Introduction to Environmental Ratings
Anderson Peeples
Associate Design Engineer, CCS-Inc.
CCS-Inc.
www.ccs-inc.com
December 13, 2012
Introduction to Environmental Ratings
In the world of industrial electronics, there are phrases that simply don’t hold much weight
when describing a system. The problem with such phrases (e.g. “waterproof” and “airtight”) is that these descriptions alone do not provide a quantitative measure of their
meaning. To address this issue, many organizing bodies have developed design standards
for engineers. Serving as a reference to customers, these standards provide specific criteria
for the intended protection rating of a system. The National Electrical Manufacturers
Association (NEMA) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) supply two of
the most predominant standards, NEMA Ratings and Ingress Protection (IP) Ratings
respectively.
---
NEMA Ratings
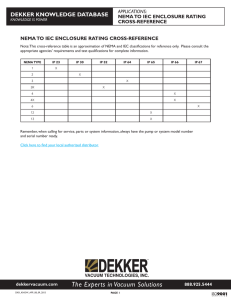
To help define the protective qualities of electronic system enclosures, NEMA has developed
a rating system for enclosures containing components less than 1000 volts. These ratings
are defined in the NEMA 250 standard and are separated into two categories: enclosures
used in Non-Hazardous Locations1, and enclosures used in Hazardous Locations2. Each set
of ratings is further divided into indoor and outdoor use, detailing features such as corrosion
resistance, fabrication requirements, material selection, and gasket aging.
Within the NEMA rating system, various industry standards have been adopted. For
example, in many non-hazardous industrial applications, such as industrial automation and
food packaging facilities, NEMA 4 and NEMA 4X have become the de facto standards. This is
due to the fact that NEMA 4 is the minimum enclosure rating that provides protection
against ingress of water. 3 This is important for applications where equipment may
frequently need to be hosed down for cleaning purposes. The addition of the “X” suffix
indicates that the system has further properties that limit its susceptibility to corrosion.
In addition to NEMA ratings, UL 50/508 and CSA C22.2 No. 94 are also used to define
protection ratings for enclosures in North America. These ratings utilize a similar numbering
method for specifying the protection level of a system. Unlike NEMA ratings, which can be
certified by the manufacturer, UL and CSA require testing by a certified lab to qualify an
enclosure’s environmental rating.
1
Appendix A - Table 1
Appendix A - Table 2
3
Appendix A - Tables 3 and 4
2
CCS-Inc.
www.ccs-inc.com
December 13, 2012
IP Ratings
Rather than, or often in conjunction with, specifying a NEMA rating for an electronic
enclosure or system, manufacturers may specify an Ingress Protection, or IP, Code. IP
codes are classified in the IEC International Standard 60529. These codes aim to provide a
concise, but comprehensive, explanation of the protection provided and testing required for
an enclosure or system.
General IP codes utilize the prefix “IP” followed by two numerals4; for example, IP65. The
first numeral in the code designates the degree to which the system is protected against
solid foreign objects. The second numeral indicates the degree to which the system is
protected against liquid ingress. As the numerical value increases, the system protection
increases. In the event that either test parameter (solid or liquid protection) is not specified,
the numeral for that portion is replaced with an X. For example, when testing a system only
for liquid ingress per classification #6, the code would be IPX6.
In addition to particulate and liquid protection ratings, IP codes may also include letters to
signify further aspects of the system. A letter may be appended to the code to specify the
degree of protection against hazardous parts.5 Additionally, a supplemental letter may be
appended to the code to signify safety information about the system.6 With these options, a
full IP code may take the form as shown in Figure A.7
Figure A. IP Code Format
As with NEMA ratings, IEC’s IP ratings are “self-certifying,” meaning that they do not
require third party test labs to certify enclosure designs. This leaves testing up to the
manufacturer of the equipment.
4
Appendix A - Tables 5 and 6
Appendix A - Table 7
6
Appendix A - Table 8
7
An additional number may be added to indicate the impact resistance of the enclosure, though this is not
included in the IEC 60529 standard.
5
CCS-Inc.
www.ccs-inc.com
December 13, 2012
Though NEMA ratings and IP codes both aim to clarify and quantify environmental
protection for electronic systems, there are key differences between the two standards.
