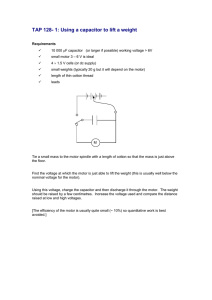
compendium of research activities 2011-2012
advertisement

JKU/2/33/65(12) DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING COMPENDIUM OF RESEARCH ACTIVITIES 2011/2012 1.0 Ongoing Research Topic Multi-Antenna Techniques for Quality of Services (QoS) Improvement in Wireless Communication System. Researcher(s) Muiga Rugara, D. O. Konditi, S. Musyoki, Langat Kibet, Kariuki Ngige. Ongoing Status of the Research Topic Researcher(s) Design and Analysis of Neural Fuzzy Based DC-DC Converter Controller Optimized with Swarm Intelligence Kanai .M Michael, John .N Nderu and Peterson .K. Hinga Status of the Research Ongoing Topic: Impact of Fuzzy and Neural Network Techniques in Dynamic Load Modelling for Voltage Stability Analysis Researcher(s): C. M. Muriithi, L. M. Ngoo, G. N. Nyakoe Status of Research: Submitted Thesis for Examination Topic Researcher(s) Possibility of Deregulating Retail Electricity Market for 5 heavy Industrial Electricity Consumers in Kenya George K Irungu Status of the Research ongoing Topic Study of existing Solar PV Home Systems with an intension of developing a customized Kenyan solar PV home system. Researcher(s) Shtomu Ohzuku, Gideon G. Kidegho, George Nyakoe Status of the Research Ongoing Topic Performance analysis of mobile ad hoc network routing protocols using Self Organising Map (SOM) Researchers Mureu Ephraim W., Stephen Musyoki and Peter Kihato Status of the Research Ongoing JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 1 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) Topic Underdetermined Blind Speech De-Noising for Enhanced Teleconferencing Using Machine Intelligence. Researchers Denis Ombati , . E N Ndun‘gu and L. M. Ngoo Status of the Research Topic: Ongoing Electronic Load Controller for Mini/Micro Hydro Power Generation Researcher(s): C. K. Kitur, J. N. Nderu, K. Kaberere Status of Research Ongoing Topic: Researcher(s): Static Voltage Stability Analysis of Nairobi Area Power Distribution Network S. Oketch, C. M. Muriithi, K. K. Kaberere Status of Research: Ongoing Topic: Adaptive Real-Time and Virtual Monocular Car Vision using Modular Artificial Neural Networks Researcher(s): Inno Odira, P. K. Kihato, S. I. Kamau Status of Research: Ongoing Topic: Application of Neural Network for Short Term Load Forecasting Researcher(s): Ireri T. Gichovi, N. O. Abungu, D. K. Murage Status of Research Ongoing Topic: Researcher(s): Enhancement Of Electrical Power Supply Using Grid Connected Photovoltaic Generation: A Case Study Of Nairobi Embakasi Suburb G.G. Kidegho, K.K. Kaberere, M.S. Mbogho Status of Research Ongoing Topic Researcher(s) Analysis and Design of Electrical machines Speed monitoring systems using Amorphous wires J.N. Nderu, Dr. P.K. Kihato, A. Muhia Status of the Research Ongoing JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 2 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) Topic Researcher(s) Status of the Research Performance Analysis of a Generator Operating on Dual Fuel Comprising of Biogas and Diesel Nelson Muchiri Gachoki, Peterson K. Hinga, Njeri S. Kahiu, Stephen Wanjii Ongoing Topic: Application of Neuro-Fuzzy Control Technique in a Three-phase Hybrid Power Filter for Harmonic Mitigation. Researcher(s): Nelson K Bett, P. K. Hinga, J. N. Nderu Status of Research Ongoing JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 3 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) 2.0 Completed Research Title Impact Of Fuzzy And Neural Network Techniques In Dynamic Load Modelling And Voltage Stability Analysis Researcher(s) C. M. Muriithi, L. M. Ngoo, G. N. Nyakoe Background: This research deals with modeling and description of the dynamic load characteristics for long-term voltage stability studies. The main component of the dynamic loads constitutes the induction motor loads. The research comprised of developing a neuro-fuzzy induction motor load model which was then incorporated in a Newton-Raphson power flow algorithm. The modified load flow incorporates a neuro-fuzzy induction motor load model that estimates the scheduled active and reactive power adjustable during each iteration process. The impact of the aggregated induction motor on the convergence characteristics of load flow are investigated using the IEEE-30 bus standard test system. Based on the load flow results, counter propagative artificial neural networks were used to classify buses in order of weakness. In this research, the neuro-fuzzy model of an induction motor load was extended into the Continuation Load flow algorithm, where the impact of different induction motor ratings on the voltage stability margin was investigated. The research finally investigates the impact of the Fuzzy Logic based Power System Stabilizer (FLPSS) in maintaining short term voltage stability in a system with Induction Motor Loads. From the analysis which compared the FLPSS with other PSS found in literature, it was shown that the FLPSS could not maintain stability of an induction motor load after being subjected to a fault. Methods: Modeling of an induction motor load using neuro-fuzzy techniques has been illustrated and a novel method of solving the load flow equations with neuro-fuzzy induction motor models. This novel load flow is tested on the IEEE 30 bus system. In addition, a novel method of solving the continuation load flow equations with neuro-fuzzy induction motor models.In this algorithm, the load increment was carried by increasing the induction motors loads modeled using neuro-fuzzy techniques. Finally, the impact of fuzzy logic PSS on short term dynamic voltage stability is investigted. The system to be evaluated was simulated in detail in Simulink®. The generators were also fitted with the governor and excitation system, with the possibility of JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 4 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) selecting different PSS to be compared in the analysis. Further an induction motor load with undervoltage protection has been modeled. In this set up, an investigation is carried out of the impact of fuzzy logic PSS in a multi machine system with a large induction motor load. Results: The conventional load flow algorithm upgraded to incorporate the non-linear neuro-fuzzy model of induction motor load showed improved accuracy, though at reduced convergence rate. Further, a novel continuation load flow algorithm that incorporates neuro-fuzzy induction motor loads has been developed and analyzed indicating the need to model loads so as to give an accurate assessment of the security margin. Finally, the effects of the excitation system equipped with PSS have been shown to be very crucial in voltage stability studies. Conclusions: The neuro fuzzy model of an induction motor load aided in assessing more accurately the security margins of a given system. This is crucial information for power system engineers. On the other hand, the Fuzzy Logic Power System Stabilizer failed to maintain the stability of the system with an induction motor load. Title Impact of Spartial Diversity Techniques In Combating Interference and Multipath Fading in Wireless Communication Systems. Researcher(s) Muiga Rugara, D. O. Konditi, S. Musyoki Background: The next-generation wireless communication systems are required to have high voice quality as compared to current cellular mobile radio standards and provide high bit rate data services (up to 2 Mbits/s). At the same time, the remote units are supposed to be small lightweight pocket communicators. Furthermore, they are to operate reliably in different types of environments: macro, micro, and picocellular; urban, suburban, and rural; indoor and outdoor. However wireless communication systems require signal processing techniques that improve the link performance in hostile mobile radio environments. Most existing wireless systems use simple antenna arrays transmitting in a fixed direction (directional antennas) or all directions (omnidirectional antennas). This causes interference between subscribers. Furthermore, with the rapid increase in cellular subscription, capacity will be an issue in future communication systems, One approach to increase capacity is to reduce interference and compensate for multipath fading and a cost effective method of achieving this is the use of diversity techniques. The technique proposed in this paper is a simple transmit diversity scheme which improves the signal quality at the receiver on one side of the link by simple processing at the transmit antennas on the JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 5 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) opposite side. The proposed transmit diversity scheme will improve the error performance, data rate, or capacity of wireless communications systems. The scheme may also be used to increase the range or the coverage area of wireless systems. Methods: To demonstrate the optimum combining in a fading environment, an experimental system will be modeled and simulated. Simulation will comprise an m transmit antennas and n receive antennas, a channel estimator will be used at the receiving antennas. The combiner builds the incoming signals that are sent to the maximum likelihood detector. These combined signals are then sent to the maximum likelihood detector which, for each of the signals uses the decision rule to determine the strongest signal combination. The resulting combined signals will be expected to be equivalent to that obtained from two-branch MRRC. The only expected difference is phase rotations on the noise components which do not degrade the effective SNR. Therefore, the resulting diversity order from the new m-branch transmit diversity scheme with n receivers is expected to be equal to that of two-branch MRRC. Results: A 2-transmit 2-receive (2x2) MIMO channel with Maximum Likelihood (ML) decoding receiver structures gives a good performance. However it is inferior to alamouti 2-transmit 2-receive STBC. However, it was found that the use 2×2 MIMO with Maximum Likelihood (ML) equalization achieves a performance closely matching the 1 transmit 2 receive antenna Maximal Ratio Combining (MRC) case. It is also apparent that the use of a higher order constellation like 64 QAM, then computing Maximum Likelihood equalization might become prohibitively complex. With 64 QAM and 2 spatial streams we need to find the minimum from 642 = 4096 combinations. In such scenarios we might need to employ schemes like sphere decoding which helps to reduce the complexity and which are outside the scope of this research. Conclusions: Use of multiple antennas at the transmitter and the receiver in wireless communication systems have been known to increase diversity to combat channel fading. Each pair of transmit and receive antennas provides a signal paths from the transmitter to the receiver. By sending signals that carry the same information through different paths, multiple independently faded replicas of the data symbol can be obtained at the receiver end; hence more reliable reception is achieved. It is also clear that the BER performance for a 2-transmit 2-receive (MIMO) Alamouti STBC Channel is much better than 1-transmit 2receive antenna MRC case. This is because the effective channel concatenating the information from 2 receive antennas over two symbols results in a diversity order of 4. In general, with N receive JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 6 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) antennas, the diversity order for 2 transmit antenna with Alamouti STBC is 2N. As with the case of 2-transmit, 1-receive Alamouti STBC, there is no cross talk after the equalizer since the matrix is diagonal and the noise term is still white. Title: Load Modeling and Comparison of Aggregation of Induction Motor Loads in a Power System for Voltage Stability Analysis Researcher(s) J.K. Muriuki, C.M.Muriithi, D.K.Murage Background: Induction motors constitutes a large percentage of power system components and may cause voltage instability if not properly controlled under fault conditions. This is more pronounced in developing nations where the demand for power surpass the supply thereby, compelling power system to operate at very low power reserves and particularly during the peak loads. The power system network is also expanding daily thereby distressing the existing generation, transmission, distribution capacity and protection controls. It is therefore important to ensure that there is enough power generation by interconnecting countries power bank to form one large power pool thus improving the power supply reliability and quality. It is also crucial to analyze and compare the parameters of the aggregate induction motors of different sizes under most of the operating conditions of the power system. The two methods are transformer-equivalent circuit (method 1) and no-load and locked rotor (method 2).The two methods of aggregation were selected because they are accurate in motor parameter identifications and therefore better suited for comparison purposes. Also the methods were selected because researches on their comparison have not been systematic. This necessitates exact modeling of the power system load which is a difficult problem because the power system loads are aggregation of many and different devices. It is vital to understand dynamic load behavior of various consumers which in more often has proved to be a challenge. Static loads are inaccurate in capturing the characteristics of the load under various operating conditions and therefore dynamic load is considered necessary when studying voltage instability because it captures the actual behavior of the load at a particular time. Methods: The two methods of aggregations were compared to identify their accuracy in identification of aggregate motor parameters for voltage stability analysis. The range of motor used was classified as small ranging from 3hp to 100hp and large motors ranging from above 100hp to 2250hp. The IEEE 16 bus system was used for the setup and analysis. A MATLAB code was written to identify the aggregate motor JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 7 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) parameters for both small and large motors. For the simulation results, the small and large induction motors whose total load was 2250hp were inserted in bus 3 of the IEEE16 bus and their parameters identified under steady-state and under system disturbance. The parameters obtained were compared to the standard motor parameters to identify their accuracy using the two methods of aggregations. Results: Further, the effects of Multi-Band Power System Stabilizer (MBPSS) on the aggregation of the motor parameters using the two methods of aggregation were compared to identify the most accurate. From the analysis carried out it has been shown that method 2 is superior to method 1 in identification of the aggregate motor parameter, and at the same time, it has shown improved results under the influence of MB-PSS under system disturbance. The aggregation method 2 showed improved accuracy in identification of the small and large aggregate motor parameters compared to method 1 under steady-state and under system disturbance. The inclusion of MB-PSS in the generator showed improved performance of the aggregate motor parameters for method 2 compared to method 1. Finally, the effects of the excitation system equipped with MB-PSS have been shown to be very crucial in voltage stability studies using method 2 of motor aggregations. Conclusions: It has been shown that static loads are unsuitable in describing the load dynamics under various power system operating conditions. They therefore, give false expression of the power system stability. The results also confirm that parameters to which the measurements have large sensitivities are observable and could be identified, while those to which the measurements have small sensitivities are hard to be identified. The accuracy of the aggregation method based on the two aggregation methods was compared. The results show that, method 1 is inferior in identification of the aggregated motor parameters for both small and large IM compared to method 2. The simulation results drawn a close resemblance thereby validating the method applied. Therefore, method 2 is best suited for voltage stability analysis. The comparison for the aggregation method 1 and 2 under the influence of Multi-Band Power System Stabilizer (MB-PSS) for voltage stability analysis was investigated. The result shows that aggregation method 2 is superior in identification of the aggregate active and reactive motor parameters compared to method1. With the implementation of method 2 under the influence of MB- JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 8 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) PSS, the power utilities are expected to benefit from good design and reliable protection controls, assist the energy policy makers to plan on system expansion with a view to providing resources. It will also help the power system engineers and operators to understand the system load dynamics characteristics under various disturbances thereby maintaining voltage stability. Finally, it will improve the process and accuracy of power system planning and operation and make coherent and economic decisions. Title Mitigation Of Harmonic Distortions and Low Power Factor In Unbalanced Three Phase System Using Fuzzy Logic Controller Researcher(s) Charles Ndung’u, L. Ngoo, J. Nderu Background: In recent time, the power quality has attracted a lot of attention due to extensive emphasis by power utility on the power system efficiency and end users awareness of power quality issues. This has occurred mainly due to the sensitivity of the modern equipment and the deregulation of the power distribution. In addition, there are usually massive losses both to power utility and end users which result in poor power quality supplies which fall below the set standards. Power quality primarily constitutes of voltage dip/ swell, power system interruptions (power outage), harmonic distortions, voltage flickers and frequency deviations. Research done on both power utility and customers revealed that power outage caused myriad complains from the customers seconded by harmonic distortion which was raised by both parties. Nevertheless, end users sector suffer more from harmonic problems than does the utility sector. Industries with Adjustable Speed Drives (ASD), arc furnace, induction furnaces, are more susceptible to problems stemming from harmonic distortions. Harmonic distortion is the change in the waveform of the supply current/ voltage from the ideal sinusoidal waveform. The primary source of distortions of the waveform is non linear loads. The non linear loads generate current harmonic distortions and reactive power from ac mains. The device or equipment is said to be nonlinear when the relationship between the instantaneous voltage and current is not linear. Examples of these kinds of loads include computers, switch mode power supplies, fax and printers. They mainly consist of electronic power supplies and with the proliferation of customer loads with electronic power supplies means that the growth in the harmonic distortion system is inevitable. These non linear loads inject back harmonic distortions into power distribution systems through the Point of Common Coupling (PCC); point where end users are connected to the power grid by the power utility. Harmonic distortions have a number of adverse effects on the distribution system and at the end users. When present in the power lines results in various problems such as; greater power losses in JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 9 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) distribution and transmission lines, problems of electromagnetic interference in communication systems, operation failure of protection devices and electronic devices. In additional, they cause erroneous measurement in the energy measurement and capacitor banks failure. These problems result in high costs for industry and commercial activities, since they can lead to a decreasing in productivity and to a reduction of quality in the products or services. Inductive load requires reactive power for proper operation (magnetization) and thus the source must supply hence increasing the current from the generator and through power lines. Total current distributed through the conductors and transformer consist of two components namely; active component and reactive component High reactive current implies increase of total current. High current makes conductors and transformers to overheat (i2R) hence demanding conductors of large cross-section area and bigger size of the