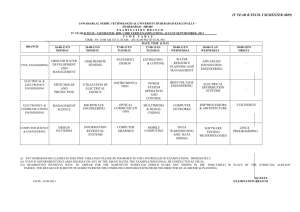
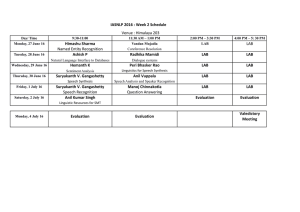
Opamps - Department of EEE
advertisement

Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 COURSE OBJECTIVES Academic Year Semester : 2013 : I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……Electrical……………… Year: ……III….. Section: A / B /C Course/Subject: …………………Opamps………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ………………R Anil Kumar………………………..Dept.: ………EEE… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR On completion of this Subject/Course the student shall be able to: S. No Objectives 1 Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2 Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 3 Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. 4 Familiarize the conversion of data from Analog to Digital and Digital to Analog. Signature of HOD Signature of faculty Date: Date: Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 COURSE OUTCOMES Academic Year Semester : 2013 : I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……..…Electrical……..… Year: ……III……….. Section: A / B /C Course/Subject: ……………Op-Amps…………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil Kumar……………………………..Dept.: …EEE……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR. The expected outcomes of the Course/Subject are: Outcomes S.No 1 Define significance of Op Amps and their importance. 2 Build circuits using Analog IC’s. 3 In-depth knowledge of applying the concepts in real time applications. 4 Ability to use OP Amp as Summer, Subtractor, Multiplier and Divider. 5 Able to use OP Amp to generate sine waveform, Square wave form, Triangular wave forms. 6 Able to use OP Amp to as analog to digital and digital to analog converter. 7 Design and explain the Analog to Digital conversion operation and vice versa. Signature of HOD Signature of faculty Date: Date: Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (An Autonomous Institute under JNTUH) Department/Program-EEE Vision of the Institute To be among the best of the institutions for engineers and technologists with attitudes, skills and knowledge and to become an epicenter of creative solutions. Mission of the Institute To achieve and impart quality education with an emphasis on practical skills and social relevance. Vision of the Department To impart technical knowledge and skills required to succeed in life, career and help society to achieve self sufficiency. Mission of the Department • • • • To become an internationally leading department for higher learning. To build upon the culture and values of universal science and contemporary education. To be a center of research and education generating knowledge and technologies which lay groundwork in shaping the future in the fields of electrical and electronics engineering. To develop partnership with industrial, R&D and government agencies and actively participate in conferences, technical and community activities. Program Educational Objectives: This programme is meant to prepare our students to professionally thrive and to lead. During their progression: PEO 1: Graduates will have a successful technical or professional careers, including supportive and leadership roles on multidisciplinary teams. PEO 2: Graduates will be able to acquire, use and develop skills as required for effective professional practices. PEO 3: Graduates will be able to attain holistic education that is an essential prerequisite for being a responsible member of society. PEO 4: Graduates will be engaged in life-long learning, to remain abreast in their profession and be leaders in our technologically vibrant society. Program outcomes. a) Ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering. b) Ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret data. c) Ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs within realistic constraints such as economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety, manufacturability, and sustainability. d) Ability to function on multi-disciplinary teams. e) Ability to identify, formulates, and solves engineering problems. f) Understanding of professional and ethical responsibility. g) Ability to communicate effectively. h) Broad education necessary to understand the impact of engineering solutions in a global, economic, environmental, and societal context. i) Recognition of the need for, and an ability to engage in life-long learning. j) Knowledge of contemporary issues. k) Ability to utilize experimental, statistical and computational methods and tools necessary for engineering practice. l) Graduates will demonstrate an ability to design electrical and electronic circuits, power electronics, power systems; electrical machines analyze and interpret data and also an ability to design digital and analog systems and programming them. Name of the Course: Op Amps Course educational objectives: On completion of this Subject/Course the student shall be able to 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 3. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. 4. Familiarize the conversion of data from Analog to Digital and Digital to Analog. Course outcomes: At the end of the course student will have ability to 1. Define significance of Op Amps and their importance. 2. Build circuits using Analog IC’s. 3. In-depth knowledge of applying the concepts in real time applications. 4. 5. 6. 7. Ability to use OP Amp as Summer, Subtractor, Multiplier and Divider. Able to use OP Amp to generate sine waveform, Square wave form, Triangular wave forms. Able to use OP Amp to as analog to digital and digital to analog converter. Design and explain the Analog to Digital conversion operation and vice versa. Assessment methods: 1. 2. 3. 4. Regular attendance to classes. Written tests clearly linked to learning objectives Classroom assessment techniques like tutorial sheets and assignments. Seminars. 1. Program Educational Objectives (PEOs) – Vision/Mission Matrix (Indicate the relationships by mark “X”) Mission of department PEOs Higher Learning Graduates will have a successful technical or professional careers, including supportive and leadership roles on multidisciplinary teams Graduates will be able to acquire, use and develop skills as required for effective professional practices Graduates will be able to attain holistic education that is an essential prerequisite for being a responsible member of society Graduates will be engaged in life-long learning, to remain abreast in their profession and be leaders in our technologically vibrant society. Research Contemporary Technical Education knowledge X X X X X X X X X X X 2. Program Educational Objectives(PEOs)-Program Outcomes(POs) Relationship Matrix (Indicate the relationships by mark “X”) P-Outcomes PEOs 1 2 3 4 a X X b X X X c X X X d X X X X e f g X X X X h X X X i X X X X j X X X X k X X l X X X 3. Course Objectives-Course Outcomes Relationship Matrix (Indicate the relationships by mark “X”) Course-Outcomes 1 2 X X X 3 4 X X X X X 5 6 7 X X X X X Course-Objectives 1 2 3 4 X X X X 4. Course Objectives-Program Outcomes (POs) Relationship Matrix (Indicate the relationships by mark “X”) P-Outcomes a C-Objectives 1 2 3 4 X X X X b X X c d e f g h i X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X X j X k l X X X X X X 5. Course Outcomes-Program Outcomes (POs) Relationship Matrix (Indicate the relationships by mark “X”) a P-Outcomes C-Outcomes 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 6. b c X X X X X X X X X X d e f X X X X X X X X X X g h i j k X X X X X X X X X X X X X X l X X X X X Courses (with title & code)-Program Outcomes (POs) Relationship Matrix (Indicate the relationships by mark “X”) P-Outcomes a b c d e f g h i Courses Op AmpsGR11A3078 X X X X X X X X X j k l X X 7. Program Educational Objectives (PEOs)-Course Outcomes Relationship Matrix (Indicate the relationships by mark “X”) P-Objectives (PEOs) 1 2 3 4 X X X X Course-Outcomes 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8. X X X X X X X X X X X X Assignments & Assessments-Program Outcomes (POs) Relationship Matrix (Indicate the relationships by mark “X”) P-Outcomes a Assessments 1 2 3 4 X X X X 9. X X b c d X X X X e f X X X g X X X h X i X X X j X X X X k l X X X X Assignments & Assessments-Program Educational Objectives (PEOs) Relationship Matrix (Indicate the relationships by mark “X”) P-Objectives (PEOs) Assessments 1 2 3 4 1 X X 2 3 4 X X X X X X X X X X Assessment process and Relevant Surveys conducted: 10. Constituencies -Program Outcomes (POs) Relationship Matrix (Indicate the relationships by mark “X”). P-Outcomes Constituencies 1 2 3 4 a b c d e f G h i j k l 5 6 Assessment Process and Areas of improvements: Prepare the following Matrix: 11. The improvements Matrix are summarized below and described in the text that follows. Hint: Example: Proposed Change Year Proposed Year Implemented Old Version New Version Comments Add new Operating System course 2013-2014 2014-2015 No operating system course in curriculum Operating System Concepts & Administration To address need for additional material for operating systems Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 GUIDELINES TO STUDY THE COURSE / SUBJECT Academic Year Semester : 2013 : I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……………Electrical…… Year: ……III………….. Section: A / B /C Course/Subject: ……………Op-Amps……… Course Code: ……GR11A3078………… Name of the Faculty: …………… R. Anil Kumar ………………………..Dept.: ……EEE………… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR/ ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR/ PROFESSOR/HOD. Guidelines to study the Course/ Subject: ……………Op-Amps…………….. Course Design and Delivery System (CDD): • • • • The Course syllabus is written into number of learning objectives and outcomes. These learning objectives and outcomes will be achieved through lectures, assessments, assignments, seminars, presentations. Every student will be given an assessment plan, criteria for assessment, scheme of evaluation and grading method. The Learning Process will be carried out through assessments of Knowledge, Skills and Attitude by various methods and the students will be given guidance to refer to the text books, reference books. The faculty be able to – • • • • • • • • Understand the principles of Learning Develop instructional objectives for a given topic Prepare course, unit and lesson plans Use appropriate teaching and learning aids like Slides and Paper Presentation. Plan and deliver lectures effectively. Provide the students of availability of the content in the textbooks and Internet. Provide feedback to students using various methods of Assessments and tools of Evaluation Act as a guide, advisor, counselor, facilitator, and motivator and not just as a teacher alone. Signature of HOD Signature of faculty Date: Date: Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 COURSE SCHEDULE Academic Year Semester : 2013 : I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……Electrical…………… Year: ………III……….. Section: A Course/Subject: …………..…Op Amps…………… Course Code: ……… GR11A3078…….… Name of the Faculty: ………R. Anil Kumar…………………………………..Dept.: ……EEE………… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR The Schedule for the whole Course / Subject is: S. No. Description Duration (Date) From To Total No. Of Periods 1. Introduction to Integrated Circuits 04-07-2013 19-07-2013 12 2. Op-Amp application 25-07-2013 08-08-2013 9 3. Active Filters and Oscillators 09-08-2013 23-08-2013 10 4. Timers and Phase Locked Loops (PLL) 29-08-2013 13-09-2013 12 5. D-A and A-D Converters 19-09-2013 04-10-2013 12 Total No. of Instructional periods available for the course: ..……55……. Hours / Periods Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 ILLUSTRATIVE VERBS FOR STATING INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES These verbs can also be used while framing questions for Continuous Assessment Examinations as well as for End – Semester (final)Examinations ILLUSTRATIVE VERBS FOR STATING GENERAL OBJECTIVES/OUTCOMES Know Understand Analyze Generate Comprehend Apply Design Evaluate ILLUSTRATIVE VERBS FOR STATING SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES/OUTCOMES: A. COGNITIVE DOMAIN (KNOWLEDGE) 1 Knowledge 2 Comprehension Understanding 3 Application of knowledge & comprehension 4 Analysis Of whole w.r.t. its constituents 5 6 Evaluation Synthesis Judgment Define Convert Demonstrate Differentiate Design Appraise Identify Describe (a Deduce Distinguish Generate Compare Label Procedure) Modify Separate Reconstruct Conclude List Distinguish Predict Revise Contrast Select Estimate Prepare Criticize State Explain why/how Relate Justify Generalize Show Interpret Give examples Solve Support Illustrate Summarize B. Adhere Assist AFFECTIVE DOMAIN (ATTITUDE) Resolve Select C. PSYCHOMOTOR DOMAIN (SKILLS) Bend Dissect Insert Perform Straighten Calibrate Draw Keep Prepare Strengthen Attend Serve Compress Extend Elongate Remove Change Share Conduct Feed Limit Replace Develop Connect File Manipulate Report Help Convert Grow Reset Weigh Influence Decrease Increase Paint Set Time Transfer Type Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 SCHEDULE OF INSTRUCTIONS COURSE PLAN Academic Year : 2013 Semester : I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……..…Electrical……..… Year: ……III……….. Section: A Course/Subject: ………………Op-Amps…………………… Course Code: …GR11A3078… Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil kumar……………………………..Dept.: ……EEE……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR. S.No Reference Text Books Author T1 Linear Integrated Circuits D. Roy Choudhury, Shail B.Jain T2 Op-amps and Linear Integrated Circuits Ramakant A. Gayakwad T3 Modern Digital Electronics R.P.Jain nd T4 Fundamentals Of Analog Circuits(2 Edition) Thomas L. Floyd, David Buchla T5 Digital Fundamentals(9th Edition) Thomas L. Floyd Unit Lesso n No. Date 1 1 04/07/2013 No. of Perio ds 1 1 2 05-07-2013 3 1 3 11-07-2013 1 1 4 12-07-2013 3 1 5 18-07-2013 1 1 6 19-07-2013 3 2 7 25-07-2013 1 2 8 26-07-2013 3 2 9 01-08-2013 1 2 10 02-08-2013 3 2 11 08-08-2013 1 Topic Objectives Outcomes Introduction, Chip size and circuit complexity Ideal and practical op-amp, its equivalent circuit Op-amp characteristics-DC characteristics, 1,3 1,2,3 References (Text Books, Journal…) Page No’s:____ to _____ T1:Pg 1 to 3 1,3 1 T1:Pg 37 to 82 1,2 1 T1:Pg 104 to 110 AC characteristics of Op amp and its compensation Techniques 741 Op Amp and its features 1,2 1 T1:Pg 110 to 120 1,2 1,2,3 T1:Pg 120 to 127 Modes of operation inverting , non inverting and differential Basic applications of op-amp, instrumentation amplifier AC amplifier, V to I and I to V converters Sample & hold circuits, LF398 Ideal Differentiator and Integrators 1,2,3 1,2,3 T1:Pg 42 to51 1,2 1,2,3,4 T1:Pg 135 to 144 1,2,3 1,2,3 1,3 2,3 T1:Pg 144 to 147 T1: Pg 153 to 154 T1:Pg 164 to 175 Practical Differentiator and Integrators, comparator, Schmitt trigger and Multi vibrators Introduction to voltage regulators features of 723 regulator 1,2,3 2,3 T1:Pg 164 to 175 1,2,3 2,3 T1:Pg 240 to 258 3 12 09-08-2013 3 3 13 16-08-2013 3 3 14 22-08-2013 1 3 15 23-08-2013 3 4 16 29-08-2013 1 4 17 30-08-2013 3 4 18 05-09-2013 1 4 19 06-09-2013 3 4 20 12-09-2013 1 4 21 13-09-2013 3 5 22 19-09-2013 1 5 23 20-09-2013 3 5 24 26-09-2013 1 5 25 27-09-2013 3 5 26 03-10-2013 1 5 27 04-10-2013 3 Introduction to filters, High Pass, Low Pass- First Order and Second Order Active Band Pass, Band Reject and All Pass Filter Oscillators- Principle and its types, RC, 2,3 1,2 T1:Pg 262 to 277 2,3 1,2 T1:Pg 277 to 282 2 1,2 T2:Pg 318 to 320 Oscillators- Wien Bridge and Quadrature type Oscillators Waveform generators- Triangular, saw tooth and square wave Introduction to 555 Timer, its specifications Functional Diagram of 555 Timer and its operation in detail Monostable operation using 555 Timer 1,3 1,2,3,5 T2:Pg 320 to 326 T2:Pg 326 to 334 1,2,3 2,3,7 T1: Pg 311 to 312 1,2 2 T1: Pg 311 to 312 1,2,3 3,7 T2: Pg 418 to 424 Astable operation using 555 timer and its applications Schmitt Trigger and its applications 1,2,3 3,7 T2: Pg 424 to 430 1,2,3 2,3 T1: Pg 324 PLL Introduction and its Block schematic, VCO-565 Introduction to Converters and their applications Types of DAC’s- Weighted type DAC, R2R Ladder type DAC Inverted R-2R Ladder type DAC 1,2,3 2,3 Types of ADC’s- Flash type ADC, Counter type ADC, Single Slope ADC, SAR type ADC DAC and ADC specifications, Dual slope ADC and its specifications Review of 1-5 Units, previously asked questions. 2,3,4 1,3,6 T2: Pg 327 to 345 T4: Pg 714 2,3,4 1,3,6 T4: Pg 715 to722 2,4 1,3,6 T4: Pg 722 to727 2,3,4 1,3 T4: Pg 734 to738 2,3,4 2,3,6 T4: Pg 734 to738 1,2,3 1,2,3 T1, T2 and T4 Signature of HOD Signature of faculty Date: Date: Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 COURSE COMPLETION STATUS Academic Year Semester : 2013 : I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……Electrical…………… Year: ………III……….. Section: A Course/Subject: …………Op Amps…………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078……… Name of the Faculty: ………R. Anil Kumar…………………………………..Dept.: ……EEE………… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Actual Date of Completion & Remarks, if any Units Remarks No. of Objectives Achieved No. of Outcomes Achieved Unit 1 Date of Completion is: 25/07/2013. More problems and theory need to be covered. 1, 2 and3 1 and 3 Unit 2 Date of Completion is: 12/09/2013. Applications of Op-amps are covered. 1,2 and 3 1,2,3 and 4 Unit 3 Date of Completion is: 27/09/2013. Real time applications of Op-amps need to be presented. 2 and 3 1, 2, 3 and 5 Unit 4 Date of Completion is: Unit 5 Date of Completion is: 03/10/2013. Diagrammatic point of view students had to get practiced. 2, 3 and 4 1, 2, 3 and 6 Signature of HOD Signature of faculty Date: Date: Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 SYLLABUS Academic Year Semester : 2013 : I UNIT NO.: ………1…………. Name of the Program: B.Tech ……..…Electrical……..… Year: ……III……….. Course/Subject: …..........……Op Amps…….........…… Course Code: …...GR11A3078...… Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil kumar……………………………..Dept.: …EEE……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR. UNIT I INTEGRATED CIRCUITS: Classification, Chip Size and Circuit Complexity, Ideal and Practical Op-Amp, Op-amp characteristics-DC and AC Characteristics. 