Unlike NEMA ratings, IEC IP ratings do not specify fabrication practices, corrosion
protection, or risk of explosion. For this reason, it is possible to have a NEMA rated
enclosure that may satisfy all requirements for IP certification; however, a less stringent IP
rating may not meet NEMA requirements.8
Determining the Appropriate Rating for Your Project’s Needs
Due to the wide variety of ratings and enclosure protections available, choosing which rating
is most appropriate for your application can be a daunting task. CCS Engineers are happy to
help you analyze your system’s environment to determine what solution would best fit your
project’s needs. To discuss your situation in detail with one of our engineers, contact us
today.
8
Appendix A - Table 9
CCS-Inc.
www.ccs-inc.com
December 13, 2012
Appendix A – Rating Criteria
Table 1. NEMA Enclosure Types for Non-Hazardous Locations
Type Standard
1
Enclosures constructed for indoor use to provide a degree of protection to personnel
against access to hazardous parts and to provide a degree of protection of the
equipment inside the enclosure against ingress of solid foreign objects (falling dirt).
2
Enclosures constructed for indoor use to provide a degree of protection to personnel
against access to hazardous parts; to provide a degree of protection of the equipment
inside the enclosure against ingress of solid foreign objects (falling dirt); and to provide
a degree of protection with respect to harmful effects on the equipment due to the
ingress of water (dripping and light splashing).
3
Enclosures constructed for either indoor or outdoor use to provide a degree of
protection to personnel against access to hazardous parts; to provide a degree of
protection of the equipment inside the enclosure against ingress of solid foreign objects
(falling dirt and windblown dust); to provide a degree of protection with respect to
harmful effects on the equipment due to the ingress of water (rain, sleet, snow); and
that will be undamaged by the external formation of ice on the enclosure.
3R
Enclosures constructed for either indoor or outdoor use to provide a degree of
protection to personnel against access to hazardous parts; to provide a degree of
protection of the equipment inside the enclosure against ingress of solid foreign objects
(falling dirt); to provide a degree of protection with respect to harmful effects on the
equipment due to the ingress of water (rain, sleet, snow); and that will be undamaged
by the external formation of ice on the enclosure.
3S
Enclosures constructed for either indoor or outdoor use to provide a degree of
protection to personnel against access to hazardous parts; to provide a degree of
protection of the equipment inside the enclosure against ingress of solid foreign objects
(falling dirt and windblown dust); to provide a degree of protection with respect to
harmful effects on the equipment due to the ingress of water (rain, sleet, snow); and
for which the external mechanism(s) remain operable when ice laden.
3X
Enclosures constructed for either indoor or outdoor use to provide a degree of
protection to personnel against access to hazardous parts; to provide a degree of
protection of the equipment inside the enclosure against ingress of solid foreign objects
(falling dirt and windblown dust); to provide a degree of protection with respect to
harmful effects on the equipment due to the ingress of water (rain, sleet, snow); that
provides an additional level of protection against corrosion and that will be undamaged
by the external formation of ice on the enclosure.
4
Enclosures constructed for either indoor or outdoor use to provide a degree of
protection to personnel against access to hazardous parts; to provide a degree of
protection of the equipment inside the enclosure against ingress of solid foreign objects
(falling dirt and windblown dust); to provide a degree of protection with respect to
harmful effects on the equipment due to the ingress of water (rain, sleet, snow,
splashing water, and hose directed water); and that will be undamaged by the external
formation of ice on the enclosure.
4X
Enclosures constructed for either indoor or outdoor use to provide a degree of
protection to personnel against access to hazardous parts; to provide a degree of
protection of the equipment inside the enclosure against ingress of solid foreign objects
(windblown dust); to provide a degree of protection with respect to harmful effects on
the equipment due to the ingress of water (rain, sleet, snow, splashing water, and
hose directed water); that provides an additional level of protection against corrosion;
and that will be undamaged by the external formation of ice on the enclosure.
5
Enclosures constructed for indoor use to provide a degree of protection to personnel
CCS-Inc.
www.ccs-inc.com
December 13, 2012
6
6P
12
13
against access to hazardous parts; to provide a degree of protection of the equipment
inside the enclosure against ingress of solid foreign objects (falling dirt and settling
airborne dust, lint, fibers, and flyings); and to provide a degree of protection with
respect to harmful effects on the equipment due to the ingress of water (dripping and
light splashing).
