Presentation
advertisement

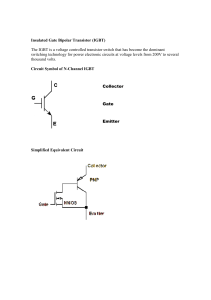
Indo German Meet Project Title IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology -Ganesh Bhalsing (06EE3009) -IIT Kharagpur - Under Guidance of Prof. H. Ryssel Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 1 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Agenda Introduction Different Power Transistors Comparison Between all Types of Power Transistors Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 2 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Agenda Introduction Power Electronic Devices Characteristics of an Ideal Switch Some Practical uses of Switches Classification of Power Semiconductors Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 3 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Introduction Power Electronic Devices Power semiconductor devices are the essential components determining the size, cost, efficiency of electronic systems for energy efficiency The proliferating demand of controllable power electronic systems has promoted research on Novel device materials Structures Circuit topologies Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 4 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Introduction Power Electronic Devices Base material used for power electronics devices – Silicon Silicon Carbide Silicon Silicon Carbide Breakdown Field 2.5 ×105 V/cm 2.2 ×106 V/cm Energy gap 1.12 eV 3.26 eV 4H-SiC Thermal Conductivity 1.5 W/cm 4.9 W/cm Also SiC shows high chemical inertness, high pressure, and radiation resistance and hence its popular in the recent days 5 Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Introduction Characteristics of Ideal Switch No driving losses : High input impedance so that the drive current is zero Zero on state or forward conduction losses : forward voltage drop is zero & high operational current density to make chip small Zero off state or reverse blocking losses : Infinitely larger reverse blocking voltage with zero leakage current No switching losses : turn on and turn off times should be zero. A small pulse of small width, tending to zero, must be used for the operations Low Cost : To reduce the cost of the electronic equipment Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 6 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Introduction Some Practical uses of Switches PWM control in DC motor control Rectifiers Air Conditioners and many more Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 7 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Introduction Some Practical uses of Switches DC motor control : RA + Vf - Armature Va Field Coil Motor used – Self excited DC motor • Flux is constant • Speed is controlled by varying Armature voltage (Va) Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 8 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Introduction Some Practical uses of Switches DC motor Control : Equations of DC motor modelling Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 9 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Introduction Some Practical uses of Switches DC motor control : Using the switch to control PWM (Pulse Width Modulation), Thus controlling Va and hence effective DC voltage supplied to motor Ref: 1 PWM generation using a switch Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 10 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Introduction Some Practical uses of Switches 3 Phase full bridge rectification : Input Circuit Output Waveform Ref: http://www.allaboutcircuits.com/vol_3/chpt_3/4.html Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 11 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Introduction Classification of Power Semiconductors Classification of Power Semiconductors Ref: 1 Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 12 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Agenda Introduction Different Power Transistors Comparison Between all Types of Power Transistors Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 13 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors Different Power Transistors BJT MOSFETs Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors Static Induction Transistors (SIT) COOLMOS Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 14 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors Power transistors Controlled Turn-on & Turn-off Characteristics : Power transistors have controlled turn-on and turn-off characteristics Region of Operation : Transistors used as switches are generally used in the saturation region, resulting in low on-state voltage drop Ratings : These power transistors come with varying switching frequencies and with different current and voltage ratings Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 15 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 1.BJT’s (Bipolar Junction Transistors) Construction : Ref: 1 Basic NPN transistor constructional design Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 16 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 1.BJT’s Input/Output Characteristics Output Characteristics Input Characteristics Ref: 1 Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 17 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 1.BJT’s Transfer Characteristics of Switch Transfer Characteristics of switch Circuit diagram (common emitter) Ref: 1 Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 18 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 1.BJT’s Switching Characteristics Switching times of BJT Model with current gain Ref: 1 Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 19 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 1.BJT’s Switching Limits Second Breakdown (SB) : Destructive phenomenon due to current flow only to small region of the base producing local hot spots. Breakdown Voltage : Voltage between two terminals for which the current rises rapidly irrespective of rise in voltage level. Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 20 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 2.Power MOSFETs A voltage controlled device Overcoming problems of BJT BJT being current controlled, current gain depends on junction temperature but this problem is removed in MOSFET Very high input impedance hence low current No problem of second breakdown phenomenon High switching speed i.e. low switching time since voltage controlled Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 21 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 2.MOSFETs Construction ‘n’ channel depletion type Ref: 1 ‘n’ channel enhancement Type Ref: 1 Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 22 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 2.MOSFETs Transfer Characteristics ‘n’ channel depletion type Ref: 1 ‘n’ channel enhancement type Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Ref: 1 23 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 2.MOSFETs Output Characteristics ‘n’ channel enhancement type Ref: 1 Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 24 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 2.MOSFETs Switching Characteristics Parasitic model of enhancement MOSFET Switching characteristics Ref: 1 Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Ref: 1 25 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology MOSFET Different Power Transistors BJT Ref: 1 Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 26 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) It combines the properties of both BJT – Low on state conduction losses & MOSFET - High input impedance Various other names are COMFET (Conductivity Modulated FET) IGT (Insulated Gate Transistor) IGR (Insulated Gate Rectifier) GEMFET (Gain enhanced MOSFET) BiFET (Bipolar FET) Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 27 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBTs - construction Unit Cell Ref: 2 It is identical to that of MOSFET except the doping on the Nsubstrate Performance close to that of a BJT than a MOSFET Four alternate PNPN layer Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 28 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBTs – equivalent circuit representation Ref: 2 N channel enhancement mode MOSFET driving a PNP bipolar transistor Presence of gate, collector and emitter Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 29 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBTs – Output & Transfer Characteristics Ref: 2 Ref: 1 Output Characteristics Gate- emitter characteristics Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 30 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBT’s Switching Characteristics Turn on characteristics Turn on takes place by voltage Low gate power requirement means that computer-controlled signals from integrated driver circuits can be used IGBT turn on is slower than the MOSFET because of the necessity of forcing both the MOSFET and BJT inside it Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 31 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBT’s Switching Characteristics Ref: 2 IGBT turn on with a resistive load When the gate voltage equals the threshold voltage Vth, the collector-emitter current Ice begins to flow and rises rapidly according to the transconductance parameter gm Eon= (Vs × I × Tc)/6 Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 32 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBT’s Switching Characteristics Turn off characteristics Ref: 2 As soon as the gate voltage ceases IGBT turns off – time to decay of collector current from 90% to 10% Decay time is composed of two halves. One due to discharge of current across Rge and Cge and second (time consuming one ) due to recombination in the N- base 33 Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBT’s Switching Characteristics Ref: 2 Effect of increasing gate resistance Effect of increasing electron dose in the N- base Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 34 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBT’s Switching Characteristics Ref: 2 Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 35 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology 3.IGBTs – Device Structures Different Power Transistors Lateral IGBT Ref: 2 Used for integration with devices for control security No JFET region is present Block voltage in both directions, due to back to back p-n junction More surface area used Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 36 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBTs – Device Structures Ref: 2 Non - Punctured Type Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Ref: 2 Punctured Type 37 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBTs – Device Structures Punctured Type Non Punctured Type Heavily doped n layer Switching time is reduced More fragile than punctured Current flow via diffusion Based on growing thick epitaxial layer on p+ substrate Less thermally stable Moderately doped Carrier lifetime is kept more Less fragile Current flow by drift Based on thin wafer technology. More thermally stable Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 38 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBTs – Device Structures Self Clamped IGBT Equivalent Circuit Ref: 2 Has integrated gate collector clamp diodes for IGBTs protection Used in automotive ignition system where it acts as a driver Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 39 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBTs – Device Structures Trench Gate IGBT Ref: 2 Ref: 2 Injection enhanced IGBT 40 Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBTs – Technologies Trench Type IGBT Normal IGBT suffers from electric current crowding and electric field crowding Current crowding reduces the conductivity modulation Solution Increase the gate length, for more conductivity