4 MHz, 7 nV/√Hz, Low Offset and
Drift, High Precision Amplifier
ADA4077-2
Data Sheet
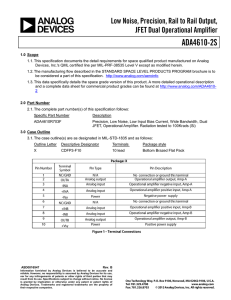
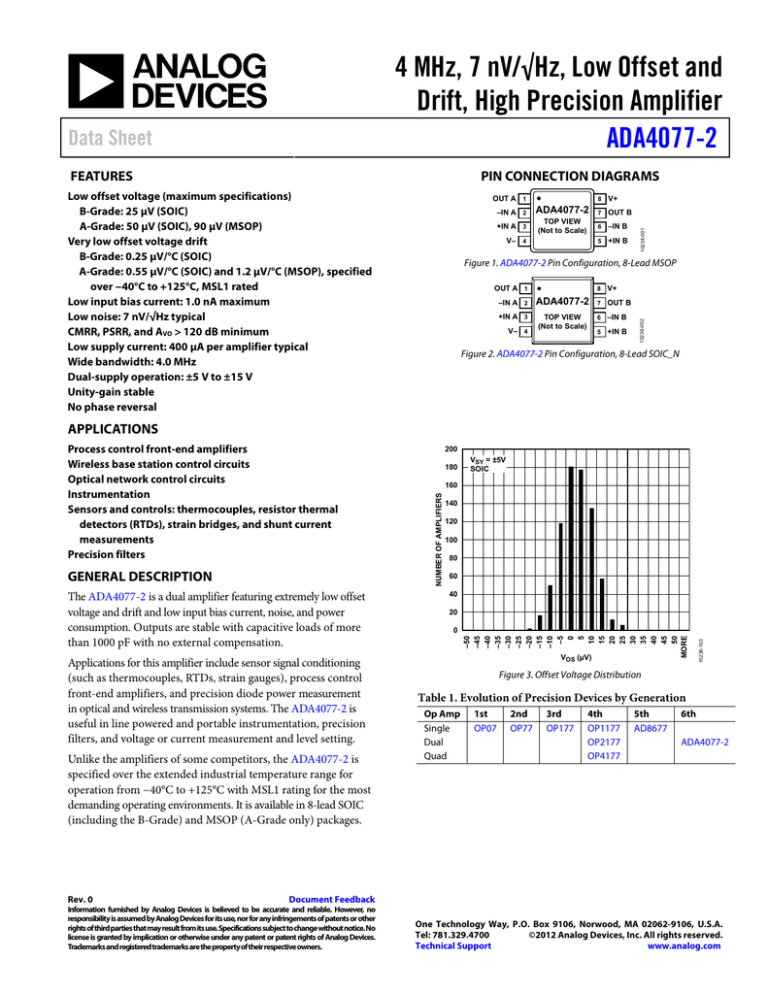
PIN CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
OUT A 1
8
V+
–IN A 2
ADA4077-2
7
OUT B
+IN A 3
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
6
–IN B
5
+IN B
V– 4
10238-001
FEATURES
Low offset voltage (maximum specifications)
B-Grade: 25 µV (SOIC)
A-Grade: 50 µV (SOIC), 90 µV (MSOP)
Very low offset voltage drift
B-Grade: 0.25 µV/°C (SOIC)
A-Grade: 0.55 µV/°C (SOIC) and 1.2 µV/°C (MSOP), specified
over −40°C to +125°C, MSL1 rated
Low input bias current: 1.0 nA maximum
Low noise: 7 nV/√Hz typical
CMRR, PSRR, and AVO > 120 dB minimum
Low supply current: 400 µA per amplifier typical
Wide bandwidth: 4.0 MHz
Dual-supply operation: ±5 V to ±15 V
Unity-gain stable
No phase reversal
OUT A 1
–IN A 2
ADA4077-2
+IN A 3
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
V– 4
8
V+
7
OUT B
6
–IN B
5
+IN B
10238-002
Figure 1. ADA4077-2 Pin Configuration, 8-Lead MSOP
Figure 2. ADA4077-2 Pin Configuration, 8-Lead SOIC_N
APPLICATIONS
Applications for this amplifier include sensor signal conditioning
(such as thermocouples, RTDs, strain gauges), process control
front-end amplifiers, and precision diode power measurement
in optical and wireless transmission systems. The ADA4077-2 is
useful in line powered and portable instrumentation, precision
filters, and voltage or current measurement and level setting.
Unlike the amplifiers of some competitors, the ADA4077-2 is
specified over the extended industrial temperature range for
operation from −40°C to +125°C with MSL1 rating for the most
demanding operating environments. It is available in 8-lead SOIC
(including the B-Grade) and MSOP (A-Grade only) packages.
