Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits
advertisement

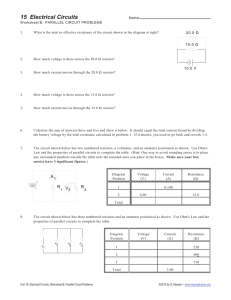
Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits • VARsC = volt-amperes-reactive (reactive power) • VA = volt-amperes (apparent power) • PF = power factor θ = angle theta ( the angle the voltage and current are out of phase with each other) Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Objectives: • Discuss the relationship of resistance (R) and capacitance (C) in an R-C series circuit. • Calculate all circuit values in an R-C series circuit. • Discuss power factors and angle theta in an R-C series circuit. Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Impedance (Z) • Total circuit impedance is the vector addition of resistance (R) and capacitive reactance (XC). • Z = √R2 + XC2 Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits • Z = total circuit impedance • I = total circuit current • ER = voltage drop across the resistor • P = watts (true power) • C = capacitance • EC = voltage drop across the capacitor Vector addition of impedance. Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Total Current (I) • Total circuit current is equal to the applied voltage divided by the impedance. • IT = E / Z Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Capacitance and Capacitive Reactance • Capacitance (C) = 1 / (2fXC) • Capacitive reactance (XC) Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Voltage Drop across the Resistor • In a series circuit, the current is the same in all parts of the circuit. Therefore, all the current flows through the resistor. This results in a measurable voltage drop across the resistor (Ohm’s law). • ER = I x R Vector addition of voltage drops. Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Voltage Drop across the Capacitor • In a series circuit, the current is the same in all parts of the circuit. Therefore, all the current flows through the capacitor. This results in a measurable voltage drop across the capacitor (Ohm’s law). • E C = I x XC True Power • True power (P) is measured in watts and is produced by only the resistor (Ohm’s law). • P = ER x I Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Reactive Power • Reactive power (VARsC) is the product of the capacitor volt drop times the current. • VARsC = EC x I Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Angle Theta • Angle theta is the number of degrees that the voltage and current are out of phase. • cosine (PF)-1 = θ • Try using the inverse or second function on your calculator to convert between the power factor and theta. Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Apparent Power • Apparent power (VA) is the product of the applied voltage times the current. • VA = ET x I • Vector addition and the Pythagorean theorem allow the use of another formula. • VA = √P2 + VARsC2 Angle theta is the degrees of separation. Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Power Factor • Power factor (PF) is a ratio of the true power to the apparent power. • PF = P / VA or PF = Watts / VA • PF = cosine θ Example circuit with values. Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Review: 1. The amount of phase angle difference between voltage and current in an R-C series circuit is the ratio of resistance to capacitance. 2. True power is only produced by resistive parts. Unit 22 Resistive-Capacitive Series Circuits Review: 3. Power factor is the ratio of true power to apparent power. 4. In a series circuit, the current is the same through all the components. Therefore, the voltage drops across the resistive and capacitive parts become out of phase with each other.