Titanium surface covered with antimicrobial coating: antibacterial
advertisement

19 ो 25 ᳳ 20150618 Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
June 18, 2015
www.CRTER.org
Vol.19, No.25
1
1
150001)
2
1(1
1500012
1 !"#$%&'()*+,-% ./01
23456789:;
2 <=>?@ABCDEFGHIJDEFKLMGHINLMFGHIOP G
HIDQR SQGHTU:;
3 VWXYZ[7\,-]^_`ab!cdeQGHfghiDQjklmnoKpqr
Z[;
1987 !"
#$%&#'()*+,
-./012345
678
9:;<
= >?@A
150001
:R318
:A
ᨬ㽕
jksKtuDQlv Iwxy `zc4 !{|}YgVW"#~%Tt
XfdeQlmno012789:;
zC&'GHI
IFTU:;
1990 1 1 2014 1 1 Scopus I
(q)lm<
m/ Titanium alloyPlantAntibacterialCoating¡deQGH¢;
£GH¤F¥$%/DEFGHIJDEFKLMGHINLMFGHI
OP GHIDQR SQGH¦¤GH§K¨uDQlv ©ªK¦«¬­®f
GH78¯r°g"#>±GH²³´Bcµ¶tu IDQlv I-w
· I¸¹ ºr78m¡lB»I¼fg½¾e78N¿_´À?Á
EÂ&'GHÃlB»I¼ÄÅ !msE;
. 19(25):4069-4075.
:2095-4344
(2015)25-04069-07
ࠄߑـġ2015-04-05
http://WWW.crter.org
!"#$[J].%&'()*+,2015
doi:10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.25.026
Titanium surface covered with antimicrobial coating: antibacterial ability and
biocompatibility
Wang Jia-qi1, Shang Jian1, Sun Ye2, Han Xin-guang1(1Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital
of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China; 2Harbin Institute of Technology,
Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang Province, China)
Wang Jia-qi, Studying for
Abstract
master’s degree, Physician,
BACKGROUND: Titanium alloy with good biocompatibility, corrosion resistance and mechanical properties have
been widely used in clinic. How to give its excellent antibacterial properties so as to cope with plant-associated
infections has become a research focus in recent years.
OBJECTIVE: To review the principle, techniques, classification and relative merits of antimicrobial coating.
METHODS: A computer-based search of Scopus database and VIP database was performed by the first author
to retrieve relevant articles published from January 1990 to January 2014 using the keywords of “titanium alloy,
plant, antibacterial, coating”.
RESULTS AND CONCLUSION: Coatings can be classified into antibiotic coating, non-antibiotic organic
antimicrobial coating, inorganic antibacterial coating, anti-adhesion coating, antibacterial bioactive polymer
coating, all of which have better biocompatibility, but also have their limitations. Current studies concerning
antimicrobial coatings mainly focus on how to enhance the binding force between antimicrobial coating and the
substrate as well as how to get a good anti-bacterial ability, biocompatibility, high wear resistance and persistence;
antibacterial phase structure and distribution effects on the bacterial colonization. The antibacterial phase
structure and distribution is the key factor for the antimicrobial properties of titanium alloys with either entirely
added anti-bacterial elements or surface coating.
ISSN 2095-4344
CN 21-1581/R
CODEN: ZLKHAH
Department of Orthopedics,
First Affiliated Hospital of
Harbin Medical University,
Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang
Province, China
Corresponding author: Shang
Jian, Professor, Chief
physician, Master’s supervisor,
Department of Orthopedics,
First Affiliated Hospital of
Harbin Medical University,
Harbin 150001, Heilongjiang
Province, China
Accepted: 2015-04-05
4069
www.CRTER.org
. Subject headings: Biocompatible Materials; Titanium; Polymers
Wang JQ, Shang J, Sun Y, Han XG. Titanium surface covered with antimicrobial coating: antibacterial ability and
biocompatibility. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2015;19(25):4069-4075.
0
Introduction
!"#$%&!'(
)*+,-./012345678+9
[1]
: ;<=>?@ABC78+23DEF500G
[2]
H I78+,JKL/MNOPQRSTU
VWXYZ
[I\]^_`abcdK
[3]
LefSgh+9:,JKL i;jkl+
[4]
9:,JKLQmg0.5%6% ;nop^YZ
qrsLtuvwxyqrz{|}Q<
M;~Ck<r!r
*v
YZ23.