transformer. If reactive power is supplied near the load, the line current can be reduced or minimized and hence reducing power losses and improving voltage regulation at the load terminals. The reactive power is defined as component of the instantaneous power with frequency equal to 100 Hz in a 50 Hz system. The reactive power oscillates between the ac source and the capacitor or reactor and also between them (inductor and capacitor) at frequency equals to two times the rated value. Due to this behavior, it can be compensated using active power filter to avoid it circulating between the load (inductive or capacitive) and the source hence improving power factor at the point of common coupling. Methods: The study provides a fast compensator of harmonic current distortions and reactive power by employing fuzzy logic controller due to its ability to adapt on variations of non linear loads. This ensure that the source only supply the active power with minimum distortions which is below the admissible levels as recommended by the power quality standards. The Pulse Width Modulation control system based on time domain, the p_q theory or ‗Instantaneous Power Theory‘ which was proposed and developed by Akagi et al in 1983, is employed to generate the reference signal for Voltage Source Inverter (VSI). Fuzzy logic controller is being used to maintain the dc side of the VSI constant. Hysteresis current controller is used to generate the gating signal for Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) which neutralizes the harmonic distortions by injecting a signal similar as line harmonic distortions but with opposite sign through the coupling inductor. In addition, the study involved data collection at different metering points of utility power company. This was to establish at which point of metering high harmonic distortions exist and hence simulate the active filter capable of eliminating harmonic distortions JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 10 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) to the point identified with high harmonic distortions. Results: The researcher collected the data at various power utility system metering points and presented it in table forms for the purpose of establishing why most of large power end users are unable to achieve a power factor that is above statutory level limit of 0.9. From the data collected, it has been found that end power users supplied with voltage 0.415kV are the most susceptible due to presence of high current harmonic distortions at the point of common coupling. The sources of current harmonic distortions are generated by the non-linear loads such as electronic devices with switch power mode supply, speed variable drives and cycloconverters. The Medium and High voltage end power users are rarely surcharged on low power factor. The reason is due to availability of voltage step down Harmonic mitigation transformer before the point of common coupling (metering point) unlike the low voltage end users where generated harmonic pollution is inject back to the power system at PCC. Harmonic distortions are found to play a key role on CPF recorded by the static energy meter due to capability of sampling analogy signals (current and voltage) at high sampling frequencies than fundamental frequency. Apparently, presence of high harmonic distortions increases apparent power recorded by the energy meter consequently resulting to low CPF. It has been shown that the simulated APF improves the harmonic filtering performance and compensate for reactive power hence giving better transient and steady state response to LV power system under unbalanced condition. Simulation was done using MATLAB-SIMULINK modeling software used for dynamic systems. Conclusions: The analysis of the data obtained on harmonic distortions on utility power system and simulation carried out of APF using MATLAB – SIMULINK environment lead to the following conclusion; (a) The three phase power end users supplied by Low Voltage were generating high current harmonic distortions beyond the recommended threshold as per IEEE 519-1992 power quality standard. This has resulted to most of these end users not to meet the power factor statutory level of 0.9 as required by the power utility. The reason for not achieving the statutory PF is due to the advent of digital meters which are capable of measuring harmonic energies. (b) The energy meter measures the harmonic order levels if it has as sampling frequency higher than twice the fundamental frequency (Nyquist theorem->100Hz). Harmonic distortions increases the apparent power (kVA) measured by the energy meter and consequently recording low power factor. JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 11 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) (c) In this study, an active power filter has been used to eliminate undesirable effects of poor power factor and current harmonic distortions for low voltage power users at PCC. The active filter was simulated using IRP p_q theory algorithm proposed by Akagi and others. (d) The IRP p_q theory has proven to provide a reasonable approach analysis and hence control compensate the reactive components of non linear load. In addition it acts as appropriate measure for mitigation of Total Current Harmonic Distortion to improvement of power quality at PCC. (e) A three phase unbalanced system with a three phase IGBT rectifier supplied a resistive single phase load. The harmonic current distortions generated by non-linear load were neutralized by injecting an opposite waveforms to the system hence eliminating the distortions and compensating for reactive power in time domain. (f) It can be summarized that the simulated shunt active power filter; Compensate dynamically the currents harmonic distortions, Compensate dynamically the reactive power hence improving the power factor at PCC and Reduces the values of the currents supplied by the source to the load by compensating the reactive current required by the supplied loads. (g) Time domain provides fast response for harmonic and reactive compensation as the system parameters are analyzed on real time. This ensured that the harmonic distortion at PCC are within the recommended level by IEEE 519-1992 and the meter records a power factor well above the statutory requirement of 0.9. Title: Determination of Reactive Power Compensation and Transmission Line Power Transfer Capability Improvement of The Kenyan Power System Researcher(s) Robert Kariuki Njoroge, Keren Kaberere, Aloys Akumu Background: To supply power, utilities usually sign a supply agreement with the consumer that states details of power supply to be connected. This allows the consumers to specify the voltage rating of any electrical equipment procured for use in their premises. Once the supply is connected, the consumer expects the voltage and frequency to be maintained nearly constant within the statutory tolerances and to experience minimum interruptions. For a utility to effectively meet the requirements of the consumers, the power system must be properly controlled, where the main parameters to be controlled are voltage and frequency. To supply the system loads, a number of generating stations are JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 12 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) interconnected through transmission lines and distribution network. The frequency of the system is controlled by ensuring real power balance of supply and demand; frequency is controlled centrally. However, the transmission and distribution systems need voltage control at various points in the system to maintain the voltage at the consumer premises within permissible limits (±6%). When aggregated, loads have two power components; the active and reactive power. In addition to the consumer loads, the lines also require reactive power to establish the electric and magnetic fields. This reactive power used by the line is referred to as the reactive power losses and affect the voltage profile in a power system. Transmission lines absorb and inject reactive power and the net effect depends on line length and loading. For a heavily loaded line, reactive power loss (absorption) is more dominant. Because of reactive power losses increasing with the length of transmission lines, reactive power should not be transmitted over long distances. Unlike real power which requires suitable sites for generation and therefore has to be transmitted to load centres, reactive power can be generated at load connections. This study assessed the reactive power requirement of the Kenyan transmission network so as to enable the transmission of all available power from Seven Forks hydro stations to the load centres. Methods: The method used to determine the required reactive power compensation and the buses to be compensated was power system simulation. To enable power system simulation, a single line diagram model of the transmission network was prepared using data collected from the utility. Four scenarios were investigated by load flow analysis. i. Case one was the base case where the system was running at a peak load of 989 MW with an emergency generator in service. The emergency power plant (EPP) was generating 61.4 MW in the network at Embakasi/Nairobi. ii. In case two, the system was running at the same peak load (989 MW) with emergency plant generation (61.4 MW) replaced with generation from Seven Forks hydro complex. The hydrology was good and also the reserves in the seven forks complex were confirmed adequate to produce the required power. iii. In case three the system was at peak load (989 MW) without emergency generation, with compensation introduced in nine selected buses. The reactive power compensation was provided using the synchronous condenser method. The synchronous condensers were introduced in the network model at the nine identified buses. JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 13 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) iv. In case four, the system load demand was raised to 1047 MW which is a hypothetical demand created to study the evacuation of the full capacity of the Seven Forks hydro complex and the compensation required to achieve it. The method used to assess the transfer capability improvement of the transmission lines between Nairobi and Seven Forks Complex was by comparison of line loading (in MVA) before