Wire Gauge Chart - WECU Surveillance
advertisement

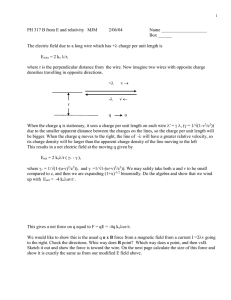
Wire Gauge Chart Determining Wire Gauge Example: Power supply voltage equals 12 volts. Load equals 3 electromagnetic locks. Each lock requires 0.280 amps of current. Total current draw equals (3 x 0.280 = 0.840 amps). Round off current to 1 Amp. (Always round off in an upward direction.) Distance from farthest electromagnetic lock equals 100 feet. Locate the 1.00 Amp 12V row from the left side of the chart. Select the distance in this row closest to the distance of the farthest lock. The wire gauge required can be found at the top of the column (#18 AWG). Total Voltage (AWG) American Wire Gauges (minimum) Amps AC or DC 12V 24V 12V 24V 12V 24V 12V 24 V 12V 24V 12V 24V 12V 24V 12V 24V 12V 24V 12V 24V 12V 10 3000 6000 1500 3000 1000 2000 800 1600 600 1200 500 1000 460 920 400 800 350 700 300 600 280 12 2000 4000 1000 2000 600 1200 500 1000 380 760 300 600 275 550 240 480 200 400 190 380 170 14 1200 2400 600 1200 375 750 300 600 240 480 200 400 170 340 150 300 130 260 120 240 100 16 750 1500 375 750 250 500 200 400 150 300 125 250 100 200 90 180 80 160 75 150 70 24V 12V 24V 560 260 520 340 160 320 200 100 200 140 60 120 .250A .500A .750A 1.00A 1.25A 1.50A 1.75A 2.00A 2.25A 2.50A 2.75A 3.00A 18 450 900 225 450 150 300 100 200 90 180 80 160 70 140 60 120 50 100 20 300 600 150 300 100 200 75 150 60 120 50 100 40 80 35 70 Total distance in feet (maximum) Types of Wire: Wire Gauge: Hookup wire is available in both solid and stranded wire types. Stranded wire is the accepted standard for system hookup as it is more flexible and less likely to break. It’s made of several small-diameter wires twisted together to form one larger-diameter conductor. To prevent the strands from separating, stranded wire is usually tinned (solder applied to ends of wire). This makes connections easier and prevents the wire from fraying. Wire is given a gauge number to classify it by its size or thickness. American wire gauge (AWG) is the most common measurement for electrical wire size – the lower the wire gauge number, the larger the wire diameter and the greater the current carrying capability. Wire Composition: Most electrical hookup wire is copper; some is copper-coated aluminum. Aluminum wire is cheaper, but copper is the preferred wire choice. Wire Insulation: The wire insulation should be UL or CSA approved for the maximum voltage to which the wire will be subjected. Normally, the wire rating is three to six times greater than the maximum voltage to be applied to the wire.