Enclosures constructed for either indoor or outdoor use to provide a degree of
protection to personnel against access to hazardous parts; to provide a degree of
protection of the equipment inside the enclosure against ingress of solid foreign objects
(falling dirt); to provide a degree of protection with respect to harmful effects on the
equipment due to the ingress of water (hose directed water and the entry of water
during occasional temporary submersion at a limited depth); and that will be
undamaged by the external formation of ice on the enclosure.
Enclosures constructed for either indoor or outdoor use to provide a degree of
protection to personnel against access to hazardous parts; to provide a degree of
protection of the equipment inside the enclosure against ingress of solid foreign objects
(falling dirt); to provide a degree of protection with respect to harmful effects on the
equipment due to the ingress of water (hose directed water and the entry of water
during prolonged submersion at a limited depth); that provides an additional level of
protection against corrosion and that will be undamaged by the external formation of
ice on the enclosure.
Enclosures constructed (without knockouts) for indoor use to provide a degree of
protection to personnel against access to hazardous parts; to provide a degree of
protection of the equipment inside the enclosure against ingress of solid foreign objects
(falling dirt and circulating dust, lint, fibers, and flyings); and to provide a degree of
protection with respect to harmful effects on the equipment due to the ingress of water
(dripping and light splashing).
Enclosures constructed for indoor use to provide a degree of protection to personnel
against access to hazardous parts; to provide a degree of protection of the equipment
inside the enclosure against ingress of solid foreign objects (falling dirt and circulating
dust, lint, fibers, and flyings); to provide a degree of protection with respect to harmful
effects on the equipment due to the ingress of water (dripping and light splashing);
and to provide a degree of protection against the spraying, splashing, and seepage of
oil and non-corrosive coolants.
CCS-Inc.
www.ccs-inc.com
December 13, 2012
Table 2. NEMA Enclosure Types for Hazardous Locations
Type Standard
7
Enclosures constructed for indoor use in hazardous (classified) locations classified as
Class I, Division 1, Groups A, B, C, or D as defined in NFPA 70.
8
Enclosures constructed for either indoor or outdoor use in hazardous (classified)
locations classified as Class I, Division 1, Groups A, B, C, and D as defined in NFPA 70.
9
Enclosures constructed for indoor use in hazardous (classified) locations classified as
Class II, Division 1, Groups E, F, or G as defined in NFPA 70.
10
Enclosures constructed to meet the requirements of the Mine Safety and Health
Administration, 30 CFR, Part 18.
Table 3. Comparison of Specific Applications of Enclosures for Indoor Non-hazardous
Locations
Provides a Degree of Protection Against
1* 2* 4 4X 5 6 6P 12 12K 13
the Following Conditions
Access to hazardous parts
X
X X
X
X X X
X
X
X
Ingress of solid foreign objects (falling dirt)
X
X X
X
X X X
X
X
X
Ingress of water (Dripping and light slapping)
X X
X
X X X
X
X
X
Ingress of solid foreign objects (Circulating
X
X
X X
X
X
X
dust, lint, fibers, and flyings**)
Ingress of solid foreign objects (Settling
X
X
X X X
X
X
X
airborne dust, lint, fibers, and flyings**)
Ingress of water (Hosedown and splashing
X
X
X X
water)
Oil and coolant seepage
X
X
X
Oil or coolant spraying and splashing
X
Corrosive Agents
X
X
Ingress of water (Occasional temporary
X X
submersion)
Ingress of water (Occasional prolonged
X
submersion)
*These enclosures may be ventilated.
**These fibers and flyings are nonhazardous materials and are not considered Class III type
ignitable fibers or combustible flyings.
CCS-Inc.
www.ccs-inc.com
December 13, 2012
Table 4. Comparison of Specific Applications of Enclosures for Outdoor Non-hazardous
Locations
Provides a Degree of Protection Against 3 3X 3R* 3RX 3S 3SX 4 4X
the Following Conditions
Access to hazardous parts
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Ingress of water (Rain, snow, and sleet**)
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Sleet***
X
X
Ingress of solid foreign objects (Windblown
X
X
X
X
X
X
dust, lint, fibers, and flyings)
Ingress of water (Hosedown)
X
X
Corrosive agents
X
X
X
X
Ingress of water (Occasional temporary
submersion)
Ingress of water (Occasional prolonged
submersion)
*These enclosures may be ventilated.