Rev. 0
VSY = ±5V
SOIC
160
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
VOS (µV)
10238-103
The ADA4077-2 is a dual amplifier featuring extremely low offset
voltage and drift and low input bias current, noise, and power
consumption. Outputs are stable with capacitive loads of more
than 1000 pF with no external compensation.
180
–50
–45
–40
–35
–30
–25
–20
–15
–10
–5
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
MORE
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
200
NUMBER OF AMPLIFIERS
Process control front-end amplifiers
Wireless base station control circuits
Optical network control circuits
Instrumentation
Sensors and controls: thermocouples, resistor thermal
detectors (RTDs), strain bridges, and shunt current
measurements
Precision filters
Figure 3. Offset Voltage Distribution
Table 1. Evolution of Precision Devices by Generation
Op Amp
Single
Dual
Quad
1st
OP07
2nd
OP77
3rd
OP177
4th
OP1177
OP2177
OP4177
5th
AD8677
6th
ADA4077-2
Document Feedback
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
©2012 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
Technical Support
www.analog.com
ADA4077-2
Data Sheet
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Pin Configurations and Function Descriptions ............................6
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
Typical Performance Characteristics ..............................................7
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 16
Pin Connection Diagrams ............................................................... 1
Applications Information .............................................................. 17
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Output Phase Reversal ............................................................... 17
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Low Power Linearized RTD ...................................................... 17
Electrical Characteristics, ±5.0 V ............................................... 3
Proper Board Layout .................................................................. 18
Electrical Characteristics, ±15.0 V ............................................. 4
Packaging and Ordering Information ......................................... 19
Absolute Maximum Ratings ....................................................... 5
Outline Dimensions ................................................................... 19
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 5
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 20
REVISION HISTORY
10/12—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 20
Data Sheet
ADA4077-2
SPECIFICATIONS
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS, ±5.0 V
VSY = ±5.0 V, VCM = 0 V, TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
Table 2.
Parameter
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Offset Voltage (B Grade, SOIC)
Offset Voltage Drift (B Grade, SOIC)
Offset Voltage (A Grade)
SOIC
Symbol
Test Conditions/Comments
Min
VOS
ΔVOS/ΔT
VOS
−40°C < TA < +125°C
−40°C < TA < +125°C
Typ
Max
Unit
10
25
65
0.25
μV
μV
μV/°C
50
105
90
220
μV
μV
μV
μV
0.55
1.2
+1
+1.5
+0.5
+1.0
+3
3
5
100
μV/°C
μV/°C
nA
nA
nA
nA
V
dB
dB
dB
dB
pF
pF
MΩ
±10
22
0.05
V
V
V
V
mA
mA
Ω
0.1
15
−40°C < TA < +125°C
MSOP
Offset Voltage Drift (A Grade)
SOIC
MSOP
Input Bias Current
50
ΔVOS/ΔT
−40°C < TA < +125°C
−40°C < TA < +125°C
IB
−40°C < TA < +125°C
Input Offset Current
IOS
−40°C < TA < +125°C
Input Voltage Range
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio
CMRR
Large Signal Voltage Gain
AVO
Input Capacitance
CINDM
CINCM
RIN
Input Resistance
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage High
Output Voltage Low
Output Current
Short-Circuit Current
Closed-Loop Output Impedance
POWER SUPPLY
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
Supply Current per Amplifier
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Slew Rate
Settling Time to 0.1%
Gain Bandwidth Product
NOISE PERFORMANCE
Voltage Noise
Voltage Noise Density
Current Noise Density
MULTIPLE AMPLIFIERS CHANNEL SEPARATION
VOH
VOL
IOUT
ISC
ZOUT
PSRR
ISY
VCM = −3.8 V to +3V
−40°C < TA < +125°C
RL = 2 kΩ, VO = −3.0 V to +3.0 V
−40°C < TA < +125°C
Differential mode
Common mode
−1
−1.5
−0.5
−1.0
−3.8
122
120
121
120
IL = 1 mA
−40°C < TA < +125°C
IL = 1 mA
−40°C < TA < +125°C
VDROPOUT < 1.6 V
TA = 25°C
f = 1 kHz, AV = +1
+4.1
+4
VS = ±2.5 V to ±18 V
−40°C < TA < +125°C
VO = 0 V
−40°C < TA < +125°C
123
120
0.25
0.5
−0.4
+0.1
140
130
−3.5
−3.2
128
400
450
650
dB
dB
μA
μA
SR
ts
GBP
RL = 2 KΩ
VIN =1 V step, RL = 4 kΩ, AV = −1
AV = +1
1
2
4.0
V/μs
µs
MHz
en p-p
en
0.1 Hz to 10 Hz
f = 1 Hz
f = 100 Hz
f = 1 kHz
f = 1 kHz
0.25
13
7
3
−120
μV p-p
nV/√Hz
nV/√Hz
pA/√Hz
dB
in
CS
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 20
ADA4077-2
Data Sheet
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS, ±15.0 V
VSY = ±15 V, VCM = 0 V, TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted.
