Lab 8 Thevenin`s Theorem and Maximum Power Transfer Objective
advertisement

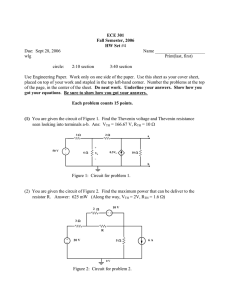
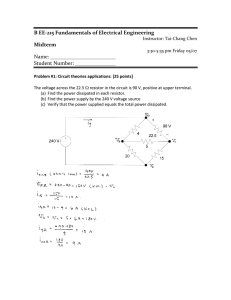
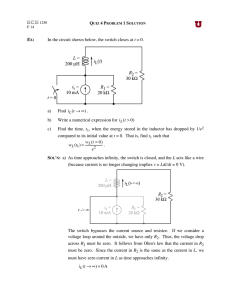
Page 1 of 2 Name: ______________________________ ECET 231 - Circuit Analysis I Lab 8 Thevenin’s Theorem and Maximum Power Transfer Objective: Students successfully completing this preparatory exercise will accomplish the following objectives: 1. Gain increased familiarity with the Superposition Theorem. 2. Determine the Thevenin equivalent of a complex circuit by both calculation and measurement. 3. Determine the value of a load resistor which will allow maximum power transfer to the load. Equipment: Power supply, Digital Multimeter (DMM), breadboard, resistors, jumper wires. Procedure: 1. Select four resistors: R1 = R2 = R3 = R4 = 2.2 kΩ. Measure the values of each of these and record your results in Table 1 below. Table 1: Measured resistor values Resistor Measured Value R1 R2 R3 R4 2. Using your measured resistor values, calculate the Thevenin equivalent external to RL for the circuit of Figure 1. Use superposition to determine ETh. Enter your calculations into Table 2. Figure 1: Parallel circuit with two sources Table 2: Thevenin equivalence calculations by superposition Quantity Vab1 (Due to E1) Vab2 (Due to E2) VTh (Vab1 + Vab2) RTh Calculation Page 2 of 2 3. Construct the circuit of Figure 1, leaving out RL. Measure the terminal voltage Vab. This is the Thevenin voltage. Does this compare favorably with your calculated value? ____________ Also measure the short circuit current Iab. Record your results in Table 4 below. 4. Install a 130 Ω resistor in the circuit as RL. Measure Vab and IL. Record your results in Table 4. 5. Replace RL with each of the following resistors one at a time: 470 Ω, 1 kΩ, 2.2 kΩ and 4.7 kΩ. Repeat the measurements of step 4 for each resistor. Record these results in Table 4. 6. Replace RL with a potentiometer. Adjust RL until the voltage Vab is equal to half the Thevenin voltage (Eth / 2). By the Maximum Power Transfer Theorem, this will be voltage at which maximum power is transferred to the load resistor. Carefully remove the potentiometer so as not to accidentally readjust it. Measure its resistance and record the result below. Calculate the percent difference between this measurement and the calculated value of Rth using the following formula: ⎛ Quantity A − Quantity B ⎞ ⎟⎟ × 100% % Difference = ⎜⎜ Quantity B ⎝ ⎠ Table 3: Comparison of RL to RTh at VRL = Eth / 2 RL (Potentiometer) 7. RTh (Previously calculated) % Difference Set a voltage source to your calculated value for the Thevenin voltage, Eth. Construct the Thevenin equivalent circuit using a potentiometer to achieve RTh. Measure the terminal voltage Vab and the short circuit current, Iab. Also measure the load resistor voltages and currents for each of the resistors of steps 4 and 5. Record your results in Table 4. Table 4: Measured load voltages and currents Load Resistance 0Ω 130 Ω 470 Ω 1 kΩ 2.2 kΩ 4.7 kΩ Open circuit Figure 1 Vab Thevenin Equivalent Iab Vab Iab % Difference Vab Iab