Simple Circuit Analysis Ohm`s Law
advertisement

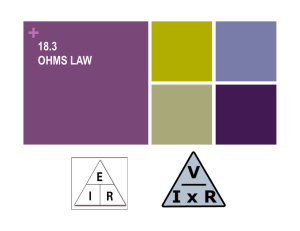
Simple Circuit Analysis Ohm’s Law ET 150 Ohm’s Law Learning Objectives In this lesson you will see: the mathematical relationship between voltage, current and resistance resistance call Ohm’ Ohm’s Law. the Ohm’ Ohm’s Law circle and use it to find the three forms of the formula examples using Ohm’ Ohm’s Law to find voltage, current and resistance the linear mathematical relationship between voltage and current the relationship between current and resistance is nonnon-linear low resistance causes current to increase quickly Ohm’s Law Ohm’s Law – a mathematical formula that relates voltage, current and resistance E 2.) R = 1.) E = IR I Three forms of Relationship Ohm’s Law Circle E E Voltage = E I Current R I R 3.) I= Resistance = I R E R E = I R Ohm’s Law Example Calculations An electric heater draws 7 A from a 120 V dc source. What is the the resistance of the heater coil? I=7 A E I 120 V R= = 17 .14 Ω (Ohms) 7A R= E=120 V R=? Ohm’s Law Example Calculations A water heater has a resistance of 10 Ω. What current will it draw from a 120 V dc source? I= ? E=120 V R=10 Ω E R 120 V I= = 12 A 10 Ω I= Ohm’s Law Example Calculations An iron draws 15 A and has a 5 ohm heating element resistance. What is the supply voltage to the iron? I=15 A E=? R=5 Ω E = IR E = (15 A)(5 Ω) = 75 V Ohm’s Law Voltage-Current Relationship Voltage is proportional to current (Linear relationship) x Oh m's Law V-I Relat ionship 140 150 Voltage (Volts) E = RI 100 V( I) y R=slope 50 0 0 0 10 0 20 30 40 I Current (Amps) As current, I increase, voltage, V increases proportionally. 40 Ohm’s Law Current-Resistance Relationship Current, I, is inversely proportional to, R, Resistance 20 ⎛1⎞ I = V⎜ ⎟ ⎝R⎠ Oh m's Law I-R Relationship 20 20 Current (amps) 15 x I( R) 10 y I( 20) As resistance decreases current increases quickly 5 1.25 0 0 5 20 40 R Resistance (ohms) 60 80 80 Note: R=0 is short circuit ET 150 Coming Next: Basic Electric Circuits- Series Connections SIMPLE CIRCUIT ANALYSIS OHM’S LAW