Table 3.
Parameter
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Offset Voltage (B Grade, SOIC)
Offset Voltage Drift (B Grade, SOIC)
Offset Voltage (A Grade)
SOIC
Symbol
Test Conditions/Comments
Min
VOS
ΔVOS/ΔT
VOS
−40°C < TA < +125°C
−40°C < TA < +125°C
Typ
Max
Unit
10
35
65
0.25
μV
μV
μV/°C
15
50
105
μV
μV
50
90
220
μV
μV
0.2
0.5
−0.4
0.55
1.2
+1
+1.5
+0.5
+1.0
+13
3
5
100
μV/°C
μV/°C
nA
nA
nA
nA
V
dB
dB
dB
dB
pF
pF
MΩ
±10
22
0.05
V
V
V
V
mA
mA
Ω
0.1
−40°C < TA < +125°C
MSOP
Offset Voltage Drift (A Grade)
SOIC
MSOP
Input Bias Current
ΔVOS/ΔT
−40°C < TA < +125°C
−40°C < TA < +125°C
IB
−40°C < TA < +125°C
Input Offset Current
IOS
−40°C < TA < +125°C
Input Voltage Range
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio
CMRR
Large Signal Voltage Gain
AVO
Input Capacitance
CINDM
CINCM
RIN
Input Resistance
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Output Voltage High
Output Voltage Low
Output Current
Short-Circuit Current
Closed-Loop Output Impedance
POWER SUPPLY
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
Supply Current per Amplifier
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Slew Rate
Settling Time to 0.01%
Settling Time to 0.1%
Gain Bandwidth Product
NOISE PERFORMANCE
Voltage Noise
Voltage Noise Density
Current Noise Density
MULTIPLE AMPLIFIERS CHANNEL SEPARATION
VOH
VOL
IOUT
ISC
ZOUT
PSRR
ISY
VCM = −13.8 V to +13 V
−40°C < TA < +125°C
RL = 2 kΩ, VO = −13.0 V to +13.0 V
−40°C < TA < +125°C
Differential mode
Common mode
−1
−1.5
−0.5
−1.0
−13.8
132
130
125
120
IL = 1 mA
−40°C < TA < +125°C
IL = 1 mA
−40°C < TA < +125°C
VDROPOUT < 1.2 V
TA = 25°C
f = 1 kHz, AV = +1
+14.1
+14
VS = ±2.5 V to ±18 V
−40°C < TA < +125°C
VO = 0 V
−40°C < TA < +125°C
123
120
+0.1
150
130
−13.5
−13.2
128
400
500
650
dB
dB
μA
μA
SR
ts
ts
GBP
RL = 2 kΩ
VIN = 10 V p-p, RL = 4 kΩ, AV = −1
VIN = 10 V p-p, RL = 4 kΩ, AV = −1
AV = +1
1
9
8
3.9
V/μs
µs
µs
MHz
en p-p
en
0.1 Hz to 10 Hz
f = 1 Hz
f = 100 Hz
f = 1 kHz
f = 1 kHz
0.25
13
7
3
−120
μV p-p
nV/√Hz
nV/√Hz
pA/√Hz
dB
in
CS
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 20
Data Sheet
ADA4077-2
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 4.
Parameter
Supply Voltage
Input Voltage
Differential Input Voltage
Storage Temperature Range
MSOP and SOIC_N Packages
Operating Temperature Range
Junction Temperature Range
R and RM Packages
Lead Temperature, Soldering (10 sec)
THERMAL RESISTANCE
Rating
36 V
±VSY
±VSY
θJA is specified for the worst-case conditions, that is, a device
soldered in a circuit board for surface-mount packages.
Table 5. Thermal Resistance
−65°C to +150°C
−40°C to +125°C
Package Type
8-Lead MSOP
8-Lead SOIC_N
−65°C to +150°C
300°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 20
θJA
190
158
θJC
44
43
Unit
°C/W
°C/W
ADA4077-2
Data Sheet
OUT A 1
8
V+
–IN A 2
ADA4077-2
7
OUT B
–IN A 2
+IN A 3
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
ADA4077-2
6
–IN B
+IN A 3
5
+IN B
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
10238-004
V– 4
OUT A 1
V– 4
Table 6. ADA4077-2 Pin Function Descriptions, MSOP and SOIC
Mnemonic
OUT A
−IN A
+IN A
V−
+IN B
−IN B
OUT B
V+
V+
7
OUT B
6
–IN B
5
+IN B
Figure 5. Pin Configuration, 8-Lead SOIC_N (R Suffix)
Figure 4. Pin Configuration, 8-Lead MSOP (RM Suffix)
Pin No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
8
10238-005
PIN CONFIGURATIONS AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Description
Output, Channel A.
