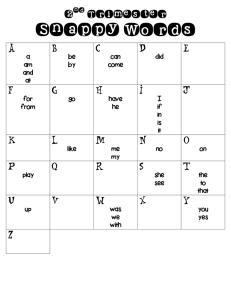
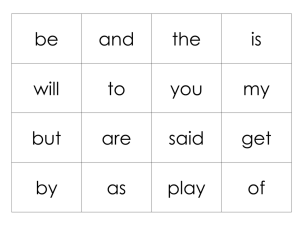
CEST Handbook: Engineering, Science & Technology at FNU
advertisement

2016 COLLEGECOLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK HANDBOOK 1 Table of Contents COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 2 GENERAL INFORMATION PAGE 3 ORGANISATIONAL STRUCTURE PAGE 6 ADMINISTRATION CONTACTS PAGE 9 CREDIT POINTS,STUDY HOURS & MODE OF DELIVERY OF ACADEMIC PROGRAMMES PAGE 11 FACULTY OF SCIENCES PAGE 12 SCHOOL OF SCIENCES PAGE 12 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL AND COMPUTING SCIENCES PAGE 34 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING PAGE 46 SCHOOL OF BUILDING AND CIVIL ENGINEERING PAGE 46 SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING PAGE 74 SCHOOL OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAGE 104 DEPARTMENT OF PRINTING TECHNOLOGY PAGE 129 FACULTY OF TRANSPORT PAGE 132 SCHOOL OF AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING AND ROAD TRANSPORT PAGE 132 FIJI MARITIME ACADEMY PAGE 151 SCHOOL OF AVIATION STUDIES PAGE 162 General Information The College of Engineering, Science and Technology (CEST) is, in terms of the programmes and units offered, the largest of the five colleges within the Fiji National University, providing technical and vocational education and higher education in engineering and sciences. The College currently has over 300 teaching and non-teaching staff. The College offers approximately 90 programmes ranging from Preliminary, Foundation, Certificates (Levels III to IV), Trade Diplomas, Higher Education Diplomas, Advanced Diplomas and Degrees, all of which comprise of more than 600 units from all the schools as stated below : Faculty of Engineering Faculty of Sciences The schools which offer programmes in the Faculty of Sciences are: • School of Sciences(SOS) • School of Mathematical and Computing Sciences(SMCS) Faculty of Transport The schools which offer programmes in the Faculty of Transport are: • School of Automobile Engineering and Road Transport (SAERT) • Fiji Maritime Academy (FMA) • School of Aviation Studies (SAS) based at Namaka Campus, Nadi Short courses are also offered throughout the year for those who: • require training in certain specific areas • are willing to study but cannot do so full-time • wish to apply for membership to various organizations (e.g. FIE) and need to • upgrade their qualifications for national and international needs. In general, all of the programmes offered by CEST have been designed and developed to suit Fiji’s industry needs. As such, there are multiple pathways of learning, with multiple entries and exits to and from programmes. Moreover, great value and emphasis have been placed upon industrial attachments, which are an integral part of most of our programmes of study. Another integral component of CEST in the university structure is TVET, which stands for Technical and Vocational Education and Training. Under this programme, students could enter the University at any level of study ranging from a Certificate to a Degree. Students could undertake basic technical programmes (like a Certificate (III-IV) (formerly Trade Certificate) and enter the job market whilst striving for Diploma, Advanced Diploma and Degree programmes at the same time. Alternatively, a student could enroll directly into the University’s Degree programmes as per the college admission regulation. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK The schools and departments which offer programmes in the Faculty of Engineering are: • School of Building and Civil Engineering (SBCE) • School of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (SEEE) • School of Mechanical Engineering (SME) • Department of Printing Technology (DPT) Nowadays, much effort is being put into sustainable technology and renewable energy technologies by every country to meet the energy challenges of reducing emissions from the generation of electricity using fossil fuels. Mindful of our own current energy-related issues, the College is planning to offer a Trade Diploma in Renewable Energy Technologies programme in the School of Mechanical Engineering CEST also intends to offer programmes at the post-graduate levels, including Post-graduate Certificate, Post-graduate Diploma, Master and Doctorate. 3 The quality of programmes offered at CEST is maintained by way of stakeholder consultation processes and reviews after every three (3) years. This is carried out to ensure programmes are of a high standard and consistent with industry requirements and to uphold consistency in the quality, taking into account the various technical innovations and advancements in the world market. The College of Engineering, Science and Technology has the required equipment and facilities for running these programmes. In short, the College offers you a wealth of opportunities. The main location of the College is at Samabula whereas the Aviation Studies programmes are running from the Namaka Campus in Nadi. A number of programmes are concurrently offered at other FNU campuses such as Ba, Lautoka and Labasa. CEST CAMPUSES COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 4 • DERRICK CAMPUS • NABUA CAMPUS • NATABUA CAMPUS • NAMAKA CAMPUS • BA CAMPUS • LABASA CAMPUS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 5 ASSOCIATE DEAN (HEP) DEAN - CEST College of Engineering, Science and Technology ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE HOS ‐ HE (SEEE) HOS ‐ HE (SBCE) HOS ‐ HE (SME) HOD ‐ Civil Engineering HOD ‐ Mechanical Engineering HOD ‐ Electrical Engineering Bachelor of Engineering ‐ Civil Bachelor of Engineering ‐ Mechanical Bachelor of Engineering ‐ Electrical & Renewable Energy HOD ‐ Electronics Engineering Bachelor of Engineering ‐ Electronics & Instrumentation ‐ Computer & Control ‐ Telecomunication & ASSOCIATE DEAN (TVET) HOS ‐ TVET (SME) HOS ‐ TVET (SBCE) HOD ‐ Building Services HOD ‐ Civil Trade Diploma ‐ Architectural Technology Trade Diploma ‐Building ‐ Quantity Surveying Trade Diploma ‐ Civil Engineering ‐ Land Surveying HOD ‐ Architecture CERT IV ‐ Carpentry & Joinery ‐ First Line Supervision CERT IV ‐ Plumbing & Sheet Metal HOD ‐ Dept. of Printing Cert IV ‐ in Printing Technology FACULTY OF ENGINEERING HOD ‐ Mechanical Engineering Trade Diploma ‐ Mechanical Engineering ‐ Renewable Energy CERT IV ‐ Fitting and Machining ‐ Fabrication and Welding ‐ Plant Maintenance ‐ Refrigeration and Airconditioning HOS ‐ TVET (SEEE) HOD ‐ Agriculture Engineering HOD ‐ Electrical HOD ‐ Electronics Trade Diploma ‐ Agriculture Engineering Trade Diploma ‐ Electrical Engineering CERT IV ‐ Agriculture Engineering CERT IV ‐ Electrical Engineering ‐ Electrical Servicemans Course Trade Diploma ‐ Electronics , Instrumentation & Control ‐ Telecommunication & Networking CERT IV ‐ Electronics Engineering ‐ Biomedical Technology ‐ Broadcast Engineering CERT - Radio Electronic and Television Servicemans Course CERT III - Mechanical Engineering ASSOCIATE DEAN (SCIENCES) HOS ‐ Sciences (HE) HOS ‐ SMCS HOD ‐ Physics HOD ‐ Chemistry Bachelor of Science ‐ in Physics ‐ Servicing Units for Faculty of Enginering Cert IV, TD & BE ‐ Foundation Science & Tech Units Bachelor of Science ‐ in Chemistry Higher Education Diploma ‐ Industrial Lab Technology ‐ Servicing Units for Faculty Enginering Cert IV, TD & BE ‐ Foundation Science & Tech Units HOD ‐ Biology BACHELOR OF SCIENCE ‐ in Biology Foundation Science & Tech HOD ‐ Environmental Science BACHELOR OF SCIENCE ‐ in Environmental Science / Management Higher Education Diploma ‐ in Environmental Science ‐ in Environmental HOD ‐ Food Technology Higher Education Diploma ‐ in Food Technology HOD ‐ Home Economics HOD ‐ Mathematics & Statistics Bachelor Of Education ‐ Major in Home Economics Bachelor of Science ‐ Mathematics ‐ Maths & Stats Servicing Units HOS ‐ TVET Certificate IV ‐ in Meteorology FACULTY OF SCIENCE HOD ‐ Computer Science & Information Systems BACHELOR OF SCIENCE ‐ Information Systems ‐ Computer Science TRADE DIPLOMA ‐ TD in Applied Computing CERT IV ‐ Cert IV in Applied Computing HOS ‐ TVET (SAERT) HOD ‐ Automotive Engineering TRADE DIPLOMA ‐ Automotive Engineering CERT IV - Automotive Eningeering ‐ Light Motor Vehicle ‐ Heavy Commercial Vehicle ‐ Heavy Mobile Plant ‐ Motor Vehicle Electrical and Electronics - Body Work - Automotive Light Machinery CERT III Automotive Engineering HOD ‐ Road Transport Technology TRADE DIPLOMA ‐ Road Transport Technology and Management HOS ‐ TVET (SAS) CERT IV ‐ Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (Mechanical) ‐ Aircraft Maintenance Engineering (Avionics) CEO ‐ FMA Head of Academic Studies HOD‐Quality Management/MR HOD ‐ Nautical Science HOD ‐ Marine Engineering HOD ‐ Safety & Survival TRADE DIPLOMA ‐ in Nautical Science ‐ Deck Cadet Officer Training ‐ Upgrading & Revalidation & Refresher Programs Trade Diploma ‐ in Marine Engineering ‐ Engineer Cadet Officer Training. ‐ Upgrading & Revalidation & Refresher Programs ‐ (17 listed courses) HOD ‐ Ship Building & Fisheries Technology Cert IV ‐ Ship Building HOD ‐ Marine Simulation (13 listed courses) FACULTY OF TRANSPORT Message from the College Dean On behalf of Team CEST I extend to you a very warm welcome and invite you to come and be part of the College of Engineering, Science and Technology (CEST) as a student, learner and become a member of our exciting team! COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 8 The College offers training programmes that are targeted to meet the human resource needs of Fiji, the region and beyond! So you can be assured that after you have completed your programme of studies and training here in CEST – there is a job waiting for you! From the sea to land and to the air - whether it is manning the ships in various capacities right up to Officers & Captains; to the land from tractors on the farm to cars and busses that run on our roads, to aviation and aeroplanes and to building roads, buildings, infrastructure, electricians, electronic communications, radio & TV, ICT and computing, sciences pure and applied, food technology and the sciences. We have more than 90 programmes to choose from, including Foundation, Certificates 3 & 4, Trade Diplomas, Higher Education Diplomas and Degrees offered in various campuses and locations – Derrick (Samabula), Nabua, Nasinu, Navua, Nadi, Lautoka, Ba and Labasa, with staff who are qualified with years of experience both in the industries as well as teaching at a university. A mixture of friendly locals and expatriate staff who are passionate about their jobs and will go out of their way to help students to achieve their goals of a good job and a successful career pathway i.e. trades, technicians, technologists and engineering levels. The modes of studies at the College varies according to the programme: a)Penster mode (8 week blocks) – Certificate 3 and 4 programmes; b)Trimester mode (15 weeks) – Certificate 4, Diplomas and Bachelor’s degree; c)Semester mode (18 weeks) – Bachelors (BE) degree & Masters. For those who do not quite meet the minimum entry requirement (MER) for the programme of study, we also offer some bridging programmes to help you achieve that mark or grade required as entry into a particular degree programme that you would like to pursue. Our programs are not just for fresh school leavers – we also have pathways for those who are working and want to pursue further studies in another program or even a degree – there are full time, part-time, evening classes, flexible modes, short courses, specialisation etc. If there is a demand – we can facilitate. We continue to develop and pursue strong linkages with strategic partners, industries, other international universities, government and relevant accrediting bodies for the sake of achieving international benchmarked accreditation for our programmes. For instance, in 2016 we will be assisted by RMIT towards the international accreditation of our Engineering programmes, from Trade Diploma or Technician level to the Bachelor of Engineering (BE) level. Please come and talk to us and we will be able to advise you on the pathways to reach your Career choice because we are here not just to provide a programme of study but also your important link to a fulfilling job out there! Administration Contacts College Administration Acting Dean/ Associate Dean (TVET/Technical) Mr. Salabogi Mavoa Phone: 338 1044 extension 1000 Email: deaneng@fnu.ac.fj : adeng@fnu.ac.fj Executive Officer Mr. Ashneel Sharan Phone: 338 1044 extension 1936 Email: EOEng@fnu.ac.fj Executive Assistant Ms. Deepika Bandhana Phone: 338 1044 extension 1018 Email: ea-cest@fnu.ac.fj Academic Officer Ms. Priya Pande Phone: 338 1044 extension 1962 Email: ao-cest.priya@fnu.ac.fj Administrative Assistant Ms. Payal Sharma Phone: 338 1044 extension 1005 Email: AAEng@fnu.ac.fj Class Auditor Ms. Swetha Sharma Phone: 338 1044 extension 1962 Email: swetha.sharma@fnu.ac.fj Associate Dean (Faculty of Sciences) Prof. Anand Tyagi Phone: 338 1044 extension 7020 Email: adscest@fnu.ac.fj Executive Officer Mr. Naoneet Deo Phone: 338 1044 extension 1970 Email: naoneet.deo@fnu.ac.fj Executive Officer (Faculty of Sciences) Ms. Sangeeta Muni Goundar Phone: 338 1004 extension 7042 Email: EO-Sciences@fnu.ac.fj Academic Officer Mr. Rajneel Richard Narayan Phone: 338 1004 extension 1006 Email: AOCEST@fnu.ac.fj Office Administrator Ms. Nousheen Hussain Phone: 338 1044 extension 1001 Email: PAEng@fnu.ac.fj Class Auditor Mr. Jone Silaira Phone: 338 1044 extension 1962 Email: jone.silaira@fnu.ac.fj Heads of Schools / Department Faculty of Engineering (FE) School of Building and Civil Engineering Mr. Sateesh Pisini (HE) Phone: 338 1044 extension: 1653 Email: HOS-SBCE@fnu.ac.fj School of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Dr. Arif Khan (HE) Phone: 338 1044 extension 1149 Email: HOS-SEEE@fnu.ac.fj School of Building and Civil Engineering Mr. Jotame Dianimoto (TVET) Phone: 338 1044 extension: 1649 Email: HOS-Building@fnu.ac.fj School of Electrical and Electronics Engineering Mr. Jiuliasi.V. Uluiburotu (TVET) Phone: 338 1044 extension 1976 Email: HOS-Electrical@fnu.ac.fj COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Executive Officer Ms. Swarti Sandhita Devi Phone: 338 1004 extension 1002 Email: EOEng@fnu.ac.fj Associate Dean (Higher Education) Dr. Anil Rana Phone: 338 1044 extension 1004 Email: anil.rana@fnu.ac.fj 9 School of Mechanical Engineering Mr. Joji Misaele Marau (HE) Phone: 338 1044 extension 1728 Email: HOS-Mechanical@fnu.ac.fj School of Mechanical Engineering Mr. Ratu Tui Toutou (TVET) Phone: 338 1044 extension 1720 Email: HOS-SME@fnu.ac.fj Faculty of Transport (FT) School of Automobile & Engineering and Road Transport Mr. Apisai Dovitana (TVET) Phone: 338 1044 extension 1600 Email: HOS-Automobile@fnu.ac.fj School of Aviation Studies Mr. Sakaraia Caucau Phone: 338 1044 extension 6700 Email: HOS-Aviation@fnu.ac.fj Fiji Maritime Academy Capt. Suren Gurusinghe (CEO) Phone: 338 1044 extension 5775 Email: ceo-fma@fnu.ac.fj COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 10 Faculty of Sciences (FS) School of Sciences Professor Anand Tyagi (HE) Phone: 3381 044 extension 7020 Email: adscest@fnu.ac.fj School of Sciences Mr. Ashneel Prasad Avishek (TVET) Phone: 3381 044 extension 4353 Email: HOS-SOS@fnu.ac.fj School of Mathematical & Computing Science Dr Maheswara Valluri (HE) Phone: 3381 044 extension 1573 Email: HOS_SMCS@fnu.ac.fj Credit Points, Study Hours & modes of delivery of Academic Programmes All academic programmes offered by the College (including short courses) are based on a credit point system, as indicated in Table 1 below. The system is based on total study hours (sum of contact hours and the self-directed learning (SDL) hours) required by a student in any teaching term. As the table shows, the total hours are as follows: 900 for semester; 750 for trimester and 400 for penster. The credit point for any unit or course is simply the total study hours divided by 15. Table 2 shows the programs, its delivery mode and the credit points. Table 1: Credit Points and Study Hours per Teaching Term Semester Trimester Penster Weeks of Contact instruction 14 12 7 In-term breaks (weeks) 1 1 0 Pre-exam Study Period (weeks) 1 1 0 Exam Period 2 1 1 18 15 8 Total Hours Available 900 750 400 Credit Points per term 60 50 27 Normal Student load/yr: Terms 2 3 5 120 150 135 No of Terms possible/yr 2 3 5 Credit Points possible/yr 120 150 135 Normal Student Load/Yr: Credits Table 2: Modes of Delivery of Academic Programs Programme Teaching Term No. of Terms Max CP’s per term Total CP’s Certificate III Trimester 2-3 25 60 Preliminary Trimester 2 44 88 Foundation Trimester 2 47 94 Penster(Till 2013) 5 27 135 Trimester(2014) 3 50 150 Trimester(2014) 5 50 250 Trade Diploma Semester(Till 2013) 4 60 240 Advanced Diploma Semester 2 60 120 Degree (Science) Trimester 9 50 360 Degree (Engineering) Semester 8 60 480 Certificate IV COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Total Weeks Available for Study 11 FACULTY OF SCIENCES SCHOOL OF SCIENCES STAFF PROFILE HIGHER EDUCATION STAFF HEAD OF SCHOOL PROF ANAND TYAGI PhD (Genetics),MSc (Genetics) Associate Dean (FS), Head of School (SOS) COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY PROF ANAND TYAGI PhD (Genetics),MSc (Genetics) Head of Department PATHIRANA NIHAL DAYAWANSA Visiting Associate Professor RAMWAT KUMAR GUPTA Assistant Professor RAVI DUTT SHARMA Assistant Professor RAMESH SUBRAMANI Assistant Professor ABHA MISHRA MSc (Microbiology) (HE) Lecturer II ROSELENE DAYAL BSc (Biotech.) (HE) Assistant Lecturer RUPANTRI NANDHIKA RAJU MSc (Bio), PGDip (Bio), BSc (Food and Nutr.), GCTT (HE) Lecturer II ASHNEETA ARTIKA CHANDRA Tutor SALIM AKBAR HUMAYOON Tutor YASHNI DEVI, HE (DILT) Lab Demonstrator DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY PROF RAJENDRA PRASAD PhD (Chem), MSc (Inorganic Chem)(HE) Head of Department Chemistry VEEJENDRA KUMAR YADAV Adjunct Professor 12 DR SUBRAMANIAN IYER, PhD (Org. Chem) Associate Professor DR NEELAM ZAIDI PhD (Chem), MSc (Chem), BSc (Chem), (HE) Assistant Professor ADRIAN AVINESH CHETTY MSc (Chem), PGD (Chem), (USP); BSc (Bio/Chem), (USP) Lecturer I (On study leave) SOFIA BANU SHAH MSc (Env.Sc.), PGDip (Env.Sc.), PGDip (Climate Change), PGCert (Edu.), BSc (Chem/Phy.), Cert.(Sec.Teach.) (HE) Lecturer II RANJINI DEVI Lecturer II WAISEA VOTADROKA MSc (Env. Law), PGDip (Dev. Stud.), PGDip (Chem.), BSc (Chem/Bio), Cert.(Teach.) (HE) Lecturer II SUNIL KUMAR BSc (Maths/Chem), PGDip (Chem), Cert.(Edu.) Dip.