KL78+9:gTu
+9:,JK
[5-6]
Lv ;
78+jWT#V 4@¡
y¢qr£-¤¥¦\]^§¨©ª
«¬+¤K­78+®<¢QKL¯°q
[7]
r±ª²%³´µ¶ ;KLQ·¸°qr¥
[8]
¦<78+¹+eº qr»¼½3+
º¾¿§¨ÀÁÂ3I+eº¹MÃÄUe§
[9]
¨ÅÆ ;78+qr¥¦|}|FVÇÈu
ÉÊqr!qËV+ÌÍ,ÎÂ3ÉeÏÐ
¦<78+9:Ñqr¥¦ÒÓ§
[10-11]
;qr<¹+eºM}Ô[|}
+9:,JKLQÕÖ×Ø
Ùu
8¨£-¤ÚÛqrsLqrÜ|FÝÞ!¥º
7
8+{z78+ßàáâãäÓ±+9:
[12]
,JKLQ ;å
+eº¹æçqr<
78+¥¦ÜWX
78+,JKLQ
;èKL.éQê¨ë|}/ìÆíîïT
[13]
WXðñ ;ò¼Pxr Õóô
õrö÷Pøùrg~
Ckúûüý;
røù/þVg¨|Fø!
!!z!
ô
Wr tu9:ø<¨;rú
û=<VÇÊrøù23e
rXÕó\"røù
¨Pr!+,-!'
[14]
! /°úûJ!íî "r,#!
$%©4qr8úû&/¡¨']r(
)/øù*r,#!$%/+,
[15-18]
r J!
;
4070
1Data and methods
1.1 -.TÂ`/01990C1122014C1
1Scopus²34!=>56²34(O78),J
9 : / 0 J ! ; g h Titanium alloy Plant AntibacterialCoating"78+røùi
;
1.2 ˖9<¯=7-2røù$d
*>WJ?T@ABC~QÑ<DEFGQ
WTH9<;
˖Oúû"Meta$I"7-!²3
J¡`;
1.3 K/0Û9:609L==99:102
LM99:507LNÆúû,JO*7PQ!O9:Rz97LSTw9:õU=;
2
Results ì3øùudÜô$gdøù!V
dW§rWøù!§rWdøù!¥¦ø
ù!r+X+øù;
2.1 Y¼YZ23}2347
[16]
8+v= IY¼Z[W\]^ýÕ_
`WX[+a#¶*b<c
'[;d
døù/r9:eúûfxrÂ3
[17]
g!hij!cký ;
20lm70CHn.eoz@p=<Y
[18]
Jqrs=Qt_`rÂ3 ;78+øùÜV|
[19]
FKu!vVYZKL ;7wxy4z{
|d}~W,©01r/
Wü>¯V/d
[20]
øù=23ã01T
;W01r
Õr!!x!
!%x
Gx.e34r78+ø
[21-23]
ù
;
/.W+,-
@¡
[24]
+$v¨ ;Üe]vÛ]
[25]
78+øù IKXøù)
®<Tíî 'ÚV}#Õ
[26]
Åc ;>
^v[
%
¡¢>­UV<_`£¡WXW%
[27]
;3úû¤Ü|F¥¨<78+
[21]
¹TùK¦§øù duno^
v[%ÜV¨v©ª10«W%y,©4¬
­øøù®UVpÛ_`£¡
P.O. Box 10002, Shenyang
110180
www.CRTER.org
www.CRTER.org
. A
B
C
D
2 /
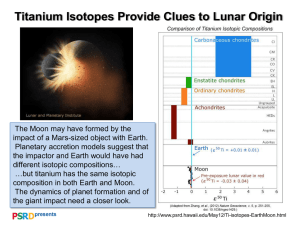
7 d !"#[66]
AC BD /!
"
[42]
}~O
;Îp;
!çè¯67
;fLðñ òó!9aô
õö÷NøùúNû
2.3
üòóýþn¨
Ldf}ñ¯°Þ!cdfCD!
YL_!f¾½}~O¾½£O
1 $
TiO2 %&'()*+,-./0[57]
"
L@Vq{!cY
[28-29]
!"#1$48 h%!
[30]
&'()*+,80%-.
012345
892:
!/
6701
[31]
L!"omn6r
OLÖOLMNL
[44]
L²aòóHB
[43]
rK
[45]
Lg¹Ð
[46]
ãA Rë!!"MNO
#ʯ
°HR!
df¾}~O!/$%&
[47]
; "<=>?@AB<CDEF!%G
OK
&O
%¯°HR! ST'ê
HBIJKLMNOPQHR!KL"%GST
[48]
*{ V}U£!67
UMNOVW$XF
[32]
YZ[\KL]^O
(¾)>
[49]
CD+zÄÅ!Y,JÓ-.JÓ/0 1
[50]
23Ö456789:
fghi!YZjkclmnop
?
qorLmns>tu"%qv!wxyz{
BCDOEFGHI,
df|n}~O!f;A6
!y¦?pJ|LYy
K
2.2
[33-34]
}Up; !
fL!Y2
oMNO
[35-36]
cL?
eoMNO ¡!¢£"¤¥@y¦>?!§
Yb?R¨©ª¤:^«¬­®
R!6±²aTiO2
µ±¶
[37]
¯°H
HB³"W´hi%
f¯°(e·¸`
g¹!º»V¼V}Ue½N
!{f¾
½K
}~O!}Ue,NO!¿df¾½
ÀO
[39]
Ç)ÈÉ
,
=ú>
[53]
@A~!Íòóýþ!
