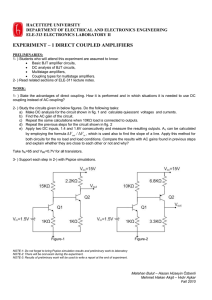
ÿþM icrosoft W ord - EE 3 2 2 - Jordan University of Science and
advertisement

Jordan University of Science and Technology Faculty of Engineering EE322 Electrical Engineering Department Electronic Circuits Laboratory Catalog Data Electronic Circuits Laboratory (0–3–1)– 1 credits Textbook D. Neamen, Electronic Circuit Analysis and Design, 2nd Edition, McGraw-Hill, 2001. References 1. D. L. Schilling et al, Electronic Circuits, Discrete and Integrated, 3rd Edition, McGrawHill, 1989. 2. T. F. Bogart, Jr., J. S. Beasley, and G. Rico, Electronic Devices and Circuits, 6th Edition, Prentice-Hall, 2004. 3. T. F. Bogart, Jr., and J. W. Brown Sr., Experiments in Electronic Devices and Circuits, 4th Edition, Prentice-Hall, 1997. Course Objectives 1. Ability to assemble basic circuits, verify theoretical concepts, and interpret experimental results concerning the characteristics of diodes and bipolar and field-effects transistors. Frequency response of CE, CB, CC, CS and CD amplifiers; multistage amplifiers; cascade CE-CE, cascade CE-CC, cascade CB-CE; RC and direct coupled amplifiers; Darlington amplifiers; differential amplifiers; emitter coupled amplifiers; operational amplifiers familiarization, applications of inverter and noninverter, differentiation and interpretation; oscillators. Pre-requisites: 243161, 243201 2. Ability to assemble basic circuits, verify theoretical concepts, and interpret experimental results concerning device applications including multistage amplifiers, differential amplifiers, operational amplifiers, and oscillators. PreRequisites by Topic 1. Electric circuit theory. Topics 1. Introduction to laboratory procedure and test & measurement equipment 3 Hours 2. Diode characteristics and waveshaping 3 Hours 3. Bipolar transistor characteristics 3 Hours 4. BJT amplifiers and frequency response 3 Hours 5. JFET characteristics and applications 3 Hours 6. Multistage amplifiers 3 Hours 7. Differential amplifier 3 Hours 8. Operational amplifier characteristics 3 Hours 9. Operational amplifier applications: summation, differentiation, and integration 10.Oscillators 3 Hours 2. Electronic devices and circuits. Computer Usage None Estimated Content Engineering Science Engineering Design Prepared by M. S. ALEM Date 12. 2 . 2008 EE322 – Electronic Circuits Lab 3 Hours 0.5 Credits 0.5 Credits Electrical Engineering Department Jordan University of Science and Technology Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department Mapping of course (EE322) objectives to program outcomes Program outcomes Course Objective 1. Ability to assemble basic circuits, verify theoretical concepts, and interpret experimental results concerning the characteristics of diodes and bipolar and field-effects transistors. 2. Ability to assemble basic circuits, verify theoretical concepts, and interpret experimental results concerning device applications including multistage amplifiers, differential amplifiers, operational amplifiers, and oscillators. Delivery Methods Assessment Methods (a) (b) Lectures Lab Experiments Documentation Reports Assignments Quizzes Exams X X X X X Lectures Lab Experiments Documentation Reports Assignments Quizzes Exams X X X X X (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) (k) ABET a-k Engineering and Technology program outcomes (a) An ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering (b) An ability to design and conduct experiments, to analyze and interpret data (c) An ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs (d) An ability to function on multidisciplinary teams EE322 – Electronic Circuits Lab (e) An ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems (f) An understanding of professional and ethical responsibility (g) An ability to communicate effectively (h) The broad education necessary to understand the impact of engineering solutions in a global and societal context (i) A recognition of the need for, and an ability to engage in life-long learning (j) A knowledge of contemporary issues (k) An ability to use the techniques, skills, and modern engineering tools necessary for engineering practice Electrical Engineering Department