741 Op-Amp and its Features, Modes of operation-inverting, non-inverting, differential. UNIT II OP-AMP APPLICATIONS: Basic Applications of Op-Amp, Instrumentation Amplifier, AC Amplifier, V to I and I to V Converters, Sample & Hold Circuits. Differentiators and Integrators. Comparators. Schmitt Trigger. Multivibrators, Introduction to Voltage Regulators Features of 723 Regulators. UNIT III ACTIVE FILTERS & OSCDLLATORS: Introduction. First. Order and Second Order Low Pass. High Pass and Band Pass Filters. Active Band Reject and All Pass Filters. Principle of Operation and Types of Oscillators â ” RC, Wien Bridge and quadrature type. Waveform Generators - Triangular. Saw Tooth, Square Wave. UNIT IV TIMERS & PHASE LOCKED LOOPS: Introduction to 5.55 Timer, Functional Diagram, Monostable and Astable Operations and Applications, Schmitt Trigger, PLL- Introduction, Block Schematic, Principles and Description of individual Blocks of 565, VCO, UNIT V D-A AND A- D CONVERTERS: Introduction, Basic DAC Techniques - Weighted Resistor Type. R2R Ladder Type, inverted R-2R Type. Different types of ADCs - Parallel Comparator Type. Counter Type. Successive Approximation Register Type and Dual Slope Type DAC and ADC Specifications. Jul//2013 T/PRIN/06/G/01/13-14 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND E LECTRONICS ENGINEERING III BTech ( EEE )A - I Semester 9:009:50DAY/ HOUR 9:50 10:40 MONDAY 10:40- 11:30 BREAK 12:00 12:45 12:45-1:30 1:30-2:15 11:30-12:00 TUESDAY 12:00-12:30 WEDNESDAY 12:00-12:30 THURSDAY 11:30-12:00 OPA (1-2) 2304 RAK,DA FRIDAY 11:30-12:00 OPA (1-2) 2304 RAK,DA SATURDAY Issue 1 2:15-3:00 12:00-12:30 OPA (2-3) 2304 RAK,DA Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 SCHEDULE OF INSTRUCTIONS UNIT PLAN Academic Year : 2013 Semester : I UNIT NO.: ………1…………. Name of the Program: B.Tech ……..…Electrical……..… Year: ……III……….. Section: A Course/Subject: ………Op Amps…………………… Course Code: …GR11A3078… Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil kumar……………………………..Dept.: …EEE……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR. Lesson No. 1 04/07/2013 No. of Period s 1 2 05-07-2013 3 Date Topics / Sub - Topics References (Text Book, Journal…) Page Nos.: ____to ____ T1:Pg 1 to 3 Objectives Outcomes Introduction, Chip size and circuit complexity 1,3 1,2,3 3 Ideal and practical op-amp, its equivalent circuit 1,3 1 T1:Pg 37 to 82 11-07-2013 1 Op-amp characteristics-DC characteristics, 1,2 1 T1:Pg 104 to 110 4 12-07-2013 3 1,2 1 T1:Pg 110 to 120 5 18-07-2013 1 AC characteristics of Op amp and its compensation Techniques 741 Op Amp and its features 1,2 1,2,3 T1:Pg 120 to 127 6 19-07-2013 3 Modes of operation inverting , non inverting and differential 1,2,3 1,2,3 T1:Pg 42 to51 Signature of HOD Signature of faculty Date: Date: Note: 1. ENSURE THAT ALL TOPICS SPECIFIED IN THE COURSE ARE MENTIONED. 2. ADDITIONAL TOPICS COVERED, IF ANY, MAY ALSO BE SPECIFIED IN BOLD 3. MENTION THE CORRESPONDING COURSE OBJECTIVE AND OUT COME NUMBERS AGAINST EACH TOPIC. OPAMPS Unit-1 1 Integrated Circuits • Upto 1950 ‘Vacuum Tubes’ were used. • Transistor was first invented in 1947 by 1. William B. Shockley, 2. John Bardeen and 3. Walter H. Brattain (refer below figure). This was invented in BELL TELEPHONE Laboratories 2 Integrated Circuits (contd..,) • Further development has introduced the Integrated Circuits (IC’s). • This concept of IC’s was introduced during 1960 by both Texas Instruments and Fairchild Semiconductors . 3 Classification of IC’s • Linear (Analog) IC’s: These are connected to devices that collect signals from the environment or send signals back to the environment. Ex: a microphone converts fluctuating vocal sounds into an electrical signal of varying voltage (Op-Amp). • Digital IC’s: These are designed to accept only voltages of specific given values. Circuit design with binary quantities, “on” and “off” representing 1 and 0. Ex: Microcontroller and Microprocessors consisting large number of Digital Circuits. 4 • Based on the above requirements two distinct types of IC’s had developed 1. Monolithic IC’s: Derived from Greek ‘monos’ means ‘single’ and ‘lithos’ means ‘stone’. 5 2. Hybrid or Multi-chip IC’s: The active components are diffused transistors or diodes. The passive components may be group of diffused resistors or capacitors on a single chip, or they may be thin-film components. Ex: Hybrids ICs are widely used for high power audio amplifier applications from 5 W to more than 50 W. 6 Drawbacks of Monolithic IC’s • • • • Low power rating (Max power rating <1W) Poorer isolation between components. No possibility of fabrication of inductors. Small range of values of passive components used in the ICs. • Lack of flexibility in circuit design as for making any variation in the circuit, a new set of masks is required. 7 • Based on their chip size IC’s can be further classified as: 1. Small scale integration (SSI)—3 to 30 gates/chip.(Logic gates, Fliip-flops) 2. Medium scale integration (MSI)—30 to 300 gates/chip. (Counters, Multiplexers, Adders) 3. Large scale integration (LSI)—300 to 3,000 gates/chip. (8-Bit Microprocessors, ROM, RAM) 4. Very large scale integration (VLSI)—more than 3,000 gates/chip. (16 and 32 Bit Microprocessors) 8 Ideal Op-amp Vs Practical Op-amp Characteristics Ideal Practical Open Loop gain A ∝ 105 Bandwidth BW ∝ 10-100Hz Input Impedance Zin ∝ >1MΩ 0Ω 10-100 Ω Output Impedance Zout Output Voltage Vout CMRR (discussed later) Depends only on Vd = (V+−V−) Differential mode signal ∝ Depends slightly on average input Vc = (V++V−)/2 CommonMode signal 10-100dB 9 Ideal Op-Amp Ideal Op-amp Equivalent circuit of an Op-amp (ideal and practical) Open loop Circuit 10 Modes of operations Analysis Method : Two ideal Op-Amp Properties: (1) The voltage between V+ and V− is zero V+ = V− (2) The current into both V+ and V− terminals is zero For ideal Op-Amp circuit: (1) Write the Kirchhoff node equation at the noninverting terminal V+ (2) Write the Kirchhoff node equation at the inverting terminal V− (3) Set V+ = V− and solve for the desired closedloop gain 11 Non-Inverting Amplifier (1) Kirchhoff node equation at V+ yields, V+ = Vi V + in (2) Kirchhoff node equation at V− yields, V o − Ra Rf V− − 0 V− − Vo + =0 Ra Rf (3) Setting V+ = V– yields Rf Vi Vi − Vo Vo + = 0 (or) = 1+ Ra Rf Vi Ra Open loop gain 12 Practical Non-Inverting Amplifier Equivalent circuit of Non-Inverting amplifier Using KCL write input and output nodal equations and solve Input node equation is Solve the whole equation and find out the GAIN 13 Inverting Amplifier (1) Kirchhoff node equation at V+ yields, V+ = 0 Rf Ra V ~ in − V o + (2) Kirchhoff node equation at V− yields, Vin − V_ Ra Vo − V− + =0 Rf (3) Setting V+ = V– yields − Rf Vo = V in Ra Notice: The closed-loop gain Vo/Vin is dependent upon the ratio of two resistors, and is independent of the open-loop gain. This is caused by the use of feedback output voltage to subtract from the input voltage. 14 Practical Inverting Amplifier Equivalent circuit of Inverting amplifier Thevenin’s Equivalent circuit of Inverting amplifier Using KVL write input and output equations and solve Solve the whole equation and find out the GAIN, output and input feedback resistances also. Refer Linear Integrated Circuits- D. Roy Choudhury, Shail B. Jain 15 • Closed loop gain is: • Input Resistance: • Output Resistance: 16 Differential Amplifier • This amplifies the differences between the two signals. • Used in Instrumentation circuits. NOTE: Using the nodal equations find out the GAIN 17 Difference mode and Common Mode Gains • The output voltage depends on difference voltage (vd) and average voltage of input signals called as common mode (vCM) signals. • The output voltage is expressed as 18 Contd.., say 19 Common Mode Rejection Ratio (CMRR): the relative sensitivity of an op-amp to a difference signal as compared to a common mode signal is called as CMRR ( ). 20 Block diagram of Op-amp 21 DC Characteristics • Input offset current • Input offset voltage • Input bias current • Thermal drift 22 Input offset current: The difference between the bias currents at the input terminals of the op- amp is called as input offset current. Input offset voltage: A small voltage applied to the input terminals to make the output voltage as zero when the two input terminals are grounded is called input offset voltage Input bias current: Input bias current IB as the average value of the base currents entering into terminal of an op-amp IB= IB+ + IBThermal Drift: Bias current, offset current and offset voltage change with temperature. A circuit carefully nulled at 25oc may not remain so when the temperature rises to 35oc. This is called drift. 23 Input bias current To compensate this current resistance is added between Non-inverting and ground 24 Input offset current 25 Input offset voltage 26 Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 SCHEDULE OF INSTRUCTIONS UNIT PLAN Academic Year : 2013 Semester : I UNIT NO.: ………2…………. Name of the Program: B.Tech ……..…Electrical……..… Year: ……III……….. Section: A Course/Subject: ………Op Amps…………………… Course Code: …GR11A3078… Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil kumar……………………………..Dept.: …EEE……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR. Lesson No. 7 Date No. of Periods 25-072013 26-072013 1 9 01-082013 1 10 02-082013 3 11 08-082013 1 8 3 Topics / Sub - Topics Basic applications of op-amp, instrumentation amplifier AC amplifier, V to I and I to V converters Sample & hold circuits, LF398 Ideal Differentiator and Integrators Practical Differentiator and Integrators, comparator, Schmitt trigger and Multi vibrators Introduction to voltage regulators features of 723 regulator References (Text Book, Journal…) Page Nos.: ____to ____ T1:Pg 135 to 144 Objectives Outcomes 1,2 1,2,3,4 1,2,3 1,2,3 T1:Pg 144 to 147 T1: Pg 153 to 154 1,3 2,3 T1:Pg 164 to 175 1,2,3 2,3 T1:Pg 164 to 175 1,2,3 2,3 T1:Pg 240 to 258 Signature of HOD Signature of faculty Date: Date: Note: 1. ENSURE THAT ALL TOPICS SPECIFIED IN THE COURSE ARE MENTIONED. 