(Tertiary Teach.) (HE) Assistant Lecturer SHALVIN VIKASH KUMAR Tutor MAMBATTA SANKARA PRATIBHA, Research Fellow ADIMAITOGA T WILLIAM RABUKU Lab Demonstrator JOSLIN ASHNA SINGH Lab Demonstrator ROLINI PRITIKA NAND BSc (Env.Sc.), Dip (Ind. Lab.), Dip (Env.Sc.), Cert (Ind. Lab.Tech.) (HE) Laboratory Demonstrator JREETA Lab Demonstrator AMIT KUMAR Lab Demonstrator REENA DEVI PRASAD Lab Technician DEPARTMENT OF INDUSTRIAL LAB TECH DHIRAJ DEO RAJ Bsc (Maths/Chem)(HE) Lecturer II NIRBHAY CHAND PGD (Bio),BSc (Agr.Sc.),Dip (Agri.Sc),Adv.Cert (Teaching) Senior Lecturer DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS DR ABDUL QAYYUM MALIK PhD (Phy), MSc (Nuc.Tech), MSc (Phy), BSc (Phy/Maths) (HE) Head of Department Physics ARISHMA RAM MSc (Env.Sci); BSc (Env. Sci) Lecturer I DR RAMAL COOREY PhD, MSc, BSc (He) Assistant Professor DR TILIKA MITRA PhD, MSc, BSc (HE) Assistant Professor RAVITA DEVI PRASAD MSc (Phy), PGDip (Phy), PGCert (Edu), BSc (Maths/Phy) (HE) Lecturer I PARNESH KUMAR DUTT MEng (Electrical), PGDip (Electrical/Electronics), BTech (Electrical), Dip (Ter.Teach.) (HE) Lecturer II ANISH DAYAL B.Sc. (HE) Lecturer II PRIYA SINGH BSc (HE) Assistant Lecturer – MET DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENT SCIENCE DR SATYANARAYAN SHASHTRI PhD in Env. Sci, MSc (Org. Chem, BSc (Botany, Geology, Chem (Hons)) Assistant Professor, Head of Department Environmental Science DR AJANTHA PERERA PhD, MSc, BSc (HE) Assistant Professor DEPARTMENT OF FOOD TECHNOLOGY DR KHAIRUL AZAM PhD (Food Science), MSc (Food Technology) Visiting Professor MOHAMMED SAHAHIDUL ALAM MOZNU Bachelor of Food Science and Technology Lecturer II NILESHNI LATA PRASAD Dip (Food Tech), Cert. (OHS), ISO Cert. Laboratory Demonstrator TVET STAFF HEAD OF SCHOOL ASHNEEL AVISHEK PRASAD MSc (Phy), PGD (Phy), BSc (Maths/Phy) EXECUTIVE OFFICER SANGEETA MUNI GOUNDER MSc (Chemistry), BSc (Chemistry/Mathematics with Stats) OFFICE ADMINISTRATOR JYOTIKA DEVI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK KUNAL KUSHA DAYAL BSc (Phy/Maths), PGCert (Edu), PGDip (Ren.Energy) (HE) Lecturer II DEPARTMENT OF HOME ECONOMICS SUMANTLA DEVI VARMAN M(Public Health), BSc (Edu/Food and Nutri.), Dip. (Edu/Home Eco), (FCAE) (HE) Head of Department Home Economics ILAITIA VUDIKARIA SARAQIA B.A.Sc. (Env.Sc), (AUT); Dip (Env.Sc), (FIT); Cert (Lab.Tech) Lecturer II SALANIETA TUISUVA MATAI PGDip (Env. Sci); BA. Sci (Env. Sc); Dip (Env.Sc; IDTT; CILT (HE) Lecturer II 13 PROGRAMME DETAILS AND DURATION Science Programme Preliminary Foundation Foundation HE Diploma Degree Science Science Technology Level Delivery Mode Trimester Trimester Trimester Trimester Trimester Total number of units to complete the 10 units programme 10 units 10 units 16-18 units 20-24 units Number of units to complete per tri5 units mester 5 units 5 units 1- 4 units 1- 4 units Number of trimesters to complete all 2 trimesters units 2 trimesters 2 trimesters 6 trimesters 9 trimesters Number of weeks per trimester 15 15 15 15 Minimum period required for industrial attachment - - 6 months 6 months Credit Points per Programme 94 82 240 360 6 months 6 months 2 years 3 years 15 88 Minimum period to complete the whole 6 months programme COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 14 Entry Qualifications Preliminary Science Form 5 pass with minimum of 50% in Science or Technology subjects OR Completed Form 6 level (Science) but DID NOT PASS FSLC exam or equivalent. Foundation Science & Technology Form 6 pass, with minimum of 50% in Science or Technology subjects OR Completed but not successful in Form 7 (FSFE) level Science or equivalent OR Pass 8 Units in Preliminary Science programme. HE Diploma (Industrial Laboratory Technology, Food Technology, Environmental Science) A pass in Form 7 with 200 out of 400 marks with 50% minimum marks in English and any 3 subjects including the majoring subjects. Bachelor of Science (all Majors) Pass in Form 7 with 200 out of 400 marks with 50% minimum marks in English and any 3 subjects including the majoring subjects OR Foundation Science with GPA of 2.00 or more. Programmes, Units and Credit Points TVET Program PRELIMINARY SCIENCE TRIMESTER 1 TRIMESTER 2 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE MTH301 Preliminary Mathematics I CHM301 Preliminary Chemistry I PHY301 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE 10 MTH302 Preliminary Mathematics Il 10 9 CHM302 Preliminary Chemistry II 9 Preliminary Physics I 9 PHY302 Preliminary Physics II 9 BIO301 Preliminary Biology I 8 BIO302 Preliminary Biology II 8 LNG301 Preliminary English I 8 LNG302 Preliminary English II 8 Total CP CP 44 CP 44 FOUNDATION SCIENCE TRIMESTER 2 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE CHM402 Foundation Chemistry I BIO403 Foundation Biology I PHY402 MTH404 COM403 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE 8 CHM403 Foundation Chemistry II 8 10 BIO404 Foundation Biology II 10 Foundation Physics I 9 PHY403 Foundation Physics II 9 Foundation Mathematics I 10 MTH409 Foundation Mathematics II 10 Communication Studies I 10 COM404 Communication Studies II 10 Total CP CP 47 CP 4 FOUNDATION TECHNOLOGY TRIMESTER 1 TRIMESTER 2 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE CHM403 Foundation Chemistry I CP 10 COM404 Communication Studies Il CP 10 MTH404 Foundation Mathematics I 10 MTH409 Foundation Mathematics II 10 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK TRIMESTER 1 15 Higher Education Program Higher Education Diploma in Industrial Laboratory Technology (HEDILT) The HE Diploma in Industrial Laboratory Technology program develops students’ knowledge and skills of analytical processes and techniques in an attempt to provide for the demand that exists in industrial laboratories today. The program is designed to be the building block for the Advanced Diploma in Industrial Laboratory Technology and covers a wide range of topics in applied chemistry, microbiology, biotechnology and biochemistry along with providing a sound background in biology, chemistry, physics, electronics, communication in science, occupational health and safety and mathematics. YEAR 1 TRIMESTER 1 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE TRIMESTER 2 CP TRIMESTER 3 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE CP UNIT CODE MTH510 Elementary Algebra & Statisctics 12 LNG501 English For Academic Purposes 12 ETH501 Ethics,Values & Governance 12 CHM503 General Chemistry 12 CHM504 Organic Chemistry 12 FDT504 Food Biotechnology 16 BIO508 Cell Biology 12 PHY506 Introductory Physics 12 CHM502 Analytical Chemistry 12 CIN506 Computer Principles 16 36 Total 40 Total 52 Total YEAR 2 TRIMESTER 1 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE TRIMESTER 2 CP TRIMESTER 3 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE CP UNIT CODE CHM612 Industrial Chemistry 14 CHM601 English For Academic Purposes 14 ISO601 Competence Of 14 Testing & Calibration Of Laboratory Equipment MTH602 Statistical Mathematics 14 CHM614 Industrial Hygiene & Chemical Safety 16 BIO602 Applied Microbiology 12 PHY601 16 Total Environmental Physics 44 Total 30 CHM613 Analytical Research Report 16 Total 42 After completion of 16 out of 18 units, students can proceed to 6 months of industrial attachment. 16 Higher Education (HE) Diploma in Food Technology HE Diploma in Food Technology has been designed so that several areas of science applied to food studies are taught in a wider, more encompassing approach. The Diploma provides its graduates skills, knowledge and inspiration to address the needs of the local food industry. The program covers a wide range of topics in food chemistry, microbiology, food biotechnology and biochemistry, along with providing a sound background in biology, chemistry and physics. YEAR 1 TRIMESTER 1 UNIT TITLE CP TRIMESTER 3 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE CP UNIT CODE MTH510 Elementary Algebra & Statisctics 12 LNG501 Englisg for Academic Purposes 12 ETH501 Ethics, Values & Goverance 11 CHM503 General Chemistry 12 PHY506 Introductory Physics 12 FDT504 Food Biotechnology 16 BIO508 Cell Biology 12 FDT503 Food Microbiology 14 CIN506 Computer Principles 16 FDT502 Nutrient Studies 14 52 Total Total 50 Total 27 YEAR 2 TRIMESTER 1 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE FDT605 Food Processing Technology I FDT603 Practical Food Microbiology CHM606 Food Chemistry TRIMESTER 2 CP TRIMESTER 3 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE CP UNIT CODE 16 FDT606 Food Processing Technology II 18 FDT602 Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point 7 14 FDT607 Food Engineering 20 FDT604 Food Security 12 14 Electives (1 Only) Total 44 Total 38 CHM601 Instrumental Chemistry 14 MTH602 14 Total Statistical Mathematics 47 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK UNIT CODE TRIMESTER 2 17 Higher Education (HE) Diploma in Environmental Science The HE Diploma in Environmental Science is a two year program towards the Bachelor of Science (Environmental) The programme will prepare persons for employment in the environmental sector and environmental related private and government organizations. YEAR 1 TRIMESTER 1 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 18 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE CIN506 Computer Principles ENS501 BIO511 TRIMESTER 2 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE CP UNIT CODE 16 LNG501 English For Academic Purposes 12 CHM505 Introductory Chemistry 12 Introduction To Environment 12 ENS502 Organic Chemistry 12 MTH503 General Mathematics 12 Introductory Biology 12 MTH514 Probability and 12 Statistics PHY506 Introductory Physics 12 ETH501 Ethics,Value & Governance 12 Total CP TRIMESTER 3 40 Total 36 Total 48 YEAR 2 TRIMESTER 1 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE ENS602 Environmental Issues & Management ENS603 Environmental Law TRIMESTER 2 CP TRIMESTER 3 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE CP UNIT CODE 16 ENS601 Environment Biology 16 ENS605 Biodiversity & 14 Conservation In South Pacific Region 16 ENS604 Environmental Research Project 14 BIO604 Ecology/ Bio-Diversity 14 CHM604 Environment Chemistry 14 Total 42 CHM601 Instrumental Chemistry 14 Total 46 Total 30 Bachelor in Science (Double Majors) The Bachelor of Science (B. Sc.) program would give students a chance to choose their majoring units and the field they would like to study to further develop their knowledge and skills in science, laboratory practices and principles, as well as laboratory research, problem solving, data gathering, analysis and reporting. B. Sc. Program also emphasizes quality control concepts both in theory and via practical methods. The following tables show the units offered in different departments. Students can study double major in different combinations like Biology and Chemistry, Chemistry and Physics, Physics and Biology, Biology and Environmental Science, Chemistry and Environmental Science, Chemistry and Food Science etc. DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY CP BIO508 Cell Biology 12 BIO509 Botany 12 BIO510 Zoology 12 ELECTIVE UNITS BIO503 Introduction to Ecology 12 BIO507 Environmental Biology 12 BIO511 Introductory Biology 12 Year 2 CP BIO603 Genetics and Evolution 15 BIO604 Ecology/Biodiversity 15 ELECTIVE UNITS BIO601 Applied Biotechnology 15 BIO602 Applied Microbiology 15 BIO605 Invertebrate Biology 15 BIO606 Tropical Plant Biology 15 Year 3 CP BIO702 Applied Animal Physiology 20 BIO703 Applied Plant Physiology 20 ELECTIVE UNITS BIO704 Marine Biology 20 BIO705 Molecular Biology and Biotechnology 20 BIO706 Embryology (Plants and Animals) 20 BIO707 Evolution 20 PRE-DEGREE BIO403 Foundation Biology I 8 BIO404 Foundation Biology II 8 BIO301 Preliminary Biology I 8 BIO302 Preliminary Biology II 8 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Year 1 19 DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY Year 1 CP CHM503 General Chemistry 12 CHM504 Organic Chemistry 12 ELECTIVE UNITS CHM501 Applied Chemistry 12 CHM502 Analytical Chemistry 12 CHM505 Introductory Chemistry 12 BIO511 Introductory Biology 12 Year 2 CP CHM602 Physical Chemistry 15 CHM603 Inorganic Chemistry 15 ELECTIVE UNITS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK CHM601 Instrumental Chemistry 15 CHM604 Environmental Chemistry 15 CHM605 Quantum Chemistry 15 CHM606 Food Chemistry 15 CHM607 Marine Chemistry 15 Year 3 CHM701 CP Modern Instrumentation Methods and Techniques 20 ELECTIVE UNITS CHM702 Advanced Organic Chemistry 20 CHM704 Chemistry of Materials and Polymers 20 CHM705 Chemistry of Dyes and Pigments 20 CHM706 Advanced Inorganic Chemistry 20 CHM707 Advanced Physical Chemistry 20 CHM708 Medicinal Chemistry 20 CHM709 Chemical Analysis of Foods 20 PRE DEGREE CHM402 Foundation Chemistry I 8 CHM403 Foundation Chemistry II 8 CHM301 Preliminary Chemistry I 9 CHM302 Preliminary Chemistry II 9 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS Year 1 CP PHY504 Mechanics and Fluids 12 PHY505 Electricity and Magnetism 12 PHY510 Oscillation, Waves and Optics 12 ELECTIVE UNITS PHY501 Applied Physics 12 PHY502 Applied Electronics 12 PHY503 Electronics and Instrumentations 12 PHY506 Introductory Physics 12 PHY508 Introduction to Astronomy 12 Year 2 CP PHY607 Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics 15 PHY609 Modern Physics 15 ELECTIVE UNITS 20 PHY601 Environmental Physics 15 PHY602 Electronics and Electronic Circuits 15 PHY603 Electromagnetism 15 PHY503 Electronics and Instrumentations 12 PHY506 Introductory Physics 12 PHY508 Introduction to Astronomy 12 Year 3 CP ELECTIVE UNITS PHY705 Solid State and Semiconductor Physics 20 PHY704 Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Physics 20 PHY701 Control Systems 20 PHY703 Renewable and Sustainable Energy 20 PHY706 Medical Physics 20 PHY707 Nuclear and Particle Physics 20 PHY708 Principles of Energy Conservation and Utilisation 20 PRE DEGREE Foundation Physics I 10 PHY403 Foundation Physics II 10 PHY301 Preliminary Physics I 10 PHY302 Preliminary Physics II 10 Certificate IV in Meteorology Trimester 1 MTH404 Foundation Mathematics I 10 PHY402 Foundation Physics I 9 MET402 Atmospheric Science I 5 MET404 Synoptic Meteorology I 5 MET406 Tropical Cyclone Genesis Climatology & Forecasting 5 Trimester 2 MTH409 Foundation mathematics II 10 PHY403 Foundation Physics II 9 MET403 Atmospheric Science II 5 MET405 Synoptic Meteorology II 5 MET407 Climate Variability, Variability & Prediction 5 Trimester 3 ETH401 Ethics Values & Governance B 9 LNG401 English for Academic Studies 13 DEPARTMENT OF HOME ECONOMICS YEAR 1 CP HEC501 Food Science 12 HEC502 Food, Nutrients and Health 12 HEC503 Science and Consumer 12 HEC504 Fashion Design and Tailoring 12 HEC504 Fashion Design and Tailoring 12 YEAR 2 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK PHY402 CP HEC601 Food Principles 15 HEC602 Dimensions of Food and Meals 15 HEC603 Textile Design, Decoration and Enterprising 15 HEC604 Family Financial and Social issues 15 21 YEAR 3 CP HEC701 Individual and Family Resource Management 15 HEC702 Apparel Design and Pattern Making 15 HEC703 Advanced Apparel and Design 15 HEC704 Nutrients Requirement and Metabolism 15 HEC705 Community Nutrition 15 HEC706 Consumer Economics and Housing Concepts 15 HEC707 Life Cycle Nutrition 15 HEC708 Advanced Tailoring 15 DEPARTMENT OF FOOD SCIENCE YEAR 1 CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK FDT501 Basic Food Science 14 FDT502 Nutrients Studies 14 FDT503 Food Microbiology 14 FDT504 Food Biotechnology 16 FDT505 Properties of Food 14 FDT506 Food Technology Research Project 14 YEAR 2 CP FDT601 Food production and Preservation 14 FDT602 Hazards Analysis Critical Control Point 14 FDT603 Practical Food Microbiology 14 FDT604 Food Security 12 FDT605 Food Processing Technology I 16 FDT606 Food Processing Technology II 18 FDT607 Food Engineering 20 YEAR 3 CP FDT701 Quality Assurance and Legislation 26 FDT703 Food Packaging 26 FDT704 Food Product Development 26 DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE YEAR 1 CP ENS501 Introduction to our Environment 12 ENS502 Introduction to Natural Resources 12 ENS503 Introduction to Environmental Geology 12 YEAR 2 CP ENS601 Environmental Biology 16 ENS602 Environmental Issues and Management 16 ENS603 Environmental Law 16 ENS604 Environmental Research Methodologies 14 ENS605 Biodiversity & Conservation in South Pacific Region 14 ENS606 Environmental Pollution and Control 16 ENS607 Wastes to Resources 16 ENS608 Fundamentals of Environmental Science 16 ENS609 Fundamentals of Environmental Management YEAR 3 22 16 CP ENS701 Climate Change and the South Pacific 20 ENS702 Marine Ecology 20 ENS703 Fiji and South Pacific Freshwater Ecology 20 ENS704 Fiji and South Pacific Terrestrial Ecology 20 ENS705 Fiji and South Pacific Coastal Management 20 ENS706 Environmental Impact Assessment 20 ENS707 Mining and its Environment 20 ENS708 Geographic Information Systems 20 ENS709 Field Research Project 20 ENS710 Environmental Impact Assessment Practicum 20 ENS711 Environmental and Natural Resources Economics 20 ENS712 Environmental Health and Society 20 Unit Descriptors BIO509: Botany This unit will provide a broad introduction to the many disciplines in the science of Plant Biology. The unit will examine the diversity of photosynthetic organisms and the major groups of plants will be discussed in terms of morphology, anatomy, physiology, life cycles, phylogeny and the ecology. BIO302: Preliminary Biology II The course is a continuation of Preliminary Biology 1 and will provide basic understanding of various living organisms. This course deals with basic plant and animal biology and basic ecology. Prerequisite: Pass in Form 5 Biology or equivalent BIO510: Zoology This unit introduces students to the diversity, functional morphology, and evolution of the major groups of animals, and protozoan. The unit provides a broad understanding of animal diversity, morphology, and life processes of animals so as to build a solid foundation for more advanced units in animal Biology. BIO403: Foundation Biology I The purpose of this unit is to explain the fundamental concept of genetics, the cell, microbial, plant life and other biological processes pertaining to life. Moreover, its purpose is to identify the similarities within the diversities of the plant kingdom. BIO404: Foundation Biology II The purpose of the unit is to identify the similarities within the diversity of the animal kingdom, describe the main stages in Hominid evolution and apply biological knowledge to identify appropriate ways to address problems relating to the life of man and his living environment BIO503: Introduction to Ecology To promote understanding of how biotic elements interact with one another and the biotic environment. To familiarize learners with the process of collecting ecological field data, its analysis and presentation. BIO507: Environmental Biology This unit explains and identifies current global and local environmental concerns, discuss the structure of biological communities and ecological succession BIO508- Cell Biology The course will provide with the basic knowledge, concepts and fundamental theories of cell structure, function, and the molecular mechanisms of life activities at the level of molecules, sub-cells and cells. The course is a general introduction to Cell Biology, Biochemistry, Molecular Genetics and Microbiology. BIO511: Introductory Biology This unit introduces students to the fundamentals of biology, its relevance to the ecosystem, applications including studying of bacteria, planktons and the hierarchy of existence in the biological environment, animal and plant kingdoms and evolutionary process. BIO601: Applied Biotechnology This unit explains Mendelian Genetics, describes the recombination in bacteria, demonstrates the techniques of tissue culture and Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) electrophoresis and the process and application of DNA fingerprinting and describes gene cloning BIO602: Applied Microbiology The purpose of this unit is to give the students an appreciation of the scope of industrial microBiological Sciences terms of: The numerous fermentation processes in which the production of alcohols, organic acids, glycerol, acetone and other substances are end results; and certain aspects of food – manufacturing processors, such as baking and the making of cheese, butter, pickles in which microbial agencies take a significant and important accessory part BIO603: Genetics and Evolution This unit provides knowledge on genetics, heredity, population genetics and evolution, which all play an important role in combining all other areas of biological studies and have considerable impact on our daily lives. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Biology Major: BIO301: Preliminary Biology I The course will provide basic understanding for further studies in biology. This course deals with cell and molecular biology, genetics, ecology and biodiversity. Prerequisite: Pass in Form 5 Biology or equivalent 23 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 24 BIO604: Ecology/Biodiversity This unit will provide a foundation in ecology, defined as the interactions between organisms and their environment, operating on small and large temporal and spatial scales. In addition to studying organisms, populations, and communities, this unit will also discuss ecological limits caused by the physical environment, ecosystem ecology and flows of energy and nutrients, biodiversity and conservation, biogeography, macroand global ecology. and bacterial genetics, control of gene expression in prokaryotes and eukaryote, understanding of principles of DNA recombinant technology, use of microbial, plant, marine, medicine and forensic biotechnology. BIO605: Invertebrate Biology This unit enables student to acquire knowledge and understanding of the invertebrates and their identification, adaptations in certain ecosystems, embryonic development and life cycle. Chemistry Major: BIO606: Tropical Plant Biology This unit enables students to understand composition and distribution of community types in the tropics and the factors underlying these patterns, biodiversity as it relates to tropical communities and explain hypotheses for high, tropical diversity, recognize common adaptations of plants to tropical environments that enable them to, survive in the various tropical environments, understanding of human impacts on the tropical environment and recognize how interactions between climates, soils and specific plant lineages, both present and in the past, have contributed. BIO702: Applied Animal Physiology This unit will enable students to acquire the relevant knowledge-base and understanding of body-systems function in animals. Emphasis will be placed on the mechanisms by which animals perform their life‐ sustaining functions. The unit will provide knowledge and understanding to the variations in the physiological functions and adaptations of various animals including human. BIO703: Applied Plant Physiology This unit explains the principles and processes of plant physiology and their practical applications by providing in-depth knowledge about the physiology of plant growth and development, at whole plant level, under in vivo and in vitro conditions. In addition this unit examines the responses of plants to changes in the environment. BIO704: Marine Biology This unit enables students to understand marine environment and its inhabitants, major groups of marine organisms in terms of their detailed biological and ecological characteristics, analysis of the unique adaptations of different marine organisms, which result in the various life strategies in the ocean, current biological knowledge of various marine invertebrates, vertebrates, and algae in Fiji and globally. BIO705: Molecular Biology and Biotechnology This unit enables students to analyse concepts of molecular biology and biotechnology which includes nucleic acids structure, function and replication, viral BIO706: Embryology (Plants and Animals) This unit explains foetal development in plants and animals together with the necessary competencies in testing and practical methodology in experiments that goes with this unit. CHM301: Preliminary Chemistry I The purpose of this chemistry unit is to gain an understanding and appreciation for chemistry and learn the underlying principles behind the science. Chemistry is a physical science defined as the study of matter and the changes it undergoes. In the delivery of this unit, emphasis will be placed on the conduct of practical experiment and demonstration of safe and accurate use of apparatus and chemicals, developing skills in using scientific methods of solving problems, understanding of common chemical principles and their application to a range of everyday situation and technology. CHM302: Preliminary Chemistry II The purpose of this chemistry unit is to gain an understanding and appreciation for chemistry and learn the underlying principles behind the science. Chemistry is a physical science defined as the study of matter and the changes it undergoes. CHM402: Foundation Chemistry I The purpose of this unit is to provide the basic foundation concepts in chemistry required by those who will continue to study chemistry at tertiary level. This unit is concerned in further broadening the knowledge of the specified major patterns of chemical behavior and understanding these patterns according to various chemical principles. CHM403: Foundation Chemistry II The purpose of this unit is to provide basic foundation concepts in chemistry required by those who will continue to study chemistry at tertiary level. This unit is concerned with further broadening the knowledge of the specified major patterns of chemical behavior and understanding these patterns according to various chemical principles. Prerequisite: Pass in Form 6 Chemistry or CHM301& CHM302 or equivalent CHM405: Foundation Material Science The purpose of this unit is to introduce students to engineering materials and their property structure relationships. In addition, it provides an appreciation of the various mechanisms for modifying materials with respect to both properties and form, and an insight into the use of materials in the built environment and how this has changed. CHM501: Applied Chemistry This unit describes the synthesis of industrially important classes of compounds, lists the raw materials used in manufacturing of industrially important compounds; the performance of various analytical tests for clarity of purity for such important class of compounds and explains modes of action of pharmaceuticals and pesticides. CHM502: Analytical Chemistry This unit explains safe working methods in a chemical laboratory, describes and performs techniques of separation and purification of both organic and inorganic samples and performs the following Titrimetric for quantitative analysis; Acid-Base titration; Complexion titration- EDTA as a complexion; Oxidation-reduction titration and Precipitation titration. CHM504: Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry course will provide students with a well-rounded, integrated background at the first year level covering key concepts in the area of organic chemistry with a particular emphasis on their relevance to industrial and biological processes. It is focused on an in-depth analysis of several types of organic reactions from a mechanistic and stereo chemical outcome viewpoint. Particular references are made to natural products and synthesis of compounds of biological and commercial importance. It also introduces physical methods used in the study of organic compounds. CHM613: Analytical Research Project This unit provides students with the opportunity to undertake largely self-directed work, which involves some form of investigation with results presented in both a written and oral form. To encourage students to exercise independent learning and source information from the Library and the internet and to enable students to demonstrate the ability to plan and prioritize tasks involved in a project. CHM601: Instrumental Chemistry This unit describes the types of chromatographic techniques used in separation of compounds: thin layer chromatography, column chromatography, and gas chromatography and high performance liquid chromatography and calculates column resolution, number of theoretical plates, plate height selectivity factor and capacity factor. CHM603: Inorganic Chemistry The purpose of this unit is to expand student’s knowledge base in inorganic chemistry by providing new ways of understanding molecular orbitals, bonding and reactivity. The transition and nontransition elements with an emphasis on structure and reactivity of the elements and their compounds will be discussed. Coordination chemistry of transition metals including organometallic and bioinorganic chemistry be discussed in significant depth. Primary focus of the coordination chemistry component will be on the stability, bonding, properties and reactivity of the coordination compounds and their importance in biological and industrial systems. The applied aspects of inorganic compound viz silicates, aluminosilicates, polyphosphates and organometallic and coordination compounds be emphasized. CHM604: Environmental Chemistry The purpose of this unit is to understand the way in which the undisturbed environment (air, soil & water) works, and then study the impact of human activities on these natural systems. This unit will also bring to attention some pressing issues such as global warming, climate change, and greenhouse effect, with their causes and effects. It is important to accurately evaluate the activities of humans to be able to control and reduce these issues, so that the forthcoming generations are able to live in a healthy environment. This unit will also include the pollutants released into our environment, chemical reactions taking place, and the toxic products formed. CHM605: Quantum Chemistry The course consists of two components, both essential to proper understanding of advanced concepts in chemistry. The concept, mathematics includes topics on functions, graphs, differential and integral calculus, matrices and vectors etc., and would prepare students to apply mathematics to chemistry particularly to physical chemistry, quantum mechanics and molecular modelling. Without delving into abstract mathematics rigors application for these concepts with practical applications be emphasized. The second part of the course on quantum mechanics would present mathematical account of atomic and molecular structure. Topics on quantum mechanics include schroedinger wave equation, postulates of quantum mechanics and their application to atomic and molecular structure and their spectroscopes. CHM606: Food Chemistry Food chemistry course is designed to train students for food quality control, food preservation, nutrition and health and agriculture sciences. It aims to provide an overview of main principles of food chemistry by integrating the principles of chemistry and biochemistry COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK CHM503: General Chemistry General chemistry course is designed to cover the needs of a wide variety of students by offering abroad introduction to chemical concepts. The course serves not only as a sound foundation in chemistry, but also as a useful and necessary background for those whose main interests lie in education, engineering, geology, physical, food or biological sciences. The emphasis is on developing knowledge and understanding of a basic set of chemical concepts and facts. CHM602: Physical Chemistry The purpose of this unit is to study the principles and applications of thermodynamics, quantum chemistry, and chemical kinetics. This unit will also focus on fuel cells, corrosion, and surface and colloidal chemistry. 25 CHM501: Applied Chemistry This unit describes the synthesis of industrially important classes of compounds, lists the raw materials used in manufacturing of industrially important compounds; the performance of various analytical tests for clarity of purity for such important class of compounds and explains modes of action of pharmaceuticals and pesticides. CHM502: Analytical Chemistry This unit explains safe working methods in a chemical laboratory, describes and performs techniques of separation and purification of both organic and inorganic samples and performs the following Titrimetric for quantitative analysis; Acid-Base titration; Complexion titration- EDTA as a complexion; Oxidation-reduction titration and Precipitation titration. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 26 CHM503: General Chemistry General chemistry course is designed to cover the needs of a wide variety of students by offering abroad introduction to chemical concepts. The course serves not only as a sound foundation in chemistry, but also as a useful and necessary background for those whose main interests lie in education, engineering, geology, physical, food or biological sciences. The emphasis is on developing knowledge and understanding of a basic set of chemical concepts and facts. CHM504: Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry course will provide students with a well-rounded, integrated background at the first year level covering key concepts in the area of organic chemistry with a particular emphasis on their relevance to industrial and biological processes. It is focused on an in-depth analysis of several types of organic reactions from a mechanistic and stereo chemical outcome viewpoint. Particular references are made to natural products and synthesis of compounds of biological and commercial importance. It also introduces physical methods used in the study of organic compounds. CHM613: Analytical Research Project This unit provides students with the opportunity to undertake largely self-directed work, which involves some form of investigation with results presented in both a written and oral form. To encourage students to exercise independent learning and source information from the Library and the internet and to enable students to demonstrate the ability to plan and prioritize tasks involved in a project. CHM601: Instrumental Chemistry This unit describes the types of chromatographic techniques used in separation of compounds: thin layer chromatography, column chromatography, and gas chromatography and high performance liquid chromatography and calculates column resolution, number of theoretical plates, plate height selectivity factor and capacity factor. CHM602: Physical Chemistry The purpose of this unit is to study the principles and applications of thermodynamics, quantum chemistry, and chemical kinetics. This unit will also focus on fuel cells, corrosion, and surface and colloidal chemistry. CHM603: Inorganic Chemistry The purpose of this unit is to expand student’s knowledge base in inorganic chemistry by providing new ways of understanding molecular orbitals, bonding and reactivity. The transition and nontransition elements with an emphasis on structure and reactivity of the elements and their compounds will be discussed. Coordination chemistry of transition metals including organometallic and bioinorganic chemistry be discussed in significant depth. Primary focus of the coordination chemistry component will be on the stability, bonding, properties and reactivity of the coordination compounds and their importance in biological and industrial systems. The applied aspects of inorganic compound viz silicates, aluminosilicates, polyphosphates and organometallic and coordination compounds be emphasized. CHM604: Environmental Chemistry The purpose of this unit is to understand the way in which the undisturbed environment (air, soil & water) works, and then study the impact of human activities on these natural systems. This unit will also bring to attention some pressing issues such as global warming, climate change, and greenhouse effect, with their causes and effects. It is important to accurately evaluate the activities of humans to be able to control and reduce these issues, so that the forthcoming generations are able to live in a healthy environment. This unit will also include the pollutants released into our environment, chemical reactions taking place, and the toxic products formed. CHM605: Quantum Chemistry The course consists of two components, both essential to proper understanding of advanced concepts in chemistry. The concept, mathematics includes topics on functions, graphs, differential and integral calculus, matrices and vectors etc., and would prepare students to apply mathematics to chemistry particularly to physical chemistry, quantum mechanics and molecular modelling. Without delving into abstract mathematics rigors application for these concepts with practical applications be emphasized. The second part of the course on quantum mechanics would present mathematical account of atomic and molecular structure. Topics on quantum mechanics include schroedinger wave equation, postulates of quantum mechanics and their application to atomic and molecular structure and their spectroscopes. CHM606: Food Chemistry Food chemistry course is designed to train students for food quality control, food preservation, nutrition and health and agriculture sciences. It aims to provide an overview of main principles of food chemistry by integrating the principles of chemistry and biochemistry behaviours of inorganic molecules and materials. Advanced concept of bonding, spectra and magnetic properties would be discussed with an objective of imparting knowledge of newer materials and techniques. The importance of inorganic compounds in the development of new magnetic materials, semiconducting and superconducting materials as well in host guest recognitions be discussed. Laboratory/ Project component will include hands on training in synthesis, characterization and studies of new inorganic materials and complexes. CHM709: Chemistry Analysis of Food Chemical analysis of food and beverages course will help students, entrepreneurs and professionals in mastering fundamental concepts in analytical chemistry, while keeping pace and rapidly evolving methodologies in the analysis of foods and beverages. Topics include: quality control of analytical methods and quality norms, analysis of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, additives, preservatives and chromatographic methods of separation and cleanup. Laboratory/Project component will include hands-on training in the use of above methods and their