1 Phys 201A Lab 8 - Current and Voltage Part II – Ohm`s Law
advertisement

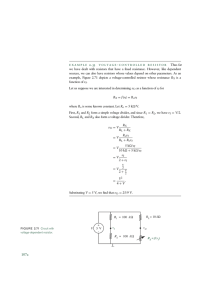
Phys 201A Lab 8 - Current and Voltage Part II – Ohm’s Law Name___________________________ In the last lab, learned the following: We used an ammeter to measure the current in a series circuit. How do the currents through two bulbs in series compare with each other? We measured the current through two identical bulbs in parallel, I2 and I3 . How did these currents relate to the current through the battery, I 1 ? What happened to the brightness of the bulb in one branch when the other bulb was unscrewed from its socket? Finally, we measured the current through a bulb in series with a parallel pair of bulbs. What happened to the current through this bulb when one of the parallel bulbs was unscrewed from its socket? We found that the current model that we developed in the last lab was not able to explain the last result. We need to develop a model based on the voltage across each bulb to understand circuits. First, however, we need to understand the relationship between current and voltage. Set up the circuit shown below. Rx is a resistor, a coil of wire wrapped in ceramic. There are four resistors on the cart. You will make measurements on one of the resistors and a long bulb. Note: The voltmeter is connected across the resistor - it is said to be connected in parallel across Rx! 1 We will be using a power supply instead of the battery of cells we used till now. The symbol for the power supply in the circuit diagram is the same as that for a battery. Note: You MUST get the circuit checked by the instructor before you turn the power supply on! Do NOT exceed 10V on your power supply when you use the resistors! Do NOT exceed 5V for the long bulb! Record your data in an excel spreadsheet in the format shown below. Then repeat the measurements for the long bulb. Voltage (V) Current (A) Plot a graph of I vs. V for the resistor and the light bulb. What kind of plot do you get for the resistor? What is the relationship between the current I through a resistor and the voltage V across the resistor? For example if we double the voltage across the resistor, what happens to the current? If we triple the voltage across the resistor, what happens to the current? Measure the slope of the graph. Slope of the graph for Rx ______________ 2 What physical quantity does the inverse of the slope represent? How would the slope of the graph change if you had chosen a resistor with a smaller resistance? We say that the resistor obeys Ohm’s Law if the current is directly proportional to the voltage. Does the long bulb obey Ohm’s Law? Explain. If time permits…… Resistance is a property of a resistor that depends not only on the kind of material that it is made of but also on its dimensions. Resistance and Length of the resistor Take a single coffee straw and a timer from the cart. Inhale deeply, filling your lungs with air (as much as you can!). Now start the timer and exhale the air out of the single straw. Repeat with two straws taped end to end and three straws taped end to end. What happens to the flowrate of air as you increase the “length” of the straw? Does the resistance to the flow increase or decrease with length? Does the resistance to current (flow of charge) in a wire increase or decrease with the length of the resistor? Resistance and area of cross -section of the resistor Next take a bundle of straws and exhale out the same amount of air (same person should inhale the same maximum amount both times). Note the time taken to do this. How does the area of cross-section affect the resistance to the flow of air? Do you expect thicker resistors to have lower or higher resistances compared to thinner resistors? 3