Inverting Input, Channel A.
Noninverting Input, Channel A.
Negative Supply Voltage.
Noninverting Input, Channel B.
Inverting Input, Channel B.
Output, Channel B.
Positive Supply Voltage.
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 20
Data Sheet
ADA4077-2
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
140
120
VSY = ±5V
MSOP
NUMBER OF AMPLIFIERS
80
60
40
20
100
80
60
40
20
–50
–45
–40
–35
–30
–25
–20
–15
–10
–5
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
MORE
10238-006
–50
–45
–40
–35
–30
–25
–20
–15
–10
–5
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
MORE
VOS (µV)
VOS (µV)
Figure 6. Offset Voltage Distribution
Figure 9. Offset Voltage Distribution
200
200
VSY = ±5V
SOIC
180
VSY = ±15V
SOIC
180
160
NUMBER OF AMPLIFIERS
160
140
120
100
80
60
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
20
0
0
10238-144
VOS (µV)
–50
–45
–40
–35
–30
–25
–20
–15
–10
–5
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
MORE
40
–50
–45
–40
–35
–30
–25
–20
–15
–10
–5
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
MORE
NUMBER OF AMPLIFIERS
10238-003
0
0
VOS (µV)
10238-009
NUMBER OF AMPLIFIERS
VSY = ±15V
MSOP
120
100
Figure 10. Offset Voltage Distribution
Figure 7. Offset Voltage Distribution
10
16
VSY = ±5V
8
VSY = ±15V
14
6
12
10
VOS (µV)
2
0
–2
8
6
–4
4
–6
–10
–50
–25
0
25
50
TEMPERATURE (°C)
75
100
125
Figure 8. Offset Voltage vs. Temperature
0
–50
–25
0
25
50
TEMPERATURE (°C)
75
100
Figure 11. Offset Voltage vs. Temperature
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 20
125
10238-010
2
–8
10238-007
VOS (µV)
4
ADA4077-2
Data Sheet
80
VSY = ±15V
SOIC
70
TCVOS (µV/°C)
Figure 12. TCVOS, MSOP
10238-008
0.35
MORE
0.30
0.25
0.20
10238-130
TCVOS (nV/°C)
0.15
0
0.10
0
–0.35
10
–0.75
–0.70
–0.65
–0.60
–0.55
–0.50
–0.45
–0.40
–0.35
–0.30
–0.25
–0.20
–0.15
–0.10
–0.05
0
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0.25
0.30
0.35
0.40
0.45
0.50
0.55
0.60
0.65
0.70
0.75
2
0
20
0.05
4
30
–0.05
6
40
–0.10
8
50
–0.15
10
60
–0.20
12
–0.25
14
NUMBER OF AMPLIFIERS
NUMBER OF AMPLIFIERS
16
VSY = ±15V
MSOP
–0.30
18
Figure 15. TCVOS, SOIC
10
0.9
0.8
0.7
SUPPLY CURRENT (mA)
VOS (µV)
5
0
–5
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
VSY (V)
–0.1
10238-134
–10
0
5
10
Figure 13. VOS vs. Supplies
20
25
30
35
Figure 16. ISY vs. VSY
100
800
AVERAGE +3σ
80
15
SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
10238-126
0
VSY = ±15V
700
VSY = ±15V
60
AVERAGE +3σ
600
20
500
IB (pA)
AVERAGE
0
–20
AVERAGE
400
300
AVERAGE –3σ
–40
200
–60
AVERAGE –3σ
–100
–20
–15
–10
–5
0
100
5
VCM (V)
10
15
20
Figure 14. VOS vs. VCM
0
–20
–15
–10
–5
0
5
10
VCM (V)
Figure 17. Input Bias Current vs. VCM
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 20
15
20
10238-115
–80
10238-112
VOS (µV)
40
Data Sheet
ADA4077-2
350
400
VSY = ±15V
VSY = ±5V
350
150
MORE
0
Figure 21. Input Bias Current
0
0
VSY = ±5V
VSY = ±15V
–0.1
–0.1
–0.2
–0.2
+IB
–IB
–IB
–0.3
IB (nA)
IB (nA)
–0.1
–0.2
–0.3
–0.4
–1
INPUT BIAS CURRENT (nA)
Figure 18. Input Bias Current
10238-016
INPUT BIAS CURRENT (nA)
10238-013
0
MORE
–0.1
–0.2
–0.3
–0.4
–0.5
–0.6
0
–0.7
0
–0.8
50
–0.9
50
–0.5
100
–0.6
100
200
–0.7
150
250
–0.8
200
300
–0.9
NUMBER OF AMPLIFIERS
250
–1.0
NUMBER OF AMPLIFIERS
300
–0.4
–0.3
–0.4
–0.5
–0.5
–0.6
–0.6
–25
0
25
50
75
100
125
TEMPERATURE (°C)
–0.7
–50
10238-014
–0.7
–50
–25
0
25
50
75
100
125
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 19. Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
10238-017
+IB
Figure 22. Input Bias Current vs. Temperature
1800
1800
VSY = ±5V
1400
1200
0.001
0.01
0.1
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
1
10
Figure 20. VOL vs. Load
1600
1400
1200
0.001
0.01
0.1