combinations. Environmental Science Major: ENS601: Environment Management This unit enhances awareness and perception of the environment and to develop a clear understanding of the impact of human activities upon it, with emphasis upon local examples, and familiarize students with current attempts to balance controls or reverse environmental degradation – their nature, their successes and their shortcomings. ENS602: Environmental Issues This unit discusses climate and atmospheric issues, demonstrates an understanding of the roles of industrialization, population growth and changes in living standards on the depletion of non-renewable energy resources. ENS603: Environmental Law This unit focuses on providing students with a clear ENS604: Environmental Research Project I The course will allow students to carry out an investigation into a scientific or technological problems where they will develops skills in experimental design; literature searching; the collection, treatment, interpretation and reporting of results. Students will present the results of their investigation in the form of a project report, PowerPoint presentation and diary. ENS701: Fiji and South Pacific Biology and Marine Organisms 6 Investigation of life histories and ecological adaptations of plants and animals within the marine environment; systematics, anatomy, physiology, life cycles, reproduction, and general ecology ENS702: Fiji and South Pacific Marine Ecology 7 This unit provides and advanced multi-disciplinary research in the marine environment, including ocean dynamics, biological interactions within animal and plant communities, and their unique adaptations to various physical environments; sampling and experimentation within a variety of marine ecosystems. ENS703: Fiji and South Pacific Freshwater Ecology This units aims to give students a basic understanding of limnology,. It covers the basic principles of the freshwater system and an overview of the discipline of limnology is provided, including the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of freshwater habitats; freshwater ecology; field techniques and the basis for analysis of field data. ENS704: Fiji and South Pacific Marine Terrestrial Ecology 6 An understanding of community concepts especially in relation to the evolutionary and historical context of Fijian terrestrial biota; collection of terrestrial field data, its analysis and presentation; critical assessment of ecological concepts; methods for sampling terrestrial animals. ENS705: Fiji and South Pacific Marine Coastal Management 7 Understanding of the geomorphology, ecosystems and resources associated with coastal environment; critical assessment of the issues associated with resource allocation and use and the range of techniques utilized in coastal zone management. ENS706: Environment Impact Assessment The course will allow students to carry out an investigation into a scientific or technological problem where they will develops skills in experimental COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK CHM708: Medicinal Chemistry Medicinal chemistry course will provide structural and mechanistic concepts central to the study of the drug action in a logical way. Emphasis is given to molecular and biomedical principles encompassing all the major categories of drugs and all main types of human diseases. Topics include properties of drug molecules, characteristics of drug receptors, nature of drugreceptor intentions, drugs designed to target various families of receptors involved in human disease viz endogenous molecules, macromolecules, cellular organelles, messengers and exogenous pathogens; molecular modelling techniques, high throughput screening. grasp of the historical and political setting for the creation of Environmental Law and the role of Government in the formulation of environmental law in Fiji, ability to comprehend the concept of “sustainability” in resource management law, and have a clear understanding of the legal underpinnings for the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) process in Fiji 27 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 28 design; literature searching; the collection, treatment, interpretation and reporting of results. Students will present the results of their investigation in the form of a project report, PowerPoint presentation and diary. any human, animal or environmental health, safety and ethical concerns in relation to the research. Prerequisites: Pass in 10/11 units in Year 1, must be done concurrently with FDT505 ENS708: Geographic Information Systems This unit compares and contrasts different map classifications, map projections, and coordinate systems, performs common GIS operations, applies GIS to various applications, and critically discusses the role of GIS. FDT601: Food Production and Preservation This unit describes the structure and functional properties of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins, Describes the essential chemical and physical properties of food and aseptic techniques in food microbiology Prerequisite: FDT501 ENS709: Field Project The course will allow students to carry out an investigation into a scientific or technological problem where they will develops skills in experimental design; literature searching; the collection, treatment, interpretation and reporting of results. Students will present the results of their investigation in the form of a project report, PowerPoint presentation and diary. Food Science and Technology(s) Major: FDT501: Basic Food Science This unit explains the manufacture of soft drinks, frozen desserts and flour-based products, describes thermal processing techniques and effects on foods, identifies the food-borne pathogens and describe their incubation requirements and explain the aspects of seafood biochemistry and identify the micro flora of seafood. FDT502: Nutrients Studies This unit explains the structural chemistry of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins and describes the physiologic functions of nutrients in the human body FDT503: Food Microbiology This unit describes the characteristics of common pathogens; demonstrates media preparation, inoculation techniques and aseptic methods and the analysis of food samples for microbial contamination FDT504: Food Biotechnology This unit describes the role of biotechnology in food science; explains the production of foods using biotechnological methods and relates enzymatic to its uses in the meat, baking, brewing and dairy industry FDT505: Properties of Food This unit explains water activity, phase transitions and thermal properties of food, demonstrates the measurement of chemical and physical properties of food, demonstrates enzyme action, and describes the properties of leavened foods, sugar confectionery and gels. FDT506: Food Technology Research Project Gathers, summarizes and evaluates scientific literature, preliminary survey data and relevant information to formulate a literature review. Prepares a suitable experimental design with respect to the aim and assesses feasibility of the project and identifies FDT 602 Hazard Analyses Critical Control Point This unit aims to equip students with the knowledge of developing and implementing a workable HACCP Plan. FDT603 Practical Food Microbiology This unit will equip students with the knowledge and skills to effectively and efficiently carry out microbial analysis of various foods through accurate selection of enumeration techniques, proper sampling, precise microbial analysis, result interpretation and presentation in conjunction with the required Food Standards and Legislations. FDT 604 Food Security The course provides a definition of food security and its relationship to the concepts of vulnerability, hunger, malnutrition and poverty. It also provides guidelines on how to interpret and use conceptual frameworks for food security analysis and illustrates how food prices relate to, and affect, food security and vulnerable households. FDT605: Food Processing Technology I This unit introduces students to technological methods used to process food and elucidate the related principles. It is also to elucidate ambient, heat and cold processing methods, equipment’s and effect on foods along with post processing operations. Prerequisite: FDT503 FDT606: Food Processing Technology II This unit aims to further the knowledge of students on the applications of food processing technologies for the processing and preservation of specific categories of foods and beverage. Unit also teaches students the stages and operations for manufacturing different categories of basic food products. FDT607: Food Engineering The purpose of this unit is to provide students with a detailed study of numerous unit operations and a fundamental understanding of momentum, heat and mass transfer relevant to food processing. FDT701: Quality Assurance and Legislation The purpose of this unit is to introduce students to local and international guidelines and legislations relevant to the food industry. FDT 703: Food Packaging This unit aims to bring to light packaging techniques and processes through which foods are contained, distributed and stored safely. Process control will be taught and it will also enable students to understand the properties and appropriate uses of packaging materials. FDT704: Food Product Development To provide students with the opportunity to investigate a relevant food related area of knowledge, to experiment with local products, product improvement, processing, analysis, equipment design, microbiological research or a special topic approved by the coordinator. The unit allows students to learn literature searching, critical reviewing, experimental design and hypothesizing, preparing proposals as well as handling experimental data, interpreting and reporting results. Physics Major: PHY301: Preliminary Physics I To introduce students to the basic concepts and principles involved in physics. This course attempts to motivate the student through practical examples that demonstrate the role of physics in other disciplines. Practical sessions will be used to enhance the theoretical concepts studied in lectures. PHY302: Preliminary Physics II To introduce students to the basic concepts and principles involved in electrical physics. This unit attempts to motivate the student through practical examples that demonstrate the role of physics in other disciplines. Practical sessions will be used to enhance the theoretical concepts studied in lectures. PHY402: Foundation Physics I This course introduces mechanics, the study of motion and its course. This is a natural starting point; everyday experience offers abundant examples of mechanical principles, more than for any other area of physics. In this course we introduce several elements of language of physics, including units, calculation techniques and PHY403: Foundation Physics II The purpose of this unit is to provide basic foundation concepts in physics required by those who intend to continue studying physics or a related area of study at tertiary level. This unit is broadening the knowledge of electrical physics. The topics covered give a very firm foundation to in the area of electrical physics. PHY404: Foundation Applied Mechanics The purpose of this unit is to introduce the fundamental principles of applied engineering mechanics in a clear and unpretentious manner, intelligible to the beginner. PHY405: Foundation Electronics The purpose of this unit is to introduce the fundamentals of electronic engineering principles to the students. PHY501: Applied Physics This unit discusses the basic concepts of physics and develops fundamentals of mechanics, outlines fundamental laws of heat energy and thermodynamics, the fundamental concepts and laws of optics and optical instruments and explains renewable energy concepts including solar power, hydropower, and wind power and energy storage. PHY502: Applied Electronics This unit identifies electrical hazards and causes of electrical accidents and states essential precautions, explains the basic components of electronic and electrical circuits, uses Ohms Law and Kirchhoff’s laws to analyze simple circuits and uses the theory of electromagnetic induction and relates this to the function of electric motors, transformers and generators. PHY503: Electronics and Instrumentation This unit provides students with knowledge about the basic components of electronics and electrical circuits, the essence of electronic principles in laboratory instruments and ways to construct simple electronic devices for use in the laboratory. Unit also provides students with knowledge of the measurement and control of physical systems through the use of relevant laboratory instruments. PHY504: Mechanics and Fluids This is an introductory course to kinematics, dynamics, momentum and energy, rigid body rotation, elasticity and fluids. This is the first semester mainstream physics for students wishing to complete a BSc focussing on Physics of students in the Bed programme who wish to have a thorough grounding in physics. It is followed by PHY505 Electricity and Magnetism in the 3rd semester. PHY505: Electricity and Magnetism He unit provide the students with the fundamental, theoretical and practical knowledge of electricity and Magnetism and prepare them for more advanced study in this area. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK LNG501: English for Academic Purposes This unit offers learners the opportunity to grasp various components of English for research purposes. It begins with visiting core grammatical constituents. Learners will be exposed to the mechanics of the planning and writing processes, honing the skills of data collection, and acknowledging sources of literature and ideas in referencing. Students will learn to plan, prepare and present proposals/seminars. This unit makes students aware that plagiarism is unacceptable. The students should be able to use English for academic and specific purposes accurately and appropriately; read academic articles and discuss, analyse and express academic comments accurately and fluently; use spoken and written English for academic purposes correctly and appropriately, write essays, reports and proposals using every day and field-related topics accurately and suitably. vector algebra. 29 PHY506: Introductory Physics A comprehensive course in general physics, intended for physical science and engineering majors who do not plan to pursue further studies in physics. This course can be started in either year and is offered in trimester. PHY510: Oscillation, Waves and Optics This unit aims to provide students with the basic concepts and principles of oscillatory motion, waves and optics to strengthen the understanding of the concepts and principles of Physics through a broad range of interesting applications to the real world. Practical sessions will be used to enhance the theoretical concepts studied in lectures. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 30 PHY601: Environmental Physics To introduce students to the physical processes on Earth that are closely associated with life systems, especially the transfer of energy and water. This unit aims to provide students with a clear and logical presentation of the basic concepts and principles of Environmental Physics, and to strengthen the understanding of the concepts and principles of Environmental Physics through a broad range of interesting applications to the real world. Practical models will be used to enhance the theoretical concepts studied in lectures. PHY602: Electronic and Electronic Circuits The purpose of this unit is to develop the fundamentals of electric circuit theory from the scientific principles of electrical engineering and provide students with sound knowledge and understanding of the more commonly used analogue and digital devices and circuits. PHY603: Electromagnetism In-depth coverage of topics such as electrostatics, magneto statics and electromagnetic theory will be made to have a firm knowledge of electromagnetism. In the delivery of this unit, emphasis will be placed on the conduct of practical experiment and demonstration of safe and accurate use of apparatus and chemicals, developing skills in using scientific methods of solving problems, understanding of common chemical principles and their application to a range of everyday situation and technology. This unit requires a high level of mathematical ability. This unit is suitable for students who wish to major in disciplines other than physics. PHY607: Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics This module aims to provide students with an understanding on the concepts and principles of thermodynamics and fluid mechanics and its application in resolving real-life problems. PHY609: Modern Physics To introduce students to the concepts of modern Physics which began in 1900 with Max Planck’s discovery of the role of energy quantization in blackbody radiation, a revolutionary idea soon followed by Albert Einstein’s equally revolutionary theory of relativity and quantum theory of light. This unit aims to provide students with a clear and logical presentation of the basic concepts and principles of Modern Physics and to strengthen the understanding through a broad range of interesting applications to the real world. Practical models will be used to enhance the theoretical concepts studied in lectures. PHY701: Control Systems This unit is intended to introduce students to concepts and techniques of classical control and to briefly introduce some concepts of modern control and discrete-time. The main goal is to enable students to analyze, design, and synthesize linear control systems. Students will become familiar with analytical methods and will be exposed extensively to the use of computers for analysis and design of control systems. Prerequisite: PHY602 PHY703: Renewable and Sustainable Energy To introduce students to the alternative energy sources for the generation of electricity. This unit aims to provide students with a clear and logical presentation of the alternate energy sources, how energy can be harnessed from these sources and the advantages of it. This unit intends to strengthen the understanding through a broad range of interesting applications to the real world and practical models will be used to enhance the theoretical concepts studied in lectures. PHY704: Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Physics This module is generally for students who are interested to major in Physics. But If you’re interested in the fundamental laws of modern physics and how mathematics is used to state and apply these laws, this module is for you. In this module, you will learn the fundamental principles of quantum mechanics and the mathematical techniques needed to state and apply them, for instance, to study the structure of atom with a single electron, many electrons. Quantum mechanics will also be used to study the bonding between atoms to form molecules. PHY705: Solid State