Ch. 18 Network Theorems
advertisement

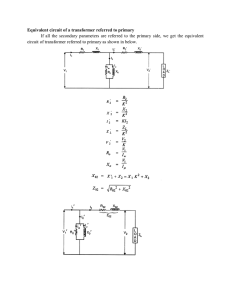
7/31/2014 Chapter 18 AC application of Chapter 9 ◦ Superposition theorem for independent and dependent sources. ◦ Thévenin’s theorem for independent and dependent sources. ◦ Norton’s theorem for independent and dependent sources. ◦ Maximum power transfer to a load in an ac network with independent or dependent sources. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 2 1 7/31/2014 18.1-18.2 ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 3 “The current through, or voltage across, any element of a network is equal to the algebraic sum of the currents or voltages produced independently by each source” ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 4 2 7/31/2014 In general, the theorem can be used to do the following: ◦ Analyze networks that have two or more sources that are not in series or parallel. ◦ Reveal the effect of each source on a particular quantity of interest. ◦ Solve networks with AC and DC sources ◦ Solve for multi-frequency networks NOT used directly for finding power FIG. 9.1 Removing a voltage source and a current source to permit the application of the superposition theorem. 3 7/31/2014 FIG. 18.1 Example 18.1. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 7 FIG. 18.3 Determining the effect of the voltage source E1 on the current I of the network in Fig. 18.1. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 8 4 7/31/2014 FIG. 18.4 Determining the effect of the voltage source E2 on the current I of the network in Fig. 18.1. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 9 ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 10 FIG. 18.5 Determining the resultant current for the network in Fig. 18.1. 5 7/31/2014 FIG. 18.6 Example 18.2. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC FIG. 18.8 Determining the effect of the current source I1 on the current I of the network in Fig. 18.6. 11 FIG. 18.9 Determining the effect of the voltage source E1 on the current I of the network in Fig. 18.6. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 12 6 7/31/2014 FIG. 18.10 Determining the resultant current I for the network in Fig. 18.6. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 13 Mixed sources require careful approach In DC ◦ Capacitors are ______ ◦ Inductors are _______ FIG. 18.12 Example 18.4. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 14 7 7/31/2014 DC FIG. 18.13 Determining the effect of the dc voltage source E1 on the voltage v3 of the network in Fig. 18.12. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 15 AC FIG. 18.14 Redrawing the network in Fig. 18.12 to determine the effect of the ac voltage source E2. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 16 8 7/31/2014 FIG. 18.15 Assigning the subscripted impedances to the network in Fig. 18.14. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 17 FIG. 18.17 The resultant voltage v3 for the network in Fig. 18.12. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 18 9 7/31/2014 18.3 ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 19 Simplify VOLTAGE source from the load’s perspective ONE FREQUENCY PER EQUIVALENT FIG. 18.23 Thévenin equivalent circuit for ac networks. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 20 10 7/31/2014 ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 21 Find VR FIG. 18.25 Assigning the subscripted impedances to the network in Fig. 18.24. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 22 11 7/31/2014 FIG. 18.26 Determining the Thévenin impedance for the network in Fig. 18.24. FIG. 18.27 Determining the open-circuit Thévenin voltage for the network in Fig. 18.24. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 23 Load returned to circuit FIG. 18.28 The Thévenin equivalent circuit for the network in Fig. 18.24. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 24 12 7/31/2014 Find Thevenin equivalent FIG. 18.29 Example 18.8. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 25 FIG. 18.31 Determining the Thévenin impedance for the network in Fig. 18.29. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 26 13 7/31/2014 FIG. 18.32 Determining the open-circuit Thévenin voltage for the network in Fig. 18.29. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 27 FIG. 18.33 The Thévenin equivalent circuit for the network in Fig. 18.29. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 28 14 7/31/2014 For any circuit ◦ ◦ ◦ = = = ◦ Dependent Sources Same formulas, controller values used as placeholders ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 29 18.4-18.5 ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 30 15 7/31/2014 Simplify CURRENT source from the load’s perspective ONE FREQUENCY PER EQUIVALENT FIG. 18.60 The Norton equivalent circuit for ac networks. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 31 32 16 7/31/2014 FIG. 18.61 Conversion between the Thévenin and Norton equivalent circuits. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 33 Find Norton equivalent FIG. 18.62 Example 18.14. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 34 17 7/31/2014 FIG. 18.63 Assigning the subscripted impedances to the network in Fig. 18.62. FIG. 18.64 Determining the Norton impedance for the network in Fig. 18.62. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 35 FIG. 18.65 Determining IN for the network in Fig. 18.62. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 36 18 7/31/2014 Must be converted to real components Load returned to circuit FIG. 18.66 The Norton equivalent circuit for the network in Fig. 18.62. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 37 ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 38 FIG. 18.67 Example 18.15. 19 7/31/2014 FIG. 18.68 Assigning the subscripted impedances to the network in Fig. 18.67. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 39 ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 40 FIG. 18.69 Finding the Norton impedance for the network in Fig. 18.67. 20 7/31/2014 FIG. 18.71 Determining IN for the network in Fig. 18.67. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 41 FIG. 18.72 The Norton equivalent circuit for the network in Fig. 18.67. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 42 21 7/31/2014 FIG. 18.73 Determining the Thévenin equivalent circuit for the Norton equivalent in Fig. 18.72. FIG. 18.74 The Thévenin equivalent circuit for the network in Fig. 18.67. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 43 “When applied to ac circuits, the maximum power transfer theorem states that maximum power will be delivered to a load when the load impedance is the conjugate of the Thévenin impedance across its terminals.” = =− ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 44 22 7/31/2014 will be purely resistive ◦ =1 Fixed load resistance ◦ = FIG. 18.81 Defining the conditions for maximum power transfer to a load. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 45 FIG. 18.83 Example 18.19. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 46 23 7/31/2014 FIG. 18.84 Determining (a) ZTh and (b) ETh for the network external to the load in Fig. 18.83. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 47 Find where max power is available ◦ = ℎ + ◦ = ◦ = ◦ + = FIG. 18.90 Example 18.21. ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 48 24 7/31/2014 No questions covering dependent sources are assigned ECET 207 AC Circuit Analysis, PNC 49 25