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
Figure 23. VOL vs. Load
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 20
1
10
10238-122
VOL – VSS (mV)
1600
10238-118
VOL – VSS (mV)
VSY = ±15V
ADA4077-2
Data Sheet
1200
1200
VSY = ±15V
VSY = ±5V
800
0.1
1
10
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
800
600
0.001
0.01
0.1
Figure 24. Output Dropout Voltage vs. Load
10
Figure 27. Output Dropout Voltage vs. Load
120
135
120
90
90
90
90
60
45
60
45
135
PHASE
0
GAIN
30
–45
VSY = ±5V
RL = 2k
CL = 100pF
100k
0
–90
10M
1M
–45
VSY = ±15V
RL = 2kΩ
CL = 100pF
10238-022
–30
10k
0
FREQUENCY (Hz)
PHASE MARGIN (Degrees)
0
OPEN-LOOP GAIN (dB)
GAIN
PHASE MARGIN (Degrees)
PHASE
30
–30
10k
100k
–90
10M
1M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 25. Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs. Frequency
Figure 28. Open-Loop Gain and Phase vs. Frequency
6
14.4
VOH
4
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING (V)
14.2
VSY = ±5V
2
0
–2
VOL
–4
14.0
13.8
13.6
VOL
VSY = ±15V
–25
0
25
50
75
100
TEMPERATURE (°C)
125
Figure 26. Output Voltage Swing vs. Temperature
13.2
–50
–25
0
25
50
75
1
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 29. Output Voltage Swing vs. Temperature
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 20
125
10238-140
–6
–50
VOH
13.4
10238-021
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SWING (V)
OPEN-LOOP GAIN (dB)
1
LOAD CURRENT (mA)
10238-027
0.01
10238-119
600
0.001
1000
10238-121
VDD – VOH (mV)
VDD – VOH (mV)
1000
Data Sheet
ADA4077-2
120
120
VSY = ±15V
100
100
80
80
PSRR (dB)
PSRR (dB)
VSY = ±5V
60
PSRR–
40
60
PSRR–
40
PSRR+
20
20
0
0
10k
1k
100k
1M
10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
–20
100
10238-034
–20
100
10k
1k
100k
1M
10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 30. PSRR vs. Frequency, ±5 V
10238-037
PSRR+
Figure 33. PSRR vs. Frequency, ±15 V
152
159
151
VSY = ±15V
VSY = ±5V
158
150
149
157
CMRR (dB)
CMRR (dB)
148
147
146
145
156
155
144
143
154
–25
0
25
50
TEMPERATURE (°C)
75
100
125
153
–50
10238-030
141
–50
–25
Figure 31. CMRR vs. Temperature
0
25
50
TEMPERATURE (°C)
75
100
125
10238-033
142
Figure 34. CMRR vs. Temperature
133
140
VSY = ±15V
VSY = ±5V
VSY = ±5V TO ±15V
132
120
131
100
PSRR (dB)
80
60
129
128
127
40
126
20
1k
10k
100k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
1M
10M
124
–50
–25
0
25
50
75
TEMPERATURE (°C)
Figure 35. PSRR vs. Temperature
Figure 32. CMRR vs. Frequency
Rev. 0 | Page 11 of 20
100
125
10238-035
0
100
125
10238-029
CMRR (dB)
130
ADA4077-2
Data Sheet
50
40
30
CLSOED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
G = 10
20
10
G=1
0
–10
–20
G = 10
20
10
G=1
0
–10
–20
–40
–50
1k
10k
100k
1M
10M
10238-028
–40
–50
1k
100M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
100M
VSY = ±15V
100
100
AV = 100
10
1
ZOUT (Ω)
AV = 10
AV = 1
0.1
0.01
0.01
1k
10k
100k
1M
10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
0.001
100
AV = 10
AV = 1
1k
10k
100k
1M
10M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 37. Output Impedance vs. Frequency
Figure 40. Output Impedance vs. Frequency
10238-040
VOLTAGE (1V/DIV)
VSY = ±5V
VIN = 1V p-p
AV = 1
RL = 2kΩ
CL = 300pF
TIME (100µs/DIV)
AV = 100
1
0.1
10238-036
ZOUT (Ω)
10M
1k
VSY = ±5V
VOLTAGE (0.2V/DIV)
1M
Figure 39. Closed-Loop Gain vs. Frequency
1k
0V
100k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 36. Closed-Loop Gain vs. Frequency
0.001
100
10k
10238-031
–30
–30
10238-039
CLSOED-LOOP GAIN (dB)
30
10
VSY = ±15V
G = 100
0V
VSY = ±15V
VIN = 4V p-p
AV = 1
RL = 2kΩ
CL = 300pF
TIME (100µs/DIV)
Figure 41. Large Signal Transient Response
Figure 38. Large Signal Transient Response
Rev. 0 | Page 12 of 20
10238-043
40
50
VSY = ±5V
G = 100
VSY = ±5V
VIN = 200mV p-p