** External operating mechanisms are not required to be operate when the enclosure is
covered.
***External operating mechanisms are operable when the enclosure is ice covered.
Table 5. IP Characteristics – Protection against Solid Foreign Objects
First
Test Means
Numeral
0
No test required
1
Rigid sphere without handle or guard - 50mm Diameter
2
Rigid sphere without handle or guard - 12.5mm Diameter
3
Rigid steel rod with edges free from burrs - 2.5mm Diameter
4
Rigid Sphere without handle or guard - 50mm Diameter
5
Dust chamber with or without underpressure
6
Dust chamber with underpressure
CCS-Inc.
www.ccs-inc.com
6
6P
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
ice
Test Force
50N ± 10%
30N ± 10%
3N ± 10%
1N ± 10%
December 13, 2012
Table 6. IP Characteristics – Protection against Water Ingress
Second
Test Means
Numeral
0
No test required
1
Drip box
2
Drip box with 15° tilt
Flow
Rate
Duration of
Test
1mm/min
3mm/min
Water spray at ±60° from vertical, no more than
200mm from EUT
Water spray at ±180° from vertical, no more than
200mm from EUT
Water jet from 6.3 mm diameter nozzle at a distance of
2.5-3 m
0.7l/min
10 min
2.5 min for
each
position
10 min
0.07l/min
10 min
12.5l/min
6
Water jet from 12.5 mm diameter nozzle at a distance
of 2.5-3 m
12.5l/min
7
Immersion tank
Water Depth: 0.15m above enclosure top, 1m above
bottom
Immersion tank
Water Depth: Specified by manufacturer
1 min/m2
At least 3
min
1 min/m2
At least 3
min
30 min
3
4
5
8
By
agreement
Table 7. IP Characteristics – Additional Letter for Hazardous Parts
Additional
Level of Protection
Letter
A
Protected against access with the back of the hand
B
Protected against access with a finger
C
Protected against access with a tool
D
Protected against access with a wire
CCS-Inc.
www.ccs-inc.com
December 13, 2012
Table 8. IP Characteristics – Additional Safety Information
Supplementary Significance
Letter
H
High-voltage apparatus
M
Tested for harmful effects due to the ingress of water when the movable
parts of the equipment are in motion
S
Tested for harmful effects due to the ingress of water when the movable
parts of the equipment are stationary
W
Suitable for use under specified weather conditions and provided with
additional protective features or processes
Table 9. NEMA – IP Comparison
IP Rating Needed
IP20
IP22
IP24
IP53
IP54
IP55
IP66
IP67
IP68
Minimum NEMA Rating Required
1
2
3R, 3RX
5
12, 12k, 13
3, 3X, 3S, 3SX
4, 4X
6
6P
NEMA 250-2003. Copyright National Electrical Manufacturers Association. Reprinted by
permission.
The author thanks the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) for permission to
reproduce Information from its International Publication IEC 60529 ed.2.1 (2001). All such
extracts are copyright of IEC, Geneva, Switzerland. All rights reserved. Further information
on the IEC is available from www.iec.ch. IEC has no responsibility for the placement and
context in which the extracts and contents are reproduced by the author, nor is IEC in any
way responsible for the other content or accuracy therein.
IEC 60529 ed.2.1 Copyright © 2001 IEC Geneva, Switzerland.www.iec.ch
CCS-Inc.
www.ccs-inc.com
December 13, 2012
Appendix B – Organizing and Standards Bodies
National Electrical Manufacturers Association
1300 North 17th Street
Suite 1752
Rosslyn, Virginia 22209
Phone: 703-841-3200
Fax: 703-841-5900
International Electrotechnical Commission
3, rue de Varembé
P.O. Box 131
CH - 1211 Geneva 20, Switzerland
Phone : +41 22 919 02 11
Fax : +41 22 919 03 00
Canadian Standards Association
178 Rexdale Blvd.
Toronto, Ontario
Canada M9W 1R3
Phone: 800-463-6727
Underwriters Laboratories
2600 N.W. Lake Rd.
Camas, WA 98607-8542
Phone: 1-877-854-3577
Fax: 1-360-817-6278
CCS-Inc.
www.ccs-inc.com
December 13, 2012