compensation (case two) and after compensation (case three). The difference was computed as a percentage of the initial line loading (case 2). The method used to assess the transmission line loss reduction was by comparison of line system losses as obtained from the load flow results before compensation (case two) and after compensation (case three).The reduction was computed as a percentage of the system losses in case two Results: The following results were obtained: The analysis of base case scenario revealed seven buses experience low bus voltage (less than 0.95 pu) during peak period and therefore voltage support is already needed at those buses. The buses experiencing low voltage were: Kiganjo, Nanyuki, Kisumu, Sondu, Chemosit, Tana and Thika. When the emergency generator at Embakasi was replaced with generation from Seven Forks hydro in case 2, voltages at 28 buses dropped below 0.95 pu limit and 14 generating units reached their maximum reactive power limits a and therefore could not support voltage any further. It was not possible to evacuate the total available power from Seven Forks without reactive power compensation in the transmission network. To transmit the maximum power available at Seven Forks (603 MW) without causing the low voltage situation, reactive power compensation is required at the following ten buses: Juja Road Embakasi Nairobi North Ruaraka Nanyuki Kiganjo Chemosit Kisumu Muhoroni Thika 75 MVAr 90 MVAr 36 MVAr 36 MVAr 18 MVAr 18 MVAr 16 MVAr 12 MVAr 30 MVAr 10 MVAr JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 14 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) There was a significant real and reactive power loss reduction in the transmission system. The reduction in real power losses was by 29.4 % of the losses experienced before compensation while the reactive power losses reduction was by 25.8 % of the reactive power losses experienced before compensation. The analysis of transmission line power transfer capability of the four transmission lines connecting Nairobi and Seven Forks indicate an improvement by 11.6%, 10.4%, 10.5%and 1.3% for Kiambere-Embakasi 220 kV line, Kamburu-Dandora 220 kV Line 1, Kamburu-Dandora 220 kV Line 2 and Kindaruma-Juja Road 132 kV line respectfully. The analysis of transmission line loss reduction indicates a reduction by 29.4% in real power and 25.8% in reactive power compared to losses before compensation (case 2). The results of power flow analysis show that the emergency plant can only be displaced with hydro power from the Seven Forks if 331 MVAr is installed at nine locations identified in the transmission network. In addition, the results show that to evacuate 603 MW which is the anticipated effective capacity after Kindaruma unit 3 and Karura plant are commissioned, 341 MVAr needs to be installed in the transmission system for voltage support. A financial analysis carried out at discount rates of 12%, 10% and 8% using the Net Present Worth criterion indicate the project is feasible at interest rates of 12%, 8% and 5% with a positive value of over 12.5 billion shillings and a Payback Period of less than one year in all the cases. Conclusions: Title Researcher(s) Background: It is recommended that 341MVAr reactive power compensation should be installed at ten identified buses in the transmission network of the Kenyan power system to make it possible to transfer all the available power from Seven Forks hydro complex during favourable hydrology without causing low bus voltage in the network. Design and Simulation of a Fuzzy Logic Traffic Signal Controller for a Signalized Intersection Mwangi C.M, Kang‘ethe S.M , Nyakoe G.N The road transportation system relies on the physical infrastructure and the traffic management system. In recent years, private cars and public vehicles in Nairobi indicates a steady increase at a rate of over ten percent per annum which has resulted in perennial traffic jam, especially during peak hours. This has resulted in the need to consider viable options to make the road transport more efficient. Improving the physical road infrastructure is one such measure. This entails road expansion, introducing dual carriageways, and replacing intersections and roundabouts with flyovers and is JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 15 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) Methods: Results: currently being implemented on the main highways leading into the Nairobi city. This measure requires a huge capital investment and might not be tenable within the city centre where land for expansion is not readily available, leaving us with the option of improving the transport management system. The City Council of Nairobi (CCN), the body mandated to control and manage transport within city centre of Nairobi, is currently using fixed-time controllers to control signal timing of traffic lights. Basically, a fixed-time controller repeats fixed preset signal timings derived from historical traffic patterns. However, during peak hours traffic police are deployed to manage and control traffic on the major roundabouts and intersections because the fixed-time controller are incapable of handling huge volumes of traffic. The traffic problem is a dynamic problem that requires a real-time solution which the fixed-time controllers are incapable of delivering. This research discusses the implementation of an adaptive controller using fuzzy logic technology to control traffic lights. Fuzzy logic technology allows the implementation of real-life rules similar to the way humans would think. The system acquires realtime traffic data using sensors and uses this data to adjust the signal phasing and signal timing settings in response to real- time traffic demands. Software based on MATLAB has been developed to simulate a signalized intersection in different traffic conditions. Simulation modeling is an increasingly popular and effective tool for analyzing a wide variety of dynamical problems which are not amenable to study by other means. Specifically, simulation models are mathematical/logical representations of real-world systems, which take the form of software executed on a digital computer in an experimental fashion. The research presents a Simulation model of the Fuzzy Logic Traffic signal controller using the MATLAB software. MATLAB offers a good environment for ―rapid prototyping‖ as it provides a stable environment for mathematical modeling together with a number of libraries (toolboxes) implementing more evolved tasks. It also provides users with easy methods for analysis of their results. The development of Fuzzy Logic input and output parameters membership functions and rules is implemented using the Graphical User Interfaces (GUI) on MATLAB. The simulation model has been developed using SIMULINK and SIMEVENTS toolboxes as well as MATLAB workspace environment. The performance of fuzzy and fixed-time signal controllers is compared by simulating them in an isolated traffic intersection model. The results of the simulation of the vehicles on each approach are then illustrated figures for comparison. It is seen that the number of vehicle queues in fixed-time controller are longer than those of the fuzzy controller. It is also seen that vehicles spend more time in an intersection using fixed-time controller than the one using Fuzzy controller. Vehicles using the intersection with fixed-time controller spend 13 minutes JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 16 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) Conclusions: more, on every hour spent on traffic jam, as compared to those on the fuzzy logic controlled intersection. The fixed-time controller on average serves 52 cars/min while the fuzzy controller serves approximately 56 cars/min i.e. 4 extra cars every minute. Moreover, it is seen that the sequence of fixed-time controller follows the sequence of 1-2-3-4 representing the four approaches. The phase sequence of the fuzzy controller is dictated upon by the weight of each phase with the one with highest priority granted green phase. In this research, the traffic model and traffic controller are developed using MATLAB software. To test the effectiveness of fuzzy controller to control the traffic flow at an isolated intersection, the MATLAB simulation has been done. The comparison of the proposed controller with the fixed-time controller has shown overall improvement, the fuzzy logic controller shows improved performance when controlling traffic flow. The effectiveness of the fuzzy controller is superior because it is able to adapt to the different traffic conditions. The fuzzy logic controller model can be modified to suit any intersection by varying the input membership functions which further increases the suitability of this traffic control system. Based on the results realized, implementing this project on all signalized and nonsignalized intersections can result in a lot of savings in terms of fuel, time and reduce stress and pollution levels considerably JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 17 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) 3.0 Publications Name of Lecturer / Authors: Kanai .M Michael, John .N Nderu and Peterson .K. Hinga Title of Publication: Name of Journal: Design and Analysis of Neural Fuzzy Based Buck Converter Controller Optimized with Swarm Intelligence This paper presents an application of Adaptive Neural Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) controller for DC-DC (Buck) converter optimized with swarm collective intelligence. First, an adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy controller of the Buck converter is designed and simulated using MATLAB/SIMULINK package; the ANFIS has the advantage of expert knowledge of the Fuzzy inference system and the learning capability of neural networks. Secondly, the ANFIS is optimized by Particle Swarm optimization methodology. Simulation results demonstrates that the designed ANFIS-Swarm controller realize a good dynamic behavior of the Buck converter, a perfect voltage tracking with smaller overshoot, steady state error and short settling time as well as high robustness than those obtained by traditional ANFIS controller. Journal of Global Engineers and Technologist Review, GETview, . Month and Year of Publication: November 2011 Name of Lecturer / Authors: Kanai .M Michael, John .N Nderu and Peterson .K. Hinga Title of Publication: Design and Analysis of Neural Fuzzy Controller for Improved Power Quality in AC-DC Converters This paper presents an application of Adaptive Neural Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) controller for AC-DC converter in a three phase Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Three-Level AC-DC converter system, often referred as Improved Power Quality Converters (IPQC). Three-phase Three-level AC-DC converters have been developed to a matured level with improved power quality in terms of power-factor correction, reduced total harmonic distortion at input ac mains, and regulated dc output. However, for best performance, the controller parameters used must be tuned according to the nature of the system – while the design is generic, the parameters depend on the specific system. The parameters of converter, which vary with the operating conditions of the system, are adapted in order to maintain desirable response for output voltage and power factor. A Neural Fuzzy system is employed in order to obtain the controller parameters assuring improved response at selected load and start-up. The Three-level AC-DC converter controller is modeled in MATLAB environment. The response of the developed controllers is compared to Proportional Integral Differential (PID) controller. The developed method is more proficient in improving the controller loop settling time, the rising time and overshoot and hence the disturbances do not affect Abstract: Abstract: JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 18 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) the performances of Three-Level AC-DC converter. Name of Conference proceedings Month and Year of Publication: Name of Lecturer / Authors: Kenya Society of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (KSEEE) and Japan Society of Applied Electromagnetic and Mechanics (JSAEM) November 2011 Month and Year of Publication: Clement, Karanja M. Peter, Mutiso J. Ndanu , Mutahi M. Gathiru , Kanai M. Michael Obstacle Avoidance, Way-finding and Localization System for the Visually Impaired Based on Wireless Sensor Networks We propose to develop a hand-held device to perform obstacle avoidance and way-finding by use of range finding sensors. Using a micro-controller, the spatial map of the immediate environment is presented to the user using vibrotactile feedback. The localization system uses wireless sensor networks as a model. The user will query for their location from these wireless sensor devises (motes) installed as landmarks, each with a unique location code. This code is wirelessly sent to the handheld for enunciation for via auditory feedback. A network management system to allow for easy management of the wireless network will be developed. Various parametric data items that illustrate the status of the network shall be collected and a User Interface (UI) developed that can, at a glance, show the state of the network. To increase the resolution of the localization scheme, we shall measure the Received Signal Strength Index (RSSI) value for each response for a location query, so as to only respond with the closest mote. Kenya Society of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (KSEEE) and Japan Society of Applied Electromagnetic and Mechanics (JSAEM) November 2011 Name of Lecturer / Authors: Kanai .M Michael, John .N Nderu and Peterson .K. Hinga Title of Publication: Design and Analysis of Neural Fuzzy Based Buck Converter Controller Optimized with Swarm Intelligence This paper presents an application of Adaptive Neural Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) controller for DC-DC (Buck) converter optimized with swarm collective intelligence. First, an adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy controller of the Buck converter is designed and simulated using MATLAB/SIMULINK package; the ANFIS has the advantage of expert knowledge of the Fuzzy inference system and the learning capability of neural networks. Secondly, the ANFIS is optimized by Particle Swarm optimization methodology. Simulation results demonstrates that the designed ANFIS-Swarm controller realize a good dynamic behavior of the Buck converter, a perfect voltage tracking with smaller overshoot, steady state error and short settling time as well as high robustness than those Title of Publication: Abstract: Name of Conference proceedings Abstract: JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 19 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) Name of Conference proceedings Month and Year of Publication: obtained by traditional ANFIS controller. 9th international Conference on Power System Operation and Planning (ICPSOP) January 2012 Name of Lecturer / Authors: Title of Publication: C. M. Muriithi, L. M. Ngoo and G. N. Nyakoe Investigating The Impact Of Power System Stabilizers In A Multi Machine System With An Induction Motor Load Abstract: The high reactive power demand by the induction motor load during fault condition due to reduced bus voltages may cause a generator to behave like a voltage source behind the synchronous reactance and its terminal voltage reduces leading to the possibility of a voltage collapse scenario. For reliability of these systems, and in an attempt to reduce system oscillations, Power System Stabilizers (PSS) have used to add damping by controlling the excitation system. Studies on a SMIB and those using static loads have shown that a well-tuned PSS using a Fuzzy Logic Controller (FLPSS) can effectively improve power system dynamic stability. This paper investigates the impact of the FLPSS in maintaining voltage stability in a system with induction motor loads. A large induction motor is introduced as a load in a multi machine system, and the impact of the FLPSS are investigated by introducing a temporary three phase fault. For comparison the FLPSS is compared to other PSS found in literature. Results indicate that the FLPSS may lead the generator to lose its capability to maintain constant voltage and hence lead to the stalling of the induction motor load soon after the fault is cleared. Name of Conference Proceedings Month and Year of Publication: IEEE AFRICON 2011, Livingstone, Zambia September 2011 Name of Lecturer / Authors: Title of Publication: J.K. Muriuki, C. M. Muriithi,D.K Murage Study of accuracy of small-scale and large-scale induction motors aggregation in a power system Abstract: Aggregation of different sizes of induction motors (IM) connected to a power system has diverse precision on the identification of the aggregate model parameters. Earlier work on the aggregation of various motors sizes has not been extensive to identify their accuracy on the identification of the model parameters. Also IM loads forms the highest component in power system load. Therefore, the paper proposes to investigate the accuracy of the aggregate model parameters of a group of IM of different sizes and validate the results by comparing with the individual induction motor parameters. The simulations and the analysis are carried out using Matlab/Simulink-based software package. The performance of the developed model show that, small-scale induction motors gives better accuracy of the aggregate motor parameter when compared JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 20 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) with the individual motors parameters. It is found that the proposed small-scale aggregation model gives acceptably accurate results than the large-scale aggregation model. Name of Conference Proceedings: Month and Year of Publication: 6th JKUAT Annual Scientific Technological and Industrialization Conference Year 2011 November 2011 Name of Lecturer / Authors: Title of Publication: Abstract: Obiri L.K , Kinyua J. M, Mureithi C. M Short term voltage stability analysis of an aggregated industrial load Environmental constraints have limited expansion of transmission line networks. And with power systems being operated close to their security limits, the likelihood of voltage collapses occurring has increased [1]. In most industries, the induction motor forms about 50% of the total electric load and this call for a thorough analysis of their effects on the whole power system [2].After a disturbance, stalling can occur if the electrical torque does not overcome the mechanical load, causing further voltage drop and eventually voltage collapse [3]. An aggregate motor model is simulated in MATLAB-SIMULINK. If a three phase fault is not cleared in time, the motor will decelerate continuously and eventually stall. Name of Conference Proceedings 6th JKUAT Annual Scientific Technological and Industrialization Conference Year 2011. Month and Year of Publication: November 2011 Name of Lecturer / Authors: Kinyua J. M, Mureithi C. M , Murage D. K. , L.Obiri Title of Publication: Comparison of aggregation methods of induction motor models for transient stability load modeling This paper focusses on the comparison of the aggregation methods of multiple induction motors (IM) connected in parallel on the same bus into a single equivalent model using the no-load and lockedrotor and transformer method. The opearation for the former method is based on assumptions that in the no-load operating condition, the slips of all the IM are equal to zero while for the locked-rotor, the slips are unity. The latter method assumes that all the motors are represented by the transformer equivalent circuit model and thus the name transformer method. This study has been necessitated by the strong effects that the non-linear loads have on power system characteristics and therefore erroneous modeling of these devices continues to be an area of greater uncertainty. Abstract: Though various methods of aggregations have been used, comparison on their suitablity and accuracy has not been extensively explored. Appropriate dynamic load model aggregation reduces the JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 21 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) computation time and provides a faster and efficient model derivation and parameters identification that are most sensitive to load dynamics. The simulations and analysis are carried out using Simulink. The performance is validated by evaluating the results obtained from individual and aggregate IM on IEEE 16 Bus standard system found in literature. The transient characteristics due to voltage disturbances of