and Semiconductor Physics To provide students with a strong knowledge to develop insight into the key principles of semiconductor physics, and their relevance to current development in physics. The course introduces the major theory and fundamentals of semiconductor physics. It is a mainstream course for students majored in physics. PHY707: Nuclear and Particle Physics This course is confined to students reading B. Sc. Phys. degree. It is part of a set of courses that explore selected topical areas of pure and applied physics, building on the foundations provided by earlier sets of physics courses. The aim is to provide adequate exposures to advanced topics sufficient to ensure a well-rounded physics education. PHY708: Principles of Energy Conservation and Utilization This course aims to provide students with basic knowledge on basic energy-use devices and patterns in buildings and transport systems; advanced energy-efficient systems and technologies; renewable energy options and practical applications; supply and demand side management; and energy codes and energy efficiency registration schemes. TDR401: Foundation Technical Drawing The purpose of this unit is to introduce the students to the many aspects and application of technical drawing while developing fundamental principles and techniques on which the discipline is based, enabling students to practice logical thought and decision making; become more technically literate; relate to a wide range of studies and vocations; gain skills applicable to a range of domestic and leisure activities; and prepare the student for advanced graphics courses. Home Economics Major: HEC502: Food Nutrients and Health The purpose of this course is to prepare students to understand the relationship between food, nutrients and their functions in the body. This course will enable the students to take a critical look at the food they eat and how it affects their body. This course examines the sources, functions and metabolism of nutrients in detail. The content will extend prior studies leading to deeper understanding of nutrition as well as address contemporary nutrition science topics. This course aims to provide in depth and advanced level understanding and knowledge of nutrition in relation to health. HEC504: Fashion Design and Tailoring The purpose of this unit is to study basic construction and fitting techniques, equipment, concept of quality, sewn apparel production and construction analysis. It presents basic techniques necessary for the construction of simple garments. This is a skills-oriented class designed to develop strong competencies required by the beginning sewer who wishes to become proficient in constructing professional apparel. This course gives the opportunity to develop construction techniques and apply these in constructing apparel using commercial patterns. HEC601: Food Principles The purpose of this course is to prepare students to understand the principles of food preparation, selection and storage, basic food preparation. This course aims to provide students with the ability to understand HEC602: Dimensions of Food and Meals The focus of the course is on nutritional meal planning and food preparation practices. This course examines the psychological, sociological, and historical aspects of food patterns. It looks at the proper approaches to plan and prepare a healthy meal for the family. This course is designed to prepare the teacher trainees with meal management and culinary skills. It involves reacquainting the student with cooking equipment, food handling, safety and exploration meal planning and preparation techniques. The food production lab and lecture will feature complete meal preparation techniques for breakfasts, lunches and dinners. Information related to the planning of nutritionally balanced and aesthetically pleasing meals is the focus of this course. This unit will incorporate choosing healthy foods to plan and prepare breakfast, lunch, dinner, appetizers, snacks and desserts that reflect the individual’s specific dietary needs. Food preparation terms and techniques, safety guidelines, table etiquette, are an integral part of this course. HEC603: Textile Design, Decoration and Enterprising The purpose of this unit is to give students an opportunity to develop skills in using and making fabrics special. The unit provides students with an understanding of production methods for special fabrics, the resulting fabric properties and the implications for use The unit also enables students to explore a range of methods and techniques in fabric decoration. A range of techniques such as batik, tie-dying, screen-printing, appliqué, silk printing and embroidery is covered. The scientific principle of printing and dyeing textiles supports the practical aspects of fabric decoration. In addition the students will learn to recycle, renovate and enterprise their creations. HEC604: Family Financial and Social Issues This course provides an understanding on financial planning for individuals and families, including net worth, budgeting, cash management, use of credit, income taxes, investment basics, insurance, making wise consumer decisions, consumer redress, and ethical behavior in the marketplace. It also enables students to explore the reciprocal relationships between families and their environment and issues of individuals and families as consumers that affect the quality of life. It provides students an understanding of family as an institution and a mode for personal hire: marital adjustment, parent-child relationships, changing family patterns, and disorganization and reorganization. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK HEC501: Food Science Food science is the study of the physical, chemical and biological properties of foods and their constituents and the changes they undergo (including nutritional) when subjected to handling, preservation, processing, storage and. Practical exercises will be conducted to demonstrate the theoretical principles involved and to develop practical skills. Attendance at practical classes is COMPULSORY. Practical sessions commence in Week 3.The practical session in Week 2 will involve introduction to the practical work, laboratory familiarization with lab rules and safety. and integrate scientific principles relevant to food. It introduces students to the Food Safety regulations of the country and the Food Safety programs followed internationally. It also covers topics on food selection, food evaluation, general processing principles, preservation, food analysis techniques and basic product development techniques. Practical exercises will be conducted to demonstrate the theoretical principles involved and to develop practical skills. 31 It allows them to explore the various theoretical and conceptual approaches to understanding the internal dynamics of families, such as family structure, family conflict, multigenerational influences on family relationships and family stress. HEC701: Individual and Family Resource This course involves family resource management and management theory and application, including individual and family decision-making behaviours related to acquisition and allocation of resources in socially responsible ways. It also covers the modern management theory and evaluation to the decision making and problem solving within the family. This unit also highlights the principles of planning, implementing and evaluating needs in household settings. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK HEC702: Apparel Design and Pattern Making The purpose of this unit is to provide an overview of the background, structure, and operation of the everchanging world of the fashion industry. The study enables students to explore the dimensions of current fashion and develop skills in fashion design as well as translate the designs into patterns from a basic block. This unit also equips students with designing and pattern adaptation skills. HEC703: Advanced Apparel and Design The purpose of this unit is to explore creative designing process through integrating the theories and skills of sketching, pattern making, draping, and construction in the production of ready-to-wear clothing. It also provides a chance to practice visual presentation skills. The course will enable students to use the understanding of textile science and apparel and design to develop appropriate solutions for problems related to selection, care and use of textiles for specified end uses. HEC704: Nutrients Requirement and Metabolism The purpose of this course is to prepare students to understand the Nutritional biochemistry and physiology as it relates to establishment of nutrient requirements and Dietary Reference intakes. This involves the Digestion, absorption, metabolism, storage, and excretion of nutrients and other markers of nutritional adequacy or excess with emphasis on micronutrients. It focuses on the Functions of nutrients, in bone, muscle, blood, growth and development. Nutritional requirements of the different human physiological conditions and the basis on which recommended dietary allowances are derived will be examined. The concepts of nutritional status and nutritional assessment will be explored. HEC705: Community Nutrition This course is an introduction to the field of community nutrition and its role in health and health care. The processes and theoretical foundations of nutrition 32 education and the theories, methods and research perspectives applicable to community nutrition will be examined. Special attention will be given to the social determinants of health and the Population Health Promotion. This also focuses on the factors that influence eating behaviour and the processes available for planning, delivering and evaluating community nutrition services. HEC706: Consumer Economics and Housing Concepts This course studies housing as a complex process and product that meets individual, family, and community needs. Housing is demanded by consumers and supplied by the private, non-profit, and government sectors of the economy. Broader issues such as crowding, poverty and mobility of people are considered with reference to how these factors affect family wellbeing. Topics addressed include defining housing, housing constraints, construction, styles, interior decoration, housing tenure, financing home ownership, the housing market, housing for special populations, and social issues related to housing. HEC707: Life Cycle Nutrition These is a study of nutrition related to critical periods throughout the life cycle and presents the role of nutrition during specific phases of the Life Cycle Nutritional needs during pregnancy, infancy, childhood, adolescence, Adulthood and in aging are included. Consideration is given to related physiological, psychological and socioeconomic factors. Biology of the life cycle including development, growth, maturation, and aging and its impact on nutritional requirements of humans from the zygote to the elderly is considered. How to meet these nutritional requirements is discussed relative to the feeding issues and context of each major life stage. Course emphasizes the critical analyses of beneficial and adverse outcomes of various nutrient intakes and dietary patterns on the nutritional status and wellbeing through integration of nutrition and other health sciences in understanding nutritional needs during the life cycle. HEC708: Advanced Tailoring This course enables students to elevate their basic sewing skills learnt in HEC505 and HEC705 to an advanced level. Students learn to construct a jacket utilizing hand- and machine-tailored methods, taking some of the traditional tailoring techniques and interweaving them into the commercial patterns for that clean-cut tailored appearance. Students will cover pattern fit, construction details, which include interfacing, shaping, lining, bound buttonholes & stitching techniques together with pressing, welt pockets and notched collars. For More Information Contact: Professor Anand Tyagi Head of School Phone: 3389286 E-mail: enquiry-engineering@fnu.ac.fj ; adscest@fnu.ac.fj EO - Ms Muni Sangeeta E-mail: EO-Sciences@fnu.ac.fj Ext : 7042 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 33 SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICAL AND COMPUTING SCIENCE Staff Profile HIGHER EDUCATION STAFF HEAD OF SCHOOL Dr. MAHESWARA RAO VALLURI, PhD, M.Phil. M.Sc. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 34 RITESHNI MAHARAJ NAIDU PGdip (Chemstry), BSc (Mathematics & Chemistry) Tutor DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS AND STATSTICS Dr. NIRMAL MITRA Ph.D., MSc Visiting Professor DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & INFORMATION SYSTEMS Mr. BIMAL A KUMAR M.Sc., PGD B.Sc. Head of Department SHELLY CHRISTOPHER Ph.D, MSc, BSc Assistant Professor DR. RAVI BHUSAN MISHRA Ph.D., M. Tech. B. Tech Visiting Professor RAJNESH LAL M.Sc., MBA, B.Ed., B.Sc. Lecturer I DR. AKASH D DUBEY Ph.D., B.Tech Assistant Professor SANDEEP AMEET KUMAR MSC, PGD, BSc.GCE Lecturer I VISHAL SHARMA MCIS; PGDip CS, BSc, CCNA, IDTT1-3 Lecturer I SHAILENDRA NARAYAN MSc; PGDAMA; BSc; STTC Lecturer II VIGNESHWAR KRISHNA BSc, IDTT Lecturer II VIMI KAPADIA M.Sc.; B.Ed. Lecturer II ANISCHAL KAVISH NAICKER BIT, Certified Cisco Lecturer II RAJNESH KRISHNAN MUDALIAR M.Sc.; PGDAMA; BScGCEd (Maths/Physics) Lecturer II PRIYA MOHITE MTech, BTech Lecturer II MAHIMA CHATURVEDI M.Sc.; B.Ed.; B.Sc. Lecturer II ATIN CHAUDHARY M.Sc CSIS, PGDip CSIS, B.Sc CSIS Lecturer II RISHAL AMAR SINGH PGDip, BSc Lecturer II SUKA BUADROMO B.CA Lecturer II PARMESH RAJ NAICKER PGDip, BSCGCED, Certificate Google Webmaster Lecturer II SEMI GAGA B.Sc. (USP), BCMS (Waikato, NZ) Lecturer II DR SURENDRA GUPTA Ph.D, MSc, BSc Professor RAIJIASA SAVU TAOI BSc. CScience and IS Lecturer II ALVEEN ADITYA CHAND MSc, BSc Lecturer II SHALVEEN ASHNEEL KUMAR PGDip CS/IS, BSc CS/IS Assistant Lecturer RONAL CHAND BSc (Mathematics & Physics), GCEd Tutor RANU VINDHYA SEWAK BiT, B. Computer App Assistant Lecturer RONIL RITESH CHAND PGDPIT (In Progress); B.Sc Assistant Lecturer ANAL DIP KUMAR BIT; PGDIT; Pursuing Masters Tutor PRAMITESH YOGESH PRASAD PGDip in IT(IS), B.Com Assistant Lecturer JONASA RINAKAMA B.Com(Information System) Tutorial Assistant SHAMINA HUSSEIN PGD; B.Sc.; DTT Tutor OFFICE ADMINISTRATOR SHIKHA MAHARAJ B.Com HERMANN KEN JAMNADAS B.Com (Accounting and IS) Tutor PAYAL PRASAD BA SHANEEL CHANDRA Bachelor of Information Technology Tutor MUNIL SHIVA GOUNDAR B. Information System Tutor ENTRY QUALIFICATION PROGRAMS DETAILS AND DURATION Certificate IV in Applied Computing Pass in Form 6 with 200 out of 400 marks with 50% minimum marks in English and Mathematics, and any 2 subjects OR Preliminary Science with GPA of 2.00 or more Trade Diploma in Applied Computing Pass in Form 6 with 200 out of 400 marks with 50% minimum marks in English and Mathematics, and any 2 subjects OR Preliminary Science with GPA of 2.00 or more Higher Education Diploma in Information Systems Pass in Form 7 with 200 out of 400 marks with 50% minimum marks in English and Mathematics, and any 2 subjects OR Foundation Science with GPA of 2.00 or more. Bachelor Programme Pass in Form 7 with 200 out of 400 marks with 50% minimum marks in English and Mathematics, and any 2 subjects OR Foundation Science with GPA of 2.00 or more. TVET PROGRAMS: CERTIFICATE IV IN APPLIED COMPUTING Units Core Units CP CIN410 Microcomputer Applications 16 CIN411 Hardware Fundamentals and Practices 16 MTH404 Foundation Maths 1 10 CIN514 System Support 16 CIN535 Multimedia and Communication 16 CIN544 Database Application Development 16 ETH401 Ethics Values and Governances 2 9 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK JAMES RAJESH CHANDRA BCOM (IT) Tutor 35 LNG401 Foundation English 1 13 LNG402 Foundation English 2 13 Internship Directed Industrial Attachment (1 Trimester) Total CP 125 TRADE DIPLOMA IN APPLIED COMPUTING COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 36 CORE UNITS UNIT TITLE CP CIN411 Hardware Fundamentals and Practice 16 CIN410 Microcomputer Application 16 CIN501 Productivity Software 16 CIN507 Operating System 1 16 CIN511 Web Design and Management 16 CIN514 System Support 16 CIN535 Multimedia and Communication 16 CIN544 Database Application Development 16 CIN545 Introduction to Business Networking 16 CIN546 System Administration 16 CIN502 Information Systems in Organization 16 CIN531 Foundation of Programming 16 MTH404 Foundation Mathematics 1 10 Service Units (Compulsory for all majors) ETH501 Introduction to ethics and Governance 11 LNG401 Foundation English 1 13 LNG402 Foundation English 2 13 Directed Industrial Attachment (2 Trimester) Total CP 239 Higher Education Programs Bachelor of Science - Computer Science and Information Systems This section describes the delivery of Computer Science and Information Systems as double major program YEAR 1 Trimester 1 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE CSC511 Foundation of Programming LNG501 English for Academic Purposes CIN502 Information Systems on Organizations Total Credit Points Trimester 2 CP Trimester 3 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE CP 16 CSC512 Object Oriented Programming 16 8 CIN501 Productivity Software 16 16 ETH501 Intermediate Ethics and Governance 40 Total Credit Points UNIT CODE Discrete Mathematics 12 CIN535 Multimedia and Communication 16 11 CIN628 Internet and Programming 16 43 Total Credit Points 44 YEAR 2 Trimester 1 Trimester 2 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE CP CSC622 Artificial Intelligence CIN603 Systems Analysis and Design Trimester 3 UNIT CODE UNIT TITLE CP UNIT CODE 16 CSC625 Software Engineering 16 CSCxxx Elective Unit 16 CIN623 Database Design and Programming 16 Cryptography 16 16 YEAR 3 Trimester 1 TITLE CSC720 Design and Anaysis and Algorithms CIN711 CSC7XX CP Trimester 3 UNIT CODE TITLE CP UNIT CODE 16 CIN707 IT Project 16 Industrial Social Professional Issues in Computing 16 CSC722 Data Communications and Networks 16 16 Elective Unit 16 Elective Unit 16 16 Total Credit Points 48 Total Credit Points 48 TITLE CP 16 Total Credit Points BACHELOR OF SCIENCE - MATHEMATICS AND COMPUTER SCIENCE This section describes the delivery of Mathematics and Computer Science as double major program YEAR 1 Trimester 1 UNIT CODE TITLE CSC511 Foundation of Programming LNG501 English for Academic Purposes MTH515 ETH501 Trimester 2 CP Trimester 3 UNIT CODE TITLE CP UNIT CODE TITLE CP 16 CSC512 Object Oriented Programming 16 MTH516 Solid Geometry & Multivariable Calculus 12 8 MTH514 Probability & Statistics 12 MTH511 Discrete Mathematics 13 Single Variable Calculus 12 CIN501 Productivity Software 16 CIN628 Internet and Programming 16 Ethics and Value an Goverance 11 48 Total Credit Points Total Credit Points 48 Total Credit Points 45 YEAR 2 Trimester 1 UNIT CODE TITLE CSC622 Artificial Intelligence MTH611 Real Analysis Trimester 2 CP Trimester 3 UNIT CODE TITLE CP UNIT CODE TITLE CP 16 CSC625 Software Engineering 16 MTH613 Linear