Operational amplifier applications
advertisement

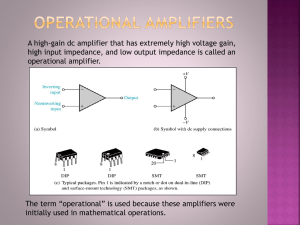
Operational amplifier applications - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operational_amplifier_applications Operational amplifier applications From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia This article illustrates some typical applications of solid-state integrated circuit operational amplifiers. A simplified schematic notation is used, and the reader is reminded that many details such as device selection and power supply connections are not shown. The resistors used in these configurations are typically in the kΩ range. <1 kΩ range resistors cause excessive current flow and possible damage to the device. >1 MΩ range resistors cause excessive thermal noise and make the circuit operation susceptible to significant errors due to bias currents. Note: It is important to realize that the equations shown below, pertaining to each type of circuit, assume that it is an ideal op amp. Those interested in construction of any of these circuits for practical use should consult a more detailed reference. See the External links and References sections. Contents 1 Linear circuit applications 1.1 Differential amplifier 1.1.1 Amplified difference 1.1.2 Difference amplifier 1.2 Inverting amplifier 1.3 Non-inverting amplifier 1.4 Voltage follower 1.5 Summing amplifier 1.6 Integrator 1.7 Differentiator 1.8 Comparator 1.9 Instrumentation amplifier 1.10 Schmitt trigger 1.11 Inductance gyrator 1.12 Zero level detector 1.13 Negative impedance converter (NIC) 2 Non-linear configurations 2.1 Precision rectifier 2.2 Peak detector 2.3 Logarithmic output 2.4 Exponential output 3 Other applications 4 See also 5 References 6 External links Linear circuit applications 1 of 9 2/2/07 10:50 AM Operational amplifier applications - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operational_amplifier_applications Differential amplifier The circuit shown is used for finding the difference of two voltages each multiplied by some constant (determined by the resistors). The name "differential amplifier" should not be confused with the "differentiator", also shown on this page. Differential Zin (between the two input pins) = R1 + R2 Differential amplifier Amplified difference Whenever R1 = R2 and Rf = Rg, Difference amplifier When R1 = Rf and R2 = Rg (including previous conditions, so that R1 = R2 = Rf = Rg): Inverting amplifier Inverts and amplifies a voltage (multiplies by a negative constant) Zin = Rin (because V - is a virtual ground) A third resistor, of value , added between the non-inverting input and ground, while not necessary, minimizes errors due to input bias currents. Inverting amplifier Non-inverting amplifier 2 of 9 2/2/07 10:50 AM Operational amplifier applications - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operational_amplifier_applications Amplifies a voltage (multiplies by a constant greater than 1) (realistically, the input impedance of the op-amp itself, 1 MΩ to 10 TΩ) A third resistor, of value , added between the Vin source and the non-inverting input, while not necessary, minimizes errors due to input bias currents. Non-inverting amplifier Voltage follower Used as a buffer amplifier, to eliminate loading effects or to interface impedances (connecting a device with a high source impedance to a device with a low input impedance) (realistically, the differential input impedance of the op-amp itself, 1 MΩ to 1 TΩ) Voltage follower Summing amplifier Sums several (weighted) voltages When , and Rf independent Summing amplifier When Output is inverted Input impedance Zn = Rn, for each input (V - is a virtual ground) Integrator 3 of 9 2/2/07 10:50 AM Operational amplifier applications - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operational_amplifier_applications Integrates the (inverted) signal over time (where Vin and Vout are functions of time, Vinitial is the output voltage of the integrator at time t = 0.) Integrating amplifier Note that this can also be viewed as a type of electronic filter. Differentiator Differentiates the (inverted) signal over time. The name "differentiator" should not be confused with the "differential amplifier", also shown on this page. Differentiating amplifier (where Vin and Vout are functions of time) Note that this can also be viewed as a type of electronic filter. Comparator Compares two voltages and outputs one of two states depending on which is greater Comparator Instrumentation amplifier Combines very high input impedance, high common-mode rejection, low DC offset, and other properties used in making very accurate, low-noise measurements Is made by adding a non-inverting buffer to each input of the differential amplifier to increase the input impedance. Instrumentation amplifier Schmitt trigger 4 of 9 2/2/07 10:50 AM Operational amplifier applications - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operational_amplifier_applications A comparator with hysteresis Schmitt trigger Inductance gyrator Simulates an inductor. Inductance gyrator Zero level detector Voltage divider reference Zener sets reference voltage Negative impedance converter (NIC) 5 of 9 2/2/07 10:50 AM Operational amplifier applications - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operational_amplifier_applications Creates a resistor having a negative value for any signal generator In this case, the ratio between the input voltage