the aggregate IM and that of original IM group are simulated and compared to check the effectiveness of the aggrgation methods. The results shows that aggregation based on the formrer method is accurate than aggregation based on the latter method and can be used in modeling of large motors in any complex power system because of its high accuracy Name of Conference Proceedings: 9th International Conference On Power System Operation and Planning (ICPSOP-2012) –JKUAT Month and Year of Publication: Name of Lecturer / Authors: Title of Publication: January 2012 J.K. Muriuki, C. M. Muriithi,D.K Murage, Irungu G.K. Study of accuracy of small-scale and large-scale induction motors aggregation in a power system Abstract: Aggregation of different sizes of induction motors (IM) connected to a power system has diverse precision on the identification of the aggregate model parameters. Earlier work on the aggregation of various motors sizes has not been extensive to identify their accuracy on the identification of the model parameters. Also IM loads forms the highest component in power system load. Therefore, the paper proposes to investigate the accuracy of the aggregate model parameters of a group of IM of different sizes and validate the results by comparing with the individual induction motor parameters. The simulations and the analysis are carried out using Matlab/Simulink-based software package. The performance of the developed model show that, small-scale induction motors gives better accuracy of the aggregate motor parameter when compared with the individual motors parameters. It is found that the proposed small-scale aggregation model gives acceptably accurate results than the large-scale aggregation model. Name of Conference Proceedings: Year of Publication: 6th JKUAT Annual Scientific Technological and Industrialization Conference Year 2011. November 2011 Name of Lecturer / Authors: Obiri L.K , Kinyua J. M, Mureithi C. M Title of Publication: Suitability of aggregation methods of induction motor models for transient stability load modeling of kenya power transmission and distribution system JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 22 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) Abstract: Current trend indicate that there has been increase on power outage frequency. This has partly been as a result of unstable power system with very small security margins of operation. Therefore, this paper focusses on the voltage stability of aggregation of multiple induction motors (IM) connected in parallel on the same bus of a power system into a single equivalent model using two methods of aggregations.This has been necessitated by the strong effects that the non linear loads have on power system characteristics and therefore erroneous modeling of these devices continues to be an area of greater uncertainty and may cause voltage instability. Though various methods of aggregations have been used, comparison on their suitablity and accuracy has not been extensively explored. Appropriate dynamic load model aggregation reduces the computation time and provides a faster and efficient model derivation and parameters identification that are most sensitive to load dynamics. The simulations and analysis are carried out using MATLAB/SIMULINK.The accuracy of these methods is compared to identify the most suitable parameters aggregation method of IM model. Their performance is validated by evaluating the results obtained from industrial and standard individual IM and the aggregation model on IEEE 16 Bus standard system found in literature. Further, the transient characteristics due to voltage disturbances of the aggregate IM and that of original IM group are simulated and compared to check the effectiveness of the aggrgation methods on power system. The results obtained are suitable and practical. Name of Conference Proceedings: Month and Year of Publication: The 2nd Distribution Conference For Kenya Power January 2012 Name of Lecturer / Authors: J.K. Muriuki, C. M. Muriithi,D.K Murage Title of Publication: Powerfactory Load Flow Sensitivity Analysis of an Induction Motor Load Model Abstract: PowerFacotry Load flow sensitivity is a method used to obtain certain relationship between dependent and independent variables using differential relationship among physical measure in systems. Voltage sensitivity analysis is based on the linearization of the system around the operational point resulting from a load flow calculation. Inappropriate load representation has been a major setback causing inaccurate simulation results of the dynamic load. Further, induction motor loads comprise of 60% power system loads whose understanding under various dynamics is crucial for system stability. Static loads are known to be imprecise in dynamic load simulation and therefore yield false information on the system stability. This paper presents a dynamic load model whose parameters are varied to investigate their effects on both active and reactive load dynamics. Load modeling using field measurement JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 23 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) data from power quality meter of an industrial consumer and that of standard motor models are analyzed to assess their effects on sensitivity of the system stability. Load flow sensitivity is analyzed to perform a voltage sensitivity analysis based on the linearization of the system around the operational point that results from a load flow calculation. The efficiency of the system is estimated using the IEEE 9 bus system. The result indicates that load model parameters have different sensitivity values under voltage disturbance. The results acquired are thus acceptable and rational. Name of journal : International Conference On Advances In Technology And SocioEconomic Development May (Atsed 2011)-Eldoret Polytechnic, ISSN 2223-9227 Month and Year of Publication: May 2011 Name of Lecturer / Authors: J.K. Muriuki, C. M. Muriithi, D.K Murage Title of Publication: Suitability of aggregation methods of induction motor models for voltage stability analysis Abstract: Name of journal : This paper focusses on the aggregation of multiple induction motors (IM) connected in parallel on the same bus into a single equivalent model using aggregation based on transfomer equivalentcircuit (method 1) and on no-load and locked rotor (method 2).This has been necessitated by the strong effects that the non linear loads have on power system characteristics and therefore erroneous modeling of these devices continues to be an area of greater uncertainty. Though various methods of aggregations have been used, comparison on their suitablity and accuracy has not been extensively explored. Also investigated is the suitability of multi-band power system stabilizer ( MB-PSS) on the aggregate motor under a fault.The accuracy of these methods is compared to dentify the most appropriate. Their performance is validated by evaluating the results obtained from individual and aggregate IM on IEEE 16 Bus test system. The results shows that method 2 is accurate than method 1 in identification of the motor parameters both under steady-state and under fault condition. The MB-PSS gives better damping of the oscillatory modes with method 2 than method 1. The former method can therefore be used for accurate analysis of voltage stability in a complex power system. Key words: Aggregation methods, induction motor, voltage stability, power system stabilizers GETview. Year 2012, ISSN 2231-9700, Month and Year of Publication: February 2012 JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 24 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) Name of Lecturer / Authors Title of Publication: Abstract: Month and Year of Publication: George K Irungu, Stanley I. Kamau Evolution of the Deregulated Kenyan Electricity Market Electricity is an essential stimulant of economic growth and household comfort in every country all over the world. Consumers of electricity today regarded it as an essential commodity rather than a service. In the last two decades, electricity markets have evolved from closed markets with few participants to open markets with many players. Electricity today in advanced deregulated market is traded in open electricity market on day ahead basis. A good number of countries in the developing world have deregulated their electricity markets. Kenyan electricity market saw the onset of deregulation in 1997 when generation was unbundled from transmission and distribution. This resulted into the formation of generation utility Kenya Electricity Generation Company (KenGen) and transmission and distribution utility Kenya Power & Lighting Company (KPLC). This paper presents the evolution of the Kenyan electricity market before the onset of deregulation 1908 to 1997 and the progressive history of deregulation of Kenyan electricity markets from 1997 to date. It highlights the motivation behind deregulation, the merits and demerits. It pinpoints out the challenges facing deregulation in Kenya and possibly the way forward. Proceeding of the International Conference on power Systems Operation and planning (IX ICPSOP) 2012 (16TH to 19TH January 2012 in JKUAT, pages 153-159) January 2012 Name of Lecturer / Authors: George K Irungu, Stanley I. Kamau Title of Publication: General Outlook of the Deregulated Electricity Market in Kenya Abstract: Electricity is an essential ingredient of economic growth and household comfort in any country allover the world. Worldwide electricity nowadays is regarded as a commodity rather than a service. In the last two decades, electricity markets have evolved from closed market with few participants to an open market with many players. Electricity today in advanced deregulated market is traded in open electricity market just like any other commodity in normal market or stocks in a stock market. A good number of countries have deregulated their electricity markets. Kenyan electricity market saw the onset of deregulation in 1997 when generation was unbundled from transmission and distribution. This resulted into the formation of generation utility Kenya Electricity Generation Company (KenGen) and transmission and distribution utility Kenya Power & Lighting Company (KPLC). Name of Conference Proceedings: This paper starts by giving the worldwide perspective of deregulation, then the reasons, successes and failures