Algebra 15 15 MTH6xx Elective 1(Mathematics) 15 CSC725 Cryptography 16 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK UNIT CODE Trimester 2 37 MTH611 Real Analysis 15 MTH6xx Elective 1(Mathematics) 15 CSC725 Cryptography CSC6xx Elective 1(Computer Science) 16 CSC621 Data Structure and Algorithms 16 MTH6xx Elective 15 2(Mathematics) 47 Total Credit Points 47 Total Credit Points Total Credit Points 16 46 YEAR 3 Trimester 1 UNIT CODE TITLE Trimester 2 CP Trimester 3 UNIT CODE TITLE CP UNIT CODE Industrial Attachment COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK MTH710 Complex Analysis 20 MTH7xx Elective 2 (Mathematics) 20 CSC720 Design and Anaysis and Algorithms 16 CSC7xx Elective 1 (Computer Science) 16 MTH7xx Elective 1 (Mathematics) 20 CSC7xxx Elective 2 (Computer Science) 16 56 Total Credit Points 52 Total Credit Points TITLE Total Credit Points 46 Mathematics units: Preliminary Mathematics Unit Code Unit Name Credit Point Pre-requisite MTH 301 Preliminary Mathematics I 10 Pass in Form 5 Mathematics MTH 302 Preliminary Matrhematics II 10 Pass in Form 5 Mathematics or MTH 301 Foundation Mathematics Unit Code Unit Name Credit Point Pre-requisite MTH 404 Foundation Mathematics I 10 Pass in Form 6 Mathematics or MTH 301 MTH 409 Foundation Mathematics II 10 Pass in Form 6 Mathematics or MTH 302 Bachelor of Science in Mathematics Year 1 Unit Code Unit Name Credit Point MTH 515 Single Variable Calculus 12 MTH 516 Solid Geometry and Multivariable Calculus 12 MTH 514 Probability and Statistics 12 MTH 511 Discrete Mathematics 12 Year 2 Unit Code Unit Name Credit Point MTH 611 Real Analysis 15 MTH 613 Linear Algebra 15 MTH 610 Ordinary & Partial Differential Equations 15 MTH 612 Abstract Algebra 15 MTH 614 Inferential Statistics 15 Elective Year 3 Unit Code MTH710 Unit Name Credit Point Complex Analysis 20 Numerical Analysis 20 Elective 38 CP MTH 711 MTH 712 Linear Programming 20 MTH 713 Stochastic Process 20 MTH 714 Number Theory 20 MTH 715 Integral Transforms 20 MTH 716 Classic Mechanics 20 Computer Science units: Bachelor of Science (Computering Science) Year 1 Unit Code Unit Name Credit Point CSC 511 Foundations of Programming 16 CSC 512 Object Oriented Programming 16 Year 2 Unit Code Unit Name Credit Point Data Structures and Algorithms 16 CSC 622 Artificial Intelligence 16 CSC 625 Software Engineering 16 CSC 633 Operating Systems 16 CSC 635 Mobile Computing 16 CSC 638 Compiler Design 16 Elective Year 3 Unit Code Unit Name Credit Point CSC 725 Cryptography 16 CSC 720 Design and Analysis of Algorithms 16 CSC 722 Data Communication and Networks 16 CSC 711 Automata Theory 16 CSC 715 Computer Organization and Switching Theory 16 CSC 705 Distributed Systems 16 Elective Information Systems: Bachelor of Science in Information Systems Year 1 Unit Code Unit Name Credit Point CIN 502 Foundations of Programming 16 CIN 501 Object Oriented Programming 16 CIN 535 Multimedia and Communication 16 Year 2 Unit Code Unit Name Credit Point CIN 603 Systems Analysis and Design 16 CIN 623 Database Design and Programming 16 CIN 628 Internet and Web Programming 16 CIN 607 Information Technology Project 16 CIN 611 Social Professional Issues in Computing 16 CIN 625 Information systems Management 16 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK CSC 621 Elective 39 Year 3 Unit Code Unit Name Credit Point CIN 707 Information Technology Project 16 CIN 711 Social Professional Issues in Computing 16 CIN 714 Information systems Management 16 Management Support Systems 16 Elective CIN 704 Unit Descriptors MTH301: Preliminary Mathematics I This course introduces students with basic mathematics, algebra, relations and functions, sequences and series and trigonometry. Prerequisite: A pass in Form 5 Mathematics or equivalent. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 40 MTH302: Preliminary Mathematics II Geometry is one of the oldest sciences and elementary geometry is introduced in this course. This course also provides an introduction to probability and statistics with applications. Also, calculus has widespread applications in science and engineering and is used to solve problems for which algebra alone is insufficient. Calculus builds on algebra, trigonometry, and analytic geometry and includes two major branches, differential calculus and integral calculus, which are related by the fundamental theorem of calculus. Prerequisite: A pass in Form 5 Mathematics or equivalent MTH404: Foundation Mathematics I In this unit student will be able to use different differential techniques to solve application problems on differentiation, use integration rules and techniques to integrate functions and be able to solve integrals and apply the knowledge to solve application problems. Prerequisite: Pass in Form 6Math’s or MTH301 & MTH302 or equivalent MTH409: Foundation Mathematics II The purpose of this unit is to introduce the students to limits and continuity, differentiation, integration and probability and statistics. Prerequisite: Pass in Form 6 Math’s or MTH301 & MTH302 or equivalent MTH511: Discrete Mathematics This course will prepare the students with the mathematical background for studying specifically the use of Differential Equations and Integral Calculus. The course demonstrates the use of differential and integration rules and techniques to solve application problems in differentiation and integration of functions. Prerequisite: Pass in FSFE Mathematics or MTH 404& MTH409 or equivalent MTH 514: Probability & Statistics This unit is designed as one of the core unit for students intending to major in statistics. This unit introduces students to basic applied statistics using simple ideas in probability, descriptive and inferential and descriptive statistics. With the introduction of statistical concepts this unit would provide students with a firm basis to develop skill in analyzing statistical data. Topics include: Fundamental concepts and methods of statistics with emphasis on interpretation of statistical arguments. An introduction to data analysis, correlation and regression, concepts of probability theory, sampling distributions and errors, confidence intervals, and hypothesis tests. Prerequisite: Form 7 or Foundation Mathematics MTH515: Single Variable Calculus This unit enables the students to understand the differential and integral calculus and its application in industry. Examples will be related to problems encountered in current industrial practice. The assignments will be used to enable the students to work through complex problems with tutorial guidance. All assignments will be based on standard industrial procedures. Prerequisite: Pass in FSFE Mathematics or MTH 404& MTH409 or equivalent MTH516: Solid Geometry & Multivariable Calculus The expansion from two to three (or more) dimensions requires a corresponding increase of the student’s knowledge of symbolic representation. A new element, the vector, a symbol encompassing numbers, puts in its appearance. Students will learn how to work with vectors in modeling and solving problems in multidimensional space. Following this, the calculus of vectors and their description of curves and surfaces in space is considered. Differentiation of vectors is more fully developed, extending elementary notions of differentiation to those involving multiple variables. Integration is developed to encompass double integrals and triple integrals. Finally, line and surface integrals are considered. Students will learn, with Green’s Theorem, how to transform a surface integral into a line integral and vice versa. Prerequisite: Form 7 or Foundation Mathematics or equivalent or consent from HOD MTH 610: Ordinary and Partial Differential Equations This is an introductory unit on ordinary differential equations and partial differential equations. This unit will cover basic methods for solving first and second order Ordinary Differential Equations, Systems of First Order Equations, and the basics of Partial Differential Equations. Some of the topics covered in this course Some of the topics covered in this course include first order ordinary differential equations, second order ordinary differential equations, stability of equilibrium solutions, partial differential equations which include the heat equation & wave equation. Prerequisite: Pass MTH515 or MTH516 MTH 611: Real Analysis This unit will give the in-depth knowledge of sequence and series, special subsets of real numbers, limits of functions, continuous functions on an interval, derivatives, Riemann Integral and infinite series. Prerequisite: The student must have passed Pass MTH515 or MTH516 MTH 613: Linear Algebra This unit gives an introductory treatment of linear algebra that is suitable for a first under graduate course. In this unit students examine systems of linear equations and matrices; determinants. Euclidean vector spaces; general vector spaces; eigen values and vectors; inner product spaces and linear transformations are also covered. Prerequisite: Pass MTH515 or MTH516 MTH 614: Inferential Statistics Inferential statistics looks at the techniques that may be used to describe valid inferences about population parameters from sample information. Topics includes sampling distribution, criteria of a good estimator, unbiasedness, consistency, efficiency, sufficiency, Rao-Cramer inequality, Rao-Blackwell theorem, Point estimation using maximum likelihood method, method of moments, etc. Point and interval estimators of the parameters of commonly used probability distributions, population mean, variance, proportion. Confidence intervals for the difference between two population means, difference between two population proportions and ratio of two population variances. Estimation of sample size. Basic concepts and properties of tests of hypothesis, different types of hypothesis, type I and type II errors, Critical region, Size and power of a test, Neyman Pearson lemma, Tests of hypothesis concerning a population mean, proportion and variance. Prerequisite: Pass MTH 514 MTH 710: Complex Analysis This course introduces the calculus of complex variable. It turnouts that complex differentiability is a very strong condition and differentiable function behave very well. Integration is along the complex plane. The central result of this spectacularly beautiful part of mathematics is Cauchy’s Theorem guaranteeing that certain integrals along closed paths are zero. This striking result leads to useful techniques for evaluating MTH711: Numerical Analysis This unit will prepare the students with the mathematical background for studying specifically the use of Numerical analysis. The unit demonstrates the use of different techniques to solve application problems in Numerical analysis. The students will also learn to use MATLAB to use various mathematical algorithms to solve numerical analysis problems. Prerequisite: MTH611 or MTH613 MTH 712: Linear Programming This unit focuses on a class of problems that can be modeled as a linear programming model. Formally, a linear programming model is either a minimization or maximization of a linear function of several variables constrained with linear inequalities. Surprisingly, a large number of decision problems fit into this framework. This explains why linear programming is so widely used in a variety of industries, ranging from transportation to health care, from finance to manufacturing. This methodologies development will include the simplex algorithm, theorem of duality, complementary slackness, sensitivity analysis network flows, and network simplex. Prerequisite: Pass in MTH613 MTH713: Stochastic Process This unit will prepare the students with the mathematical background for studying Statistical methods which have practical significance in real life problems. The unit demonstrates the development of stochastic process and regression analysis. Prerequisite: MTH614 MTH714: Number Theory Number theory is a subject that has interested people for thousands of years. This unit covers topics divisibility and factorization, linear Diophantine equations, congruences, applications of congruences, solving linear congruences, primes of special forms, the Chinese Remainder Theorem, multiplicative orders, the Euler function, primitive roots, quadratic congruences, and representation problems. Prerequisite:The student must have passed MTH612 MTH715: Integral Transforms This unit is one of the elective mathematics units. This unit will cover the Laplace transforms and its inverse, the solution of differential equations using Laplace transforms and Inversion formula in Asymptotic is also covered. It includes a comprehensive study of the Fourier transform, Fourier series, z transform and its inverse, which includes system transfer function concepts, system frequency response and its interpretation. Prerequisite: The student must have passed MTH610 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK MTH612: Abstract Algebra This unit will prepare the students with the mathematical background with fundamental concepts of limits, continuity sequences and series. Together with this students will be actively involved in complex analysis techniques. Prerequisite: Pass MTH515 or MTH516 real integrals based on the ‘Calculus of Residues’. Prerequisite: The student must have passed MTH611 41 MTH 716: Classical Mechanics This course of Classical Mechanics concerns the general description and analysis of the motion of systems particles acted on by forces. Assuming a basic familiarity with Newton’s law of motion and their application in simple situations, . We shall also consider the beautiful extensions of Newton’s Law due to Lagrange, EulerLagrange and Hamilton, which allow for simplified treatments of many interesting problems and which provide the foundation for the modern understanding of dynamics.Prerequisite: The student must have passed MTH610 CIN301: Computer Use and Applications This unit offers students an understanding of basic concepts of computers and enables students to apply the knowledge into all aspects of their work. Prerequisite: The student must have passed Entry Requirement of the specific Academic Program COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 42 CIN302: Computer Skills This unit offers students an understanding of the most important topics in information technology, including computer hardware, software, the Internet and e-mail. Prerequisite: The student must have passed FSLC CIN410: Microcomputer Applications This unit offers students an understanding in respect to all computer users that need to know how to use the microcomputer. The major emphasis will be on using microcomputers with the most popular kinds of computer software used in business and education today including power point, word processing, spreadsheets and database management. Prerequisite: The student must have passed Entry Requirement CIN411: Hardware Fundamentals and Practices This unit offers students an understanding of the various hardware components and simultaneously developing a wide range of fundamental skills and knowledge associated with computing and networking devices. Hardware Fundamentals and Practices relate to the tangible components of a computer system. Prerequisite: The student must have passed Entry Requirement CIN501: Productivity Software This unit offers you an understanding of the most important concepts and advanced features of Microcomputer Applications including Word Processing, Spreadsheet, Database and Presentation software. Prior computer experience with basics on these topics is essential. The major emphasis is that the students should be competent and confident in using the Microcomputer Applications to create professional business documents, solve business problems, and understand the concept of data manipulation using databases.Prerequisite:The student must have passed Entry Requirement CIN502: Information Systems in Organizations This unit offers students an understanding of the value and uses of information technology and management information systems. It provides tools needed for mastery of information systems concepts and terms that are important to the modern manager. The information era in which we live in today requires students to be equipped with an understanding of the ways in which they can effectively utilize information technologies as managers. Prerequisite:The student must have passed Entry Requirement CIN507: Operating Systems This unit offers students an understanding of a typical internal structure of a multi-user system and sufficient experience with the use of both single and multi-user operating system to effectively manage their operating environment. Prerequisite:The student must have passed CIN501 CIN514: Systems Support This unit offers students to obtain skills and knowledge to enable them to install, manage and troubleshoot operating systems, resources, devices, drivers, desktop and user environments. Prerequsite:The student must have passed in CIN411 CIN531: Foundations of Programming This unit has been designed for first year students who are interested in understanding programming concepts, constructs, and logins. Major focus of this unit will on problem solving and algorithms, and introduce concepts in programming, such as variables, control structures, functions, parameter passing, recursion, arrays, files and structures. Students will learn how to compile programs, trace errors, and debugging using modern integrated development environments (IDE) and if possible, and if possible, on different operating systems. Programming languages such as C, C++, Java, C#, Python, Smalltalk, or Perl can be used for this unit. Mainly Linux platform will be used. An IDE that works on both the platforms (Windows & Linux) will be used. Prerequisite: The student must have passed Entry Requirement CIN535: Multimedia and Communications This unit offers students an understanding about Multimedia and Communication whereby the current technology and tools such as text, images, sound and video are utilized to deliver messages and content in meaningful ways. It is about designing, organizing and producing multimedia project of all kind and avoiding technical and legal pitfalls along the way. Prerequisite: The student must have passed CIN501 CIN544: Database Application Development This course covers introduction to database, database environment, relational model, relational algebra, Normalization, SQL, entity relationship modeling and data administration. The practical part is facilitated by using MS-Access software which is used as a database tool to create database objects like, table, forms, queries and reports. Prerequisite: The student must have passed CIN410 or CIN501 CIN544: Database Application Development This course covers introduction to database, database environment, relational model, relational algebra, Normalization, SQL, entity relationship modeling and data administration. The practical part is facilitated by using MS-Access software which is used as a database tool to create database objects like, table, forms, queries