AV = 1
RL = 2kΩ
CL = 1000pF
TIME (100µs/DIV)
TIME (100µs/DIV)
INPUT
0
VSY = ±5V
AV = –100
VIN = 200mV
RL = 10kΩ
INPUT
0
14
–0.5
12
8
6
4
2
OUTPUT
0
10238-046
1
OUTPUT
10
VSY = ±15V
AV = –100
VIN = 200mV
RL = 10kΩ
5
3
–1
TIME (10µs/DIV)
–2
TIME (10µs/DIV)
Figure 43. Positive Overload Recovery
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
Figure 46. Positive Overload Recovery
0.5
INPUT
0
–0.5
0.5
INPUT
0
–0.5
OUTPUT
–3
–5
TIME (10µs/DIV)
–5
VSY = ±15V
AV = –100
VIN = 200mV
RL = 10kΩ
Figure 44. Negative Overload Recovery
–15
TIME (10µs/DIV)
Figure 47. Negative Overload Recovery
Rev. 0 | Page 13 of 20
–10
10238-051
–1
VSY = ±5V
AV = –100
VIN = 200mV
RL = 10kΩ
10238-047
OUTPUT
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
0
1
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
16
0.5
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
0.5
10238-146
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
Figure 45. Small Signal Transient Response
OUTPUT VOLTAGE (V)
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
Figure 42. Small Signal Transient Response
–0.5
0V
VSY = ±15V
VIN = 200mV p-p
AV = 1
RL = 2kΩ
CL = 1000pF
10238-044
VOLTAGE (50mV/DIV)
0V
ADA4077-2
10238-041
VOLTAGE (50mV/DIV)
Data Sheet
ADA4077-2
Data Sheet
50
50
VSY = ±5V
VIN = 200mV p-p
AV = 1
RL = 2kΩ
45
40
40
35
OVERSHOOT (%)
35
30
25
20
30
25
20
15
15
OS–
OS–
10
OS+
0
10
100
1k
10k
LOAD CAPACITANCE (pF)
0
10
100
1k
10k
LOAD CAPACITANCE (pF)
Figure 48. Small Signal Overshoot vs. Load Capacitance
Figure 51. Small Signal Overshoot vs. Load Capacitance
450
1.2
500
1
400
12
INPUT
400
0.8
VSY = ±5V
VIN = 1V p-p
AV = –1
250
200
0.6
150
100
0.4
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
300
50
OUTPUT
0
ERROR BAND VOLTAGE (mV)
INPUT
350
ERROR BAND VOLTAGE (mV)
OS+
5
10238-042
5
10238-045
10
10
300
VSY = ±15V
VIN = 10V p-p
AV = –1
8
200
6
100
4
INPUT VOLTAGE (V)
OVERSHOOT (%)
VSY = ±15V
VIN = 200mV p-p
AV = 1
RL = 2kΩ
45
OUTPUT
2
0
0.2
–50
1
2
3
4
–100
–5
TIME (µs)
0
10
0
20
15
TIME (µs)
Figure 52. Positive Settling Time
Figure 49. Positive Settling Time
100
1k
VSY = ±15V
AV = +1
VSY = ±15V
VOLTAGE NOISE CORNER (nV/√Hz)
90
100
CH A
10
CH B
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
1
10
100
1k
10k
100k
1M
FREQUENCY (Hz)
10M
0
0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 53. Voltage Noise Corner Frequency
Figure 50. Voltage Noise Density vs. Frequency
Rev. 0 | Page 14 of 20
3.0
10238-153
10
10238-053
VOLTAGE NOISE DENSITY (nV/√Hz)
5
10238-152
0
0
10238-149
–100
–1
Data Sheet
ADA4077-2
0.001
0.001
VSY = ±15V
RL = 10kΩ
VIN = 1V rms
AV = +1
100
1k
10k
100k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
0.0001
10
10238-155
100
1k
10k
100k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 56. THD + N vs. Frequency
Figure 54. THD + N vs. Frequency
VSY = ±5V
VCM = 0V
10238-058
TIME (1s/DIV)
10238-054
INPUT VOLTAGE (50nV/DIV)
INPUT VOLTAGE (50nV/DIV)
VSY = ±15V
VCM = 0V
TIME (1s/DIV)
Figure 55. 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz Noise
Figure 57. 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz Noise
0
CHANNEL SEPARATION (dB)
–20
VSY = ±15V
VIN = 3.5V p-p
AV = +1
–40
–60
–80
–100
–120
–140
–160
100
1k
10k
100k
FREQUENCY (Hz)
Figure 58. Channel Separation
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 20
1M
10238-244
0.0001
10
10238-158
THD + N (%)
THD + N (%)
VSY = ±5V
RL = 10kΩ
VIN = 1V rms
AV = +1
ADA4077-2
Data Sheet
THEORY OF OPERATION
The ADA4077-2 is the sixth generation of the Analog Devices, Inc.,
industry-standard OP07 amplifier family. The ADA4077-2 is a
high precision, low noise operational amplifier with a combination
of extremely low offset voltage and very low input bias currents.