[54]
Õp
JÓ/0KLKM!7J|cLNO
[38]
[52]
;<}9:
[51]
_`a%GHB!YZbcde8
HBÁÂÃ4ÄÅÆy?p
ÊË£Ì
[40]
! Í;
[55]
OÊ!/P 6;<}9:ÄÅ9:
"HB
[56]
!Ç)ÈÉ =ú>?p
ØÇ)ÈÉ UQRSTULVWX
Y
LfRZr?!RZK
&O
fgrKL²8/[\Ü]K
Ø^K
DO
[56-57]
(
1)f¯°HR!Í _
%G(e!%GHBK
`abcZd
á½efá|K
gh
[58]
iÊ!L
6cjkl(Ym<)nopq
[49]
Y"?rst7
474"JÓ67fgrKL8!44
4uv6jk%G^«
[59]
w7"­xyæ
}Î!ÏÂlvW´hi%ÐÑ,l!Ò6
zÛÊ¥]¥,{|@}%G44~;7J
JÓ}Ô?!ÕÖJÓ×ØÙÚÍ
|cLOV6oLOVRë!c
ÛÜÝÞßà
[41]
ÕpMNO ¡eo!
LçIRë!Wz{V,LI
;fL6>?p%}Uá8hi:â
JÓÕ?±²p`7KLK
Ø!
ã/f¯°HRW;fLf6ä
:¿KLK
K
åK
æ!çèéáêB¯°RëcÍìíîï
KLK
O!KLK
!ä
ISSN 2095-4344
CN 21-1581/R
CODEN: ZLKHAH
[60-61]
IJÓ6
4071
www.CRTER.org
. [87]
åKLñIJÓK
n0KL%Tv!
8
rÜ!¿bO!}D!Ò
ãô
dfá½èn]z?
6äåKL
[62-63]
cj;L!YV
*mÒ6pHB!¿.fW
[64-65]
y¦>?¯°
°c×V{.fRZ
LO!¿³f}f¾)>"!§YVJÓ/
[66]
0·;O! YM¡¢O,
2.4
[67-69]
HBO67[\KLhø±²![\­v
[70-71]
KL¨²
ÛÜ
¨²O
6
HBO¨®
Y°±û!c;4¥HBO7²³K
h÷K
!®¶HR!°´Êµ
·~;6¸J|c]%äLO
WòóHBøùºº
[91]
HBnoþ!nWJcLOÏoK
&O âã
[73]
iW
L.fÃaK!c
LOÆy
óù79:)*/
âã
!c@âã6)*
W;O!c¾½¨_n)*/
ÆyÄ®6{ST]K
ªÜ
]K
I4JW$¾½óB!ó
LO.fyK
[92]
{®ÐL!6
à¼áâDãR7µD
}(!7µD
î
[82]
Í
ë®6+½KL¨²È
¹ºº
80%{Rê"!bÜ]K
¨²O
¨®º¹»34 6Z¼+½KL¨²
!ã/?ÊË£4K
óÒÓÔÓ
¿rKLK
DO!»34
ÕÖÓD×TI!6Z¼J|Ü]K
¨²Oë
¨²O
6cHB34
[89]
ÆyÄ®ú±²KLºû!hü
L£GY´Êµ~;Ti6Al4V6¾½rKL
¨²/õÜ]K
õö;4Í
º%GHB !"KLK
âã
˖HBOVW$}U¯
[72]
ã/!à¼á
aUKL¨²? à¼áâã67UøùýÓ
¥O¦®OHBHB77ä',!"K
Lq§¨²©ª@«c¬é?