2. ADDITIONAL TOPICS COVERED, IF ANY, MAY ALSO BE SPECIFIED IN BOLD 3. MENTION THE CORRESPONDING COURSE OBJECTIVE AND OUT COME NUMBERS AGAINST EACH TOPIC. Op Amp Applications Unit-2 Inverting Amplifier Non Inverting Amplifier Differential Amplifier Voltage Follower Summing Amplifier (Inverting) A summing amplifier sums several voltages when and when independent Instrumentation Amplifier V to I converter (Transconductance Amplifier) V to I converter with Floating Load V to I converter with Grounded Load I to V converter (Transresistance Amplifier) Integrator Ideal Integrator Practical Integrator (Active Low Pass Filter) Differentiator Ideal Differentiator Practical Differentiator (Active High Pass Filter) Logarithmic and Anti-logarithmic Logarithmic Anti-Logarithmic Comparator Comparator with positive Feedback (Schmitt Trigger) Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 SCHEDULE OF INSTRUCTIONS UNIT PLAN Academic Year : 2013 Semester : I UNIT NO.: ………3…………. Name of the Program: B.Tech ……..…Electrical……..… Year: ……III……….. Section: A Course/Subject: ………Op Amps…………………… Course Code: …GR11A3078… Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil kumar……………………………..Dept.: …EEE……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR. Lesson No. 12 13 14 15 Date No. of Periods 09-082013 3 16-082013 22-082013 3 23-082013 3 1 Topics / Sub - Topics Objectives Outcomes Introduction to filters, High Pass, Low Pass- First Order and Second Order Active Band Pass, Band Reject and All Pass Filter Oscillators- Principle and its types, RC, 2,3 1,2 References (Text Book, Journal…) Page Nos.: ____to ____ T1:Pg 262 to 277 2,3 1,2 T1:Pg 277 to 282 2 1,2 T2:Pg 318 to 320 Oscillators- Wien Bridge and Quadrature type Oscillators Waveform generatorsTriangular, saw tooth and square wave 1,3 1,2,3,5 T2:Pg 320 to 326 T2:Pg 326 to 334 Signature of HOD Signature of faculty Date: Date: Note: 1. ENSURE THAT ALL TOPICS SPECIFIED IN THE COURSE ARE MENTIONED. 2. ADDITIONAL TOPICS COVERED, IF ANY, MAY ALSO BE SPECIFIED IN BOLD 3. MENTION THE CORRESPONDING COURSE OBJECTIVE AND OUT COME NUMBERS AGAINST EACH TOPIC. ACTIVE FILTERS and OSCILLATORS Unit-3 Oscillators Function of an Oscillator is to generate alternate current and voltage waveforms. Used in radio, television, computers and communications. Principle: It is a type of feedback amplifier in which part of the output is fed back to the input through a feedback circuit Oscillator Block diagram Types of Oscillators Types of components used RC oscillator LC oscillator Crystal oscillator Frequency of oscillations Types of waveform generated Audio Frequency (AF) Radio Frequency (RF) Sinusoidal Square wave Triangular wave Saw tooth wave etc. Note: Frequency stability is determined by ‘figure of merit (Q)’ of the circuit. Phase shift oscillator Output wave form Wien Bridge oscillator Quadrature Oscillator Wave form generators Square wave generator Triangular wave generator Triangular wave generator (model 2) Saw tooth generator Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 SCHEDULE OF INSTRUCTIONS UNIT PLAN Academic Year : 2013 Semester : I UNIT NO.: ………4…………. Name of the Program: B.Tech ……..…Electrical……..… Year: ……III……….. Section: A Course/Subject: ………Op Amps…………………… Course Code: …GR11A3078… Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil kumar……………………………..Dept.: …EEE……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR. Lesson No. 16 29-08-2013 No. of Period s 1 17 30-08-2013 3 18 05-09-2013 1 19 06-09-2013 20 21 Date References (Text Book, Journal…) Page Nos.: ____to ____ T1: Pg 311 to 312 Topics / Sub - Topics Objectives Outcomes Introduction to 555 Timer, its specifications Functional Diagram of 555 Timer and its operation in detail Monostable operation using 555 Timer 1,2,3 2,3,7 1,2 2 T1: Pg 311 to 312 1,2,3 3,7 T2: Pg 418 to 424 3 Astable operation using 555 timer and its applications 1,2,3 3,7 T2: Pg 424 to 430 12-09-2013 1 Schmitt Trigger and its applications 1,2,3 2,3 T1: Pg 324 13-09-2013 3 PLL Introduction and its Block schematic, VCO-565 1,2,3 2,3 T2: Pg 327 to 345 Signature of HOD Signature of faculty Date: Date: Note: 1. ENSURE THAT ALL TOPICS SPECIFIED IN THE COURSE ARE MENTIONED. 2. ADDITIONAL TOPICS COVERED, IF ANY, MAY ALSO BE SPECIFIED IN BOLD 3. MENTION THE CORRESPONDING COURSE OBJECTIVE AND OUT COME NUMBERS AGAINST EACH TOPIC. Timers and Phase Locked Loops (PLL) Unit4 Timer Introduction • It is highly stable device for generating accurate time delay or oscillation • It can provide time delay ranging from microseconds to hours where as counter timer can have a maximum timing range of days. Applications • Oscillator, pulse generator, ramp and square wave generator, mono-shot multivibrator, burglar alarm, traffic light control and voltage monitor etc. • There is also available counter timer such as XR-2240 which contains 555 timer and programmable binary counter in a single 16pin package. Pin Description of 555 • Pin1: Ground: All voltages are measured with respect to this terminal. • Pin2: Trigger: Output of timer depends on the amplitude of the external triggering pulse applied to it. • Pin3: Output: Two ways to connect load (max current is 200mA) i) Either between pin3 and pin1(ground) (sink current and normal off load) ii) Or between pin3 and pin8(+VCC) (source current and normal on load) Pin Description of 555 (Contd..) • Pin 4: Reset: The 555 timer can be disabled or reset by applying negative pulse to this pin. To avoid any possibility of false triggering this pin is to be connected to +VCC. • Pin 5: Control Voltage: i) When external voltage applied to this pin it changes the threshold and trigger voltage. ii) By connecting pot between pin5 and pin1 pulse width of the output waveform is varied. iii) When not used, this pin should be bypassed to ground with a 0.01µF capacitor to prevent any noise Pin Description of 555 (Contd..) • Pin 6: Threshold: this is non inverting input terminal of UC which monitors the voltage across external capacitor. • Pin 7: Discharge: i) This pin is connected internally to collector of transistor Q1. ii) When output is high Q1 is OFF and acts as open circuit to external capacitor C. iii) When output is low Q1 is saturated (ON) and acts as short circuit, shorting external capacitor C to ground. Pin Description of 555 (Contd..) • Pin8: +VCC: The supply voltage of +5V to +18V is applied to this pin with respect to ground (pin1). Functional Diagram Monostable Operation To prevent unwanted voltage spikes at output decoupling capacitor is used Wave forms of Monostable operation Different values of R and C To prevent possibility if miss triggering the multivibrator on positive pulse edges, a wave shaping circuit consisting of R, C2 and D is connected between pin2 and pin8 R and C2 must be selected such that time constant R C2 is less that the output pulse width tp Applications in Monostable operation • Missing Pulse detector • Linear ramp generator • Frequency divider • Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Astable Operation Model Wave forms Different values of R and C Applications of Astable Multivibrator • FSK generator • Pulse-Position Modulator • Schmitt Trigger Phase Locked Loop (PLL) Introduction • Evolution of PLL has began in early 1970’s. • Due to its cost it has not preferred. • As there is rapid development in IC technology, this PLL has emerged as one of the fundamental building blocks in today’s Electronic technology. Applications of PLL • • • • Frequency Modulation(FM) stereo decoders Motor speed controllers Tracking filters Frequency synthesized transmitters and receivers • FM demodulators • FSK decoders • Generation of local oscillator frequencies in TV and in FM tuners. PLL IC’s • SE/NE 560 series560, 561, 562, 564, 565, 567 • For more economical operation, discrete IC’s can be used to construct a PLL Operating Principle of PLL In short PLL goes through three states: free running, capture and phase lock. Some PLL’s can also contain Amplifiers after LPF. 1. Phase detector • It is basically a linear multiplier • When PLL is locked • The detector output voltage is • Types of Phase detector: i) Analog ii) Digital • Depending on the type of Phase detector PLL can be differentiated. • Due to simplicity, digital phase detector is explained here. • Types of Digital Phase detector i) Exclusive-OR phase detector ii) Edge-Triggered phase detector iii) Monolithic phase detector (CMOS-4044) 1. Exclusive-OR phase detector 1. Exclusive-OR phase detector (Contd.) Input and output wave forms DC output voltage vs. phase difference between fIN and fOUT 2. Edge Triggered phase detector 2. Edge Triggered phase detector (Contd.) Input and output wave forms DC output voltage vs phase difference between fIN and fOUT 3. Monolithic Phase detector 3. Monolithic Phase detector (Contd.) Input and output Transfer characteristics Low Pass Filter • Removes the high frequency components • Controls the dynamic characteristics of PLL like Lock range, Capture range, Pull in time. • As filter band width reduced its response time increases VCO Block Diagram VCO 566 Monolithic PLL (SE/NE 565) Pin Representation of 565 Internal Connection diagram of SE/NE 565 Important definition in relation to PLL • Lock in range (%fo): once PLL is locked, it can track incoming frequency. The range of frequency where PLL can maintain lock with input frequency is called ‘Lock in range’ or ‘Tracking range’. • Capture range (%fo): The range of frequencies over which PLL can acquire lock with an input signal is called ‘Capture range’. • Pull in time: The total time taken to establish lock is called ‘Pull in time’ • Pull in time depends on the initial phase and frequency differences between the two signals as well as on overall loop gain and loop filter characteristics Applications of PLL • • • • • Frequency multiplication/division Frequency Translation AM detection FM demodulation Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) demodulator Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 SCHEDULE OF INSTRUCTIONS UNIT PLAN Academic Year : 2013 Semester : I UNIT NO.: ………5…………. Name of the Program: B.Tech ……..