Terminal Sides of Angles (Definitions)
advertisement

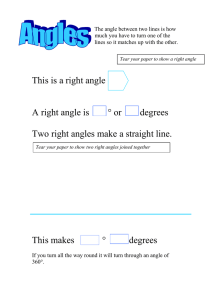
Terminal Sides of Angles Positive Angles: Positive angles are angles such that their initial side is the positive x-axis and their “terminal” side is determined by turning in a counterclockwise direction. Negative Angles: Negative angles are angles such that their initial side is the positive x-axis and their “terminal” side is determined by turning in a clockwise direction. Co-Terminal Angles: are angles whose terminal sides fall on the same line. How To: Determine the coordinates of a point that lies on a terminal side: draw a right triangle to the x-axis and use Pythagorean Theorem and/or SOHCAHTOA relationships to determine missing side lengths. Determine which quadrant the terminal side on an angle will fall: 0 < angle < 90 Quadrant I angle = 90 positive y-axis 90 < angle < 180 Quadrant II angle = 180 negative x-axis 180 < angle < 270 Quadrant III angle = 270 negative y-axis 270 < angle < 360 Quadrant IV angle = 360 positive x-axis * For angles greater than 360, you must subtract 360(or multiple) from the angle until the result is between 0 and 360. Find Co-Terminal Angles: Positive Co-terminal: angle + 360 Negative Co-terminal angle: angle - 360 Special angles: A positive 90o angle’s terminal side falls on the positive y-axis (same as a negative 270o) A positive 180o angle’s terminal side falls on the negative x-axis (same as a negative 180o) A positive 270o angle’s terminal side falls on the negative y-axis (same as a negative 90o)