and the input current (thus the input resistance) is given by: for more information see the main article Negative impedance converter. Negative impedance converter Non-linear configurations Precision rectifier Behaves like an ideal diode for the load, which is here represented by a generic resistor RL. This basic configuration has some limitations. For more information and to know the configuration that is actually used, see the main article. Super diode Peak detector When the switch is closed, the output goes to zero volts. When the switch is opened for a certain time interval, the capacitor will charge to the maximum input voltage attained during that time interval. The charging time of the capacitor must be much shorter than the period of the highest appreciable frequency component of the input voltage. Peak detector Logarithmic output 6 of 9 2/2/07 10:50 AM Operational amplifier applications - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operational_amplifier_applications The relationship between the input voltage vin and the output voltage vout is given by: Logarithmic configuration where IS is the saturation current. If the operational amplifier is considered ideal, the negative pin is virtually grounded, so the current flowing into the resistor from the source (and thus through the diode to the output, since the op-amp inputs draw no current) is: where ID is the current through the diode. As known, the relationship between the current and the voltage for a diode is: This, when the voltage is greater than zero, can be approximated by: Putting these two formulae together and considering that the output voltage Vout is the inverse of the voltage across the diode VD, the relationship is proven. Note that this implementation does not consider temperature stability and other non-ideal effects. Exponential output The relationship between the input voltage vin and the output voltage vout is given by: where IS is the saturation current. Exponential configuration Considering the operational amplifier ideal, then the negative pin is virtually grounded, so the current through the diode is given by: 7 of 9 2/2/07 10:50 AM Operational amplifier applications - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operational_amplifier_applications when the voltage is greater than zero, it can be approximated by: The output voltage is given by: Other applications audio and video pre-amplifiers and buffers voltage comparators differential amplifiers differentiators and integrators filters precision rectifiers voltage regulator and current regulator analog-to-digital converter digital-to-analog converter voltage clamps oscillators and waveform generators Schmitt trigger Gyrator Comparator Active filter Analog computer See also Current-feedback operational amplifier Operational transconductance amplifier Frequency compensation References Paul Horowitz and Winfield Hill, "The Art of Electronics 2nd Ed. " Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1989 ISBN 0-521-37095-7 Sergio Franco, "Design with Operational Amplifiers and Analog Integrated Circuits," 3rd Ed., McGraw-Hill, New York, 2002 ISBN 0-07-232084-2 External links Introduction to op-amp circuit stages, second order filters, single op-amp bandpass filters, and a simple intercom (http://ourworld.compuserve.com/homepages/Bill_Bowden/opamp.htm) Op Amps for Everyone (http://focus.ti.com/lit/an/slod006b/slod006b.pdf) PDF A table of standard applications (http://www.rfcafe.com/references/electrical/opamps.htm) Hyperphysics — descriptions of common applications 8 of 9 2/2/07 10:50 AM Operational amplifier applications - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operational_amplifier_applications (http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/electronic/opampvar.html) Single supply op-amp circuit collection (http://instruct1.cit.cornell.edu/courses/bionb440/datasheets/SingleSupply.pdf) PDF Op-amp circuit collection (http://www.national.com/an/AN/AN-31.pdf) PDF A Collection of Amp Applications (http://www.analog.com/UploadedFiles/Application_Notes/28080533AN106.pdf) PDF — Analog Devices Application note Basic OpAmp Applications (http://www.ligo.caltech.edu/~vsanni/ph5/BasicOpAmpApplications.pdf) PDF Handbook of operational amplifier applications (http://focus.ti.com/lit/an/sboa092a/sboa092a.pdf) PDF — Texas Instruments Application note Low Side Current Sensing Using Operational Amplifiers (http://focus.ti.com/analog/docs/gencontent.tsp?familyId=57&genContentId=28017) Logarithmic amplifier (http://www.play-hookey.com/analog/logarithmic_amplifier.html) Precision half-wave rectifier (http://www.play-hookey.com/analog/half-wave_rectifier.html) Precision full-wave rectifier (http://www.play-hookey.com/analog/full-wave_rectifier.html) Log/anti-log generators, cube generator, multiply/divide amp (http://www.national.com/an/AN/AN-30.pdf) PDF Logarithmically variable gain from a linear variable component (http://www.edn.com/archives/1994/030394/05di7.htm) Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operational_amplifier_applications" Categories: Electronic amplifiers | Integrated circuits This page was last modified 16:54, 16 January 2007. All text is available under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License. (See Copyrights for details.) Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a US-registered 501(c)(3) tax-deductible nonprofit charity. 9 of 9 2/2/07 10:50 AM