…Electrical……..… Year: ……III……….. Section: A Course/Subject: ………Op Amps…………………… Course Code: …GR11A3078… Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil kumar……………………………..Dept.: …EEE……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR. Lesson No. 22 23 24 25 Date 19-092013 20-092013 26-092013 27-092013 No. of Periods 1 3 1 3 26 03-102013 1 27 04-102013 3 Topics / Sub - Topics Objectives Outcomes Introduction to Converters and their applications Types of DAC’s- Weighted type DAC, R-2R Ladder type DAC Inverted R-2R Ladder type DAC 2,3,4 1,3,6 References (Text Book, Journal…) Page Nos.: ____to ____ T4: Pg 714 2,3,4 1,3,6 T4: Pg 715 to722 2,4 1,3,6 T4: Pg 722 to727 Types of ADC’s- Flash type ADC, Counter type ADC, Single Slope ADC, SAR type ADC DAC and ADC specifications, Dual slope ADC and its specifications Review of 1-5 Units, previously asked questions. 2,3,4 1,3 T4: Pg 734 to738 2,3,4 2,3,6 T4: Pg 734 to738 1,2,3 1,2,3 T1, T2 and T4 Signature of HOD Signature of faculty Date: Date: Note: 1. ENSURE THAT ALL TOPICS SPECIFIED IN THE COURSE ARE MENTIONED. 2. ADDITIONAL TOPICS COVERED, IF ANY, MAY ALSO BE SPECIFIED IN BOLD 3. MENTION THE CORRESPONDING COURSE OBJECTIVE AND OUT COME NUMBERS AGAINST EACH TOPIC. D-A converter and A-D converter Unit 5 Binary weighted type D-A converter Graph of output versus input R-2R Ladder type Equivalent circuit when switch b3 is closed Output versus Input Performance characteristics of DAC • Resolution: It is the reciprocal of maximum number of discrete steps in the output. Ex: For n-bit DAC Resolution is given as 1x100/(2n-1). • Accuracy: It is a comparison of the actual output of a DAC with the expected output. Ex: Converter has full scale deflection of 10V and accuracy is 0.1% then maximum error for any output voltage is (10V)(0.001)=10mV. • Linearity: A linear error is a deviation from the ideal straight-line output of a DAC. Performance characteristics of DAC (contd.) • Monotonicity: A DAC is monotonic if it does not miss any steps when it is sequenced over its entire range of input bits. • Settling time: it is defined as the time it takes a DAC to settle within ±1/2 LSB of its final value when a change occurs in the input code. Analog to Digital converter Concepts of ADC Resolution: • An ADC translates a continuous analog signal into a series of binary numbers. • The Resolution of an ADC can be expressed as the number of bits used to represent each value of the analog signal. Ex: A 4-bit ADC can represent 16 different values of analog signal. Analog to Digital converter (Contd.) • Conversion time: The conversion of a value on an analog waveform into a digital quantity is not instantaneous event, but it is a process that takes a certain amount of time (Refer figure in next slide). • Sampling theory: In ADC an analog waveform is sampled at a given time and the sampled value is then converted to a binary number. Ex: if ADC make one conversion in 1ms then 1000 conversions can be made in ______. Analog to Digital converter (Contd.) [Note: Nyquist Rate: In order to represent the analog waveform, the minimum sample rate must be greater than twice the maximum frequency component of analog signal. This minimum sample rate is called as Nyquist rate.] Analog to Digital converter (Contd.) Quantization Error: • Quantization refers to determining a value for an analog quantity. • An analog signal may change during conversion time, its value at the end of conversion may not be the same as it was at the beginning (unless it is DC). • This change in value of the analog signal during the conversion time produces the error called as ‘Quantization Error’. • Method to reduce the error is using sample and hold circuit at input to the ADC. Analog to Digital converter (Contd.) Analog to Digital converter (Contd.) Types of ADC’s Flash ADC or Comparator type ADC Requires 2n-1 comparators for conversion to nbit binary code. Advantage: • Provides fast converting time. Types of ADC’s Stairstep-Ramp/Digital-Ramp/Counter type ADC Types of ADC’s Single Slope type ADC Types of ADC’s Dual Slope type ADC Types of ADC’s Dual Slope type ADC working stage 1 Types of ADC’s Dual Slope type ADC working stage 2 Types of ADC’s Dual Slope type ADC working stage 3 Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……04-07-2013……. I Name of the Program: B.Tech …………Electrical… Year: ………III..……….... Section: A Course/Subject: …Op Amps………………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil Kumar…………………………..Dept.:…EEE…………. Designation Lesson No: 1 : ASST.PROFESSOR Duration of Lesson: 60min………………. Lesson Title: Introduction, Chip size and circuit complexity INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. TEACHING AIDS TEACHING POINTS • • • • : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER. : 5 min.: Taking attendance 10 min.: Introduction to types of IC’s 40 min.: Fundamental technology used in IC design, Advantages of Integrated Circuits will be covered. 5min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Classify the types of IC’s and form a table. (Obj: 1, 3/Out: 1,2,3) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year : 2013 Semester : Date: ……05-07-2013…… I Name of the Program: B.Tech …………Electrical… Year: ………III..……….... Section: A Course/Subject: …Op Amps………………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil Kumar…………………………..Dept.:…EEE…………. Designation Lesson No: 2 : ASST.PROFESSOR Duration of Lesson: 120 min………………. Lesson Title: Ideal and practical op-amp, its equivalent circuit INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. TEACHING AIDS TEACHING POINTS • • • • : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER. : 5 min.: Taking attendance 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. 100 min.: Introduction to Op-amps and its classifications, equivalent circuit of practical op-amps. 5min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Derive the equations of voltage and current for practical op-amp. (Obj:1,3/Out:1) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year : 2013 Semester : Date: ……11-07-2013……. I Name of the Program: B.Tech …………Electrical… Year: ………III..……….... Section: A Course/Subject: …Op Amps………………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil Kumar………………………….Dept.:…EEE…………. Designation Lesson No: 3 : ASST.PROFESSOR Duration of Lesson: 60min………………. Lesson Title: Op-amp characteristics-DC characteristics. INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. TEACHING AIDS TEACHING POINTS • • • • : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER : 5 min.: Taking attendance 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. 40 min.: DC characteristics of Op-amp, 741 basic Op-amp explanation. 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Explain compensation methods of Op-amp. (Obj:1,2/Out:1) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year : 2013 Semester : Date: ………12-07-13……. I Name of the Program: B.Tech …………Electrical… Year: ………III..……….... Section: A Course/Subject: ………………Op Amps…………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil Kumar…………………………..Dept.:…EEE…………. Designation Lesson No: 4 : ASST.PROFESSOR Duration of Lesson: 120 min………………. Lesson Title: AC characteristics of Op amp and its compensation Techniques INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. TEACHING AIDS TEACHING POINTS • • • • : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER : 5 min.: Taking attendance 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. 100 min.: AC characteristics of Op-amp and its compensations. 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Explain the Frequency compensation method used to compensate or AC characteristics with diagrams. (Obj:1,2/Out:1) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……18-07-2013……. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: …………….…Op Amps…………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar..........……..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: ………5 Duration of Lesson: 60 min………………. Lesson Title: 741 Op Amp and its features INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 40 min.: General features of 741 Op amp, • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Explain the features of 741 Op amp. (Obj:1,2/Out:1,2,3) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……19-07-13……. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: …………Op Amps………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar........………..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: …………………6…………… Duration of Lesson: ……120 min…………. Lesson Title: Modes of operation inverting , non inverting and differential INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 3. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 100 min.: Closed loop gain of Inverting and Non Inverting amplifier • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Obtain the Voltage gain formula for Inverting, Non Inverting and Differential Amplifier. (Obj:1, 2, 3/Out:1,2,3) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……25-07-13……. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: …Op amps………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar............……..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: …………………7………………… Duration of Lesson: 60min………………. Lesson Title: Basic applications of Op-amp, Instrumentation Amplifier INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 40 min.: General implementations of Op-amp, connecting op-amp to work it as Instrumentation Amplifier and its applications. • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Derive the voltage equation if voltage follower is having some gain resistance. (Obj:1,2/Out:1,2,3,4) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……26-07-13……. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: ………Op amps………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar.........………..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: …………………8………………… Duration of Lesson: 120 min…………… Lesson Title: AC amplifier, V to I and I to V Converters, Sample and Hold Circuits, LF 398 INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 3. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 100 min.: AC Amplifier and different converters operation of op-amps and Sample and hold circuits. • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Obtain the maximum and minimum ranges of current value when load is connected to V to I converter. (Obj:1,2,3/Out:1,2,3) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……01-08-13……. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: …………..…Op amps……………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar....…………..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: …………………9……………… Duration of Lesson: 60min………………. Lesson Title: Ideal differentiator and Integrator INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 40 min.: Explain the working operation of Integrator, Differentiator • 5min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. • Assignment / Questions: Derive the Voltage equations for Integrator and Differentiator. (Obj:1,3/Out:2,3) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……02-08-13……. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: …Op amps……………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar.................…..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: …………………10……………… Duration of Lesson: 120min………………. Lesson Title: Differentiators, Integrators, Comparator, Schmitt Trigger and Multivibrators INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 3. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 100 min.: Explain the working operation of Schmitt Trigger and Multi vibrator. • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class • Assignment / Questions: Derive the Voltage equations for of Integrator, Differentiator, Comparator, Schmitt Trigger and Multi vibrator. (Obj:1,2,3/Out:2,3) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……08-08-13………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: …Op Amps…………..……………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar.........………..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: …………………11……………… Duration of Lesson: 60min………………. Lesson Title: Introduction to Voltage Regulators, Features of 723 Regulator INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 3. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 40 min.: Explain the working operation of Voltage Regulator • 5min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Explain 723 voltage regulator with its pin configuration. (Obj:1,2,3/Out:2,3) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……09-08-13………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: …….…Op Amps………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar.............……..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: …………………12……………… Duration of Lesson: 120min………………. Lesson Title: Introduction to Filters, First order, Second order- Low pass, High pass and Band Width Filter. INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 2. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 100 min.: Classification of Filters, order of the filters design, types of filter designs • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Classify the types of filters and design a second order Butterworth lowpass filter for frequency of 1KHz. (Obj:2,3/Out:1,2) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ………16-08-13………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: …………Op Amps………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar....…………..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: ……………………13…………… Duration of Lesson: 120min………………. Lesson Title: Active Band Reject filter and All Pass filter INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 2. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 100 min.: Explain the operation of Band stop filters and All pass filters, problems to be solved. • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Explain the response of All pass filter. (Obj:2,3/Out:1,2) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ………22-08-13………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: ……Op Amps…….……………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar...............…..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: ……………………14…………… Duration of Lesson: 60min………………. Lesson Title: Principle of operation and types of oscillators RC INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 40 min.: Explain the working operation of RC phase shift oscillator • 5min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Design aa RC phase shift oscillator for frequency of 10KHz. (Obj:2/Out:1,2) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ………23-08-13………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: ………Op Amps………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar.............……..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: ………………15……………… Duration of Lesson: 120min………………. Lesson Title: Oscillators- Wien Bridge and Quadrature type Oscillators, Waveform generationTriangular, Saw tooth and Square wave INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 100 min.: Explain the working operation of Wien Bridge and Quadrature Oscillator and also different types of waveform generators and their applications. • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Explain the Triangular wave oscillator with a neat circuit diagram. (Obj:1,3/Out:1,2,3,5) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……29-08-13………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: …………Op Amps………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar.............……..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: ………………16……………… Duration of Lesson: 60min………………. Lesson Title: Introduction to 555 Timer and its specifications INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 3. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 40 min.: Explain the working operation of 555 Timer and its specifications • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Briefly explain the working operation of 555 timer and its specifications? (Obj:1,2,3/Out:2,3,7) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……30-08-13………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: …………Op Amps………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar.............……..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: ………………17……………… Duration of Lesson: 120min………………. Lesson Title: Functional Diagram of 555 Timer and its operation in detail INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 100 min.: Explain the working operation of 555 Timer and its applications • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Briefly explain the working operation of 555 timer and its applications? (Obj:1,2/Out:2) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……05-09-13………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: ……………Op Amps……………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar.........………..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: ………………18………………… Duration of Lesson: 60min………………. Lesson Title: Monostable operation using 555 Timer INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 3. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 40 min.: Explain the working operation of 555 Timer as Monostable operation. • 5min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Explain the operation of monostable multivibrator using 555 timer. (Obj:1,2,3/Out:3,7) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……06-09-13………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: …………Op Amps………………… Course Code: ……Gr11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar.............……..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: ………………19………………… Duration of Lesson: 120min………………. Lesson Title: Monostable and Astable operation and applications INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 3. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 100 min.: Explain the working operation of 555 Timer as Astable and Monostable operation. • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Explain the operation of Astable multivibrator using 555 timer. (Obj:1,2,3/Out:3,7) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……12-09-13………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: …………Op Amps………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar.....…………..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: ………………20………………… Duration of Lesson: 60min………………. Lesson Title: Schmitt trigger and its applications INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 3. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 40 min.: Explain the working operation of 555 Timer as Schmitt Trigger • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Explain the operation of Schmitt Trigger in detail. (Obj:1,2,3/Out:2,3) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……13-09-13………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: …Op Amps………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar........………..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: ………………21……………… Duration of Lesson: 120min………………. Lesson Title: Schmitt trigger, PLL- Introduction, block schematic, VCO (565) INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 3. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 100 min.: Explain the working operation of 555 Timer, IC 565 and VCO. • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Explain the operation of VCO in detail. (Obj:1,2,3/Out:2,3) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……19-09-13………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: …Op Amps………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar.....................Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: ………………22………………… Duration of Lesson: 60min………………. Lesson Title: Introduction to Converters and their applications INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 2. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. 3. Familiarize the conversion of data from Analog to Digital and Digital to Analog. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 40 min.: Explain the real time applications of A to D and D to A conveters • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Explain the specifications used to consider a good converter (Obj:2,3,4 & Out:1,3,6) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2012-2013 : Date: ……20-09-13………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: ………Op Amps ………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar............……..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: ………………23………………… Duration of Lesson: 120min………………. Lesson Title: Types of DAC’s-Weighted Resistor type, R-2R ladder type, INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 2. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. 3. Familiarize the conversion of data from Analog to Digital and Digital to Analog. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 100 min.: Explain the working operation of binary-weighted-input DAC and R/2R ladder type DAC • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Derive the output voltage expression for R/2R type DAC. (Obj:2,3,4 & Out:1,3,6) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2012-2013 : Date: ……26-09-13………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: ………Op Amps………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar.................…..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: ………………24………………… Duration of Lesson: 60min………………. Lesson Title: Inverted R-2R Ladder type DAC INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 2. Familiarize the conversion of data from Analog to Digital and Digital to Analog. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 40 min.: Explain the working operation of binary-weighted-input DAC and R/2R ladder type DAC • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Derive the output voltage expression for Inverted R/2R type DAC. (Obj:2,4 & Out:1,3,6) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……27-09-13………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: ………Op Amps………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar.........………..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: ………………25……………… Duration of Lesson: 120min………………. Lesson Title: Types of ADC’s- Flash type ADC, Counter type ADC, Single Slope ADC, SAR type ADC INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 2. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. 3. Familiarize the conversion of data from Analog to Digital and Digital to Analog. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 100 min.: Explain the working operation of different types of ADC’s. • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Explain the operation of Flash type ADC. ( Obj: 2,3,4 & Out:1,3) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2013 : Date: ……03-10-13……. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: …Op Amps………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar.................…..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: ………………26………………… Duration of Lesson: 60min………………. Lesson Title: Dual Slope type ADC, DAC and ADC specifications INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 2. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. 3. Familiarize the conversion of data from Analog to Digital and Digital to Analog. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 10 min.: Re collecting the contents of previous class. • 40 min.: Explain the working operation of Dual Slope ADC. • 5 min.: Doubts clarification and Review of the class. Assignment / Questions: Explain the working operation of Dual slope ADC. (Obj:2,3,4 & Out:2,3,6) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 LESSON PLAN Academic Year Semester : 2012-2013 : Date: ……04-10-13………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……….EEE………… Year: ………III…….. Section: A Course/Subject: ………Op Amps………………… Course Code: ……GR11A3078…… Name of the Faculty: ……………R Anil Kumar.........………..Dept.: ……Electrical……… Designation: ASST.PROFESSOR Lesson No: ………………27……………… Duration of Lesson: 120min………………. Lesson Title: Review of Unit 1 to Unit 5 and Previous university question papers INSTRUCTIONAL/LESSON OBJECTIVES: On completion of this lesson the student shall be able to: 1. Provide a strong foundation on Linear Circuits. 2. Familiarize students with applications of various IC’s. 3. Have a broad coverage in the field that is relevant for engineers to design Linear circuits using Op-amps. TEACHING AIDS : LCD PROJECTOR, WHITEBOARD, MARKER, DUSTER TEACHING POINTS : • 5 min.: Taking attendance • 25 min.: Ask objective questions from units 1 to 5 • 90 min.: Conduct seminar on the topic selected by the students Assignment / Questions: Write short notes on types of Multivibrators and their applications. (Obj:1,2,3/Out:1,2,3) Signature of faculty Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 ASSIGNMENT SHEET – 1 Academic Year : 2013 Semester : Date:……………………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech …………Electrical… Year: …III..……….. Section: A/B/C Course/Subject: …Opamps………………………………………………….. Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil Kumar……………………..Dept.:…EEE…………. Designation : ASST.PROFESSOR This Assignment corresponds to Unit No. / Lesson ………………1…………………………. Q1. For an op-Amp, PSRR=70dB(min), CMRR=105, differential mode gain Ad=105, The output voltage changes by 20v in 4µseconds. Calculate i. Numerical value of PSRR ii. CMRR iii. Slew rate. Q2. (a) What is a level translator circuit? Why it is used with the Cascaded Differential amplifier? (b) What is a cascode amplifier? List the characteristics of Cascode amplifier. Q3. Explain the various techniques used to compensate for thermal drift in Op-Amps. Q4. Calculate (i) Maximum output offset voltage caused by the input offset voltage Vios. (ii) Maximum output offset voltage caused by the input bias current IB, for an inverting amplifier with R1=100KΩ and Rf =10KΩ. Here 741 Op-amp is used with Vios=6mV and IB=500nA. Q5. Draw and explain the practical circuit for offset voltage measurement of Op-Amps. Objective Nos.: …………1,2 and 3………………………………………………. Outcome Nos.: ………1 and 3…………………………………………………………………. Signature of HOD Date: Signature of faculty Date: Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 ASSIGNMENT SHEET – 2 Academic Year : 2013 Semester : Date:……………………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech …Electrical……… Year: ……III..……….... Section: A/B/C Course/Subject: …Opamps…………………………………………….. Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil Kumar………………………..Dept.:…EEE…………. Designation : ASST.PROFESSOR This Assignment corresponds to Unit No. / Lesson ………………2…………………………. Q1. In the circuit of figure shown below, R1=100Ω, Rf =4.7KΩ CMRR=90 db. If the amplitude of the induced 60-Hz noise at the output is 5mv (rms), calculate the amplitude of the common-mode input voltage Vcm: Q2. (a) Explain the current limiting feature of 723 regulator. (b) If a 741 IC is configured as an I-to-V converter, what is the lowest value of current that may be measured. Q3. For the strain gauge bridge circuit as shown in figure below, given that Vab= Assume that under the strained conditions the resistances RT1and RT3 decreases and that of . Also RT1= RT2 = RT3 = RT4 = R, under RT2 and RT4 increases by the same amount unstrained conditions. Q4. Calculate (i) Maximum output offset voltage caused by the input offset voltage Vios. (ii) Maximum output offset voltage caused by the input bias current IB, for an inverting amplifier with R1=100KΩ and Rf =10KΩ. Here 741 Op-amp is used with Vios=6mV and IB=500nA. 5Q. For the integrator circuit as shown in below figure, the input is a sine wave with a peak-topeak amplitude of 5V at 1kHz. Draw the output voltage waveform if R1CF= 0.1ms and RF=10R1. Assume that the voltage across CF if initially zero. Objective Nos.: …………1,2 and 3…………………………………………………………… Outcome Nos.: ………1,2 and 3………………………………………………………………. Signature of HOD Date: Signature of faculty Date: Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 ASSIGNMENT SHEET – 3 Academic Year : 2013 Semester : Date:……………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……Electrical……… Year: …III..