PHYS 155 Midterm 2 Slides
advertisement

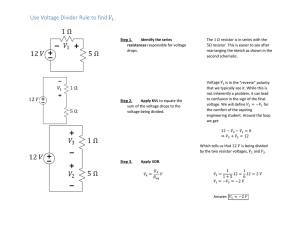
PHYS 155 Midterm 2 Tutorial Example 1: Photoelectric Effect A phototube with a zinc cathode is created and connected to a variable voltage supply. The work function for zinc is 4.31 eV. A. What is the lowest frequency of light that will release photoelectrons from the zinc surface? Assume the voltage supply is supplying no voltage. B. If photons of wavelength 225nm are incident on zinc, what is the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected photoelectrons? C. What minimum stopping voltage is required to keep emitted photoelectrons from reaching the anode? Note: h = 6.626 x 10-34 Js Example 1: Photoelectric Effect Answers A. 1.042 x 1015 Hz B. 1.20eV C. 1.20V Note: h = 6.626 x 10-34 Js Example 2: Resistivity A tungsten wire (ρ = 5.6 x 10-8 Ωm) of length L has a cross-sectional area of 0.600mm2. A. Plot the power P dissipated in the wire as a function of length L from L=0m to L = 5m. B. What is the power dissipated by the wire at L = 1.5m? What is the current through the wire? C. What would happen to this plot if the radius of the wire was decreased by a factor of 2? Example 2: Resistivity Answers A. P = 8.678571/L B. P = 5.7857W; I = 6.43A C. Plot is scaled down by a factor of 4 P = 2.169643/L Example 3: Mesh Analysis Write current equations for the following circuit with a maximum 3 current loops. What happens to the current through the 2Ω resistor if the 1V battery is changed to a 10V battery? Example 3: Mesh Analysis Solution -4V = 3I1 + 0I2 + 0I3 5V = 0I1 + 2.8I2 – 0.8I3 -3V = 0I1 – 0.8I2 + 0.8I3 Example 4: Superposition Take the simplified circuit from Example 3 and prove the independence of the 1V battery from the 2Ω resistor using superposition. Also, find the current through the 4Ω resistor. Example 4: Superposition Solution Current through 4 Ω resistor = 1.11A 1V battery is independent because the rest of the circuit is short circuited when the other batteries are short circuited. Example 5: RC Transient Properties Consider the following circuit and answer the questions: A. Switch 1 and 2 closed: find charging time to 85% of supply voltage, total charge and energy at 85%. Switch 1 becomes open when charge hits 85% while Switch 2 stays closed: find discharge time to 10% of supply voltage. Example 5: RC Transient Properties B. Switch 1 and 2 are closed for a long time. Switch 1 and 2 are then opened. Switch 2 and 3 are then closed at the same time. What is the time it takes for the voltage across the capacitors to each 18V? What is the instantaneous current flow at this time?