Unlike JFET amplifiers, the low bias and offset currents are
relatively insensitive to ambient temperatures, even up to 125°C.
The Analog Devices proprietary process technology and linear
design expertise have produced a high voltage amplifier with
superior performance to the OP07, OP77, OP177, and OP1177
in tiny, 8-lead SOIC and 8-lead MSOP packages. Despite its
small size, the ADA4077-2 offers numerous improvements,
including low wideband noise, wide bandwidth, lower offset
and offset drift, lower input bias current, and complete freedom
from phase inversion.
The ADA4077-2 has a specified operating temperature range of
−40°C to +125°C with a MSL1 rating, which is as wide as any
similar device in a plastic surface-mount package. This is
increasingly important as PCB and overall system sizes
continue to shrink, causing internal system temperatures to rise.
In the ADA4077-2, power consumption is reduced by a factor
of four from the OP177, and bandwidth and slew rate have both
increased by a factor of six. The low power dissipation and very
stable performance vs. temperature also act to reduce warm-up
drift errors to insignificant levels.
Inputs are protected internally from overvoltage conditions
referenced to either supply rail. Like any high performance
amplifier, maximum performance is achieved by following
appropriate circuit and PCB guidelines.
Rev. 0 | Page 16 of 20
Data Sheet
ADA4077-2
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
OUTPUT PHASE REVERSAL
Phase reversal is defined as a change of polarity in the amplifier
transfer function. Many operational amplifiers exhibit phase
reversal when the voltage applied to the input is greater than the
maximum common-mode voltage. In some instances, this can
cause permanent damage to the amplifier. In feedback loops, it can
result in system lockups or equipment damage. The ADA4077-2 is
immune to phase reversal problems even at input voltages
beyond the supplies.
Calibration of the bridge is made at the minimum value of
the temperature to be measured by adjusting RP until the
output is zero.
To calibrate the output span, set the full-scale and linearity
potentiometers to midpoint and apply a 500°C temperature to
the sensor or substitute the equivalent 500°C RTD resistance.
Adjust the full-scale potentiometer for a 5 V output. Finally,
apply 250°C or the equivalent RTD resistance and adjust the
linearity potentiometer for 2.5 V output. The circuit achieves
better than ±0.5°C accuracy after adjustment.
+15V
0.1µF
2
500Ω
ADR4525
4.12kΩ
1
4.37kΩ
200Ω
6
4.12kΩ
1/2
ADA4077-2
100Ω
7
VOUT
5
CH2 5.00V
M10.0ms
T 0.000%
A CH1
300mV
49.9kΩ
100Ω
RTD
Figure 59. No Phase Reversal
LOW POWER LINEARIZED RTD
2
A common application for a single element varying bridge is an
RTD thermometer amplifier, as shown in Figure 60. The excitation
is delivered to the bridge by a 2.5 V reference applied at the top
of the bridge.
RTDs can have a thermal resistance as high as 0.5°C to 0.8°C
per mW. To minimize errors due to resistor drift, the current
through each leg of the bridge must be kept low. In this circuit,
the amplifier supply current flows through the bridge. However,
at the ADA4077-2 maximum supply current of 500 μA, the
RTD dissipates less than 0.1 mW of power, even at the highest
resistance. Errors due to power dissipation in the bridge are
kept under 0.1°C.
