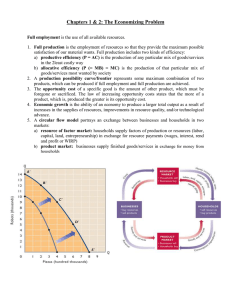
Eurobodalla Shire Housing Needs, Supply and Market Issues Paper
advertisement

Eurobodalla Shire Housing Needs Study EUROBODALLA HOUSING NEEDS, SUPPLY AND MARKET ISSUES PAPER Final Paper Prepared by Kim Houghton and George Porter For Eurobodalla Shire Council 30 April2014 Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 CONTENTS Introduction 1. The area and its population ............................................................................................................ 1 Recent population trends ................................................................................................................... 1 Age structure....................................................................................................................................... 2 Households ......................................................................................................................................... 2 Source: ABS Census 2011 .................................................................................................................... 3 Migration trends ................................................................................................................................. 3 Incomes ............................................................................................................................................... 4 Key conclusions ................................................................................................................................... 6 2. The current housing market and dwelling stock............................................................................. 7 Housing profile .................................................................................................................................... 7 Purpose-built housing for older people .............................................................................................. 9 Vacant dwellings ............................................................................................................................... 10 House prices ...................................................................................................................................... 11 Housing market segments ................................................................................................................ 15 Key conclusions ................................................................................................................................. 16 3. Recent housing market trends ...................................................................................................... 17 Residential Construction ................................................................................................................... 17 Dwelling types ................................................................................................................................... 19 Price Trends ...................................................................................................................................... 19 House purchase affordability ............................................................................................................ 20 Rental affordability ........................................................................................................................... 26 Key conclusions ................................................................................................................................. 27 4. Population projections .................................................................................................................. 28 Projected population growth ............................................................................................................ 28 Factors affecting population growth ................................................................................................ 29 Age structure of the future population ............................................................................................ 30 Household types ............................................................................................................................... 32 Demand for dwellings ....................................................................................................................... 32 Key conclusions ................................................................................................................................. 33 5. Parameters and Drivers of Change ............................................................................................... 34 The Policy context ............................................................................................................................. 34 Local planning and land supply ......................................................................................................... 36 The economic and employment context .......................................................................................... 39 Drivers within the housing market ................................................................................................... 40 Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 6. Key issues ...................................................................................................................................... 45 Market sectors and their needs ........................................................................................................ 45 Potential gaps in future dwelling supply........................................................................................... 46 Land supply and associated zoning controls..................................................................................... 46 Economics of development .............................................................................................................. 47 Local development/ construction industry ....................................................................................... 47 Impact of the wider economy ........................................................................................................... 47 Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 1. The area and its population Recent population trends The estimated resident population of Eurobodalla Shire, according to the ABS, was 37,048 at June 2012. This represents a population decline of 38 people over the previous 12 months, the first time the Shire’s population has declined in recent times. As the table shows, there has been a slowing rate of population growth since 2001, despite a slight revival in 2010. Table 1: Change in resident population, year on year, Eurobodalla Year (ending June 30) 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 Change in number +600 +616 +471 +336 +193 +248 +198 +161 +345 +275 -34 Change in percent +1.8 +1.8 +1.4 +1.0 +0.5 +0.7 +0.5 +0.4 +0.9 +0.7 -0.1 Source: Based on ABS data, presented in Profile.id by .id, the population Between the 2006 and 2011 Census this ‘usual resident’ population grew by a net 816. But there was a lot of churn in the population, with some 6,000 people moving into the Shire in that period, and 5,000 moving out. The newcomers are described further below. Temporary residents Temporary residents are non-resident ratepayers and other visitors. Eurobodalla had 31% of its homes unoccupied on Census night 2011 – one of the highest percentages in areas researched by the National Sea Change Task Force in its 2013 report1. A typical daily average of 7,175 people are in Eurobodalla on any given day who do not describe themselves as ‘usual residents’ of the Shire. And in addition, it was estimated that another 4,121 are in full-time tourist accommodation on any given day. These averages add another 13,000 people to the Shire’s resident population. 1 Time and tide: moving towards an understanding of temporal population changes in coastal Australia; National Sea Change Task Force, April 2013 Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 1 Age structure Eurobodalla’s population is significantly older than that in most other parts of NSW, with the exception of certain coastal areas such as Lake Macquarie. In 2011, 25.9% of residents were aged 65 and over, representing growth in this age group of nearly 2 percentage points since 2006. As the charts shows, the Shire has a larger proportion of residents in the 50 and upwards age groups than the average for Regional NSW, and a lower proportion in all the younger age groups. Figure 1: Service age groups 2011 25.0 Eurobodalla Regional NSW % Percent 20.0 15.0 10.0 5.0 0.0 0 to 4 5 to 11 12 to 17 18 to 24 25 to 34 35 to 49 50 to 59 60 to 69 70 to 84 85 + Source: Based on ABS data, presented in Profile.id by .id, the population experts Households In the 2011 census there were approximately 15,000 households in the Eurobodalla Shire of which 9,846 were occupied by families and, 4,973 by either single persons, group or visitor only households. Figure 2: Household Structure 2% couple family, no children couple family, with children 29% 36% one parent family other family 1% lone person households 11% 21% Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 group households 2 Source: ABS Census 2011 The most notable aspect of the household structure is that it is dominated by one and two person households, who make up well over half of all households. This is in large part a result of the large number of older households, almost all of which comprise one or two people. Migration trends In the 5 years to 2011 while the total population of Eurobodalla Shire rose by only 816 people, almost 6,000 people moved into the Shire. The great majority came from elsewhere in NSW (especially Sydney) and the ACT. More details on where they came from are shown below. Table 2 Migration between Eurobodalla Shire and other States/Territories State / Territory In migration Out migration Net migration New South Wales Sydney Victoria Queensland South Australia Western Australia Tasmania Northern Territory Australian Capital Territory Total % of resident population 3,505 1,237 481 416 92 129 91 57 1,218 5,989 17% 2,899 700 463 651 74 97 76 51 859 5,170 15% 606 537 18 -235 18 32 15 6 359 Source: ABS. Compiled and presented in profile.id by .id, the population experts. Almost matching this in-migration, some 5,170 people (15% of the population) left the Shire to live elsewhere. These people mostly went to NSW (Sydney, Capital Region), the ACT and Queensland. In net terms, there was a sizeable net loss of 18-24 year olds, and a net gain of pre-retirees (55-64 year old). However, as analysis later in this report shows (see Figure 33), there is substantial outward migration of older seniors (aged 70 or more). Figure 3 Net migration by age group Source: ABS, compiled and presented in Profile.id by .id, the population experts Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 3 Incomes Most households in Eurobodalla had incomes between $300 and $1000 per week in 2011, although 7% had an income below $300 and 32% had an income of $1000 or more per week. On average, households in the Shire have lower incomes than those found across Regional NSW - the proportion of very low income households is higher and the proportion of high income households is much lower than most other Regional LGAs. Incomes are significantly lower incomes than those across NSW as a whole. At the time of the Census in 2011, the median weekly household income for Eurobodalla was $784. This is considerably less than the average for Regional NSW which was $961. Figure 4: Weekly Household Income, 2011 18.0 16.0 14.0 Percent 12.0 10.0 8.0 6.0 4.0 2.0 0.0 Source: ABS, based on data from Profile .id by .id, the population experts The proportion of middle income households is similar across all the small areas under consideration, although there is more significant variation in the proportion of higher income households as the next chart shows. The areas with the largest numbers of higher income residents are along the Central parts of the coast, from the Malua Bay are to the Broulee area. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 4 Figure 5: Weekly household income by small areas, 2011 Percent 0.0 10.0 20.0 30.0 40.0 50.0 Surfside - Long Beach - Maloneys Beach - North Batemans Bay Batemans Bay - Catalina Surf Beach - Batehaven - Sunshine Bay - Denhams Beach Malua Bay - Lilli Pilli - Rosedale - Guerilla Bay Up to $599 $600-1499 Broulee - Tomakin - Mossy Point $1499+ Urban Moruya - Moruya Heads Tuross Head Dalmeny Narooma - North Narooma - Kianga Source: ABS, based on data from Profile .id by .id, the population experts Change in Household Income 2001-2011 Eurobodalla’s population is becoming wealthier at a faster rate for incomes up to $2,500 per week ($130,000pa) per household. The graph below shows the change in weekly household income in Eurobodalla and the rest of NSW (excluding Sydney) between 2001 and 2011. The rest of NSW has had larger increases in the two highest income brackets, but Eurobodalla shire has had larger percent increases in those households with incomes between $600 and $2,500. Both Eurobodalla Shire and the rest of NSW have had losses in the number of households with lower incomes. Figure 6 Change in weekly household income 2001-11 $3,000 or more Weekly household income $2,500-$2,999 $2,000-$2,499 $1,500-$1,999 $1,250-$1,499 $1,000-$1,249 $800-$999 $600-$799 Rest of NSW (exc. Sydney) Eurobodalla $400-$599 $300-$399 $200-$299 $1-$199 Negative/Nil income -500% 0% 500% 1000% Change between 2001 and 2011 1500% Source: ABS Census 2011 Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 5 Key conclusions Population growth in the Shire had slowed considerably by 2013. This is due to the Shire’s reliance on inbound migration to maintain its population. (Migration trends are reviewed in the next chapter.) The Shire’s households are characterised by three main features: a large proportion of older people, a small proportion of children, and a predominance of 1 and 2 person households. The Shire’s households have a very low median income. Certain suburbs have a slightly higher proportion of higher income households, but even these have a lower median than the average across regional NSW. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 6 2. The current housing market and dwelling stock Housing profile In the 2011 census there were 14,819 recorded households but there were 22,350 recorded dwellings of which 15,337 were occupied on Census night. This ratio fits with the estimate from the Temporary Populations report2 that 31% of dwellings in Eurobodalla were unoccupied on Census night. The great majority of vacant houses are owned by non-residents. Typically they are used part time as holiday homes although a significant proportion of owners (27%)3 intend to move in eventually (generally in two to ten years time), most likely when they retire. There was an average of 2.3 people per household and 1.6 motor vehicles per occupied dwelling The majority of the occupied dwellings were separate houses - 12, 720 (Figure 7). The proportion of units and attached homes is low compared to many parts of NSW, and these higher density homes are concentrated around the urban centres, particularly Batemans Bay. Figure 7: Percentage of occupied dwelling types 6.44% 3.27% 0.13% Separate house 7.22% Joined housing Flat, unit or apartment 82.94% Other dwellings Dwelling structure not stated Source: ABS Census 2011 The largest number of dwellings were owned outright at 6,839 (44.6% compared with 31% nationally) but significant numbers were also owned with a mortgage outstanding or rented - see Figure 8. 2 Time and tide: moving towards an understanding of temporal population changes in coastal Australia; National Sea Change Task Force, April 2013 3 Ibid, p92 Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 7 Figure 8: Percentage of tenure types of occupied dwellings 1.1% 6.8% Owned outright 24.9% Owned with a mortgage 44.6% Rented Other tenure type Tenure type not stated 22.6% Source: ABS Census 2011 There was a marked difference in proportions of the types of tenure between the top 68% and bottom 32% of the household incomes. The majority of the property being purchased through a mortgage was by households in the upper income bands. A larger proportion of the lower income group rented. In the lower income group nearly 60% of the dwellings were owned fully compared to about 45% in the higher household income group (Figure 9). This is consistent with the owners either being retired or having acquired and paid for the property as a 2 or more income household, but now reduced to a single income. Figure 9 Percentage tenure type for each income group 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% Rented 50% Being purchased 40% Owned outright 30% 20% 10% 0% Lowest 32% Upper 68% Source: ABS Census 2011 The proportions of ownership fully paid and paid off varied across the suburbs from about 60% at Surfside, Moruya Heads and Moruya to above 75% at North Narooma, Denham’s Beach, Kianga and Batehaven. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 8 Figure 10 Proportion of household owning a dwelling or paying off a mortgage, by suburb Batehaven Kianga Denhams Beach North Narooma Tuross Head Tomakin Batemans Bay Dalmeny Maloneys Beach Narooma Sunshine Bay Rosedale Lilli Pilli Surf Beach Broulee North Batemans Bay Malua Bay Catalina Mossy Point Long Beach Moruya Moruya Heads Surfside Owned outright Owned with a mortgage 0% 50% 100% Source: ABS Census 2011 Purpose-built housing for older people The vast majority of older people live in “mainstream” housing that was designed and built for the general market. The match between the preferences of older people and the existing stock is discussed in the next chapter. However, a minority of older people want or need housing specifically designed for seniors. This agespecific housing falls into three categories: Accessible housing Accessible housing meets the needs of people with disabilities and older people experiencing declining mobility. In some cases it is purpose built (usually under the provision of the SEPP (Housing for Older People and People with a Disability) and more often, facilities are retrofitted (eg. ramps, grab-rails, accessible showers). There is no data on the supply of such housing, which community housing stakeholders interviewed indicated was limited in the Shire. Retirement village accommodation Retirement villages are a popular option among older seniors, especially those aged over 75, and a large proportion of those who relocate at this stage in life move into retirement villages. They are attracted by the access to emergency care, the community of like- minded people, and the easy-tomanage accommodation. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 9 The 2011 Census reported 211 retirement village dwellings in Eurobodalla. The following villages have been identified: IRT The Clyde, Retirement Village, Batemans Bay Cooinda Retirement Village, Retirement Village, Batemans Bay Principal Edgewood Park , Denhams Beach The Manor Batemans Bay Retirement Village, Batemans Bay Banksia Village, Broulee IRT Moruya, Moruya IRT Dalmeny IRT Coastwatch, Dalmeny Retirement villages accommodate only about 3% of over 65s in the Shire, a figure that is below the NSW average and well below that found in many coastal areas of NSW, where up to 10% live in villages. Residential aged care Only a small proportion of older people will ever enter residential care, and in almost all cases this will occur only when their health has seriously deteriorated and round-the-clock support or medical oversight is required. Eight residential aged care facilities have been identified in Eurobodalla, providing 323 High Level Care places and 298 Low Level Care. High Low Banksia Village BROULEE 0 50 Edgewood Park Res Aged Care Facility DENHAMS BEACH 77 32 IRT - Crown Gardens BATEMANS BAY 0 40 IRT - Lakeview DALMENY 55 35 IRT - Moruya Village MORUYA 0 30 Maranatha Lodge BATEHAVEN 60 34 Sir James at Dalmeny Aged Care Facility DALMENY 66 50 The Glen Residential Care Centre CATALINA 65 27 TOTAL 621 323 298 Care facilities are funded and regulated by the Commonwealth Government, which subsidises care places on the basis of a population ratio (88 places per 1000 people aged 70 or more). Vacant dwellings The proportion of vacant dwellings in Eurobodalla is very high – indeed, the ABS Census in 2011 found that, at 31.4%, it was the highest for any LGA in NSW. The proportion of vacant dwellings varies greatly across the Shire. In the main urban centres about one in five homes are vacant, but in the Malua Bay - Lilli Pilli – Rosedale - Guerilla Bay precinct it was exceptionally high at 49.4%. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 10 Figure 11: Percentage of vacant dwellings 2011 Source: ABS Census 2011 The high rate of vacancy is predominantly due to the purchase of holiday homes by non-residents who live in them only for short periods, although it is understood that in many cases the owners intend to retire there eventually. This high level of holiday home ownership has a profound impact on the local housing market, in particular making it vulnerable to changes in the external economy which can lead to large variations in the propensity of outsiders to invest in a second home. House prices Dwelling prices were obtained from the Allhomes.com website on 17/12/2013. These are by their nature asking prices and therefore in most cases marginally higher than any purchase price but some prices indicated a range and the lower value was recorded, in these cases the value is most likely an underestimate. The summary of the data for houses (not rural properties, units, apartments or town houses) is shown in Table 3 while the distribution of house prices for the Eurobodalla Shire is shown in Figure 12. Table 3 Asking price for houses Allhomes.com on 17/12/2013 Count Mean Mode Median Minimum Maximum 789 $512,578 $399,000 $450,000 $90,000 $4,100,000 Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 11 Figure 12 Distribution of house prices in the Allhomes data 250 Nuber of houses 200 150 100 50 0 Asking price (thousand $) Twenty four percent of dwellings on offer were units, apartments and town houses, a figure significantly higher than the census figure of 13.6% of dwelling being of this type. These were generally about 50% of the price of separate houses (see Table 2 and Figure 13). Table 4 Asking price for units, apartments and town houses Allhomes.com on 17/12/2013 Count Mean Mode Median Minimum Maximum 194 $300,219 $250,000 $255,000 $119,000 $1,100,000 Figure 13 Distribution for units, apartments and town houses prices in the Allhomes data 120 Nuber of units 100 80 60 40 20 0 Asking price (thousand $) Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 12 House prices, and therefore affordability, varied significantly over the various localities within the Eurobodalla Shire (Figure 14). Figure 14 Percent of house prices in price bands by suburban area. Arranged in ascending order of prices below $400,000 Thousand $ Urban Moruya, Moruya Heads 100-199 Batemans Bay, Catalina 200-299 Surfbeach, Batehaven, Sunshine Beach, Denhams Beach 300-399 400-499 Tuross Head 500-599 600-699 Dalmeny 700-799 Narooma North, Narooma Kianga 800-899 Surfside, Long Beach, Maloneys Beach, North Batemans Bay 900-999 1000-1099 Broulee, Tomakin, Mossy Point 1100-1199 Malua Bay, Lilli Pilli, Rosedale, Guerilla Bay 1200+ 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% There were too few units, apartments and town houses on offer for a similar disaggregated analysis of price to be meaningful. The 2011 census give a good estimate of the prevalence of unit type dwellings in each suburb however it is not a full count because unoccupied dwellings are not separated into dwelling types (Figure 16). Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 13 Figure 15 Total numbers of houses and units on offer by suburban groupings, Allhomes data Narooma North, Narooma Kianga units, appartments and townhouses Dalmeny Tuross Head houses Urban Moruya, Moruya Heads Broulee, Tomakin, Mossy Point Malua Bay, Lilli Pilli, Rosedale, Guerilla Bay Surfbeach, Batehaven, Sunshine Beach, Denhams Beach Surfside, Long Beach, Maloneys Beach, North Batemans Bay Batemans Bay, Catalina 0 50 100 150 200 Figure 16 Number of dwellings by type in suburb groupings, 2011 census Narooma North, Narooma, Kianga "Units" Houses Dalmeny Other Tuross Head Unoccupied Urban Moruya, Moruya Heads Broulee, Tomakin, Mossy Point Malua Bay, Lilli Pilli, Rosedale, Guerilla Bay Surfbeach, Batehaven, Sunshine Beach, Denhams Beach Surfside, Long Beach, Maloneys Beach, North Batemans Bay Batemans Bay, Catalina 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000 Source: ABS Census 2011 The percentage of units varied widely by suburb from zero at Rosedale, Kianga and Mossy Point to 33.4% in Batemans Bay. Table 5 shows the suburbs where more than 10% of the occupied premises were units. A problem with grouping suburbs becomes obvious when the grouped data in Figure 16 is compared to the suburb-level data in Table 5. For example the high percentage of units in Batemans Bay shown in Table 5 becomes lost when grouped with the data from Catalina in Figure 16. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 14 Table 5 Individual suburbs with "units" constituting more than 10% of occupied dwellings Suburb Batemans Bay North Batemans Bay Surf Beach Narooma Batehaven Denhams Beach % occupied dwellings 33.4 23.1 15.0 14.3 12.0 11.2 Source: ABS Census 2011 Housing market segments The most significant aspect of the local housing market is that it has two discrete components: Local residents. Non-residents. Non-residents are typically older households (45% 45-64 years old compared with 31% 45-64 years old in the general Shire population) who buy a home either intending to move to the Shire (just over a quarter) or using their property as a holiday home for some time (21%)4. At the time of writing, real estate agents report that non-residents comprise the great majority of home buyers, despite the decline in inward migration to the LGA. A reliance on non-resident buyers, although common in coastal areas, is particularly marked in smaller settlements along the South Coast of NSW. Drawing on stakeholder feedback, including the experience of real estate agents in Eurobodalla (from this study) and other NSW coastal areas (from previous studies), as well as from review of the population's composition and review of real estate advertising in Eurobodalla, five sub-markets have been identified: 1. Sea change baby boomers. Typically looking to buy a 2 or 3 bedroom detached home in an attractive coastal location, most members of this group can afford a house at or above the local median price, based on their housing assets built up in Sydney or Canberra. In the past, the typical buyer would be a couple in their 50s with grown up children, buying a holiday home with a view to retiring into it when their children leave home. Despite current market conditions, this group is estimated to represent over half the buyers in Eurobodalla, and possibly over three quarters in some areas. 2. Downsizing retirees. Many older people want to move to somewhere smaller and more manageable when they feel their health or mobility is declining. They may also want to move somewhere with shops and doctors close by, because they no longer wish to drive so much. A substantial minority move into a retirement village at this stage. It appears that this market is not well served in Eurobodalla, so this group represents a small section of the market. A large number of people leave the Shire after the age of 70. 3. Families with children. Home buying families with children generally want to live in detached housing that is accessible to their workplace. Depending on income they may be looking to buy a cheap, older-style house or a luxury home, and they trade up when they can, often to 4 Sea Change Task Force, op cit p50 and p38. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 15 a modern home with up to five bedrooms. Buyers from this market segment make up most of the “resident” buyers in Eurobodalla. 4. Small local households. There are many local resident households with only one or two members. Despite the small household size, the available evidence is that this group prefers detached housing or two-to-three bedroom attached housing (eg townhouses). However some have a strong preference for a particular location that offers good facilities and recreational options, and some want to be close to their workplace, so there is some localised demand for smaller one and two bedroom units, especially if these are very affordable. 5. Low income renters. Many households cannot buy a home, because their income is too low or they are reliant on employment benefits, disability pension or casual work. A quarter of households in the Shire are renters, but much of the Shire’s housing stock is not affordable to those on low incomes, despite rents in the Shire being comparatively low – and social housing supply in the area is very limited. The most affordable options are typically olderstyle units, which are concentrated in the northern part of the Shire, particularly around Batemans Bay. This sub-market does not include middle and higher income renters, typically working age locals who can afford a suitable home in a suitable location. Key conclusions 1. The great majority of homes in Eurobodalla are detached. 2. Incoming migrants and second home buyers comprise a very large proportion of the Shire’s housing market, and a slowdown in these sectors has weakened the local housing market. 3. The Shire has an exceptionally high proportion of vacant homes, as a result of holiday home investment. This market sector sometimes has a de-stabilising effect on the local housing market. 4. High value housing is concentrated in certain suburbs, mainly in the central section of the coast from Lilli Pilli south to Broulee. 5. There is limited housing stock specifically built to address demand from older people. This is probably not a major issue for people in their 50s or 60s, but the poor supply of options for downsizing to a small block or a unit, or to a retirement village, and limits on specialist medical services available in the Shire may help explain some of the exodus of people aged 70 or more. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 16 3. Recent housing market trends An important issue for residential demand and supply is the extent to which construction activity is tied to ongoing population growth. This is particularly important given the slowdown in the Shire’s actual population growth this last decade. The rate of growth in the Shire’s population fell from 1.6%pa between 2001 and 2005 to 0% pa in 2012. It is not yet clear if this is a temporary slow-down or whether it is a sign of the ‘sea-change’ phenomenon has faded? In either case, the implications for the Shire’s economy and housing market are significant. Residential Construction The chart below shows that the value of residential development in recent years in Eurobodalla has been between $80 and $120 million per annum and has been trending down since 2008-09. Figure 17 Value of DAs determined 2007-08 to 2012-13 140,000,000 Value of DAs determined ($) 120,000,000 100,000,000 80,000,000 60,000,000 40,000,000 20,000,000 0 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 Source: DOP Local Development Performance Monitoring Reports (2007 to 2013) from www.planning.nsw.gov.au/en-us/developmentproposals/performancemonitoring A longer term perspective shows that the value of activity peaked in 2002, early in the housing boom, at over $230 million pa (in 2002 dollars), and the total value has been around the level of recent years ($100 million pa plus or minus $20 million) since 2006. According to ABS Census data, the housing stock in Eurobodalla increased by 2,841 dwellings between 2001 and 2011, or approximately 15%. This is an annual increase of around 280 new dwellings each year, and the chart below shows that most of these were new single dwellings. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 17 Figure 18 DAs determined by dwelling type 2007-8 to 2012-13 300 250 200 150 Single new dwellings number of DA determined 100 New second occupancy number of DA determined 50 0 Source: Local Development Performance Monitoring Reports (2007 to 2013) The chart below shows that most of the construction activity was valued at under $500,000, with the $0-$100,000 category accounting for the largest number of DAs. The chart shows that there is some consistency to this pattern over recent years, though there were signs of a slight increase in the number of DAs over $500,000 up until 2011. Figure 19 Number of DAs determined by value, 2007-08 to 2012-13 600 548 539 468 467 421 500 400 362 315 256 261248 242 300 200 100 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 189 127 125 9692 78 39 14 15 20 21 16 12 7 6 4 7 6 3 1 2 1 1 0 2 0 Number of DA determined of value $0 Number of DA determined of value $0-$100k Number of DA Number of DA Number of DA Number of DA determined of determined of determined of determined of value $100k- value $500k-$1m value $1M-$5M value $5M-$20M $500k Source: Local Development Performance Monitoring Reports (2007 to 2013) Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 18 Dwelling types As noted in the previous chapter, 83% of dwellings in the Shire are separate houses. In order to diversify housing choice in response to growth in the number of small households, as well as to make better use of urban land and infrastructure, the State Government and Eurobodalla Council have sought to promote higher levels of medium density development in the Shire. During the decade 2001 to 2011, 23.6% of the additional homes constructed in Eurobodalla were medium density in format. The great majority of these were attached housing, with a smaller number of apartments. The following table shows the change in the housing stock in each of the urban precincts. It shows that, over the decade, development activity has been distributed across the Shire. There has been some medium density development in all the precincts. In the area from Batemans Bay south to Surf Beach, around a third of new construction was medium density housing. In the remaining areas, the proportion was around one fifth. Figure 20: Additions to housing stock, small areas, 2001-2011 0 Additional dwellings 200 400 Surfside - Long Beach - Maloneys Beach… Batemans Bay - Catalina Surf Beach - Batehaven - Sunshine Bay… Malua Bay - Lilli Pilli - Rosedale… Broulee - Tomakin - Mossy Point Urban Moruya - Moruya Heads Tuross Head Dalmeny Narooma - North Narooma - Kianga Separate house Medium density Source: ABS, based on data from Profile.id, by .id, the population experts Price Trends In November 2013, the median house price in Eurobodalla LGA was reported to be $347,000 and the median unit price was $256,000. Ten years earlier, at the end of 2003, median prices were approximately $330,000 for houses and $260,000 for units, so over the last decade houses have risen in value less than inflation and units have registered no rise. During this period, prices have been very volatile, as the next chart shows. However, agents report some pick-up in the housing market over recent months, particularly for houses at the lower end of the price spectrum (under $300,000 for detached houses). Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 19 Figure 21 Annual change in median price, Eurobodalla LGA Houses Units Source: domain.com.au Prices vary significantly across the region. The next section of this report looks at affordability, and is based on suburb level data showing that the most expensive suburbs (highest median prices) are Maloneys Beach, Mossy Point, Rosedale and Lilli Pilli, closely followed by Malua Bay, Broulee, North Narooma and Moruya Heads. The lowest prices are in North Batemans Bay and Tomakin. House purchase affordability Housing affordability has two components: the cost of housing (rent or mortgage repayments) and household income. A commonly used measures used for ‘housing stress’ is housing expenditure (rent or mortgage repayments) of less than 30% of household income (HIA5). A second empirical measure for the purchase of a dwelling is that the purchase price should be less than 5 times the annual household income (Bank West6). The NSW Centre for Affordable Housing specifically monitors affordability for lower income groups and in particular those at the lower margins of affordability. Its most recent summary found that in 2013, 46% of the dwellings sold in Eurobodalla were at a price that was affordable to a “moderate income household” (ie. a household with gross income that is 80-120% of the Shire median). That assessment is consistent with the findings in this report presented below and represents a dramatic increase in affordability since 2010, when only 26% of dwellings were affordable to this group. House Prices and Incomes The relationship between the price of houses or units on offer and the ability of residents of the Eurobodalla Shire to afford them is shown in Figure 22 and Figure 23. The analysis found that around 50% of houses on the market are affordable for about 25% of Eurobodalla households while units are more affordable with 50% affordable for about 45% of households. Figure 22 shows the distribution of incomes in Eurobodalla and the relative affordability of homes for sale in Eurobodalla. The distribution of incomes (blue column) shows that 50% of households have incomes up to $799 (all weekly income figures here are gross household incomes) per week, and that almost 75% of households have incomes up to $1,249 per week. The relative affordability of houses (red column) shows that to be able to afford half the houses on offer, households need a 5 HIA-Commonwealth Bank Housing Affordability Reports available from http://economics.hia.com.au/publications/hia_cba_affordability_report.aspx 6 Bank West Key Worker Housing Affordability Report 2011 Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 20 weekly income of $1,250 - $1,499 ($65,000 - $78,000 pa). Households with incomes in the $1,000 $1,249 pw range can afford 25% of the houses on offer, and a household income of less than $1,000 pw enables purchasing of only the cheapest homes on offer. % Figure 22 Household income and detached housing affordability 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 household incomes affordable houses weekly household income Source: ABS Census 2011, SES calculations Figure 23 applies the same analysis to units rather than freestanding houses, and shows that affordability is much improved. The blue columns have the same pattern as the previous figure as they show the same data – the distribution of household incomes in Eurobodalla. The red columns again show affordability, and indicate that the lower prices of most units mean that a household income of $800-$999 pw would enable purchase of over 65% of the units on offer. Household incomes of $600-$799 pw would enable purchase of some 30% of the units on offer. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 21 % Figure 23 Household income and unit affordability 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 household incomes affordable units weekly household income Source: ABS Census 2011, SES calculations Another aspect of affordability across the suburbs can be obtained by comparing, on a suburb by suburb basis, the Allhomes.com list of asking prices with the household income profile. From this data it is possible to estimate what proportion of houses on offer is affordable (less than 5 times annual income) to defined proportions of local households. The first calculation estimates the proportion of households that cannot afford anything other than a negligible proportion (0.1%) of the houses on offer (Figure 24). The biggest influence on these estimates is the presence or absence of low priced houses (<$200,000). Moruya, North Batemans Bay and Tomakin all had at least 1 house advertised for under $200,000. The chart shows that about 50% of households could not generally afford to buy a house at the moment (although the actual figure is much lower as many will already own their house or have started paying mortgages on a lower purchase price many years ago). The main impact is on potential first time buyers who are likely to fall within lower half of the income range, that is, the 50% of households that could not afford 99.9% of the homes available. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 22 Figure 24 Estimate of the percentage of households that can only afford 0.1% of houses on offer Basis of calculation asking price in suburb and household income in Eurobodalla asking price in suburb and household income in suburb 0 50 100 % of households with an income that can afford only 0.1% of houses on offer Source: ABS Census 2011, SES calculations The second set of calculations presents two estimates of affordability for those with adequate income for house purchase: the percentage of houses on offer that are affordable to 65% and 95% of households in each suburb (Figure 25 and Figure 26). The calculations combine the varying income of suburb residents with the varying house prices in their suburb to look for suburbs of high income/high house prices and low incomes/low house prices. The data for 65% is the most sensitive measure as it is closer to the point at which houses become unaffordable to those on lower incomes. The 95% data is a less sensitive measure but a better representation of the suburb as a whole. The charts show, for each suburb, the proportion of houses that can be afforded by locals from the suburb (reflecting the income range in that suburb) and also the proportion affordable to the wider Shire population. The difference in affordability is a result of different income levels and different property values. The charts show that Some high-income suburbs (such as Denham’s Beach, Mossy Point and Rosedale) have high levels of local affordability because their residents have higher incomes than the Shire average, and can therefore afford a more expensive house; and Low income suburbs such as Batehaven and Surf Beach show the opposite – being more affordable to average Eurobodalla residents than to local residents in these suburbs. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 23 Figure 25 Estimate of the percentage of listed houses that can be afforded by 65% of households Basis of calculation asking price in suburb and household income in Eurobodalla asking price in suburb and household income in suburb 0 5 10 15 20 % of houses on offer affordable to 65% of households Source: ABS Census 2011, SES calculations Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 24 Figure 26 Estimate of the percentage of listed houses that can be afforded by 95% of households Basis of calculation asking price in suburb and household income in Eurobodalla asking price in suburb and household income in suburb 0 20 40 60 80 % of houses on offer affordable to 95% of households Source: ABS Census 2011, SES calculations The 2011 Census also gives another view of the affordability of purchasing dwellings by estimating the incidence of ‘mortgage stress’ where mortgage payments exceed 30% of household incomes. Using the freely available ABS data it is possible to compare the pattern of mortgage repayments with the pattern of household incomes of those paying a mortgage (Figure 27). The chart shows that mortgage stress (red columns) is more common amongst mortgagees on lower incomes (under $1,000-1,249pw). This is expected in most areas as most low income households are either younger or post retirement, and housing stress is common amongst people entering the housing market while on moderate incomes. But it is somewhat surprising in the context of Eurobodalla’s older age profile, and the related higher proportion of households owning their homes already. In an older community like Eurobodalla it might be expected that there are many old mortgages with low levels of monthly repayments which might be manageable even on a low monthly income. But it seems that if there are old mortgages in Eurobodalla, the incomes of these homebuyers are very low indeed, making the mortgage payment over 30% of income. Overall, the incidence of mortgage stress falls once incomes exceed $1,500pw, though there are still a few households with high incomes and very large mortgages. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 25 Figure 27 Mortgage stress Comparison between mortgage repayments and income of those making the repayments, based on 2011 census data. 600 500 Mortgage more than 30% of income Number 400 300 Mortgage less than 30% of income 200 100 0 Household income per week Source: ABS Census 2011, SES calculations Rental affordability The 2011 Census has cross tabulated individual data on rents paid and household income. Figure 28 Rent paid and income, 2011 census figures 800 rent more than 30% household income 700 Number 600 500 400 rent less than 30% household income 300 200 100 0 household income/week Source: ABS Census 2011, SES calculations Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 26 Rental payments were more than 30% of the income for the vast majority (about 80%) of those with household incomes of less than $1000 per week ( Figure 28, red columns). Rental costs were much less of an impost on those with an income of $1000pw or more with just 4% of them paying more than 30% of income. There were too few rental residential properties advertised (2-5 per suburb) to make any valid comments about the distribution of current rental prices and affordability. However, across the Shire as a whole, rents have not kept pace with inflation in recent years, and have fallen over the last two years, particularly for units7. Current median rents are $200 per week for a 2 bedroom unit, and for a 3 bedroom house $300. Key conclusions 1. The Shire’s housing stock increased by 15% in the decade to 2011. However, at $84.3 $million for 2012-13 the value of DA approvals is currently low compared to the level of $100 -120 million for 2008-11, and well below the peak of $230 million for 2002. 2. While building activity levels have remained vibrant, most of the activity is of moderate value. 3. Most existing housing is detached and only 14% is medium density. However, 24.6% of dwellings constructed in the decade to 2011 were medium density. 4. Despite pronounced volatility from year to year, median housing prices in the LGA have barely risen during the last decade and have failed to keep up with inflation. 5. Despite housing prices which are low compared to many parts of NSW, home ownership is not affordable to at least half the households in the Shire. 6. Housing is most affordable in Batehaven and Surf Beach. 7. The great majority of renting households with an income of under $1000 a week are in housing stress. 7 Data from NSW Centre for Affordable Housing Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 27 4. Population projections Projected population growth Population projections 2011- 2031: Eurobodalla Shire The estimated resident population of Eurobodalla Shire in 2011 was approximately 37,000 people. Projections for Council prepared by demographic consultants ID8 suggest that By 2021 the population will be about 39,500. By 2031 the population will be about 42,600. This represents population growth of around 5,600 people over 20 years. Projections independently prepared by the NSW Department of Planning reach similar conclusions, with slightly greater growth of 6450 people by 2031. Small area projected population 2011 to 2031 It is expected that population growth will not be evenly distributed, as Figure 29 shows Figure 29: Projected population growth to 2031 by small areas. Surfside - Long Beach - Maloneys Beach - North Batemans Bay Batemans Bay - Catalina Surf Beach - Batehaven - Sunshine Bay - Denhams Beach Malua Bay - Lilli Pilli - Rosedale - Guerilla Bay Broulee - Tomakin - Mossy Point 2011 Urban Moruya - Moruya Heads 2031 Tuross Head Dalmeny 7000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2000 1000 0 Narooma - North Narooma - Kianga Source: Based on data from Forecast.id, by .id the population experts 8 Note that all the data in this chapter is drawn from IDs projections prepared for Council, except where referenced otherwise. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 28 Among the small areas, particularly strong growth is anticipated along the central section of the coast, from Tomakin to Moruya and Moruya Heads: Northern precincts (Long Beach/Batemans Bay/Malua Bay): 1447 additional residents Central precincts (Tomakin/Broulee /Moruya) 2623 additional residents Southern precincts: 913 additional residents. Significantly, very limited population growth is expected in the existing urban centre of Batemans Bay, with growth focussed on areas to the north and south of the town. It is useful to consider the growth in population in percentage terms, because a small increase in the population can have a significant impact in a small settlement. From this perspective, the most substantial population growth is projected for the Malua Bay area and the Moruya area. Figure 30 Percentage population growth 2011-2031 Surfside - Long Beach - Maloneys Beach - North Batemans Bay Batemans Bay - Catalina Surf Beach - Batehaven - Sunshine Bay - Denhams Beach Malua Bay - Lilli Pilli - Rosedale - Guerilla Bay Broulee - Tomakin - Mossy Point Urban Moruya - Moruya Heads Tuross Head Dalmeny Narooma - North Narooma - Kianga 0 10 20 30 40 Source: Based on data from Forecast.id, by .id the population experts Factors affecting population growth Population projections are based on predictions about “natural” population growth (births minus deaths) plus net migration (inward migration less outward migration). The projections described here make the following estimates for Eurobodalla Shire over the period 2012 to 2031. Births Deaths Net migration +6513 -9021 +8067 These figures illustrate the crucial point that population growth in the Shire will be entirely dependent on inbound migration. Without this, the population would decline. Changing expectations about levels of migration have led to major revisions of population projections for the Shire. The projections used in this report were prepared in 2012. Earlier Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 29 projections for the 2007 South Coast Regional Strategy suggested that the population would grow more than four times as much as currently expected. This was based on an assumed continuation of the high levels of inward migration experienced in the period from the mid 1990s up to the Global Financial Crisis. Consequently, future changes in economic conditions and price trends in housing markets can be expected to affect population growth in the Shire quite strongly, leading to increases or decreases in the rates of migration. Age structure of the future population Eurobodalla’s population structure is weighted towards older age groups, and this will become accentuated over the next 20 years as a result of inward migration of older people and the ageing of the existing population. Despite the expected growth in the overall population, very little growth is predicted for all the age groups from 0 to 65 years old. On the other hand, strong growth is predicted for the age groups 6580 years old, particularly over the decade to 2021. Figure 31 Population projections Eurobodalla Shire 4000 3500 Population 3000 2500 2000 2011 1500 2021 1000 2031 Age Group 80 to 84 75 to 79 70 to 74 65 to 69 60 to 64 55 to 59 50 to 54 45 to 49 40 to 44 35 to 39 30 to 34 25 to 29 20 to 24 15 to 19 5 to 9 10 to 14 0 to 4 0 85 and over 500 Source: Based on data from Forecast .id, prepared by .id, the population experts The next chart shows the projected change in numbers in each age group over the period. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 30 Figure 32: Change in age structure 2011-2031 Source: Based on data from Forecast.id, by .id the population experts Underlying these changes is a continuing trend for inward migration by older people, particularly those in their 60s. At the same time, large numbers of younger people, particularly those in their 20s, are expected to leave the Shire, continuing an existing trend. Figure 33: Projected net migration by age group 2011-2031 Source: Based on data from Forecast.id, by .id the population experts Projected rates of net migration reflect current trends, which include substantial numbers of departures by young people, particularly those in their twenties; modest net inward movement by younger families with children; and high levels of net inward migration among early retirees, with a peak at age 60. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 31 Perhaps surprisingly, the forecasts suggest significant net outward migration from the Shire of people aged 70 and over, particularly around age 75. On a small area basis, this outward migration trend is most marked in the Batemans Bay and Moruya urban areas. Reasons may include a desire to move closer to family members, a desire to be close to facilities, or a desire for forms of accommodation (particularly retirement villages or small homes on small lots) that are not available in their existing location. Household types Figure 34: Forecast household types 2011-2031. Source: Based on data from Forecast.id, by .id the population experts The Shire’s household mix currently includes a larger proportion of lone person households and a smaller proportion of families with children than the average for the State. It is projected that these trends will continue, although the growth of the overall population should lead to an increase in absolute numbers for all households except group households. Consequently, the composition of housing demand is not expected to change greatly, at least in terms of the balance between key market segments, with over two thirds of households comprising only one or two persons (lone persons 40% of households, couples 30%). Demand for dwellings Projected demand for additional dwellings has been revised downwards as a result of the recent slowdown in population growth. Council’s Residential and Rural Residential Land Supply Report 2012-13 estimates a demand for approximately 3,000 new dwellings in residential areas by 2013. These estimates are broadly in line with the NSW Department of Planning’s latest estimates. Future housing growth to meet this demand is spread across the urban precincts, according to ID, as shown in the next table. It shows the highest projected growth will be found in areas south of Batemans Bay and down the coast to Moruya. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 32 Table 6: Estimated distribution of potential additional dwellings to 2031 Surfside - Long Beach - Maloneys Beach - North Batemans Bay- 492 Batemans Bay – Catalina 144 Surf Beach - Batehaven - Sunshine Bay - Denhams Beach 275 Malua Bay - Lilli Pilli - Rosedale - Guerilla Bay 739 Broulee - Tomakin - Mossy Point 547 Urban Moruya - Moruya Heads 567 Tuross Head 175 Dalmeny 260 Narooma - North Narooma - Kianga 177 Total Urban Precincts 3376 Shire Total inc Rural 4076 The types of housing that will be built to address these future needs will be determined by the market. There has been significant policy discussion about the limited diversity of housing in the Shire and in particular about the need to promote medium density development. The settlement strategies outlined in the next chapter suggest that a large part of future need can and should be met by smaller homes, particularly medium density housing, and a previous report to Council9 suggested that the predominance of small households means that there will be strong demand for medium density homes in future. However, in reality the link between household size and dwelling preference is a complex one, and the factors that may influence future demand are discussed in the next chapter. Key conclusions 9 Modest population growth – less than 1% a year – is predicted for the urban precincts. Population growth will entirely depend on inbound migration to Eurobodalla. Consequently, any rise or fall in the number of migrants will have a substantial impact on the Shire’s population. Indeed, a significant reduction in inbound migration could result in a decline in the Shire’s population. The majority of inbound migrants are empty nesters and younger retirees. This group already makes up a very large proportion of the population, and this will increase over the next 20 years. Demand for additional housing in Eurobodalla will come primarily from incoming migrants (and probably also from holiday home buyers). Most of the additional households will comprise only one or two persons. On current estimates, around 4000 additional homes will be required in Eurobodalla over the next 20 years, about 85% of them within the urban precincts. Current projections suggest that the highest level of housing construction will occur in the Malua Bay to Guerilla Bay precinct, in the Broulee to Mossy Point precinct, and in and around Moruya. Note, however, that estimates of the distribution of new development are based to a significant extent on the availability of residential land in each precinct rather than on estimates of demand. Judith Stubbs and Associates, Draft Eurobodalla Housing Strategy, 2008 Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 33 5. Parameters and Drivers of Change The Policy context Dwelling targets Formal dwelling targets were last published at the time of the release of the State Government’s South Coast Regional Strategy in 2007. At that time, the housing market was very active and inbound migration to the Shire was running at a high level. The strategy said that there would be a need for 10,700 additional dwellings in Eurobodalla dwellings by 2031. Since that time, population projections, including those of the Department of Planning, have been dramatically revised. Current estimates suggest a need for up to 4,000 additional dwellings by 2031, and it is expected that a target of this order will be included in a new Regional Strategy if this is developed in the short to medium term. The contrast between recent projections and previous estimates illustrates the reality that the future is uncertain: changed economic conditions or other factors can result in substantial falls or increases in the rate at which people relocate into (or out of) the Shire. For this reason, it is advisable for Council to ensure that land supply can respond to an upturn in demand that exceeds formal projections. The Strategy says that existing vacant urban land (mostly between Malua Bay and north Batemans Bay) should accommodate about three quarters of the new dwellings, with the balance expected to be in ‘medium density development and investigation areas’. It notes that the current housing mix is dominated by low density detached dwellings which “will not meet the need of future households which will be dominated by singles and childless couples”. While it remains the case that additional housing demand will be mainly from couples and lone persons, the recent reduction in the projections of migration means that families will probably make up a greater share of the additional demand than the 17% projected in 2007. Moreover, as noted elsewhere in this report, it is likely that most of the additional households (including 1 and 2 person households) will prefer detached housing, other than in locations where medium density dwellings are sought as a result of location-specific demand (eg. closeness to facilities) or affordability issues. Settlement Strategies South Coast Regional Strategy (2007) The settlement principles underpinning the Regional Strategy were spelled out in the accompanying Settlement Planning Guidelines. In general these remain valid today. Key points include: About 70 per cent of the Eurobodalla area’s future population growth should be accommodated in existing vacant urban land. “Infill housing and new residential subdivisions located adjacent to existing well serviced centres and towns will be given priority in land release planning.” Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 34 The regional settlement hierarchy identifies Batemans Bay as a regional centre and Moruya and Narooma as major towns. These settlements, along with their associate extended urban areas, will continue to be a focus for new residential development. The Strategy does not support new towns or villages or major developments outside the defined urban areas. The target split is 60:40 detached homes to medium density including dual occupancy within the identified urban precincts. (This is intended to promote the provision of smaller homes while also making better use of land and local infrastructure.) Future housing mix should better match the needs of smaller households and aged residents – that is, there is a need for greater housing choice. “The identification and encouragement of suitable locations for housing that is appropriately adaptable for an ageing population, close to amenities and services is important for meeting the housing needs of the Region.” Eurobodalla Settlement Strategy (2006) Council’s own Strategy predates the Regional Strategy but reflects many of the same principles. Key points include: population growth and investment housing needs are accommodated within existing settlement boundaries (5.3.2) urban residential land is developed in an orderly sequence that responds to the market and is able to be serviced economically (5.3.2) Medium density development is to be located in areas where existing housing stock is obsolete and/or in close proximity to commercial centres (5.3.3). Facilitate a range of housing styles, types and sizes across the Shire to cater for an ageing population, declining occupancy rates and socio-economic profiles (5.7.3). Draft Eurobodalla Housing Strategy (2008) The draft Eurobodalla Housing Strategy was prepared in January 2008 and while comprehensive, had a focus on two particular groups: 1. Low to moderate income households who require more affordable rental housing 2. Older people and those with a disability. In considering housing demand, the study found that demand was expected to be greatest from net migration of lower income, older people. It suggested that this market is not well aligned with supply trends, which were mostly detached houses (with more bedrooms), though there was some increase in units to 2006. While it increased, the actual number of additional units (133) was much less than the increase in number of detached homes (896) in the same period. The draft strategy looked at cost and affordability and found that with the median cost of a home in the LGA was around $320,000, “it is clear that home purchase would be generally unaffordable to around 90% or more of typical first home buyers in the area. Rental would be affordable to more households, but more than half would still be excluded from a median-rental dwelling, which supports findings related to housing stress among renters above”. On the interaction between housing demand/supply interaction the study found that: “9,912 and 10,903 dwellings required by 2031 to accommodate the resident populations’ needs. This projection is similar to that of the South Coast Strategy’s 10,700 additional dwellings required albeit at the higher end of the range. The additional increase required as projected by the model amounts to approximately 396-436 dwellings per year. The range in the model reflects the additional dwellings required as holiday letting. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 35 90% of net increase in demand will be from 1 and 2 person households, the vast majority of which will be older households requiring smaller, more manageable and preferably well-located dwellings close to transport, shops and services. A smaller number will be required for younger families and singles, including separate homes and higher density accommodation.” The draft strategy predicted a shortfall of some 200 in Independent Living Units by 2016, plus demand for some 200 more ‘manageable dwellings’ every five years. The current authors have reviewed the 2008 report and make the following comments: As already noted, current projections of population growth are much lower than those available at the time of the study. It remains true that the largest component of additional housing demand will come from older people, and mostly from 1 and 2 person households. However the conclusion that all or most of these smaller households will want smaller medium density homes is empirically unsubstantiated. The current authors have found in other coastal areas of NSW that incomers in the 50-70 age groups typically prefer a 2-3 bedroom detached home (ie. one bedroom, one spare bedroom for visitor, and one bedroom used as storage or for computers etc). The demand for smaller units comes from those in their 70s and 80s who wish to move to somewhere more manageable that is located close to services and facilities, and small young households who seek good access to recreational facilities. Demand for retirement village accommodation is probably greater than estimated in the study as it is market-driven rather than need-driven. A wider choice of retirement villages would probably reduce outward migration by those in their 70s and would promote a higher level of inbound migration. Housing affordability has improved somewhat since the report was written. An overview of current affordability is found in Chapter 3 of this report. Local planning and land supply Local Environmental Plan 2012 The current LEP is based on the NSW template. The principle urban residential zones are: Zone R2: Low density residential development that is consistent with the character of the area. Zone R3: Medium density development including a variety of dwelling types. Zone R5: Large lot development (not generally used in urban precincts). In addition, shop top housing is permitted in B1 and B2 Business zones. The LEP includes a range of provisions that control residential development including: Minimum lot size provisions, to ensure that lot patterns reflect the neighbourhood. Coastal development, to ensure ongoing public access and to minimise environmental impacts Height limits. The following table shows the types of housing permitted (generally with consent) in the Residential Zones, under the 2012 LEP and relevant SEPPs. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 36 Residential Zonings (R1 and R4 not used) Attached dwellings Boarding houses Dual occupancies (attached) Dual occupancies (detached) Dwelling houses Group homes (permanent) Group homes (transitional) Multi dwelling housing Residential flat buildings Rural worker's dwellings Secondary dwellings Semi-detached dwellings Seniors housing Residential care facilities Shop top housing R2 Low density R3 Med density R5 Large Lot N N C C C C C C N N A N C C C C C C C C C C C C N A C C C C N N C N C N N N N N A N N N N N= Not permitted C= With Consent A= Secondary dwellings are classed as complying development under the NSW SEPP (Affordable Rental Housing) 2009 Note: Attached dwelling means a building containing 3 or more dwellings, where: (a) each dwelling is attached to another dwelling by a common wall, and (b) each of the dwellings is on its own lot of land Land availability The following table summarises Councils assessment of vacant and suitably zoned residential land across the Shire, as shown in its Urban Residential Land Monitor. Data has been arranged to show availability in each of the Small Areas that comprise the subject of this study. Council’s Urban Land Monitor data also includes some land in settlements which lie within the Rural Hinterland areas, and these are separately identified at the end of the table. Locality/District Total no. of existing dwellings Vacant residential lots Potential additional lots Potential additional lots from Land Release Areas Total vacant lots (inc potential) Surfside - Long Beach Maloneys Beach - N Batemans Bay 1897 410 228 68 706 Batemans Bay - Catalina 2076 107 69 0 176 Surf Beach - Batehaven - 3314 103 240 0 343 Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 37 Sunshine Bay - Denhams Beach Malua Bay - Lilli Pilli - Rosedale Guerilla Bay 1895 278 242 993 1513 Broulee - Tomakin - Mossy Point 1993 153 430 0 583 Urban Moruya - Moruya Heads 1670 161 565 41 767 Tuross Head 1659 169 105 0 274 Dalmeny 1092 111 0 320 431 Narooma - North Narooma Kianga 2045 140 147 287 574 Urban within B/Bay Rural 406 42 7 0 49 Urban within Moruya Rural 100 22 0 0 22 Urban within Narooma Rural 348 66 7 148 221 TOTAL AVAILABLE URBAN LOTS (ID Urban areas) TOTAL AVAILABLE URBAN LOTS (Incl Urban in ID Rural areas) 5367 5659 The data shows that there are potentially 5367 vacant lots in the urban precincts identified for the study, or 5659 lots if urban land in other locations is included. A larger number of dwellings is possible if medium density assumptions are included. Council calculates that the available land, plus some intensification within existing urban areas, can deliver 8286 dwellings which includes some dual occupancy of urban lots. The quantum of available lots may appear adequate given the projected demand for around 4000 dwellings over the next 20 years. However, only 1762 are current vacant lots – the balance are potential lots, over half of them being potential lots from Land Release Areas (915 of which are located at Rosedale). Council additionally calculates that there may be another 388 lots across the Shire as a result of further subdivisions in urban areas. Given the needs of the development industry (relating to the locations of demand, infrastructure availability, permitted form of housing, existing land ownership, etc), it is likely that some of the land identified in the Land Monitor may not be considered suitable. Discussions with some of the Shire’s builders, developers and real estate agents for this report indicated that there is broad satisfaction with the planning emphasis on future housing in the ribbon south of Malua Bay. Demand seems to be strong enough, and is likely to be satisfied with that area as long as the local infrastructure continues to improve (such as the supermarkets at Tomakin and Broulee, the school at Broulee and the medical facilities at Moruya). There is a perception that there will be hard limits to the scale of new release lands available south of Moruya, driven by State Government guidelines on LEPs. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 38 The economic and employment context The scale of future population growth will be strongly influenced by economic factors, both external to and within the Shire. As recent years have shown, economic uncertainty and a weak housing market lead to significant reductions in the numbers of people migrating into the Shire. Internal growth, based on increased economic activity within the Shire, could be expected to lead to numerous benefits, including a reduction in outward migration and increased incomes for many households, in turn supporting growing housing demand. Economic Development and Employment Lands Strategy Council’s Economic Development and Employment Lands Strategy recognises a variety of drivers for the Shire’s economy – national and local – which will influence business and resident location decisions, and business growth capability. Examples include: Competition from Asia in manufacturing Population aging Retail consolidation Domestic tourism trends Construction business cycles The Strategy is based on a modest job growth forecast – in line with expected population growth. In terms of land supply, an estimate of the job capacity of existing and potential future employment lands identifies a potential shortfall of commercial land and a potential excess of industrial land by 2030. However, as demonstrated by the Employment Land Audit, a number of retail jobs (bulky goods retail, wholesale retail) are provided in industrial areas, so an undersupply of jobs on commercial land and an oversupply on industrial land is not unexpected or inappropriate. The Strategy recommends a package of locally-driven economic development measures, and strategic planning to determine the hierarchy of industrial land and release timetable, starting with low occupancy existing industrial land. Eurobodalla Strategic Influences Study This study was commissioned by Council in late 2010 to identify the nature and scale of factors likely to influence the Shire’s population and economy in the coming decade. One weakness highlighted is the current reliance in the Shire’s economy on population growth as a driver of economic activity. The weakness is that the dependence on growth reflects a continuing hope that the Shire will be attractive to new residents and that in-migration will continue to be strong. But the nature of the inmigrants (younger low income families and older low income couples/singles) is such that there are many other places they may choose to move to and the Shire may not be able to rely on the flows it has seen in the past. Housing affordability is being compromised by dominance in the labour market of low skilled and seasonal jobs, with the wages gap between the Shire and the State growing even as the unemployment gap narrows. Economics of residential development Discussions undertaken for this report with some Shire builders, developers, real estate agents and housing providers shows that while there is clearly little movement in the market at present for homes priced over $300,000, there is still scope for new developments to be completed economically (profitably for the developers). However it is also clear that the margins are tight, with stakeholders commenting that the land cost in the Shire is relatively high, trades costs are seen as quite high for a country area, and government fees constitute a significant part of the development Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 39 cost. Despite these constraints, each of those interviewed acknowledged that it is possible to build to the market, and to do that on a commercial basis. It seems that very few homes are being built speculatively at present (ie. homes constructed for sale on the open market) due the to soft market, and with local trades costs reported as ‘high’ many buyers are having new homes built by larger firms who can build more cheaply to a formula – such as Hotondo and Masterton. The economics of multi-unit development are more challenging, with most such developments aiming at mid-low price points. While most of the people interviewed felt there is a good market for higher price point multi unit developments, there is considerable nervousness amongst developers at present and none of the recent approved projects has proceeded to the construction phase. The relatively low cost of much of Eurobodalla’s freestanding housing stock means that it can be difficult for new quality medium density homes to be price competitive. Drivers within the housing market Demand for medium density housing It was noted in Chapter 2 that the fact that most older household comprise 1 or 2 persons does not necessarily mean that they prefer very small homes. A similar