and reports. Prerequisite: The student must have passed CIN410 or CIN501 CIN546: Systems Administration The unit offers students an understanding of Linux administration, including installation, software, software updates, installation of web server technology, setting up networks and become an expert in shell scripting. System administration is management and configuration of one or more computers with: • Multiple Operating Systems; • Multiple hardware architecture • Multiple software suites Together with the shared resources necessary, such as networks, to make them work together. The aim of this course is to give the students an overview of operating system and how OS works with other hardware in a computer system. The lab will cover the tasks involved in installing, configuring and maintaining different types of operating systems. Prerequisite: The student must have passed CIN506 or CIN411 CIN603: Systems Analysis and Design This unit offers students an understanding of how to analyze and design an information system to solve business problems using appropriate computer application software. Prerequisite: The student must have completed CIN502. CIN607: Human Computer Interaction This unit offers students with the understanding of the factors (psychological, ergonomics, organizational, social etc.) that determines how people operate and make use of computer technology effectively. Students will also learn how to translate this understanding into development of tools and techniques to help designers ensure computer systems are suitable for the activities for which people will use them in order to CIN611: Electronic Commerce Electronic commerce is a term which means the sharing of business information, maintaining business relationships, and conducting business transactions by means of telecommunication networks. The course explains what electronic commerce is, what are associated business strategies and management issues, security issues, technology standards and protocols. Of major importance in the discussion are the global social, political, legal, and cultural implications of electronic commerce. Students will write the necessary documents to build and deploy commercial e-commerce systems in Fiji and the Region. Advanced e-commerce features will be added to their projects and challenges and issues of e-commerce in Fiji will also be identified through surveys and case studies. Prerequisite: The student must have passed CIN502. CIN623: Database Design and Programming This unit offers students an understanding of fundamental concepts of database management system including database design, database languages, and database system implementation. Students will also be able to learn to configure a server, preferably WAMP, XAMPP, or LAMP and use this server for creating database and dynamic website that interacts with a database. MySQL, Oracle or PostgreSQL database will be used for this unit. PHP, ASP, or JSP scripting language will be used for dynamic web application. Prerequisite: The student must have passed CIN501 and CSC511. CIN625: Business Application Development This unit offers students an understanding of software development using a high-level language widely used in business and administrative data processing. It introduces students to the fundamental concepts of programming. Next, the students will learn how to write procedures, entity, collection and adapters. The course is designed to provide students with an opportunity to design and solve interesting real-world problems and will also contain programming quizzes and intensive lab exercises to give students practice designing programs on their own. Prerequisite: The student must have passed CSC511 or CIN501. CIN628: Internet and Web Programming This unit offers students an understanding of developing their analytical, logical, and reasoning capacity while increasing their technical knowledge of web applications, information technology, and programming. The course provides the student with a practical foundation in using high level languages that are common in developing, integrating, and interfacing to business and other organizational information systems.Prerequisite: The student must have passed CSC511 or CIN501. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK CIN545: Introduction to Networking This unit offers students an understanding of the principles and practice of computer networking and how networks impact our lives daily. It also provides students with both the knowledge and hands-on skills necessary to work with network operating systems in a network administration environment. By focusing on troubleshooting and not on an exam, this unit offers a comprehensive introduction to Networking and to advances in software, wireless and network security. Updated content reflects the latest networking technology and operating system including Windows XP and Windows7. Prerequisite: The student must have passed CIN502 achieve efficient, effective and safe Human Computer Interaction (HCI) for individuals and groups. Prerequisite: The student must have passed CIN502. 43 CIN704: Management Support System The unit provides a fundamental understanding of what constitutes a management support system and is particularly biased towards Decision Support Systems. Its main objective continues to be the search for optimal solutions to problems. There is also a section on Logic which culminates in studying fuzzy logic application for providing real world solutions to control and optimization problems. Practical skills will also be developed in solving optimization problems on any of the various applications available including the solver on MS-Excel. Prerequisite: The student must have passed CIN534 & CIN623. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 44 CIN707: Information Technology Project Information Technology Projects (Projects) offers students real-world experience understanding and solving Information Technology software and system problems. The course involves a set of projects from clients such as local corporations and other institutions. In the classroom we study project management software. The project issues include project specification, consulting project management, technology planning and training, and communicating to management. The project management software issues include distributed system design, software standardization, and technology trends. Prerequisite: The student must have passed any CIN6XX level units. CIN711: Social & Professional Issues in Computing This unit aims to introduce students to the basis of the ethical and legal systems that govern the supply and used of computer and communications technology. The sources of law regulating electronic transactions arising related to these technologies will be emphasized. Developing and understanding of the regulatory framework relation to electronic business transactions, staring with the simple formation of a binding electronic contract, and moving to complex issues of data protection, intellectual property rights, electronic liabilities, e-payments and financial transactions, dispute resolution and code of conduct in IT. Prerequisite: The student must have passed any CIN6XX level units. CIN714: Information Systems Management This unit aims to introduce students to the basis of the ethical and legal systems that govern the supply and used of computer and communications technology. The sources of law regulating electronic transactions arising related to these technologies will be emphasized. Developing and understanding of the regulatory framework relation to electronic business transactions, staring with the simple formation of a binding electronic contract, and moving to complex issues of data protection, intellectual property rights, electronic liabilities, e-payments and financial transactions, dispute resolution and code of conduct in IT. Prerequisite: The student must have passed any CIN6XX level units. CSC621: Data Structures & Algorithms This unit adds on to Introduction to Programming. It concentrates on the construction and implementation of various data structures. It certainly raises the level of programming required to a higher one and hopefully this will empower the student to be more efficient and creative when attempting to come up with possible solutions to how a relevant problem may be solved. CSC622: Artificial Intelligence This unit formally introduces some basic concepts that are crucial in the field of Artificial Intelligence. It is aimed at those student who might like to go on and do further studies/researches in the field. The ability to program is critical; as such, it is recommended, as an elective, for students interested in further graduate work that may heavily be dependent on programming and coding. The student is expected to spend a lot of self-directed learning hours planning and writing codes for programs that implement the AI components of the unit. Prerequisite: CS601. CSC625: Software Engineering This unit offers the students a detailed study of the development, implementation and the maintenance of the software. The unit specifies the stages and the phases that must be completed for the development of efficient software and the different models that have been proposed for it till now. This unit provides the detailed study of the requirements for the developments of a software using Software Requirement Specification (SRS). The students will also go through the basic concepts of the software architecture, flow charts, Low Level Design and Modularization of software. The Software Measurement and Metrics such as Halestead’s Software Science, Function Point (FP) Based Measures and Cyclomatic Complexity Measures will help the students to study the quality of the software. Also, the software engineering unit will help the students to know what types of testing are done on software before they are out in the market. This unit offers the students a detailed study of the development, implementation and the maintenance of the software. The unit specifies the stages and the phases that must be completed for the development of efficient software and the different models that have been proposed for it till now. This unit provides the detailed study of the requirements for the developments of a software using Software Requirement Specification (SRS). The students will also go through the basic concepts of the software architecture, flow charts, Low Level Design and Modularization of software. The Software Measurement and Metrics such as Halestead’s. Software Science, Function Point (FP) Based Measures and Cyclomatic Complexity Measures will help the students to study the quality of the software. Also, the software engineering unit will help the students to know what types of testing are done on software before they are out in the market. Prerequisite: Pass in CSC511 and CSC512 CSC635: Mobile Computing This unit introduces the basic concepts and principles in mobile computing. This includes the major techniques involved and networks & systems issues for the design and implementation of mobile computing systems and applications. This course also provides an opportunity for students to understand the key components and technologies involved and to gain hands-on experiences in building mobile applications. Prerequisite: Pass in CSC511 CSC705: Distributed Systems This unit offers students an understanding of building distributed systems. It will also teach both fundamentals as well as systems where these fundamentals on designing in distributed systems are applied in practice. CSC711: Automata Theory This unit offers, the students will be introduced to the theory of automat which is closely related to the working of the software and hardware of recent times. This unit will provide an insight on the grammar to be used in machines. This unit also provides the concept of deterministic finite automata(DFA) and non-deterministic automata (NFA). The unit explains the regular expressions and the context free grammar (CFG), their ambiguity and context free language. The unit introduces the concept of Push Down Automata (PDA), deterministic PDA and their conversions. The unit explains the turing machines used for the machines and the software. students a deep study of the compilers design which are used by the computers to translate high level language to low level language i.e. machine language. This unit will discuss about the role of lexical analyzer in the compilers, its capabilities and the implementation. The unit will also discuss about the parsing techniques of the compilers and the intermediate code generation by compiler. Also, this unit will discuss the run time memory management and the errors which are encountered by the compilers. Prerequisite: Pass in CSC511 and MTH511 CSC722: Data Communication and Networks Data Communications & Networks – a subject that studies the principals and practice of data communication and computer networking. This unit has been designed for final year students who are interested in digital environment of communications and the management necessary to control it. Students will be able to study the structure and components of computer networks using OSI layered architecture of networks as an organization principle. It covers all the concepts necessary for a complete understanding of the design of practical telecommunication networks, whether they are meant to carry voice, data, facsimile, telemetry, video, or any combination of these. Students will also be able to understand CSC725: Cryptography In this unit, the students will be introduced to the concept of cryptography and cyber security related to the computers. The students will learn the types of attacks that a computer encounters from the hackers, the classical and the modern techniques used in the cyber security. The algorithms like Triples DES, Blowfish, International Data Encryption Algorithm, RCS, CAST128, Simplified DES, Block Cipher Principles and DES Standard will be taught to the students. Also, different concepts life hash functions, and authentication applications will be introduced to the students Prerequisite: Pass in CSC511 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK CSC638: Compiler Design This unit offers students a deep study of the compilers design which are used by the computers to translate high level language to low level language i.e. machine language. This unit will discuss about the role of lexical analyzer in the compilers, its capabilities and the implementation. The unit will also discuss about the parsing techniques of the compilers and the intermediate code generation by compiler. Also, this unit will discuss the run time memory management and the errors which are encountered by the compilers. Prerequisite: Pass in CSC511 and MTH511 CSC715: Computer Organization & Switching Theory This unit offers students a detailed view of the switching theory and the computer organization of the computer system. This unit introduces the number system to the students i.e. octal, decimal and hexadecimal and their conversion from one format to another. The unit also focuses on the Boolean algebra and the combinational logic circuits. The different types of flip flops will also be introduced to the students along with shift registers, faults and hazards. This unit also gives a detailed view of the computer organization including bus, register, memory and input/output devices. Prerequisite: Pass in CSC511 and MTH511 For More Information Contact: Dr Maheshwara Valluri Head of School Phone : 3381044 E-mail : HOS_SMCS@fnu.ac.fj OA - Ms Shikha Maharaj Ext: 1561 Email:oa.smcs@fnu.ac.fj 45 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCHOOL OF BUILDING AND CIVIL ENGINEERING STAFF PROFILE HIGHER EDUCATION STAFF HEAD OF SCHOOL MR SATEESH PISINI M.Tech (Civil) PROFESSOR DR PALLAV KUMAR COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK DR DARGA NANDYALA PhD (Geotechnical Engineering), Master in Geotechnical Engineering, Bachelors in Civil Engineering PRINCIPAL LECTURER VIJAYA K .GUDE M.Tech. (Irrigation Water Management), B.E. (Civil Engineering), Dip (Civil Engineering) DULCE DE ASA BSc (Civil Eng.) [Philippines]; Master’s in Public Administration [Philippines] LECTURER P.M.B RAJ KIRAN NANDURI ADMINISTRATION OFFICER MOHAMMED FAZIL FARUK B.COM OFFICE AMINISTRATOR ASHMEETA ASHWINI LATA DIPLOMA TVET STAFF HEAD OF SCHOOL JOTAME DIANIMOTO VAKACEGUVINAKA B.Const. (Quant. Surveying), Dip. (Civil Eng.), Adv. Cert. (Building), Cert. (Carpentry & Joinery) SENIOR LECTURER NIMILOTE RATUDINA B. Architecture, B. Applied Sc. (Architectural Studies), Dip. (Architectural Technology), Cert. (Foremanship Studies), (City & Guilds); Cert. (Carpentry & Joinery), Teacher Training Cert SUPRATIK BHATTACHARYA 46 CYRIL BERNARD RACHMAN M.E. (Civil and Environmental Engineering), B.E. (Civil Engineering) WILI OLO TAGICA BSc (Hons) Construction Management; HND-Building; IDTT, OTD Building and Civil Eng; (DTI) Cert. (Carpentry & Joinery), LECTURER I FAIJAL ALI Adv. Dip (Civil Eng.) ; Dip. (Civil Eng.);Adv. Dip (CADD Eng. India].CL III Plumber Cert. [FNTC] YUYUN QOMARIYAH B.E (Urban and Regional Planning) M. Eng (Urban and Regional Planning) ROHITESH PRASAD BA, Dip. (Geometics), Dip. (GIS) LECTURER II VILIAME SAKITI RAVIKANT RITESH SINGH Adv. Dip. (Civil Eng., Dip. (Civil Eng.) MAUSIO RUPENI ANISE B.Tech. (Surveying) (UNITECH - PNG), Dip. (Surveying) (PNG); Cert. GPS [AUS); Forest Rangers Cert. [India] VAKAREWA K. TUIWAI Dip.; IDTT; Cert. ILIESA JALE QISAVOLA Dip. (Building);Adv. Cert. (Building); Craft Cert. (Building), (C&G of London) APAKUKI K. TUKANA Dip. Bldg, Dip. Quant. Survey,DTT, Cert.First Line Supervision, Cert. (Plumbing and Sheetmetal), Craft Apprenticeship in Plumbing & Sheet metal. LUKE RAVULA DILOI BTech National and HNC (Building Engineering Services), Vocational Teachers Certificate FTC Building Craft (City & Guilds),Craft and Advanced Craft Plumbing (City & Guilds), Trade Certificate in Plumbing and Sheet Metal (NSW); Craft Apprenticeship,Class One Trade Test Plumber General SUNDAR SINGH Adv. Plumbing Cert., Full Cert. (Plumbing and Sheetmetal) RUPENI WAQABACA Adv. Craft Cert. (City and Guild) [DTI]; Full Cert. (Car pentry and Joinery), (DTI) JONE SEKINABOU Ordinary Dip. (Construction Studies), Adv. Craft and Ordinary Craft Certificates, (City & Guild – London,) Cert. (Teaching and Adult Education). MANIKAM GOUNDAR Cert. (Carpentry & Joinery),Cert. (OHS) ABDUL AZIZ Cert. First Line Supervision, Cert (Plumbing & Sheetmetal), Craft Apprenticeship in Plumbing & Sheet metal AMEET KUMAR PILLAY Trade Cert. (Plumbing and Sheetmetal) ANIL KUMAR Dip. (Building), DTT, Pipe Fitter Cert. MAIKALI LEVUKAICIWA Dip. (Building), Dip. (Quantity Surveying), Dip. (Education), Trade Cert. (Carpentry & Joinery) NILESH KUMAR Trade Cert. (Plumbing and Sheetmetal), Cert. (First Line Supervision) NIRAJ DHARMENDRA PRASAD Dip. Education Dip. Arch. SETAREKI TUKANIA Trade Cert. (Plumbing and Sheetmetal) RAVIKANT SINGH Adv. Dip. (Civil