Rev. 0 | Page 17 of 20
5kΩ
V+
8
1/2
ADA4077-2
1
VOUT
3
4
V–
Figure 60. Low Power Linearized RTD Circuit
10238-064
CH1 5.00V
20Ω
10238-063
100Ω
ADA4077-2
Data Sheet
PROPER BOARD LAYOUT
The ADA4077-2 is a high precision device. To ensure optimum
performance at the PCB level, care must be taken in the design
of the board layout.
To avoid leakage currents, maintain a clean and moisture-free
board surface. Coating the surface creates a barrier to moisture
accumulation and helps reduce parasitic resistance on the board.
Keeping supply traces short and properly bypassing the power
supplies minimizes power supply disturbances caused by output
current variation, such as when driving an ac signal into a heavy
load. Connect bypass capacitors as closely as possible to the
device supply pins. Stray capacitances are a concern at the
outputs and the inputs of the amplifier. It is recommended that
signal traces be kept at least 5 mm from supply lines to
minimize coupling.
A variation in temperature across the PCB can cause a
mismatch in the Seebeck voltages at solder joints and other
points where dissimilar metals are in contact, resulting in
thermal voltage errors. To minimize these thermocouple effects,
orient resistors so heat sources warm both ends equally. Input
signal paths should contain matching numbers and types of
components, where possible, to match the number and type of
thermocouple junctions. For example, dummy components
such as zero value resistors can be used to match real resistors
in the opposite input path. Place matching components in close
proximity to each other and orient them in the same manner.
Ensure that leads are of equal length so that thermal conduction
is in equilibrium. Keep heat sources on the PCB as far away
from amplifier input circuitry as is practical.
The use of a ground plane is highly recommended. A ground
plane reduces EMI noise and helps to maintain a constant
temperature across the circuit board.
Rev. 0 | Page 18 of 20
Data Sheet
ADA4077-2
PACKAGING AND ORDERING INFORMATION
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
3.20
3.00
2.80
8
3.20
3.00
2.80
5.15
4.90
4.65
5
1
4
PIN 1
IDENTIFIER
0.65 BSC
0.95
0.85
0.75
15° MAX
1.10 MAX
0.80
0.55
0.40
0.23
0.09
6°
0°
0.40
0.25
10-07-2009-B
0.15
0.05
COPLANARITY
0.10
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-187-AA
Figure 61. 8-Lead Mini Small Outline Package [MSOP]
(RM-8)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
5.00 (0.1968)
4.80 (0.1890)
1
5
6.20 (0.2441)
5.80 (0.2284)
4
1.27 (0.0500)
BSC
0.25 (0.0098)
0.10 (0.0040)
COPLANARITY
0.10
SEATING
PLANE
0.50 (0.0196)
0.25 (0.0099)
1.75 (0.0688)
1.35 (0.0532)
0.51 (0.0201)
0.31 (0.0122)
45°
8°
0°
0.25 (0.0098)
0.17 (0.0067)
1.27 (0.0500)
0.40 (0.0157)
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MS-012-AA
CONTROLLING DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETERS; INCH DIMENSIONS
(IN PARENTHESES) ARE ROUNDED-OFF MILLIMETER EQUIVALENTS FOR
REFERENCE ONLY AND ARE NOT APPROPRIATE FOR USE IN DESIGN.
Figure 62. 8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_N]
Narrow Body
(R-8)
Dimensions shown in millimeters and (inches)
Rev. 0 | Page 19 of 20
012407-A
8
4.00 (0.1574)
3.80 (0.1497)
ADA4077-2
Data Sheet
ORDERING GUIDE
Model 1
ADA4077-2-ARMZ
ADA4077-2ARMZ-R7
ADA4077-2ARMZ-RL
ADA4077-2ARZ
ADA4077-2ARZ-R7
ADA4077-2ARZ-RL
ADA4077-2BRZ
ADA4077-2BRZ-R7
ADA4077-2BRZ-RL
1
Temperature Range
−40°C to +125°C
−40°C to +125°C
−40°C to +125°C
−40°C to +125°C
−40°C to +125°C
−40°C to +125°C
−40°C to +125°C
−40°C to +125°C
−40°C to +125°C
Package Description
8-Lead Mini Small Outline Package [MSOP]
8-Lead Mini Small Outline Package [MSOP]
8-Lead Mini Small Outline Package [MSOP]
8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_N]
8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_N]
8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_N]
8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_N]
8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_N]
8-Lead Standard Small Outline Package [SOIC_N]
Package Option
RM-8
RM-8
RM-8
R-8
R-8
R-8
R-8
R-8
R-8
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
©2012 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D10238-0-10/12(0)
www.analog.com/ADA4077-2
Rev. 0 | Page 20 of 20
Branding
A2X
A2X
A2X