âã_nÊp)*
[88]
[84]
[90]
(
2)
G0HBO!Y£¤n4
%¯°HR!Í)*cj }(!â
df
¾½]%ä!67¾¿)ÈÉ"À@9Á!³
LOcµÂ4ÃaJ|
[74]
¯°ÄR!K
O)DO
[82]
!c6hJ|%GLO
îïz!OLDO
dfA
L¨²aä7HBÍÅÆ7Ç'}|[\O±¶
|¯°Þ!ã/c"%HçnW¯
(INOX)>?p!7cHBä7O
°
4
È10 µΩ cmHB7Ç'yÂ"wfLÉ@KL¨
²øqÊ
[75]
!VW$¨²O
˯°Ì
˖6¯Y
!§Y¦®OÙÚ34
¼Ú
[76]
6Z¼ÏoQRSTULH^STUL²
m45
[77]
¼2ÍÙÚÎ
[78]
! Ðf¾½L³J|·DOI
[79-80]
Ó!YÑÒÓÔÓÕÖÓD×Ë4
¨²O
Øé?VjkKL¨²
"%G:Ù!ÇÚy
ÛÜÛÜ
pHB34
ÝÞß
ºº¨®ôõö
÷¨²O
2.5
DOIÓ!Yà¼áâ
ãRdfKL¨²L
[81-82]
à¼
áâãÕâãà¼á4Ãa!dDO
!BC}~Oϵ;äOLO
[83]
r5LåækçO,
âã6èn]éK
I4!J|c²8êëO)DO
Ü]K
HH9
[84-85]
à¼áâãdf¦
L!Oìy¦?põí]îïæ­îóî
ïíïðñ
DO
[86]
à¼áâã
òóIÓyºa!6ènÜ]K
²
4072
3䅼䆎Discussion ùòó}^«W¬7{
ªªg Ï[\!!è·ËL
%G¯Â!¯°¬V"Âdf|gú
L !fg+½KL²Çky
Û
ÜÆ+½òó}^« ¡'¸$to#
¥BC$Lkl!%&'()*+,Å·jO>?-ð%G!.Åhi
[93]
8/!Åvæ­0;Å12hi8/ !;
[94]
3|!<=45!Y#×tohMNLÏÂ pË02%&Ø^L6!8â12%&e
[95]
!7Ã2%^«MNÉ !>89:
;jk.Å<«wåÅv=â^
«!Upw>ÜçoefX:Ù^«,·j
[96-97]
?
YZ6?úL8â6
ú%G !VW$A½¯°Ì{
ç@½qI%¯°Ü¹!L%G ÛÜ
y¦?p<=W
Az{%G:Ù
^«V·j^«qB.´!O¯ÂJ
|îïzCDL%G !Up·j
òó}^«f¬é÷E
P.O. Box 10002, Shenyang
110180
www.CRTER.org
www.CRTER.org
. ˖
˖
˖
˖!"#$%&'()*+#$%,-./0
1&234(5426$7289:;2<=>?@ABC
!"DE
FGHI&JK-L!"#$% MNOP
QRK+STUV!"&'WXYZ[\]^_`.abcd
ef
!"Dg.hijk!"&'-
qr
!"s2tus2vw_s2dxs)yzMN
{|}~!"l2"
l$m.nop
MN.a)$
%!")U&'#$%.!"
l2
)!"sE {
,.a.a
¡¢.£¤¥¦.§¨©
4
খ㗗᭛⤂ References
[1]
Geetha M,Singh AK,Asokamani R,et al.Ti based biomaterials,
the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implantsea review. Prog
Mater Sci.2009;54:397-425.
,,,.2007-2008
[2]
[J].,2009,8(4):117-118.
[3]
Cristina A.Biomaterial-centered infection:microbial adhesion
versus tissue integration.Science.1987; 237(4822):
1588-1595.
[4]
Campoccia D,Montanaro L,Arciola CR.The significance of
infection related to orthopedic devices and issues of antibiotic
resistance.Biomaterials.2006;27:2331-2339.
[5]
Uçkay I,Hoffmeyer P,Lew D,et al.Prevention of surgical site
infections in orthopaedic surgery and bone trauma:
state-of-the-art update.J Hosp Infect.2013;84(1):5-12.
[6]
Arciola CR,Campoccia D,Speziale P,et al.Biofilm formation in
Staphylococcus implant infections. A review of molecular
mechanisms and implications for biofilm-resistant materials.
Biomaterials.2012;33(26):5967-5982.
[7]
Andrej T,Werner Z.Antimicrobial Agents in orthopaedic
Surgery. Drugs.2006; 66(5):1089-1105.
[8]
Williams DL,Sinclair KD,Jeyapalina S,et al.Characterization of
a novel active release coating to prevent biofilm implantrelated infections.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;
101(6):1078-1089.
[9]
Monteiro DR,Gorup LF,Takamiya AS,et al.The growing
importance of materials that prevent microbial adhesion:
antimicrobial effect of medical devices containing silver. Int J
Antimicrob Agents.2009;34:103-110.
