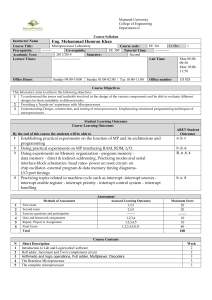
Course Outline
advertisement
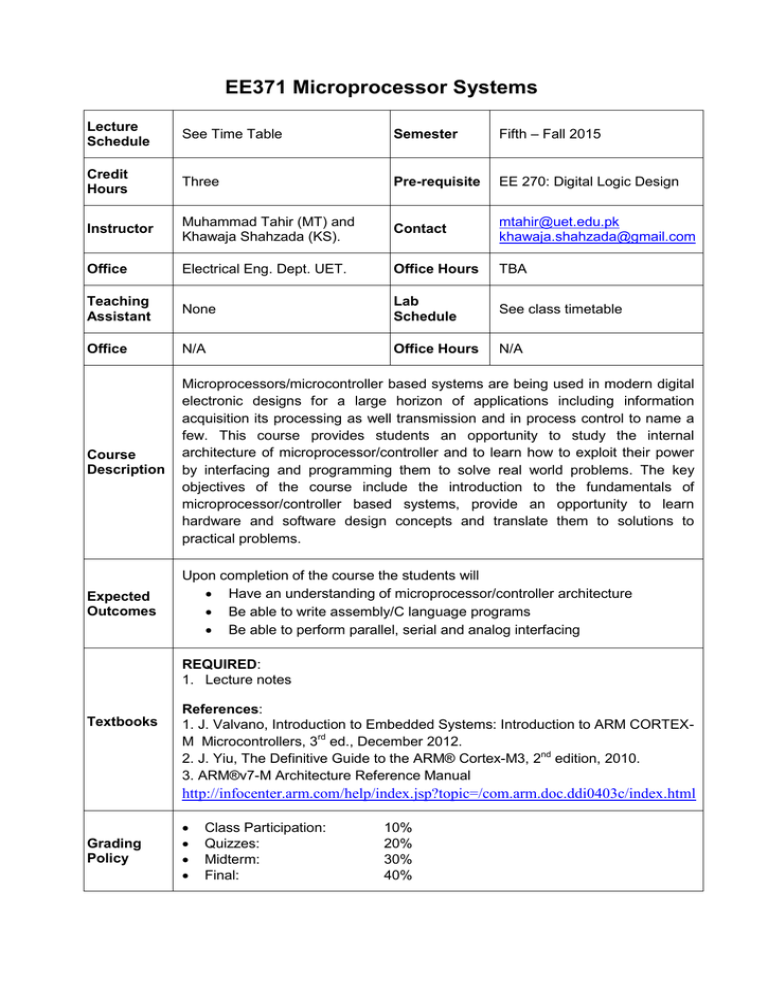
EE371 Microprocessor Systems Lecture Schedule See Time Table Semester Fifth – Fall 2015 Credit Hours Three Pre-requisite EE 270: Digital Logic Design Instructor Muhammad Tahir (MT) and Khawaja Shahzada (KS). Contact mtahir@uet.edu.pk khawaja.shahzada@gmail.com Office Electrical Eng. Dept. UET. Office Hours TBA Teaching Assistant None Lab Schedule See class timetable Office N/A Office Hours N/A Course Description Microprocessors/microcontroller based systems are being used in modern digital electronic designs for a large horizon of applications including information acquisition its processing as well transmission and in process control to name a few. This course provides students an opportunity to study the internal architecture of microprocessor/controller and to learn how to exploit their power by interfacing and programming them to solve real world problems. The key objectives of the course include the introduction to the fundamentals of microprocessor/controller based systems, provide an opportunity to learn hardware and software design concepts and translate them to solutions to practical problems. Expected Outcomes Upon completion of the course the students will Have an understanding of microprocessor/controller architecture Be able to write assembly/C language programs Be able to perform parallel, serial and analog interfacing REQUIRED: 1. Lecture notes Textbooks References: 1. J. Valvano, Introduction to Embedded Systems: Introduction to ARM CORTEXM Microcontrollers, 3rd ed., December 2012. 2. J. Yiu, The Definitive Guide to the ARM® Cortex-M3, 2nd edition, 2010. 3. ARM®v7-M Architecture Reference Manual http://infocenter.arm.com/help/index.jsp?topic=/com.arm.doc.ddi0403c/index.html Grading Policy Class Participation: Quizzes: Midterm: Final: 10% 20% 30% 40% Lecture Plan Weeks* Topics Readings 0.5 Overview of the course, embedded systems, microprocessor vs. microcontroller, classification of processor architectures, development tools Chapter 1 (Lecture notes) 1.5 Why ARM architecture? Introduction to ARM- Cortex-M3, architecture, registers, ALU, Buses, Operating modes, Memory Map, Reset Sequence, Pipelining Chapter 2 (Lecture notes) 1.0 Why assembly programming? Introduction to Cortex–M assembly programming Chapter 4 (Lecture notes) 1.0 Shift & arithmetic operations, other useful data processing instructions Chapter 5 (Lecture notes) Quiz1 1.5 Memory access instructions, use of stack and parameter passing, memory addressing modes Chapter 6 (Lecture notes) 2.0 Branch instructions, unconditional and conditional branches, functions Chapter 7 (Lecture notes) 0.5 Introduction to ARM based microcontrollers Chapter 8 (Lecture notes) Mid Term 1.0 I/O, Stellaris LM4F I/O pins, Basic concepts of I/O ports and Interfacing, Clock sources and Clock configuration, the concept of PLL Chapter 8 (Lecture notes) 1.0 ARM Cortex-M interrupt architecture, interrupt configuration, interrupt vector table, interrupt handling Chapter 3 (Lecture notes) 1.0 I/O synchronization, Interrupt concepts, Peripherals Interrupts, Nested Interrupts Chapter 9 (Lecture notes) 1.0 Timers, configuration and their interrupts, SysTick Timer, Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Chapter 10 (Lecture notes) Quiz 2 1.5 Serial Communication (Asynchronous UART and Synchronous SPI, I2C), basic configuration, polling & interrupt driven transmission & reception Chapter 11 (Lecture notes) 1.5 Analog I/O, A/D and D/A conversion, Real-time data acquisition Chapter 12 (Lecture notes) 1 Networking of embedded systems (advanced topics) Class notes Final List of Experiments Sr. No. Title of the Experiment 1 Introduction to laboratory hardware and tools 2 Introduction to C Language Programming 3 Assembly Language Programming fundamentals 4 Assembly Language Instructions 5 Use of memory addressing modes 6 Controlling the execution sequence 7 Use of stack and parameter passing 8 Digital Input/Output interfacing and programming 9 Interfacing Seven Segment display parallel interfacing 10 External/internal Interrupts and ISR programming 11 Timers and time base generation 12 Asynchronous serial interfacing (UART) 13 Analog interfacing 14-15 16 Mini project Project evaluations