DirkCheap817
advertisement

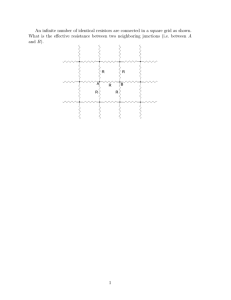
DirkCheap817 Another DC SSR from the DIGWDF Engineers Assembly and User Guide Overview The DirkCheap817 is a compact (3.5” x 1”) solid state relay (SSR) that uses four inexpensive NPN-type transistors and four resistors as its main current control components and uses standard cat5 control connections back to the controller. The SSR allows controlling DC-powered devices ranging from 530vdc, and can accommodate up to 5amps total current. The suggested transistor is the Fairchild KSC2328AYBU which provides 1+ amps of current per channel and temporary current draws upwards of 2 amps. Other NPN transistors may also be used; a 470 ohm base resistor is suggested if 2N2222A or PN2222ABU transistors are used instead. Full Parts BOM/quantities/items/sources/part numbers (* = optional, ** = substitute part) 4 KSC2328AYBU transistor mouser.com 512-KSC2328AYBU 4 PC817 optocouplers mouser.com 852-PC817X2NSZ0F 4 330 ohm 1/4 or 1/8 watt resistors taydaelectronics.com A-2049 (pkg 10) 5 680 ohm 1/4 or 1/8 watt resistor taydaelectronics.com A-2067 (pkg 10) 4 1K ohm 1/4 or 1/8 watt resistor taydaelectronics.com A-2123 (pkg 10) 1 DirkCheap817 circuit board DIGWDF Store 1* DIP-16 socket taydaelectronics.com 1* Side-entry RJ45 jack mouser.com 1* LED (any color) taydaelectronics.com A-261 5* 5mm terminal blocks taydaelectronics.com A-662 ** PN2222ABU transistor (1 amp) mouser.com ** PN2222 transistor (.6 amp) taydaelectronics.com A-003 649-54602-908LF 512-PN2222ABU A-109 Note: consider searching for parts on eBay and save yourself a lot of money. DirkCheap817 Assembly & User Guide – Page 1 Assembly 1. Bend the leads of resistors R5, R6, R7 and R8 (near the center of the board) and insert into the appropriate locations as noted on the PCB silkscreen. There is no polarity concern for resistors but for a cleaner, professional appearance, it’s a good idea to install them so the resistor stripes are oriented the same way. Solder the resistors is place and clip off the extra leads. Note: 330 ohm resistors are suggested if the KSD2328AYBU transistor is used; 470 ohm resistors are suggested for the PN2222ABU, 2N2222A or MPS2222A transistor. 2. Optional: mount and solder the DIP-16 socket in the location where the four PC817 chips reside. If you choose not to use the DIP-16 socket, remember that the square hole in the upperleft corner of each PC817 location is pin 1. 3. Optional: mount and solder the LED in the position marked “LED” in upper left corner of the board. The square hole is the cathode of the LED, which is also the shorter wire leg. 4. To reduce the footprint of the circuit board, the remaining 9 resistors are installed in “stand-up” mode. To make a stand-up resistor, bend only one of the leads around the side so that it’s parallel with the other lead, like the example to the right. Then the resistor is inserted into the mounting holes so that it’s “standing up” instead of lying flush on its side against the board. 5. Make five 680-ohm resistors into stand-up form, and mount/solder them into the holes next to the LED and to the left of the column of PC817 chips (or the DIP-16 socket). There is no polarity concern for resistors but for a cleaner, professional appearance, it’s a good idea to install them so the resistors are all standing the same way. 6. For resistors R1, R2, R3 and R4: make four 1K-ohm resistors into stand-up form, and mount/solder them into their locations to the right of the PC817 chips (or the DIP-16 socket). Note: it is assumed that 12vdc will be used to power the SSR. If powered by 5vdc, you may use 680-ohm resistors instead; if powered by greater than 12vdc, use 1.5K ohm resistors. 7. Optional: Install the five terminal blocks in their locations. Terminal blocks are designed so that they link together, so do that first and then insert the row of 5 together so that the openings are toward the side of the board, not toward the center; solder in place. 8. Install the transistors in their locations, orienting the transistor’s outline to match the outline on the silkscreen. Transistors must be installed with the correct orientation or they won’t work. From left-to-right, the four holes are E-BC-B, which stands for emitter, base, collector and base. The extra base hole is for transistors which don’t follow the E-B-C format but use the E-C-B order instead. This is the case for the KSC2328AYBU. The dots beneath the transistor outline are reminders of which holes to use for the type of transistor chosen: DirkCheap817 Assembly & User Guide – Page 2 Transistors are manufactured in multiple packages and the package type for this example is called a “TO-92” case, and this format is a very economical way for manufacturers to produce transistors. However, there are variations in the shapes and sizes of the cases, but more importantly, the order of the transistor leads must be recognized. In the example to