Section 1 Electric Charge: Review Chapter Assessment Section 1
advertisement

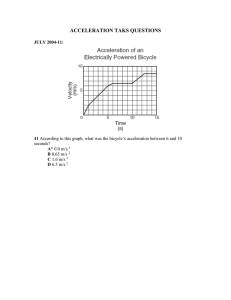
Chapter 3 Practice Problems, Review, and Assessment Chapter Assessment Section 1 Acceleration: Mastering Concepts 54. Give an example of each of the following: a. an object that is slowing down, but has a positive acceleration b. an object that is speeding up but has a negative acceleration c. an object that is moving at a constant speed but has an acceleration SOLUTION: a. if forward is the positive direction, a car moving backward at decreasing speed b. in the same coordinate system, a car moving backward at increasing speed c. a car that is moving on a circular track at a constant speed ANSWER: a. if forward is the positive direction, a car moving backward at decreasing speed b. in the same coordinate system, a car moving backward at increasing speed c. a car that is moving on a circular track at a constant speed 56. If the velocity-time graph of an object moving on a straight path is a line parallel to the horizontal axis, what can you conclude about the object’s acceleration? SOLUTION: When the velocity-time graph is a line parallel to the horizontal axis, the acceleration is zero. ANSWER: When the velocity-time graph is a line parallel to the horizontal axis, the acceleration is zero. Chapter Assessment Section 1 Acceleration: Mastering Problems 57. Ranking Task Rank the following objects according to the magnitude of the acceleration, from least to greatest. Specifically indicate any ties. (Level 1) A. A falling acorn accelerates from 0.50 m/s to 10.3 m/s in 1.0 s. B. A car accelerates from 20 m/s to rest in 1.0 s. C. A centipede accelerates from 0.40 cm/s to 2.0 cm/s in 0.50 s. D. While being hit, a golf ball accelerates from rest to 4.3 m/s in 0.40 s. E. A jogger accelerates from 2.0 m/s to 1.0 m/s in 8.3 s. SOLUTION: From least to greatest magnitude of acceleration: C < E < A < D < B. A. B. C. eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 1 ANSWER: When the velocity-time graph is a line parallel to the horizontal axis, the acceleration is zero. Chapter 3 Practice Problems, Review, and Assessment Chapter Assessment Section 1 Acceleration: Mastering Problems 57. Ranking Task Rank the following objects according to the magnitude of the acceleration, from least to greatest. Specifically indicate any ties. (Level 1) A. A falling acorn accelerates from 0.50 m/s to 10.3 m/s in 1.0 s. B. A car accelerates from 20 m/s to rest in 1.0 s. C. A centipede accelerates from 0.40 cm/s to 2.0 cm/s in 0.50 s. D. While being hit, a golf ball accelerates from rest to 4.3 m/s in 0.40 s. E. A jogger accelerates from 2.0 m/s to 1.0 m/s in 8.3 s. SOLUTION: From least to greatest magnitude of acceleration: C < E < A < D < B. A. B. C. D. E. ANSWER: From least to greatest magnitude of acceleration: C < E < A < D < B. 59. The graph in Figure 27 describes the motion of an object moving east along a straight path. Find the acceleration of the object at each of these times: (Level 1) eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero a. during the first 5.0 min of travel b. between 5.0 min and 10.0 min Page 2 ANSWER: From least to greatest magnitude of acceleration: C < E < A < D < B. Chapter 3 Practice Problems, Review, and Assessment 59. The graph in Figure 27 describes the motion of an object moving east along a straight path. Find the acceleration of the object at each of these times: (Level 1) a. during the first 5.0 min of travel b. between 5.0 min and 10.0 min c. between 10.0 min and 15.0 min d. between 20.0 min and 25.0 min SOLUTION: a. Let east be the positive direction. b. c. d. eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero ANSWER: Page 3 Chapter 3 Practice Problems, Review, and Assessment d. ANSWER: a. Let east be the positive direction. = 6.0m/min2 east b. = 0.0m/min2 c. d. = 2.0m/min2 west = 4.0m/min2 west Chapter Assessment Section 2 Motion with Constant Acceleration: Mastering Problems 68. Refer to Figure 29 to find the magnitude of the displacement during the following time intervals. Round answers to the nearest meter. a. t = 5.0 min and t = 10.0 min b. t = 10.0 min and t = 15.0 min c. t = 25.0 min and t = 30.0 min d. t = 0.0 min and t = 25.0 min SOLUTION: a. b. Area (15 m/min)(5 min) = 75 m c. eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero d. Page 4 c. d. = 2.0m/min west = 4.0m/min2 west Chapter 3 Practice Problems, Review, and Assessment Chapter Assessment Section 2 Motion with Constant Acceleration: Mastering Problems 68. Refer to Figure 29 to find the magnitude of the displacement during the following time intervals. Round answers to the nearest meter. a. t = 5.0 min and t = 10.0 min b. t = 10.0 min and t = 15.0 min c. t = 25.0 min and t = 30.0 min d. t = 0.0 min and t = 25.0 min SOLUTION: a. b. Area (15 m/min)(5 min) = 75 m c. d. ANSWER: a. 88 m b. 75 m c. 13 m d. 288 m Chapter Assessment: Applying Concepts eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero 78. Explain how you would walk to produce each of the position-time graphs in Figure 30. Page 5 a. 88 m b. 75 m c. 13 m Chapter 3 Practice Problems, Review, and Assessment d. 288 m Chapter Assessment: Applying Concepts 78. Explain how you would walk to produce each of the position-time graphs in Figure 30. SOLUTION: (1) Walk in the positive direction at a constant speed. (2) Walk in the positive direction at an increasing speed for a short time; keep walking at a moderate speed for twice that amount of time; slow down over a short time and stop; remain stopped; and turn around and repeat the procedure until the original position is reached. ANSWER: (1) Walk in the positive direction at a constant speed. (2) Walk in the positive direction at an increasing speed for a short time; keep walking at a moderate speed for twice that amount of time; slow down over a short time and stop; remain stopped; and turn around and repeat the procedure until the original position is reached. eSolutions Manual - Powered by Cognero Page 6