modulation decrease the path travelled by electrons under the emitter region Trench Gate has no JFET region hence minimizes on state losses The U shaped trench decreases the path Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 41 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBTs – Device Structures Larger injection of electron from N channel to N-base Hole current is suppressed Small forward voltage drop Ref: 2 Injection enhanced IGBT Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 42 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology 3.IGBTs – Device Structures Different Power Transistors Resurf Technology Reduced surface electric field (Resurf concept) for breakdown Voltage enhancement in Lateral IGBT High resistive P- substrate Epitaxial N- layer over it Laterally bounded by a P+ diffused region 2 diodes : Horizontal P-N- and vertical P+NBreakdown occurs at the core rather than surface By choosing proper conditions Ref: 2 Thus using high ohmic contacts and thin epitaxial layers and satisfying above condition break down voltage can be increased Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 43 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBTs – Modes of Operation Reverse Blocking Ref: 2 Positive voltage is applied to N+emitter Negative bias is applied to the P+collector Gate terminal is shorted to the emitter terminal J1 and J3 are reverse biased and J2 is forward biased. The resistivity and thickness of the N- base must therefore be optimized for the required breakdown voltage Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 44 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBTs – Modes of Operation Forward Blocking Mode Negative voltage is applied to N+emitter Positive bias is applied to the P+collector Gate terminal is shorted to the emitter terminal Ref: 2 J1 and J3 are forward biased and J2 is reverse biased. Most of the depletion layer expands into N- base Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 45 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBTs – Modes of Operation Forward Conduction Mode Ref: 2 Negative voltage is applied to N+emitter Positive bias is applied to the P+collector Positive bias to gate terminal N type conducting channel formed in the P – base region bridges across the N+ emitter and N- base Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 46 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 3.IGBTs – Protection Overvoltages : During the blocking state, any applied voltage in excess of the breakdown voltage between collector and emitter terminals causes avalanche breakdown Attach voltage arrestor in parallel to the IGBT If the reverse blocking voltage of IGBT is small, a reverse connected diode placed across the IGBT is helpful Overcurrents : Overcurrent is the current value at which junction temperature becomes more than 150°C When an overcurrent is sensed, the gate voltage is decreased by switching a zener diode across the gate terminal within a short time interval of 1μsec Transients : Ramp waveform or a two step-waveform replaces the conventional stepped voltage waveform Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 47 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 4.COOLMOS Ref: 3 Recently a new technology for high voltage Power MOSFETs has been introduced CoolMOS CoolMOS™ virtually combines the low switching losses of a MOSFET with the on-state losses of an IGBT The drastically lower gate charge facilitates and reduces the cost of controllability the smaller feedback capacitance reduces the dynamic losses Also very less R(ds) on state Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 48 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 5. SITs (Static Induction Transistors) - construction Ref: 1 Vertical structure with short multi-channels Identical to JFET except for vertical and buried gate Short channel length – low gate resistance, low gate-source capacitance, small thermal resistance Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 49 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 5. SITs - Output Characteristics Ref: 1 Its typically an ON device and a negative gate voltage holds it off Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 50 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors 5. SITs Characteristics High power, high frequency device Turn-on and turn-off times are very small, typically 0.25 µ secs On-state drop as high as 90 V for 180 A device & 18 V for 18 A Work on power with 100KVA at 100 kHz or 10 VA at 10GHz Most suitable for high power, high frequency, applications (audio, microwave amplifiers) Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 51 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors Introduction Different Power Transistors Comparison Between all Types of Power Transistors Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 52 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Comparison Chart Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Different Power Transistors Ref: 1 53 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors Thank You Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 54 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology References : 1. 2. 3. 4. Different Power Transistors ‘Power Electronics – Circuits, devices, and applications’ , Third Edition 2007, by Muhammad H. Rashid IGBT – Theory and Design, by Vinod Kumar Khanna, IEEE Press, 2003 ‘COOLMOSTM-a new milestone in high voltage power MOS’ – Paper presented in ‘Power Semiconductor Devices and ICs, 1999. ISPSD '99. Proceedings’, The 11th International Symposium, publication date: 1999 ‘Solid State Electronic Devices’, Sixth Edition 2007, by Ben G. Streetman & Sanjay Kumar Banerjee Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 55 IGBT’s Characteristics & Technology Different Power Transistors Questions ? Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur 56