the right, notice that the 2222 type is generally EBC while the KSC2328 is ECB. For the KSC2328, simply spread the leads apart a bit more and insert E into the “E” hole, C into the “C” hole and the B lead into the additional “B” hole just outside and to the right of the outline on the board. Another case type is called the “TO-18” and it’s usually a round, metal case such as the example to the left. 2N2222A transistors are often packaged this way, and the larger case type makes a difference: this type can often handle more current – 800ma in this example. Whichever case type your transistors have, just be sure that the proper transistor lead is inserted into the proper hole! NOTE: Transistors are a bit sensitive to heat, so when you solder them into the circuit board, don’t over-do it. You might solder one lead on each transistor at a time instead of all three leads in succession. This way the transistor will stay a little cooler and help prevent possible damage to it. 9. Optional: press the RJ45 jack into the space provided and solder it in place. 10. If the DIP-16 socket was installed, now insert the PC817 ICs into the socket, making certain that pin 1 of each PC817 chip is in the upper LEFT corner. 11. This completes assembly of the SSR. Turn it over, check your soldering so that each pad is nice and shiny and smooth and that there are no large solder blobs or accidental solder bridges between pads. Parts Substitutions As mentioned earlier, many NPN-type transistors can be substituted, each providing a different amount of collector current. In most cases the 470-ohm resistor will work, but you may find different resistor values may be required. Consult the data sheet for the selected transistor. It is okay to use different transistors for each of the 817’s outputs if you wish, and then each would obviously provide different current outputs. The set of four PC817 optocouplers can be replaced by a single K847PH chip. The K847PH is essentially four 817’s on a single chip. The 817’s were selected because they could be purchased on eBay for about 5cents each while the K847PH chip was far more expensive. The 680-ohm resistors for the LED and the left side of the PC817 chips can generally be replaced with other resistor values between 470-750 ohms, but performance may be affected if substituted values get too far out of this range. Remember that the current through the 680ohm resistors is coming from the controller itself and 680-ohms was chosen to keep the current draw of the SSR down so as not to overtax the controller’s output capability. DirkCheap817 Assembly & User Guide – Page 3 Using the DirkCheap817 The DirkCheap817 is designed to work in harmony with other DIY SSRs without changing controller firmware or connection settings. It uses the normal +5v connection on pin 1 of the RJ45 jack and pins 2-4-6-8 are switched to ground to turn the channel on. A connection back to the controller’s DC ground on pin 7 of the RJ45 jack will illuminate the 817’s LED showing that the SSR has a connection back to the controller, but the pin 7 connection is otherwise not required for the SSR to function. Pin 7 is a common ground connection between most DIY controllers and SSRs through the cat5 control wire. DC Power injection. External DC power must be supplied to the +DCIN- power injection point as marked on the circuit board. +V is the left terminal; -V/GND is the right terminal; the channel outputs retain the same left-right polarity order. The transistors can accommodate voltages from 5-30vdc and some may tolerate up to 40vdc). ALTERNATE power injection method: Beneath the RJ45 jack on the bottom of the SSR are markings for alternate power injection through the cat5 wire itself with +V on pin 3 and –V/GND on pin 5. To connect the power from the cat5 wire to the SSR, simply create a solder bridge between each pair of square pads on the bottom; across the pin 3 pads to connect +V and across the pin 5 pads to connect –V/Gnd. CAUTION: cat5 wires are quite thin. You must observe the proper limitations for the amount of voltage and current you can push through cat5 wire. If you do an Internet Google search for “cat5 wire current rating” you’ll be able to find out all you need to know. Take heed of the limits because putting too much electricity through too small a wire can cause a fire. Electrical Safety The DirkCheap817 does not include a fuse. It is the end user’s responsibility to provide fused electrical protection by incorporating an appropriate in-line fuse into the power injection method chosen. Connecting devices to the SSR outputs For safety, avoid connecting anything while power injection is turned on. Remember to connect the + line of the device to the + terminal of the SSR and the – or ground line of the device to the – terminal of the SSR. Remember that all devices controlled by the SSR outputs must use the same DC voltage. DirkCheap817 Assembly & User Guide – Page 4