[10] Speziale P,Pietrocola G,Rindi S,et al.Structural and functional
role ofStaphylococcus aureussurface components
recognizing adhesive matrix molecules of the host. Future
Microbiol.2009;4(10):1337-1352.
[11] Campoccia D,Speziale P,Ravaioli S,et al.The presence of
both bone sialoprotein-binding protein gene and collagen
adhesin gene as a typical virulence trait of the major epidemic
cluster in isolates from orthopedic implant infections.
Biomaterials.2009;30(34):6621-6628.
[12] Buchmann R,Khoury F.The microflora recovered from the
outer-surfaces of the Frialit-2 implanto-prosthetic
connector.Clin Oral Implants Res.2003;14(1):28-34.
ISSN 2095-4344
CN 21-1581/R
CODEN: ZLKHAH
[13] Jahoda D,Nyc O,Pokorny D,et al.Antibiotictreatment
forpreventionof infectiouscomplications injoint replacement.
Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech.2006; 73:108-114
[14] Bos R,Van Der Mei HC,Busscher HJ.Physico-chemistry of
initial microbial adhesive interactions- its mechanisms and
methods for study.FEMS Microbiol Rev.1999;23:179-229.
[15] An YH,Friedman RJ,Draughn RA,et al.Rapid quantification of
staphylococci adhered to titanium surfaces using image
analyzed epifluorescence microscopy.J Microbiol Methods.
1995;24:29-40.
[16] Jahoda D,Nyc O,Pokorny D,et al.Antibiotic treatment for
prevention of infectious complications in joint replacement.
Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech.2006;73: 108-114.
[17] Hetrick EM,Schoenfisch MH.Reducing implant-related
infections: active release strategies.Chem Soc Rev.2006;
35(9):780-789.
[18] Buchholz HW,Engelbrecht H.Uber die Depotwirkung einiger
Antibiotika bei Vermischung mit dem Kunstharz Palacos.
Chirurg.1970;41:511-515.
[19] Bernthal NM,Stavrakis AI,Billi F,et al.A mousemodel of
post-arthroplasty Staphylococcus aureus joint infection to
evaluate in vivo the efficacy of antimicrobial implant coatings.
PLoS One.2010;5:12580.
[20] Alt V,Bitschnau A,Osterling J,et al.The effects of combined
gentamicin-hydroxyapatite coating for cementless joint
prostheses on the reduction of infection rates in a rabbit
infection prophylaxis model.Biomaterials.2006;27:4627-4634.
[21] Stigter M,Bezemer J,de Groot K,et al.Incorporation of different
antibiotics into carbonated hydroxyapatite coatings on
titanium implants,release and antibiotic efficacy.J Control
Release.2004;99:127-137.
[22] Darouiche BO,Mausouri MD,Zakarevicz D,et al.In vivo
efficacy of antimicrobial-coated devices.J Bone Joint Surg
Am.2007;89:792-797.
[23] Radin S,Campbell JT,Ducheyne P,et al.Calcium phosphate
ceramic coatings as carriers of vancomycin.Biomaterials.
1997;18:777-782.
[24] Gautier H,Merle C,Auget JL,et al.Isostatic compression, a
new process for incorporating vancomycin into biphasic
calcium phosphate: Comparison with a classical method.
Biomaterials.2000;21:243-249.
[25] Jahoda D,Nyc O,Pokorny D,et al.Antibiotic treatment for
prevention of infectious complications in joint replacement.
Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech.2006;73:108-114.
[26] Taylor EN,Webster TJ.The use of superparamagnetic
nanoparticles for prosthetic biofilm prevention.Int J Nanomedi.
2009;4:145-152.
[27] Maddikeri RR,Tosatti S,Schuler M,et al.Reduced medical
infection related bacterial strains adhesion on bioactive RGD
odified titanium surfaces: a first step toward cell selective
surfacesJ Biomed Mater Res.2008;84A:425-435.
[28] Zilberman M,Elsner JJ.Antibiotic-eluting medical devices
for various applications.J Controll Release.2008;130:
202-215.
[29] Aninwene GE,Yao C,Webster TJ.Enhanced osteoblast
adhesion to drug-coated anodized nanotubular titanium
surfaces.Int J Nanomedi.2008;3:257-264.
[30] Lucke M,Schmidmaier G,Sadoni S,et al.Gentamicin coating of
metallic implants reduces implant-related osteomyelitis in
rats.Bone.2003;32:521-531.
4073
www.CRTER.org
. [31] Radin S,Ducheyne P.Controlled release of vancomycin from
thin sol-gel films on titanium alloy fracture plate material.
