come in contact, emit flammable gases e.g. sodium with water. This class is not further sub-divided but it includes both acids and bases/alkalis which can react dangerously. e.g. hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide and batteries containing acid. Class 9 Miscellaneous Dangerous Goods Class 5 Oxidising Agents and Organic Peroxides Explosives range from those which are extremely hazardous with a mass explosion hazard such as TNT, Gunpowder and Gelignite etc. Class 2 Gases: Compressed, Liquefied or Dissolved Under Pressure Dangerous substances and articles that do not fit into the above categories. e.g. dry ice, asbestos and environmentally hazardous substances. Class 5 is sub-divided into the following two Divisions: 5.1 Oxidizing agents e.g. ammonium dichromate. 5.2 Organic peroxides e.g. ethyl methyl ketone peroxide. Class 2 is subdivided into the following three Divisions: Class 6 Toxic and Infectious Substances 2.1 Flammable gases e.g. acetylene and most Aerosols. 2.2 Non-flammable, non-toxic gases e.g. helium and oxygen. 2.3 Poisonous gases e.g. chlorine. Class 6 is sub-divided into the following two Divisions: 6.1 Toxic substances e.g. cyanides, arsenic compounds and lead acetate. 6.2 Infectious substances e.g. vaccines and pathology specimens. Guidance sheet 2: Dangerous Goods Classification System 1 Subsidiary Risk United Nations (UN) Number Packing Group Many Dangerous Goods present the hazards of more than one Class or Division. Such goods are assigned to a Class according to their primary hazard. The other hazard or hazards are referred to as Subsidiary Risks. Each Dangerous Goods item listed in the Australian Dangerous Goods Code is assigned a unique number, known as the UN Number (United Nations Number or UN No.). Dangerous Goods of some Classes are further divided into Packing Groups according to the degree of danger they present, as follows: Examples: Methanol is a highly flammable liquid that is also toxic. It meets the classification criteria for both Class 3 and Division 6.1. As its flammability is its primary hazard, Methanol is assigned to Class 3. It is also shown in the Australian Dangerous Goods Code as having a Subsidiary Risk of 6.1 to cover its toxicity hazard. Packing Group I Great Danger e.g. UN No. 1090 Acetone UN No. 1789 Hydrochloric Acid Some UN numbers apply to groups of substances having similar hazardous properties that are not covered by specific chemical entity entries. e.g. UN No. 1263 Paint UN No. 1993 Flammable Liquid N.O.S. (Not Otherwise Specified) Nitric Acid, Red, Fuming is corrosive, a strong oxidising agent and toxic. It meets the classification criteria for Classes 8, 5.1 and 6.1. As its corrosivity is its primary hazard, Nitric Acid, Red, Fuming is assigned to Class 8. However, it is also allocated Subsidiary Risks of 5.1 and 6.1 to cover the other hazards. Packing Group II Medium Danger Packing Group III Minor Danger ‘Packing Group’ (referred to as ‘Packaging Group’ in earlier versions of the Regulations and Code) does not apply to those Classes/Divisions of Dangerous Good against which ‘Not applicable’ appears in the table below. The following Class/Packing Groups may be encountered: Class/Division Packing Group/s 1 Not applicable 2 Not applicable 3 I, II or III 4 I, II or III 5.1 I, II or III 5.2 II only 6.1 I, II or III 6.2 Not applicable 7 Not applicable 8 I, II or III 9 II or III Further information and advice can be obtained by contacting DEECD’s OHS Advisory Service on 1300 074 715 or your Regional OHS/WorkSafe Advisor. 2 Guidance sheet 2: Dangerous Goods Classification System