argument applies to the wider housing market (whilst noting that older households make up a large part of that market). It is true over the next 20 years most of the additional housing demand will come from small households, and also that the existing supply of smaller homes in the Shire is very limited. It would be easy to conclude that the main need will therefore be for 1 and 2 bedroom homes, but the reality is more complex. Population growth in the Shire is driven almost entirely by inbound migration, and in practice, the majority of incomers to Eurobodalla are aged in their 50s and 60s, and some of these have previously bought their home for holiday use. Overwhelmingly, this market segment prefers freestanding homes, preferably with 2 or 3 bedrooms. They want a bedroom to sleep in, a spare bedroom for visitors and often a further bedroom to be used for hobbies or storage. Many like gardening, and most want a garden. Most want a garage and some an additional carport for caravan and/or boat storage. Given the very limited diversity of housing styles in the Shire, there is undoubtedly some unmet demand from this group, in particular for alternative forms of detached homes (eg master-planned or community title schemes, small lot homes). However the key area of unmet demand arises when older households reach their 70s and 80s, and they want to downsize to an easily maintained home on one level, with only a small garden and (generally) two bedrooms. Villa homes are popular with this market segment. They also want to live close to services and facilities (eg. doctors and shops). Unfortunately, many parts of Eurobodalla do not offer the range of accessible services that may be sought, and the availability of such homes is very limited. This may explain why so many people in their 70s leave the Shire. For similar reasons, retirement villages are popular with this age group. There may also be some emerging demand for units in and around the Shire’s urban centres, from younger single people and couples whose priorities lie outside the home. However, stakeholders commented that there is currently a lack of confidence in the market based on subdued economic conditions (including, concerns about employment in the ACT), and the challenges of delivering Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 40 appropriate products profitably are not encouraging the type of development that could attract these groups. In summary, then, the following factors affect demand for smaller medium density homes: Favoured medium density locations are those that are attractive to older, downsizing retirees who want facilities nearby. Housing forms should also be attractive to older downsizing retirees, particularly villas, row housing and small lot single level homes. Affordability must be competitive with freestanding homes in the area. In Eurobodalla, it is likely that many good quality new medium density homes would be more expensive than some established freestanding homes. In a few key locations, potential demand from younger people who want easy-to-manage homes close to employment, shops, cafés and recreational facilities should be considered. , Non-resident housing Sea Change Task Force report 31% of dwellings in Eurobodalla were unoccupied on Census night in 2011. Council was part of a multi-LGA study into the characteristics and intentions of non-resident ratepayers in coastal locations published in 2013 by the Sea Change Task Force. The study found that most of these nonresident ratepayer households were headed by baby boomers (aged 45 to 64 at the time of the survey in 2012) and that in Eurobodalla’s case, 27% intend to move permanently. Within this group of intending relocators, 15% intended to move within 2 years, 31% between 2 and 5 years, 28% between 5 and 10 years - and the balance were not sure if or when they will move. These figures give an indication of potential future population growth that will arise from nonresident ownership of existing properties. While it also demonstrates the large scale of property ownership among non-resident owners, it is important to note that the level of demand relate more to external demographic and economic factors facing key source regions (notably metro NSW and Canberra) and the nation as a whole, than with factors relating to the Eurobodalla economy or housing market. Non-resident households are a discrete submarket in Eurobodalla. They tend to have higher incomes (52% earning over $104,000pa), particular preferences for housing location and type, and to be from other parts of NSW (55%) and the ACT (37%). While most non-resident households are pre-retirees (50s and early 60s), over 30% are retirees. Needs and preferences of older persons What are the housing preferences of seniors? In 2011, among the older people in Eurobodalla who lived in private housing, over 85% lived in detached homes. A further 9% lived in attached housing and about 6% lived in apartments. It has at times been suggested that such figures indicate a significant need for smaller homes, for two reasons: Most older person households comprise one or two people, and it is therefore assumed that they need small (1-2 bedroom) homes. Policy discussions tend to focus on purpose built-housing for seniors, fostering a belief that the key need is for age-specific housing products. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 41 The reality is somewhat different. The reality is that most older people choose a detached house, typically with three bedrooms and a garden. In a review of research by Wulff et al10, a key finding was that “The expectations that smaller households “need‟ smaller dwellings often results from too static a view of the lives of older persons in small households”. Nationally, the ABS Census found that while 9 out of 10 older people live in households of one or two people, four out of five older households were living in detached homes, in the great majority of cases with 3 bedrooms or more. All available research indicates that they do so by choice. In addition, despite a tendency for policy makers to focus on the “needs” of older people and hence to focus on age-specific housing products, as Pinnegar et al pointed out11, the majority of seniors want the same types of housing as other age groups. In other words they are want “mainstream” housing. Older people will, over the next 30 years, make up an increasingly large part of the mainstream housing market, with preferences and demands that are as diverse as those of any other section of the population. This applies more particularly in areas with a large population of seniors, like Eurobodalla. As Pinnegar says: “We would argue that the decisions of older households should … be seen as integral to, and operating within, the broader housing market. They already are, and will increasingly become, a key player in mainstream market dynamics and thus understanding residential decisions and behaviours of this cohort infuses much broader supply/demand considerations. The Boomers, in terms of their sheer numbers, but also in longevity post-retirement, will increasingly shape the mainstream rather than simply seen as a distinct category with distinct needs.” None of this means that there is no need to promote housing choices that may meet the needs of particular sections of the seniors market. Specific needs can arise especially when health or mobility declines, or on the death of a partner. At this stage, it is common to seek to move to somewhere more manageable, for instance with two bedrooms and a small garden or courtyard. For this group, clusters of villa homes have proved particularly popular, as have other forms of low rise housing. Location becomes important, with easy access to facilities a consideration. For some, a home in a retirement village is a favoured option. In NSW, around 5% of older households live in retirement villages, although the proportion is lower in Eurobodalla. It is at this stage that many older residents appear to leave Eurobodalla Reasons may include the absence of suitable housing choices, lack of appropriate services and facilities in the area, or a desire to move closer to families or support networks. Relocating and downsizing ABS Census data showed that in 2011, one in four people aged 55-64 had moved house during the previous five years, along with 18% of people aged 65 or more. Thus while “ageing in place” is widely discussed as the preference of older people, in many cases older households are well into retirement before they decide to stay put. In other cases people find that they have to move for health reasons. Research has found that although many older households move house, only a small proportion choose to downsize12. A recent study of a large sample of over 55s found that only 9% had moved 10 Wulff, M., Healy, E. & Reynolds, M. (2004) Why don’t small households live in small dwellings? Disentangling a planning dilemma. People and Place, 12(1), pp.58–71. 11 Pinnegar, S et al. Understanding housing and location choices of retiring Australians in the ‘baby boom’ generation., City Futures Research Centre, 2012. 12 Judd, B et al. Downsizing amongst older Australians. AHURI 2013 Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 42 house and downsized (and that many of the downsizers had moved from a large detached house to a smaller one). It was found that downsizers tended to be older, female, single/widowed, and lower income. Other research13 has investigated why seniors appear to want larger homes. According to the Census, three quarters of older people live in a house with 3 or more bedrooms. Seniors told researchers that they actually needed the extra bedrooms: 68% had at least one bedroom set aside for visitors, in particular family members. Spare bedrooms were also used for a home office or study (34%), a second guest bedroom (27%), hobbies (12%), storage (9%), ironing (4%) and reading (2%). Housing needs of seniors in Eurobodalla While it is clear that large numbers of seniors move to Eurobodalla for lifestyle reasons, and choose to buy freestanding homes, there may nevertheless be some unmet needs. Some seniors, particularly those aged over 70, prefer a manageable single level dwelling with only a small garden, in particular villa-style homes. Three appears to be a limited supply of such homes in the Shire, especially in the types of location which are usually favoured, offering good amenity and easy access to local facilities. For this reason, smaller single level detached homes are often favoured because they are more manageable than large modern homes which often have 5 bedrooms. Retirement village options appeal to a significant minority of seniors after the age of 7014 and supply and choice in Eurobodalla is very limited. Researchers suggest that urban centres can be attractive to older residents if they are planned and designed in an age friendly and attractive way. Needs of low income households Housing affordability in Eurobodalla has improved over recent years, due to stable or declining housing prices (particularly for home buyers). However, a substantial number of households still experience housing stress and many cannot access suitable, affordable housing. A review of the Eurobodalla housing market, carried out by Housing NSW’s Sales Team in 200815, concluded that the key issues for low income households in the Shire were a lack of housing diversity and inadequate supply of rental housing. Both these findings appear to remain valid today. A report prepared for Council in the same year16 proposed a range of direct actions on the part of Council aimed at improving both rental and purchase affordability, although it did not demonstrate that these actions would have a significant impact on affordability issues. 13 Judd, B et al. Dwelling, land and neighbourhood use by older home owners, AHURI 2010 Judd, B et al found that (a) 63% of survey respondents would consider a retirement village if their mobility started to decline (see 2010 report) and (b) one in 5 of the over 70s who downsized moved to a retirement village (see 2013 report). 15 Information on Eurobodalla Housing Market, Housing NSW 2008 16 Judith Stubbs and Associates, Draft Eurobodalla Housing Strategy 2008. 