of deregulation in the countries of Argentine, Spain, California State (USA) and Norway. It then gives brief review of how the regulated JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 25 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) Kenyan electricity sector started in 1908 and progressed to 1997. Finally, the paper presents the progressive history of deregulation of Kenyan electricity markets from 1997 to date. It highlights the motivation behind deregulation, the merits and demerits. It pinpoints out the challenges facing deregulation in Kenya and possibly the way forward. Name of Conference Proceedings: Month and Year of Publication: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference for Mechanical and Industrial Engineering Conference, held in Arusha, Tanzania from 16th to 17th February 2012 February 2012 Name of Lecturer / Authors: Muiga Rugara, D. O. Konditi, S. Musyoki Title of Publication: Closed-Loop Transmit Diversity for Mitigation of Interference and Multipath Fading in Wireless Communication Systems Abstract: Name of Journal : The wireless communication Channel suffers from many impairments such as the thermal noise often modeled as Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN), the path loss in power as the radio signal propagates, the shadowing due to the presence of fixed obstacles in the radio path, and the fading which combines the effects of multiple propagation paths and the rapid movement of mobile units reflectors. Deploying multiple antennas at the transmitter has been shown to increase diversity and therefore improve signal quality with increase throughput. This paper proposes a transmit diversity scheme, where multiple transmit antennas are used at the transmitter. A feedback path is provided from the receiver to communicate the channel seen by the receiver to the transmitter (closed-loop). When closed-loop transmit diversity is applied, the symbol from each transmit antenna is multiplied with a complex number corresponding to the inverse of the phase of the channel so as to ensure that the signals add constructively at the receiver. From this research it was found that sending the same information on multiple transmit antenna does not always provide diversity gain. However if the transmitted symbols are multiplied by a complex phase to ensure that the phases align at the receiver, there is diversity gain though the bit error rate performance seems to be slightly poorer than the maximal ratio combining case. Journal of Agriculture, Science and Technology (JAST) JAGST, Volume 13(2) 2011 Year Name of Lecturer / Authors: 2011 Musyimi P. M, Chege S. N , Wamoni M. Title of Publication: Microcontroller based hybrid energy management system Abstract: For a community to raise itself out of subsistence and into an JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 26 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) upward spiral of increased prosperity, certain basic services must be available and affordable. These include drinkable water, health care, education, transportation and communication. Access to reliable electricity is a pre-condition for the provision of many of these services and an active catalyst for sustainable development. As such, there has been an increase in demand for power that has resulted in increased advancement in power systems that aim at optimizing the energy sources available at ones disposal. Researchers have focused their efforts on improving power generation methods. Another alternative would be to develop an efficient energy management system that optimizes the already available power. This project aims at providing power to loads at a terminal voltage of 240V AC. It will involve combining different power sources e.g. include solar and wind in addition to mains supply. The 12V dc will be stepped up using DC-DC converter. An inverter will then invert this voltage to produce a 240V r.m.s. A microcontroller will be used to control switches between different sources depending on load requirements and also the capability of the sources to supply the required power. The microcontroller will ensure that priority is given to the renewable energy sources and hence the mains power will only be switched on as a last resort. This reduces reliance on mains supply and consequently, cost reduction. A comparator will compare output and input currents to produce a control signal for the microcontroller. The output of the comparator will be used as an input to the microcontroller for control purposes so as to produce the pulses for switching the power sources accordingly. Name of Conference Proceedings: International conference on power systems operation and planning (ICPSOP) forum 2012 Month and Year of Publication: January 2012 Name of Lecturer / Authors: A. Muhia, J. N. Nderu, P. K. Kihato and C. K. Kitur Title of Publication: Performance of Magnetostrictive Amorphous Wire Sensor in Motor Speed Measurement Abstract This paper presents the performance analysis of magnetostrictive amorphous wire in motor speed measurement. The principle of the operation of the sensor is based on Large Barkhausen Jump, a unique feature of the wire. The performance of the sensor is compared with conventional speed measurement methods through an experimental approach. A dc motor is used due to the linear relationship that exists between applied voltage and speed. The supply voltage for the dc motor is varied and motor speed measured using a digital tachometer. The frequency of the signal obtained from the magnetostrictive amorphous wire sensor is JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 27 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) measured using an oscilloscope and the motor speed calculated from this frequency. Results obtained show quite good agreement in the speed measured by amorphous wire and that of the tachometer. Month and Year of Publication: Index Terms- Magnetostrictive Amorphous wire, Large Barkhausen Jump, speed, dc motor Kenya Society of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (KSEEE) and Japan Society of Applied Electromagnetic and Mechanics (JSAEM) November 2011 Name of Lecturer / Authors: J. N. Nderu , A. M. Muhia, P.K. Kihato and C. K. Kitur Title of Publication: Microcontroller Based Amorphous Wire Motor Speed Sensor Abstract: This paper presents a microcontroller based motor speed sensing approach using magnetostrictive amorphous wire. The principle operation of the sensor is based on Large Barkhausen Jump, a unique feature of the wire. The wire generates stable voltage pulses in alternating fields. These pulses correlate well with the rotary speed of the motor hence can be used to measure the speed of the motor. The pulses are signal conditioned and fed into a microcontroller for measurement of frequency. The speed of the motor is calculated from this frequency. A graphic user interface is designed where the frequency and the speed of the motor is observed on a personal computer. The design presents a motor speed sensing mechanism with desirable accuracy. Name of Conference Proceedings: Index Terms—Large Barkhausen Jump (LBJ), Magnetostrictive Amorphous Wire, Microcontroller, Speed sensor Name of Conference Proceedings Month and Year of Publication: 2012 Mechanical Engineering Annual Conference on Sustainable Research And Innovation May 2012 Name of Lecturer / Authors: A.M. Muhia, J. N. Nderu, P.K. Kihato and C. K. Kitur Title of Publication Effect of Length and Position Relative to the Rotor of Magnetostrictive Amorphous Wire in Motor Speed Sensing Abstract The performance of the magnetostrictive amorphous wire in motor speed sensing has been shown to match that of conventional motor speed sensors. The sensor is based on Large Barkhausen Jump, a unique feature of the wire, which occurs at a given critical length of the wire. A permanent magnet is also used and therefore depending on the strength of the magnet used, the position of the sensor relative to the rotor is expected to influence the results. This paper presents experimental results on the influence of length and JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 28 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) position of the magnetostrictive amorphous wire on the performance of the sensor. A close observation on the signal waveforms indicates that there is a critical length and optimal positioning of the wire from the magnet for which the performance of the sensor is satisfactory. Index Terms—Length, Magnetostrictive Amorphous Wire, Position, Speed sensing Name of Conference Proceedings: Month and Year of Publication Name of Lecturer / Authors: 2012 Mechanical Engineering Annual Conference on Sustainable Research And Innovation May 2012 C. K. Kitur, J. N. Nderu, K. Kaberere and A. M. Muhia Title of Publication Frequency Sensing of an Isolated Pico Hydro Power Generation Plant Using Magnetostrictive Amorphous Wire Abstract: This paper presents frequency measurement of uncontrolled turbine Isolated Pico hydro power generating plant using Magnetostrictive amorphous wire (MAW). The basic principle of the measurement is based on Large Barkhausen Jump (LBJ), a sudden reversal of magnetization when the magnetic field reverses resulting in voltage spikes being induced; a pick-up coil is wound around the MAW to pick the spikes. The number of spikes recorded per second is actually the frequency of generation. This is compared with the measured frequency of the generated power as read from the generation meters and also as calculated based on measured speed of rotation and results are presented. Name of Conference Proceedings: Month and Year of Publication Name of Lecturer / Authors: 2012 Mechanical Engineering Annual Conference on Sustainable Research And Innovation May 2012 Peter Kamita Kihato, John Ndichu Nderu Title of Publication: Direct Neuro-Fuzzy Approach to Motion Tuning of Servomotors Abstract Servomotors (Servos) have in the current technological advisements played an important role in motion control. This has been made possible by both the computational ability available and the ability to have microchips that can be designated for a particular task. This paper presents a direct approach to motion tuning control where models for fuzzy controllability are not borrowed from other software like MATLAB. A fuzzy controller is designed to directly interface to the drive circuit of the