Biomaterials.2007;28:1721-1729.
[32] Tunney MM,Ramage G,Patrick S,et al. susceptibility of
bacteria isolated from orthopedic implants following revision
hip surgery.Antimicrob Agents Chemother.1998;42:
3002-3005
[33] Antoci V Jr,Adams CS,Hickok NJ,et al.Antibiotics for local
delivery systems cause skeletal cell toxicity in vitro. Clin
Orthop Relat Res.2007;462:200-206.
[34] Ince A,Schutze N,Hendrich C,et al.In vitro investigation of
orthopedic titanium-coated and brushite-coated surfaces
using human osteoblasts in the presence of gentamycin.J
Arthroplasty.2008;23:762-771.
[35] Kim WH,Lee SB,Oh KT,et al.The release behavior of CHX
from polymer-coated titanium surfaces.Surf Interface Anal.
2008;40:202-204.
[36] Barbour ME,O’Sullivan DJ,Jagger DC.Chlorhexidine
adsorption to anatase and rutile titanium dioxide.Colloids Surf
A.2007;307:116-120.
[37] Heasman PA,Heasman L Stacey F,et al.Local delivery of
chlorhexidine gluconate (PerioChip) in periodontal
maintenance patients.J Clin Periodontol.2001;28:90-95.
[38] Kozlovsky A,Artzi Z,Moses O,et al.Interaction of chlorhexidine
with smooth and rough types of titanium surfaces.J
Periodontol. 2006;77:1194-1200.
[39] Harris LG,Mead L,Muller-Oberlander E,et al.Bacteria and cell
cytocompatibility studies on coated medical grade titanium
surfaces.J Biomed Mater Res A.2006;78:50-58.
[40] Campbell AA,Song L,Li XS,et al.Development,
characterization, and anti-microbial efficacy of
hydroxyapatite-chlorhexidine coatings produced by
surface-induced mineralization. J Biomed Mater Res.2000;53:
400-407.
[41] Morra M,Cassinelli C,Cascardo G,et al.Adsorption of cationic
antibacterial on collagen-coated titanium implant devices.
Biomed Pharmacother.2004;58:418-422.
[42] Ince A,Schutze N,Hendrich C,et al.Effect of polyhexanide and
gentamycin on human osteoblasts and endothelial cells.Swiss
Med Wkly.2007;137:139-145.
[43] Lee D,Cohen RE,Rubner MF.Antibacterial properties of Ag
nanoparticle loaded multilayers and formation of magnetically
directed antibacterial microparticles. Langmuir.2005;21:
9651-9659.
[44] Li JX,Wang J,Shen LR,et al.The influence of polyethylene
terephthalate surfaces modified by silver ion implantation on
bacterial adhesion behavior. Surf Coat Technol. 2007;201:
8155-8159.
[45] Gosheger G,Hardes J,Ahrens H,et al.Silver-coated
megaendoprostheses in a rabbit model-an analysis of the
infection rate and toxicological side effects.Biomaterials.
2004;25:5547-56.
[46] Percival SL,Bowler PG,Russell D.Bacterial resistance to silver
in wound care.J Hosp Infect.2005;60:1-7.
[47] Rojas IA,Slunt JB,Grainger DW.Polyurethane coatings
release bioactive antibodies to reduce bacterial adhesion. J
Control Release.2000;63:175-189.
[48] Hardes J,Ahrens H,Gebert C,et al.Lack of toxicological
side-effects in silvercoated megaprostheses in humans.
Biomaterials.2007;28:2869-2875.
4074
[49] Zhang W,Luo Y,Wang H,et al.Ag and Ag/N(2) plasma
modification of polyethylene for the enhancement of
antibacterial properties and cell growth/proliferation.Acta
Biomater.2008;4:2028-2036.
[50] Kwok SCH,Zhang W,Wan GJ,et al.Hemocompatibility and
anti-bacterial properties of silver-doped diamond-like carbon
prepared by pulsed filtered cathodic vacuum arc
deposition.Diamond Relat Mater.2007;16:1353-1360.
[51] Ewald A,Gluckermann SK,Thull R,et al.Antimicrobial
titanium/silver PVD coatings on titanium.Biomed Eng
Online.2006;5:22.
[52] Chen W,Liu Y,Courtney HS,et al.In vitro anti-bacterial and
biological properties of magnetron co-sputtered
silver-containing hydroxyapatite coating.Biomaterials.
2006;27:5512-5517.
[53] Chung J,Hsieh MF,Huang CW,et al.Antimicrobial effects and
human gingival biocompatibility of hydro-xyapatite sol-gel
coatings.J Biomed Mater Res B. 2005;76:169-178.