14 Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 43 Rental housing According to the most recent available data17, the median rent for a 2 bedroom unit in the Shire is $200 per week, and for a 3 bedroom house is $300. Rents have fallen over the last 2 years, particularly for units. Calculations of the prevalence of housing stress, carried out by the NSW Centre for Affordable Housing18, report that housing stress is widespread among private rental tenants. (Housing stress is defined as rent costs that are greater than 30% of gross household income). For very low income households, with incomes 50% or less than the Shire median, 88% were in housing stress in late 2013 For low income households, with incomes 50-80% of the local median, 63% were in housing stress. Single person households are by far the largest group in housing stress in the private rental market in Eurobodalla, comprising 64% of those experiencing stress. Older single persons make up a significant proportion of this group. Renters are typically willing to accept smaller homes than purchasers, as rents are typically more closely tied to the size of a property, and many single or couples are seeking one and two bedroom units. A large proportion of very low income households want social housing (from Housing NSW or a housing association) but supply is very limited. There are less than 500 social housing dwellings in Eurobodalla including 67 Aboriginal Housing Office dwellings representing 2.7% of all housing in the Shire, compared to an average of 4.7% in non-metropolitan NSW. Home purchase An analysis of the overall match between house prices and household incomes was presented earlier in this report. It showed that affordability is generally quite good (so long as lower priced homes continue to be supplied onto the market). The NSW Centre for Affordable Housing found a significant increase in affordability in the Shire since 2010 for lower income groups and those at the lower margins of affordability. According to the ABS, 378 people were living in a manufactured home or caravan at the time of the Census. The majority of them are older people. While it is recognised that many older people are happy in a residential park, it is nevertheless a choice that is usually driven by affordability, and which involves a high degree of risk given the number of parks that have closed in NSW over recent years. 17 18 Rent and Sales Report, Final Quarter, 2013. HNSW for NSW Government. Local Government Housing Kit Database (Online), NSW Centre for Affordable Housing, accessed 24 Jan 2013 Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 44 6. Key issues Market sectors and their needs Resident vs non-resident (inward migrating) buyers There is considerable volatility in the non-resident market which depends primarily on perceptions of ‘affluence’ in the key source markets – metropolitan Sydney (largest) and Canberra (slightly smaller). It is likely that non-resident buyers have higher household incomes, and while they also probably have higher household expenses, are in general better able to afford higher priced property in the Shire. It is also likely that their expectations are slightly different in terms of location and amenity, though this too will vary depending on the purpose of the purchase – ie if there is a plan to move to the Shire soon or if the property is for holiday accommodation or commercial returns. As a driver of residential housing demand, and one that comes from outside the Shire, it creates significant uncertainty in estimating future demand (and hence dwelling and land supply needs). Older and young residents There is clearly significant churn in the number of younger families moving in and out of the Shire, many of whom are on moderate household incomes. At the other end of the age spectrum there is clearly a current trend and a forecast for the future, that sees residents over 70 leaving the Shire. While detailed interviewing has not been done, it is likely that two factors drive this: 1. Search for better health care; and 2. Desire to be closer to family. It is possible that there might be a third driver: low level of supply of small, manageable homes in good locations. Prices and affordability The Shire has a high proportion of dwellings owned outright, which is an indicator of lower levels of internal housing turnover (subject to personal preferences). While there is an expectation that older people will downsize, this may not be as significant as the stereotype might suggest. Research on older people’s housing preferences shows that future markets expect more choice, not less. And the Shire seems to have a fairly poor offering in terms of the diversity of new residential homes, with 4 and 5 bedroom family homes not suiting many buyers. This leaves people looking to downsize primarily considering the older housing stock. There may well be undersupply in small lot detached (new) homes and villas. There is a geographic aspect to this as well with downsizing likely to flow from expensive suburbs to less expensive ones as there is little smaller/cheaper accommodation in most of the expensive suburbs – indicating many downsizers will need to move suburbs. Units are an important part of the affordability mix, but again with little quality new stock on the market much of the price gap is based on a quality gap as many are older style and offer limited Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 45 amenity. There are signs that demand is weak – as median unit prices are lower now than they were ten years ago. Units are located mostly in central Batemans Bay, Surf Beach, central Narooma and few other locations. There is a possible mismatch with buyer expectations as this concentration leaves few multi unit options in all the Shire’s other suburbs. This highlights the need to drive multi unit development to match anticipated demand for smaller and ‘manageable’ dwellings - in ‘sensible’ well-serviced locations with good access to services. Potential gaps in future dwelling supply Supply and demand The analysis in this report fits with the views of people who have been interviewed, to the extent that broadly, supply and demand are currently quite well balanced in the Shire. The housing market is moving slowly, and mostly at the sub $300,000 price point. Some new release areas are being developed and it seems that take-up is slow, but steady. There also seems broad agreement on the future directions of land release, and that the biggest release areas (south of Malua Bay) will be attractive to the market and can play a key role in meeting demand for new housing. Within that broad picture there are some signs of gaps in particular segments. Medium density properties have not increased their share in the last decade, and the current developer perception is that while they can be built economically, demand is currently very soft. Low maintenance properties (related to medium density but as a subset) is another area where there seems to be an undersupply, though the undersupply is most likely much less than has been predicted in other studies. The 2008 study found that “90% of net increase in demand will be from 1 and 2 person households, the vast majority of which will be older households requiring smaller, more manageable and preferably well-located dwellings close to transport, shops and services.” But the findings from this report are that this overstates the nature of that demand for this market segment. This report argues that a large proportion of existing residents are small/older households, but demand for the available stock of smaller homes is limited – especially limited for apartments, and older townhouse developments. Most older person households (especially those that are couples) want a diverse array of housing options including 2, 3 and 4 bedroom free-standing homes, much of which is being supplied by the current market. The gap seems to be in small lot housing and well designed villas/townhouses in accessible locations. Land supply and associated zoning controls The rate of development of new areas has slowed somewhat since the boom in the early 2000s. The Department of Planning has also reduced its forecasts for growth in the Shire’s population. Nevertheless, as pointed out in this report, much of the demand for residential housing comes from non-resident buyers, and this component of the market is quite volatile. So it could be that if this externally-driven demand accelerates, the supply of zoned land in medium term might prove inadequate. Zoning controls themselves don’t seem to be a major impediment to development, and there is no sign that local controls such as height controls or lot size controls (FSR controls) are limiting development of multi-unit or multi story developments in urban areas. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 46 Economics of development This report documents the relatively low incomes of most households in the Shire, and the divergence in household incomes and house prices across different suburb groupings. The overall message is that affordability is limited, and this is supported by the sales rate of homes above and below the $300,000 threshold. But interviews with builders, developers, real estate agents and housing providers suggest that there is still opportunity to build and develop economically, provided the cost of acquiring land and meeting regulatory obligations is kept to reasonable levels. Of some concern are the reports that there have been very few new multi-unit developments actually completed in recent years, while several proposals have been submitted – and some approved – but proponents have then backed off. The feedback from the interviews is that this has been due to a lack of confidence in the market (“We are not like another Kiama” said one interviewee) and concern that a new quality development of this type would be relatively new concept in the Shire which might take some time to be absorbed into the market. None of the stakeholders interviews for this report identified the planning controls or processes as a reason for this lack of confidence. Local development/ construction industry Many of the market supply and demand challenges stem from the reliance on building (and development) in the Shire by smaller, local business people. Some of the mid-sized home builders play a role (such as Hotondo and Masterton, for example) in being able to provide reasonable quality housing at reasonable prices, but there is a lack of large State-wide developers. The larger groups are active down to about the Wollongong region, but have less interest further south. One implication of this is that the mid-high quality medium density/small lot villa developments (which are an important part of the mix for smaller families and couples) are not well represented in the Shire. The smaller scale local developers tend to offer more standardised detached homes in traditional sprawling ‘estates’. Impact of the wider economy The Shire has high levels of home ownership in many suburbs – indicating residents with high asset value but often low incomes. This mix provides some insulation against external economic shocks as those residents are affected positively by high interest rates and are less affected by falls in real wages or increases in unemployment. While residential construction typically operates in cycles, the scale of activity in the Shire (including the large proportion of sub $500,000 DA work each year) is large enough to maintain a viable industry base even through troughs in residential housing demand. A key wildcard in the region (as opposed the Shire) is the perception of affluence of the non-resident buyers, as demand in the Shire is influenced by factors well outside the experience and control of Shire residents or Council. The other key aspect of national socio-economics that is influencing the Shire is the aging of the baby boomer population and their housing preferences. There are many pathways emerging for the transition to retirement, meaning that one of the stereotypes (selling up in the city, moving to the coast and living on the savings) is no longer the only story. Many people approaching retirement are looking to ‘age in place’ without going through such a move. Some are indeed looking for a different style of housing in a country area, but what they are looking for is changing too. Many of the “coffee Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 47 shop generation” (as described by one interviewee) are looking for more vibrant social and recreational shopping and services, rather than in previous generations where a tinny and a boat ramp were the keys to post-retirement living. The important role of non-resident owners and people moving into the Shire as drivers of residential housing demand, means that changes in these types of consumer preferences will no doubt have significant impacts on the Shire. Housing Issues Paper, 30 April 2014 48