servomotor. This simple and novel approach not only simplifies the overall controller but also manages to give a better control tuning on an already existing controller of a servomotor thereby reducing the inherent error left for a particular servo due to cost of manufacture. The motion JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 29 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) Month and Year of Publication: responses of fuzzy controlled servos to a robot arm manipulator were verified through experiments. Keywords: Servomotor, Fuzzy modeling, Position captures, Neural topology. Kenya Society of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (KSEEE) and Japan Society of Applied Electromagnetic and Mechanics (JSAEM) November 2011 Name of Lecturer / Authors: Charles Ndung’u, J. Nderu, L. Ngoo Title of Publication: Power Distribution Efficiency Based On Reactive Power and Power Factor Abstract: This paper discusses the power factor of transmission and distribution lines for selected power utility (Kenya Power) substations. The choice of selection of lines was based on the nature of the load (domestic, industrial or hybrid) and the status of the loading (slightly, moderate or heavily loaded). Instantaneous Power Factor (IPF) was read on energy meters at specific time of the day for a period of two weeks. The data collected and analyzed revealed that some feeder lines at most of substations are distributing active power at low power factor below the grid threshold limit of 0.90. Feeder lines mainly supplying domestic loads have their power factor generally low, which could be contributed to insufficient VAr compensation and proliferation of non-linear loads. On the other hand, it was found that feeder lines supplying industrial loads have power factor well above the statutory limit, which is attributed to reactive power being compensated in the vicinity of the demand (point of common coupling). It is concluded that it is imperative to compensate the reactive current on feeder lines supplying mainly domestic loads in the vicinity of the loads i.e. near the distribution transformers to improve the power factor of these feeder lines in order to increase distribution efficiency and improve the voltage profile. Name of journal: Journal of Technology & Socio Economical Development Vol. 1 No. 1. ISSN 2223-9227 Month and Year of Publication: September 2011 Name of Lecturer / Authors: Charles Ndung’u, J. Nderu, L. Ngoo Title of Publication: Impact of Compact Fluorescent Lighting Bulbs on Power Quality Abstract: In recent time, the power quality has attracted a lot of attention due to extensive emphasis by power utility on the power system efficiency and end users awareness of power quality issues. This has occurred mainly due to the sensitivity of the modern equipment and Name of Conference Proceedings JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 30 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) the deregulation of the power distribution. In addition, there are usually massive losses both to power utility and end users due to poor power quality supplies which fall below the set standards. Power quality primarily consists of voltage dip/ swell, power system interruptions (power outage), harmonic distortions, voltage flickers and frequency deviations. This study looks at effect of CFL bulbs on power system in relation to harmonic distortions and low power factor inherently associated by CFL. It has established that the bulbs generate substantial harmonic distortions and leading a power factor. Mixing of incandescent and CFL bulbs in one circuit was noted to improves the power quality at the point of common coupling. Name of Conference: Kenya Society of Electrical Electronic Engineers 2011 International Engineering Conference Month and Year of Publication: November 2011 Name of Lecturer / Authors: Charles Ndung’u, J. Nderu, L. Ngoo Title of Publication: Analysis of Harmonic Levels at Power Lines to Improve Power Quality Abstract: This paper presents the results of investigation done to establishment of harmonic levels at various points of power utility lines. It involved collection of harmonic order levels from generation, distribution and point of common coupling (PCC). The harmonic levels data of different power stations, substations and large power consumers were collected. The analysis has ascertained that large power consumers supplied on low voltage (415V) have their harmonics current levels far beyond the threshold limit as recommended by the IEEE 519-1992, as compared with the power consumers supplied above 11,000V. In addition, voltage distortions on transmission lines were noted to be more severe vis-a -vis the current distortions. This is presumed to be because low voltage consumers feed the harmonics direct to the power line as opposed to the medium and high voltage consumers, where most of the harmonics are trapped by step down transformers at the consumer‘s premises. It can be deduced that the most affected PCC with high harmonic current distortion is low voltage supplied end users. Name of journal: Mechanical Engineering Annual Conference On Sustainable Research And Innovation, ISSN 2079-6226 – JKUAT Month and Year of Publication: May 2011 Name of Lecturer / Authors: Charles Ndung’u, J. Nderu, L. Ngoo Title of Publication: Compensation of Vars at Off Grid Power Generations Using Shunt JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 31 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) Capacitors Abstract: This paper presents the significant of VAr compensation at electricity distribution lines at off grid power generation by installation of fixed shunt capacitors. The objectives are to reduce the cost of energy per unit generated and improve the voltage at the end users. Due to presence of numerous small power rating of non linear and inductive loads, demands of reactive power are usually high as it is uneconomical to compensate the reactive power at the load points. The reactive currents required by these loads have to pass through the generator windings, switchgears, transmission cables and step-up transformers. This contributes to a substantial power loss at the distribution lines and at the generators due to additional current (reactive). The study has shown that by compensating the reactive power at the distribution line, the power losses will reduce substantially and the voltage profile at end user will improve. Moreover, fuel consumed by the generator per kWh will also reduce thus less thermo emission (green power) and low the maintenance cost of the generators. Name of Conference: 1st Information Communication Technology conference at Multimedia Unversity College of Kenya Month and Year of Publication: December 2011 Name of Lecturer / Authors: Charles Ndung’u, J. Nderu, L. Ngoo Title of Publication: Improvement of Active Power Distribution Effeciency By Compensating Reactive Power at Substations Abstract: This paper discusses the power factor of transmission and distribution feeder lines for assorted power utility substations. The choice of lines was based on the nature of the load (domestic, industrial or hybrid) and the magnitude of the load; slightly, moderate or heavily loaded. Instantaneous Power Factor (IPF) was read on energy meters at specific time of the day for a period of two weeks. The data collected and analyzed revealed that most of feeder lines at most of substations are distributing active power at comparatively low PF sometimes below grid threshold limit of 0.90. This could be contributed to proliferation of non-linear loads. These non linear loads consist of electronic devices with switched mode power supply converters such as TV‘s, computers/ laptops, and printers. Also contributing to low power factor is Compact Fluorescence Light (CFL) retrofitting the incandescent bulbs. This results in high loss on transmission and distribution feeder lines and poor voltage regulation. The analysis also reveals that feeder lines supplying domestic load have their power factor generally low due to dominance of non linear domestic loads. However, it was found out that feeder lines supplying industrial loads have power factor JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 32 of 33 JKU/2/33/65(12) well above the statutory limit which is attributed to reactive power being compensated at the vicinity of the demand (point of common coupling). Name Conference: 2nd Distribution Conference For The Kenya Power- WhiteSand Mombasa: Month and Year of Publication: January 2012 Name of Lecturer / Authors: Nelson Muchiri Gachoki; Hinga P.K; Wanjii S.M; Kahiu S. N Title of Publication: A Review on Biogas, its Application is a Dual-Fuel on Diesel Engines for Power Generation Abstract: Rising global challenges of energy generation, sustainability, cost, environmental concerns among others have triggered immense research on alternative energy sources and technologies in the recent past. Such previous works includes research into use of biogas as a substitute fuel in diesel engines. This paper focuses on how biogas is generated from solid waste and among other uses, is used for power generation, electrical energy is generated from biogas and diesel, using dual fuel (DF) generator. DF applications are considered to lower cost of operating automobile engines and power generators. Furthermore this paper focuses on reviewing alternative fuels techniques focusing on biogas properties and local potential, then on how to run internal combustion engines on biogas fuel, previous applications, their availability and costs. The paper also illustrates methods for modification of ordinary engine to run on dual fuel, considering their applications, performance and cost implication. The findings of this work are of great importance in developing a local mechanism that uses diesel as a pilot fuel and biogas as substitute fuel. The findings also will help in identification of an appropriate fuel regulation tool and in adapting the generation plant for a beneficial use. This is to provide affordable alternative source of electrical power to institutions, municipalities or in remote rural 2012 Mechanical Engineering Annual Conference on Sustainable Research And Innovation Name of Conference Proceedings: Month and Year of Publication: May , 2012 JKUAT is ISO 9001: 2008 Certified Setting Trends in Higher Education, Research and Innovation Page 33 of 33