[54] Vester H,Wildemann B,Schmidmaier Q,et al.Gentamycin
delivered from a PDLLA coating of metallic implants in vivo
and in vi-tro characterisation for local prophylaxis of
implant-related osteo-myelitis.Injury.2010;41(10):
1053-1059.
[55] Wan YZ,Raman S,He F,et al.Surface modification of medical
metals by ion implantation of silver and copper.Vacuum. 2007;
81:1114-1118.
[56] Ewald A,Gluckermann SK,Thull R,et al.Antimicrobial
titanium/silver PVD coatings on titanium.Biomed Eng Online.
2006;5:22.
[57] Chen W,Oh S,Ong AP,et al.Antibacterial and osteogenic
propeffies of silver-containing hydroxyapatite coatings
produced using a sol gel processJ Biomed Mater Res A.
2007;82(4):899-906.
[58] Bosetti M,Masse A,Tobin E,et al.Silver coated materials for
external fixation devices: In vitro biocompatibility and
genotoxicity.Biomaterials.2002;23:887-892.
[59] Secinti KD,Ayten M,Kahilogullari G,et al.Antibacterial effects
of electrically activated vertebral implants.J Clin Neurosci.
2008; 15:434-439.
[60] Feng QL,Wu J,Chen GQ,et al.A mechanistic study of the
antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and
Staphylococcus aureus.J Biomed Mater Res.2000;52:
662-668
[61] Kim JS,Kuk E,Yu KN,et al.Antimicrobial effects of silver
nanoparticles.Nanomedicine.2007;3:95-101.
[62] Li WR,Xie XB,Shi QS,et al.Antibacterial activity and
mechanism of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli.Appl
Microbiol Biotechnol.2010;85:1115-1122
[63] Kim KJ,Sung WS,Suh BK,et al.Antifungal activity and mode of
action of silver nano-particles on Candida albicans.Biometals.
2009;22:235-242
[64] Yoshinari M,Oda Y,Kato T,et al.Influence of surface
modifications to titanium on antibacterial activity in vitro.
Biomaterials.2001;22:2043-2048.
[65] Petrini P,Arciola CR,Pezzali I,et al.Antibacterial activity of zinc
modified titanium oxide surface.Int J Artif Organs.2006; 29:
434-442.
[66] Jeyachandran YL,Narayandass SK,Mangalaraj D,et al.A
study on bacterial attachment on titanium and hydroxyapatite
based films.Surf Coat Technol.2006;201:3462-3474.
P.O. Box 10002, Shenyang
110180
www.CRTER.org
www.CRTER.org
. [67] Wan YZ, Xiong GY, Liang H, et al.Modification of medical
metals by ion implantation of copper. Appl Surf Sci 2007;
253:9426-9429.
[68] Chin MY,Sandham A,de Vries J,et al.Biofilm formation on
surface characterized micro-implants for skeletal anchorage
in orthodontics.Biomaterials.2007;28:2032-2040.
[69] Gottenbos B,van der Mei HC,Klatter F,et al.Positively charged
biomaterials exert antimicrobial effects on gram-negative
bacilli in rats.Biomaterials.2003;24:2707-2710.
[70] Verran J,Whitehead K.Factors affecting microbial adhesion to
stainless steel and other materials used in medical devices.Int
J Artif Organs.2005;28:1138-1145.
[71] Legeay G,Poncin-Epaillard F,Arciola CR.New surfaces with
hydrophilic/hydrophobic characteristics in relation to
(no)bioadhesion.Int J Artif Organs.2006;29:453-461.
[72] Gallardo-Moreno AM,Pacha-Olivenza MA,Saldana L,et al.In
vitro biocompatibility and bacterial adhesion of physicochemically modified Ti6Al4V surface by means of UV
irradiation. Acta Biomater.2009;5:181-192.
[73] Aita H,Hori N,Takeuchi M,et al.The effect of ultraviolet
functionalization of titanium on integration with bone.
Biomaterials.2009;30:1015-1025.
[74] Del Curto B,Brunella MF,Giordano C,et al.Decreased
bacterial adhesion to surface-treated titanium.Int J Artif
Organs.2005;28:718-730.
[75] Koerner RJ,Butterworth LA,Mayer IV,et al.Bacterial adhesion
to titanium-oxy-nitride(TiNOX) coatings with different
resistivities: A novel approach for the development of
biomaterials.Biomaterials.2002;23:2835-2840.
[76] Roosjen A,Kaper HJ,van der Mei HC,et al.Inhibition of
adhesion of yeasts and bacteria by poly(ethylene
oxide)-brushes on glass in a parallel plateflow chamber.