……….... Section: A/B/C Course/Subject: …Opamps……………………………………………….. Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil Kumar…………………………..Dept.:…EEE…………. Designation : ASST.PROFESSOR This Assignment corresponds to Unit No. / Lesson ………………3…………………………. Q1. A certain narrow band-pass filter has been designed to meet the following specifications: fC=2kHz, Q=20, and Ap=10. What modifications are necessary in the filter circuit to change the center frequency `fc ' to 1kHz , keeping the gain and band-width constant? Q2. (a)Define the conditions on the feedback circuit of an amplifier to convert it into an oscillator? (b) Design a 60Hz Active Low Pass Filer (LPF) Q3. Design a second order IGMF band pass filter with the following specifications: fo=500Hz, gain at resonance=-5 and band width=50Hz. Use the circuit shown in figure below, assume necessary data Q4. Consider the circuit shown next (a) Calculate the output voltages of the circuit. (b) Explain the effect of C' on stability of the OP-Amp connection. Q5. F or a second order butter worth filter given C2 = C3 = 0:047µF ; R2 = R3 = 3.3kΩ; R1 = 27kΩ; and RF = 15.8kΩ (a) Determine the lower cutoff frequency fL of the filter. (b) Draw the frequency response plot of the above filter. Objective Nos.: …………1,2 and 3……………………………………………………………. Outcome Nos.: ………1,2 and 3………………………………………………………………. Signature of HOD Date: Signature of faculty Date: Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 ASSIGNMENT SHEET – 4 Academic Year : 2013 Semester : Date:……………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ………Electrical…… Year: …III..……….... Section: A/B/C Course/Subject: …Opamps………………………………………………….. Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil Kumar…………………………..Dept.:…EEE…………. Designation : ASST.PROFESSOR This Assignment corresponds to Unit No. / Lesson ………………4…………………………. Q1.(a) Explain the importance of 555 timer in designing a monostable multivibrator (b) If RA = 6.8 kΩ, RB= 3.3 kΩ, c = 0.1µF in 555 astable multivibrator, Calculate: i. thigh ii. tlow iii. Free running frequency iv. Duty cycle. Q2. Design a monostable multivibrator using 555 timer to produce a pulse width of 100msec. Q3. (a) Write about voltage controlled frequency shifter using 555 timer. (b) For the frequency shifter, calculate: i. The charge current I for input E = 0V ii. The centre frequency when E = 0V iii. The frequency shift fout for E = ±1V. Q4. What are passive loop filters in PLL consider the PLL shown in below figure Q5.(a) Explain the terms Lock range, Capture range and Pull-in time of a PLL. How are Lock ranges and Capture range determined? (b) Draw the internal circuit diagram and pin diagram (DIP) of 566 VCO. Explain its operation and derive expression for output frequency fo. Objective Nos.: …………1,2 and 3……………………………………………………………. Outcome Nos.: ………1,2 and 3………………………………………………………………. Signature of HOD Date: Signature of faculty Date: Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 ASSIGNMENT SHEET – 5 Academic Year : 2013 Semester : Date:……………. I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……Electrical……… Year: ………III.….... Section: A/B/C Course/Subject: …Opamps………………………………………………….. Name of the Faculty: ……R. Anil Kumar…………………………Dept.:…EEE…………. Designation : ASST.PROFESSOR This Assignment corresponds to Unit No. / Lesson ………………5…………………………. Q1. (a) What are the advantages of R-2R ladder type D/A converter over weighted resistor type? (b) In an inverted R-2R ladder, R=Rf=22kohms and VR=12V. Calculate the total current delivered to the op-amp and the output voltage when the binary input is 1110. Q2. (a) Write short notes on multiplying DAC’s? (b) List the specifications of a DAC IC 1408. Q3. (a) What are the sources of analog errors in an ADC? (b) What is meant by differential linearity of an ADC? Q4. Design a 4 - bit weighted resistor DAC whose full-scale output voltage is 10volts. Assume Rf = 10 k and logic `1' level as +5 volts and also logic `0' level as 0 volts. What is the output voltage when the input is 1011? Q5. Give the schematic circuit of an A/D converter widely used in digital volt-meters and explain its operation. Derive expression for output voltage. Objective Nos.: …………1,2 and 3……………………………………………………………. Outcome Nos.: ………1,2 and 3………………………………………………………………. Signature of HOD Date: Signature of faculty Date: Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 Tutorial Sheet-1 1. Explain how the input off set voltage compensated for Op-amp. 2. How fast can the output of an Op-amp change by 10V, if its slew rate is 1V/µs? 3. Define thermal drift. 4. Explain the following terms a) Total output offset voltage b) Input bias current 5. What is a level translator circuit? 6. Why it is used with the cascaded differential amplifier? 7. Explain the various techniques used to compensate for thermal drift in Op-Amps. 8. Explain the role of negative feedback in operational amplifiers. Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 Tutorial Sheet-2 1. Explain Inverting, non inverting and differential amplifier for both ideal and practical amplifier with equations 2. Consider the circuit shown in figure 1: Determine the following when, V1=1V & V2= 2V (a) Ix (b) VA (c) VB (d) Expression for VA & VB in terms of V1 & V2 . Figure 1 3. Explain in detail about Sample and Hold circuit with neat diagram 4. Explain what the circuit does as shown in figure 2 and explain its working. 5. What is the maximum value for Vin when the potentiometer is set to its maximum resistance for above circuit? Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 Tutorial Sheet-3 1. Explain the frequency responses of all types of filters. 2. Figure 1 shows the first order Butterworth LPF that uses RC network, calcu- late the gain if the filter is a function of frequency. Give gain magnitude and phase angle equations. Figure-1 3. Design a fourth order Butter worth low pass filter having upper cut off frequency 1 KHz and pass band gain of 10. 4. List out the types of Oscillators, its working principle and explain any one of them in detail. 5. How can we generate a square wave and through it a Saw tooth wave form. Explain with circuit diagrams Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 Tutorial Sheet-4 1. Design an astable multivibrator using 555 timer to produce a square wave of 2 KHz frequency and 70% duty cycle. Draw the circuit with all component values. 2. Explain how a PLL is used as a frequency multiplier. 3. What are the functions of threshold and control voltage pins in 555 Timer IC? 4. What is VCO? Give two applications of it. 5. What are passive loop filters in PLL consider the PLL shown in figure 1? Figure 1 6. Write about voltage controlled frequency shifter using 555 Timer. 7. Explain the working operation 565 VCO in detail. 8. 555 Timer as Monostable Multi vibrator explain with applications. Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 Tutorial Sheet-5 1. Determine the resolution of 16 bit D/A converter 2. Illustrate one application each of Analog to Digital and Digital to Analog converters. 3. Write a note on multiplying DACs. 4. List the specifications of a Digital-to-Analog converter IC, 1408. 5. Compare and contrast R-2R ladder type and weighted resistor type DACs. 6. The LSB of a 6-bit D/A converter represents 0.1V. What voltage value will be represented by the following binary words? i. 101010 ii. 110110 7. Explain the operation of a Successive Approximation type analog to digital converter. 8. Calculate the number of bits required to represent a full scale voltage of 10V with a resolution of 5mV approximately. Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology (Autonomous) Bachupally, Kukatpally, Hyderabad – 500 090, A.P., India. (040) 6686 4440 EVALUATION STRATEGY Academic Year : 2013 Semester : I Name of the Program: B.Tech ……Electrical… Year: ……III…….. Section: A / B /C Course/Subject: ………………………………Op-Amps……………………………….. Name of the Faculty: ………R. Anil Kumar…………………………..Dept.:……EEE….…. Designation : ASST.PROFESSOR 1. TARGET: A) Percentage for pass: 40% b) Percentage of class: 85% 2. COURSE PLAN & CONTENT DELIVERY: • PPT presentation of the Lectures • Solving exercise problems • Model questions 3. METHOD OF EVALUATION 3.1 Continuous Assessment Examinations (CAE-I, CAE-II) 3.2 Assignments 3.3 Seminars 3.4 Quiz 3.5 Semester/End Examination Signature of HOD Signature of faculty Date: Date: Gokaraju Rangaraju Institute of Engineering and Technology Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering RESULT ANALYSIS Total Academic Subject No. of Year students appeared 2011ICA 128 2012 2012ICA 143 2013 No. of students passed No. of students failed < 60% 101 27 137 06 >70% Pass % 48 60% to 70% 29 24 78.9% 15 27 95 95.80%