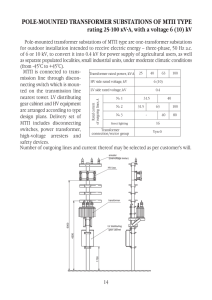
Instructor : Dr - Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering
advertisement

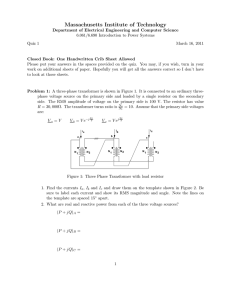
1 ANADOLU UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EEM 311 Principles of Energy Conversion Laboratory Fall, 2014-2015 Experiment 5 : Three-phase Transformer Connections and Determination of Voltage Regulation ANADOLU UNIVERSITY EEM311 – Experiment 5 2 Purpose : Using the three-phase transformer provided, to realize possible three-phase transformer connections and verify rated line voltages and currents with measurements. For all possible three-phase transformer connections, the voltage regulation will be determined. Background and Theoretical Discussion : Three-phase transformer banks are design either using a single three-phase transformer, which has internal connection depending upon the application or using three single-phase transformers, which are connected in any possible way that the application requires. As long as the redundancy is concerned, using three singlephase transformers has some advantages. One of which is that; if one of the transformer fails, threephase power can still be obtained by using two singlephase transformers at the cost of loosing some fraction of the rated power. The possible three-phase transformer connections are; Delta Delta Δ−Δ Wye Delta Y −Δ Delta Wye Δ− Y Wye-Wye Y − Y The voltage regulation of a transformer under load condition is defined as the difference between the noload voltage and the load voltage when the primary voltage and the frequency remain unchanged. The voltage regulation actually gives the percent of value of required change in primary in order to keep the secondary voltage constant. Percent regulation is given as %V V2 no load V2load 100 V2 no load Equipment List : 1 DL 1013M2 Power Supply 1 DL 1031 Digital Power Measuring Unit 1 DL 1080 Three Phase Transformer 1 DL 1017R Resistive load bank 1 DL 1017L Inductive load bank 1 Wavetek Hand Multimeter ANADOLU UNIVERSITY EEM311 – Experiment 5 3 Procedure : 1- In the laboratory, you will be provided with a transformer bank of 6 single-phase transformers each rated 190V / 70V as depicted in Figure 1. The bank with 6 transformers has a rated total power of 1000VA. First, connect upper transformers with lower ones in series to obtain three 380V / 140V single-phase transformers. Next, connect 3 single-phase transformers as a three-phase Delta Wye transformer bank, Figure 2, and connect low voltage side to R & L load bank. In this configuration, without applying the power to the experimental setup, calculate rated line voltages and currents. Verify your results with your T.A. Once your calculations are correct adjust load banks so that very low secondary current will flow, and apply rated primary voltage to the setup. Then adjust load banks to draw rated primary current. Record primary current and voltage and measure secondary voltage using handheld multimeter. Compare measurements with your calculations. ANADOLU UNIVERSITY EEM311 – Experiment 5 4 2- Adjust primary to rated voltage and keep it at that value. Using only R load (unity power factor) and RL load (lagging power factor) fill out the following table by loading the transformer at fractions of rated primary current. DELTA WYE CONNECTION cos φ Load position I Irated I / Irated V2no-load V2load %V 1 2 3 1 (resistive) 4 1.52 A 5 6 7 1 2 3 t.b.a. (inductive) 4 1.52 A 5 6 7 t.b.a.: to be arranged by your assistant ANADOLU UNIVERSITY EEM311 – Experiment 5 5 3- Repeat steps 1 and 2 for Delta Delta connection. DELTA DELTA CONNECTION cos φ Load position I Irated I / Irated V2no-load V2load %V 1 2 3 1 (resistive) 4 1.52 A 5 6 7 1 2 3 t.b.a. (inductive) 4 1.52 A 5 6 7 t.b.a.: to be arranged by your assistant Important ! All groups must perform rated line voltage and current calculations and verify the correctness of the results with T.A.s . If a group fails to calculate them correctly, that group will not be allowed to perform the measurements. This basically means that you will fail this laboratory assignment. One way of avoiding this trouble is that, since you have all necessary data, you make your calculations before coming to laboratory. Then you will make your measurements and go. Report : 1. Present your line current and voltage calculations for three-phase transformer connections and compare them with measured results. 2. Present your percent regulation results and plot percent regulation versus loading (x axis) for both resistive and inductive loading on the same graph. Explain the fact that under the lagging power factor loading percent regulation is higher 3. Comment if there is any significant variations in percent regulation under same loading but different three-phase connections. ANADOLU UNIVERSITY EEM311 – Experiment 5