Microbiology.2003;149(Pt 11):3239-3246.
[77] Gorth DJ,Puckett S,Ercan B,et al.Decreased bacteria activity
on Si(3)N(4) surfaces compared with PEEK or titanium.Int J
Nanomed.2012;7:4829-4840.
[78] Wang Q,Uzunoglu E,Wu Y,et al.Self-assembled poly(ethylene
glycol)-co-acrylic acid microgels to inhibit bacterial
colonization of synthetic surfaces.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.
2012;4(5):2498-2506.
[79] Zhang F,Zhang Z,Zhu X,et al.Silk-functionalized titanium
surfaces for enhancing osteoblast functions and reducing
bacterial adhesion.Biomaterials.2008;29:4751-4759.
[80] Harris LG,Tosatti S,Wieland M,et al.Staphylococcus aureus
adhesion to titanium oxide surfaces coated with
non-functionalized and peptide-functionalized poly(L-lysine)grafted-poly(ethylene glycol) copolymers.Biomaterials. 2004;
25:4135-4148.
[81] Singla AK,Chawla MM.Chitosan: Some pharmaceutical and
biological aspects-AN update.J Pharm Pharmacol.2001;53:
1047-1067.
ISSN 2095-4344
CN 21-1581/R
CODEN: ZLKHAH
[82]
[83]
[84]
[85]
[86]
[87]
[88]
[89]
[90]
[91]
[92]
[93]
[94]
[95]
[96]
[97]
Chua PH,Neoh KG,Kang ET,et al.Surface functionalization of
titanium with hyaluronic acid/chitosan polyelectrolyte multilayers
and RGD for promoting osteoblast functions and inhibiting
bacterial adhesion.Biomaterials.2008;29: 1412-1421.
Kim IY,Seo SJ,Moon HS,et al.Chitosan and its derivatives for
tissue engineering applications. Biotechnol Adv.2008;26:1-21.
Bumgardner JD,Wiser R,Gerard PD,et al.Chitosan:potential
use as a bioactive coating for orthopaedic and craniofacial/
dental implants.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2003;14:423-438.
Lahiji A,Sohrabi A,Hungerford DS,et al.Chitosan supports the
expression of extracellular matrix proteins in human
osteoblasts and chondrocytes.J Biomed Mater Res.2000;51:
586-595.
Khor E,Lim LY.Implantable applications of chitin and chitosan.
Biomaterials. 2003;24:2339-2349.
Martin HJ,Schulz KH,Bumgardner JD,et al.An XPS study on
the attachment of triethoxsilylbutyraldehyde to two titanium
surfaces as a way to bond chitosan.Appl Surf Sci.2008;254:
4599-4605.
Bumgardner JD,Chesnutt BM,Yuan Y,et al.The integration of
chitosan-coated titanium in bone: an in vivo study in rabbits.
Implant Dent.2007;16:66-79.
Milovic NM,Wang J,Lewis K,et al.Immobilized N-alkvlated
polyethy- lenimine avidly kills bacteria by rupturing Cell
membraves with no resistance developed.Bioeng.2005;
90:715-722
Montanaro L,Campoccia D,Arciola CR.Nanostructured
materials for inhibition of bacterial adhesion in orthopedic
implants: a minireview.Int J Artif Organs. 2008;31(9):771.
Jena P,Mohanty S,Mallick R,et al.Toxicity and antibacterial
assessment of chitosan-coated silver nanoparticles on human
pathogens and macrophage cells.Int J Nanomed.2012;7:
1805-1818.
Wang J,de Boer J,de Groot K.Proliferation and differentiation
of MC3T3-E1 cells on calcium phosphate/chitosan coatings.J
Dent Res.2008;87:650-654.
Stefánsdóttir A,Johansson A,Lidgren L,et al.
Bacterialcolonization and resistance patterns in 133 patients
undergoing a primary hip- or knee replacement in Southern
Sweden. Acta Orthop 2013;84(1).
Yasunaga H,Tsuchiya K,Matsuyama Y,et al. Analysis of
factors affecting operating time, postoperative complications,
and length of stay for total knee arthroplasty: nationwide
web-based survey. J Orthop Sci.2009;14(1):10-16.
Ridgeway S,Wilson J,Charlet A,et al.Infection of the surgical
site after arthroplasty of the hip.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2005;
87(6): 844-850.
Hanssen AD.Managing the infected knee: As good as it gets.J
Arthroplasty. 2002;17:98-101.
Ehrlich GD,Stoodley P,Kathju S,et al.Engineering approaches
for the detection and control of orthopaedic biofilm
infections.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2005;437:59-66.
4075