Eng.),Dip. (Civil Eng.) VAKAREWA TUIWAI Dip.; IDTT; Cert. PHILIP LATCHMAN SIDAL TECHNICIANS BALEYAGA VOKITILAKEBA LOGAVATU Cert. (First Line Supervision),Trade Cert. (Plumbing and Sheetmetal) NAVIN KISHOR Cert IV AKSY KARTIK KUMAR Adv. Dip SIAI SELANISA TITANGA Adv. Dip VEENIL VIKASH RATTAN Cert IV SAKIUSA QIO ASISH AMIT KUMAR OFFICE AMINISTRATOR OLIVIA PAKA VAKAMOCEA BA (Land Management & Geography), Cert in Auto COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK ASSISTANT LECTURER SAIMONI LEDUA SOVALAWA Diploma, Cert IV Cert IV DUANE LOKINGTON Trade Cert. (Carpentry and Joinery) HARJIT SINGH DTT Adv Trade Cert. (Plumbing); Trade Cert. (Plumbing and Sheetmetal); Cert. IV (Assessment in Workplace), (University of Newcastle, Aust.) JOSUA TUI MATAI 47 Programme Details and Duration CERTIFICATE IV ADVANCED DIPLOMA DEGREE 35 - 40 8 32 4 5 2 sem 8 sem 6-7 6 7-9 4 4 8 weeks 15 weeks 18 weeks 15 weeks 18 weeks 18 weeks 12 months 12 months 6 months 6 months - 6 months 2 years 2 years 2 ½ years 2 years 1 year 4 years PENSTER TRIMESTER (2014) SEMESTER TRIMESTER (2014) Total number of units to complete the programme 27 19 - 20 24 Number of pensters/trimesters/ semesters to complete all units 5 3 Number of units to complete each penster/trimester/semester 5 Number of weeks per penster/ trimester/semester Minimum Period required for industrial attachment Minimum period to complete the whole programme COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 48 TRADE DIPLOMA Trimester Mode Programmes for 2014 The college is offering Certificate IV and Trade diploma in Trimester Mode from 2014 onwards. For any enquiry on the trimester mode programmes for 2014 please contact the Head of School. Entry Qualifications Certificate IV Programmes 200 out of 400 marks in Form 6 with minimum of 50% in any 4 subjects Trade Diploma Programmes Pass in Form 6 with 200 out of 400 marks with 50% minimum marks in English, Mathematics, Physics, and any other 1 relevant subject. Advanced Diploma Trade Diploma Bachelor in Engineering [Civil Engineering] Pass in Form 7 with 280 out of 400 marks with pass (50% or more) in English, Mathematics, Physics and any other 1 Science or Technology subject OR Foundation Science with GPA of 3.00 or more. Programmes, Stages and Units CERTIFICATE IV IN PLUMBING AND SHEETMETAL (PENSTER MODE) STAGE 1 Unit code STAGE 2 Unit Name CP Unit code Unit Name CP BCE302 Trade Calculations 1 4 BCE304 Craft Science 1 4 COM201 Technical Communication 1 4 PSM305 Applied Materials 4 PSM301 P&S Drawing 1 4 PSM306 Sheetmetal Practice A 4 PSM302 Cold Water Theory A 4 BCE303 Trade Calculations 2 4 PSM303 Cold Water Practice 4 PSM307 Sheet Metal Theory A 4 OHS403 Occupational, Health and Safety 3 10 Total CP 30 Total CP STAGE 3 20 STAGE 4 Sanitation and Drainage Theory A 4 PSM413 Sheetmetal Practice B 6 BCE309 Craft Science 2 4 PSM414 Cold Water Theory B 4 PSM310 Hot Water Practice A 4 PSM415 Hot Water Theory B 4 PSM311 Hot Water Theory A 4 PSM416 Sheetmetal Construction 6 PSM412 Welding and Fabrication 4 PSM417 Sheetmetal Theory B 4 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethics 5 Total CP 25 Total CP 24 STAGE 5 PSM418 Project-Building Services 6 PSM 421 Design and Calculations 4 PSM419 Sanitation and Drainage Theory B 4 BCE422 Elementary Surveying 6 PSM420 Sanitation and Drainage Practice B 6 Total CP 26 CERTIFICATE IV IN PLUMBING AND SHEETMETAL (PENSTER MODE) Trimester 1 Unit code Unit Name CP ETH301 Fundamental of Ethical Practice 5 MTH301 Mathematics for Trade 10 OHS403 Occupational Health and Safety 6 CTP404 Building Science 9 PSM401 Plumbing & Sheetmetal Drawing 8 PSM402 Water Supply Theory 6 PSM403 Water Supply Practice 7 Total CP 51 Trimester 2 COM301 Technical Communication 5 PSM405 Water Heating Theory 8 PSM406 Water Heating Practice 8 PSM407 Sheetmetal Fabrication Practice 8 PSM408 Sheetmetal Fabrication Theory 7 PSM409 Metal Fabrication 8 CIN 302 Computer Skills 6 Total CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK PSM308 50 Trimester 3 Unit code Unit Name CP CTP414 Computer Aided Drafting 9 CTP422 Introduction to Surveying 8 49 PSM410 Sewer and Drainage Theory 7 PSM411 Sewer and Drainage Practice 9 PSM422 Building Services Project 9 PSM423 Plumbing Calculation & Design 8 Total CP 50 CERTIFICATE IV IN CARPENTRY AND JOINERY (PENSTER) STAGE 1 Unit code STAGE 2 Unit Name CP Unit code Unit Name CP BCE302 Trade Calculations 1 4 BCE304 Craft Science 1 4 COM201 Technical Communication 1 4 CJY305 Trade Practice B 4 CJY301 Applied Materials 1 4 CJY306 C&J Drawing 1 4 CJY302 Trade Practice A 4 CJY307 Trade Theory B 4 CJY303 Trade Theory A 4 CJY308 Trade Theory C 4 OHS403 Occupational, Health and Safety 3 10 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Total CP 30 Total CP STAGE 3 20 STAGE 4 BCE303 Trade Calculations 2 4 CJY413 Wet Trade Theory A 4 CJY409 Const. Materials 2 4 CJY414 Trade Practice E 6 BCE309 Craft Science 2 4 CJY417 C&J Drawing 2 4 CJY411 Trade Practice C 4 CJY415 Trade Practice F 6 CJY412 Trade Practice D 4 CJY416 Trade Theory D 4 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethics 5 Total CP 25 Total CP 24 STAGE 5 CJY418 Wet Trade Practice A 6 CJY421 Workshop Project A CJY419 Wet Trade Theory B 4 BCE422 Elementary Surveying CJY420 Wood Machining Theory A 4 Total CP 26 CERTIFICATE IV IN CARPENTRY & JOINERY (TRIMESTER MODE) Trimester 1 Unit code Unit Name CP ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethical Practice 6 OHS 403 Occupational Health and Safety 6 MTH 301 Mathematics for Trade 8 CJY 400 Construction Materials 1 8 CJY 401 Trade Theory A 8 CJY 402 Trade Practice A 8 CJY 403 Construction Drawing 1 6 Total CP 50 Trimester 2 CJY 404 Craft Science for Construction 8 CJY 405 Trade Theory B 8 CJY 406 Trade Practice B 9 CJY 407 Construction Material 8 CTP414 Computer Aided Drafting 9 CIN 302 Computer Skills 6 Total CP 48 Trimester 3 50 CJY 426 Wet Trade Theory 8 CJY 425 Wet Trade Practice 8 CJY 427 Wood Machining Theory 8 CJY 423 Construction Equipment 8 CJY 424 Construction Project 7 CTP422 Introduction to Surveying 8 COM 301 Technical Communication 6 Total CP 53 SHORT PROGRAMME IN FIRST LINE SUPERVISION STAGE 3 STAGE 4 COM401 Technical Communication II 10 BCE406 Construction Drawing 1 10 CIN302 Computing 10 BCE509 Site Production and Supervision 10 FLS500 Built Environment 10 BCE513 Surveying Procedures 10 Total CP 60 TRADE DIPLOMA IN ARCHITECTURAL TECHNOLOGY (TRIMESTER MODE) Unit code Unit Name CP COM401 Technical Communication II 10 MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 MEC450 Engineering Graphics 4 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/ EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/ Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 MEC470 Engineering Graphics Laboratory 6 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory/ Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP 55 Trimester 2 MEC451 Engineering Mechanics 8 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics II 10 MEC452 Workshop Practice 5 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/ EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/ Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 MEC472 Engineering Mechanic Laboratory 2 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory/ Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Trimester 1 50 Trimester 3 DEN400 Civil Engineering Technology 10 DEN401 Computer Aided Design 1 10 DEN402 Materials for Construction 7 51 DEN404 Construction Technology Theory 1 7 DEN405 Construction Technology Practice 1 6 DEN406 Land Surveying Theory 7 DEN407 DEN403 Land Surveying Practice 3 Materials for Construction Laboratory 3 Total CP 50 Trimester 4 DEN 500 Building Services 7 DEN 501 Computer Aided Design 2 8 DEN 502 Construction Technology II 10 DAT 408 Design Appreciation Practice 7 DAT 510 Architectural Design Theory 9 DAT 511 Environmental Design Science 9 TOTAL CP 50 Trimester 5 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK DAT 512 Architectural Design Project 9 DAT 513 Professional Practice 8 DAT 514 Architectural 3D Design DEN 503 Construction Technology III 9 DEN 504 Contract Management 8 DEN 515 Specifications Writing Practice 7 9 Total CP 48 TRADE DIPLOMA IN ARCHITECTURAL TECHNOLOGY (SEMESTER MODE) STAGE 1 STAGE 2 MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 BCE507 Construction Materials 10 COM401 Technical Communication 2 10 ARC512 Design Appreciation 10 CIN302 Computing 10 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics 2 10 BCE404 Construction Science 10 BCE506 Construction Drawing 2 [CAD 1] 10 BCE405 Construction Technology I 10 BCE500 Construction Technology 2 10 ETH401 Introduction to Ethics and Governance 9 BCE406 Construction Drawing I 10 OHS403 Occupational, Health and Safety 3 10 Total CP 70 Total CP STAGE 3 59 STAGE 4 BCE413 Surveying Procedures 10 ARC519 Computer Aided Design 2 [3D] 10 BCE414 Building Services I 10 BCE520 Contract Management 10 ARC516 Environmental Science 10 BCE515 Building Services 2 10 BCE416 Theory of Structures 1 10 ARC521 Architectural Practice 10 ARC517 Design Theory 10 BCE523 Construction Technology 3 10 BCE418 Construction Drawing 3 [CAD 2] 10 ARC524 Architectural Design Project 10 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 TRADE DIPLOMA IN BUILDING (TRIMESTER MODE) Trimester 1 52 COM401 Technical Communication II 10 MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 MEC450 Engineering Graphics 4 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/ EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/ Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 MEC470 Engineering Graphics Laboratory 6 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory/ Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP 55 Trimester 2 Engineering Mechanics 8 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics II 10 MEC452 Workshop Practice 5 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/ EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/ Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 MEC472 Engineering Mechanic Laboratory 2 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory/ Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP 50/55 Trimester 3 DEN400 Civil Engineering Technology 10 DEN401 Computer Aided Design 1 10 DEN402 Materials for Construction 7 DEN404 Construction Technology Theory 1 7 DEN405 Construction Technology Practice 1 3 DEN406 Land Surveying Theory 7 DEN407 Land Surveying Practice 3 DEN403 Materials for Construction Laboratory 3 Total CP 50 Trimester 4 DEN 500 Building Services 10 DEN501 Computer Aided Design II 8 DEN502 Construction Technology II 8 DEN510 Measurement 1 7 DBG502 Site & Project Supervision 6 DEN513 Tendering & Estimating 6 Total CP 45 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK MEC451 Trimester 5 DBG 503 Building Project 1 9 DBG 504 Building Project 2 9 DEN 506 Project Organization 8 DEN 503 Construction Technology III 9 DEN 504 Contract Management 8 DBG 505 Maintenance Management 7 Total CP 50 53 TRADE DIPLOMA IN BUILDING (SEMESTER MODE) STAGE 1 STAGE 2 MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 BCE507 Construction Materials 10 COM401 Technical Communication 2 10 ARC512 Design Appreciation 10 CIN302 Computing 10 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics 2 10 BCE404 Construction Science 10 BCE506 Construction Drawing 2 [CAD 1] 10 BCE405 Construction Technology I 10 BCE500 Construction Technology 2 10 BCE406 Construction Drawing I 10 ETH401 Introduction to Ethics and Governance 9 OHS403 Occupational, Health and Safety 3 10 Total CP 70 Total CP STAGE 3 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 54 59 STAGE 4 BCE418 Construction Drawing 3 (CAD 2) 10 BCE520 Contract Management 10 BCE414 Building Services I 10 BLG520 Building Project 4 10 BCE411 Building Law 10 BLG521 Quality Assurance 10 BCE409 Site Production and Supervision 10 BCE515 Building Services 2 10 BCE417 Tendering and Estimating 10 BCE523 Construction Technology 3 10 BCE416 Theory of Structure 1 10 BCE522 Project Organization 10 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 TRADE DIPLOMA IN CIVIL ENGINEERING (TRIMESTER MODE) Trimester 1 COM401 Technical Communication II 10 MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 Engineering Graphics 4 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/ EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/ Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 Engineering Graphics Laboratory 6 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory/ Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 MEC450 MEC470 Total CP 55 Trimester 2 MEC451 Engineering Mechanics 8 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics II 10 MEC452 Workshop Practice 5 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/ EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/ Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 MEC472 Engineering Mechanic Laboratory 2 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory/ Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP 50/55 Trimester 3 DEN400 Civil Engineering Technology 10 DEN401 Computer Aided Design 1 10 DEN402 Materials for Construction 7 DEN404 Construction Technology Theory 1 7 DEN405 Construction Technology Practice 1 3 DEN406 Land Surveying Theory 7 DEN407 Land Surveying Practice 3 DEN403 Materials for Construction Laboratory 3 Total CP 50 Trimester 4 DEN 500 Building Services 10 DCE501 Hydraulics & Fluid Mechanics 1 7 DCE503 Soil Mechanics 7 DCE505 Theory of Structures DCE507 Design of Timber Structures DCE502 Hydraulics & Fluid Mechanics 1 Laboratory 3 DCE504 Soil Mechanics Laboratory 3 DCE506 Theory of Structures Laboratory 7 10 Total CP 50 Trimester 5 DCE508 Civil Engineering Contract Management 8 DCE509 Civil Engineering Design Project 8 DCE510 Design of Concrete Structures 8 DCE511 Town and Country Planning 10 DCE513 Measurement of Civil Works 8 DCE514 Design of Steel Structures 8 Total CP 50 TRADE DIPLOMA IN CIVIL ENGINEERING (SEMESTER MODE) STAGE 1 Unit code Unit Name STAGE 2 CP Unit code Unit Name CP COM401 Technical Communication 2 10 CIV500 Computer Aided Design I 10 BCE405 Construction Technology 1 10 BCE407 Construction Materials 10 CIN302 Computing 10 BCE416 Theory of Structures 1 10 MTH405 Engineering Mathematics 1 10 BCE413 Surveying Procedures 10 10 BCE404 Construction Science 10 CIV510 Civil Engineering Technology 1 BCE403 Construction Drawing 1 10 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics 2 10 ETH401 Introduction to Ethics and Governance 9 OHS403 Occupational Health and Safety 3 Total CP 10 70 Total CP STAGE 3 69 STAGE 4 CIV512 Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics 1 10 BCE520 Contract Management 10 CIV514 Theory of Structures 2 10 CIV521 Civil Engineering Design Project 10 CIV513 Engineering Surveying 10 CIV522 Structural Design 2 10 BCE515 Building Services 2 10 CIV518 Measurement of Civil Engineering Works 10 CIV516 Structural Design 1 10 CIV519 Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics 2 10 CIV515 Soil Mechanics 10 CIV520 Highway Engineering 10 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 3 55 TRADE DIPLOMA IN QUANTITY SURVEYING (TRIMESTER MODE) Trimester 1 Unit code Unit Name COM401 Technical Communication II 10 MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 MEC450 Engineering Graphics 4 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/ EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/ Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 MEC470 Engineering Graphics Laboratory 6 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory/ Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Total CP 55 Trimester 2 MEC451 Engineering Mechanics 8 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics II 10 EWP452 Workshop Practice 5 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/ EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/ Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 MEC472 Engineering Mechanic Laboratory 2 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory/ Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP 50 Trimester 3 DCE400 Civil Engineering Technology 10 DEN401 Computer Aided Design 1 10 DEN402 Materials for Construction 7 DEN404 Construction Technology Theory 1 7 DEN405 Construction Technology Practice 1 3 DEN406 Land Surveying Theory 7 DEN407 Land Surveying Practice 3 DEN403 Materials for Construction Laboratory Total CP 3 50 Trimester 4 DEN 500 Building Services 8 DEN 504 Building Regulation 8 DEN 501 Computer Aided Design 2 8 DEN 502 Construction Technology II 8 DEN 510 Measurement 1 7 DQS 502 Quantity Surveying Practice 6 DEN 513 Tendering and Estimating 6 Total CP 56 CP 51 Trimester 5 DBG 503 Quantity Surveying Project 1 9 DBG 504 Quantity Surveying Project 2 9 DEN 506 Project Organization 8 DEN 503 Construction Technology III 9 DQS 504 Measurement 2 8 DEN 505 Specification Writing Practice 7 Total CP 50 TRADE DIPLOMA IN QUANTITY SURVEYING (SEMESTER MODE) STAGE 1 Unit code Unit Name STAGE 2 CP Unit code Unit Name CP Engineering Mathematics I 10 BCE407 Construction Materials 10 COM401 Technical Communication 2 10 QSY501 Measurement 1 10 CIN302 Computing 10 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics 2 10 BCE404 Construction Science 10 BCE410 Construction Technology 2 10 BCE405 Construction Technology I 10 BCE406 Construction Drawing 2 [CAD 1] 10 BCE403 Construction Drawing I 10 ETH401 Introduction to Ethics and Governance 9 OHS403 Occupational Health and Safety 3 10 Total CP 70 Total CP STAGE 3 59 STAGE 4 BCE414 Building Services I 10 QSY501 Quantity Surveying Project 4 10 BCE520 Contract Management 10 BCE515 Building Services 2 10 BCE411 Building Law 10 BCE523 Construction Technology 3 10 QSY517 Measurement 2 10 QSY524 Measurement 3 10 BCE417 Tendering and Estimating 10 BCE522 Project Organization 10 BCE418 Construction Drawing 3 (CAD 2) 10 QSY523 Quantity Surveying Practice 10 Total CP 64 Total CP 60 TRADE DIPLOMA IN LAND SURVEYING (TRIMESTER MODE) Trimester 1 Unit code Unit Name CP COM401 Technical Communication II 10 MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 MEC450 Engineering Graphics 4 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/ EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/ Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 MEC470 Engineering Graphics Laboratory 6 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory/ Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK MTH405 55 Trimester 2 MEC451 Engineering Mechanics 8 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics II 10 EWP452 Workshop Practice 5 57 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/ EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/ Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 MEC472 Engineering Mechanic Laboratory 2 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory/ Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP 50 Trimester 3 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK DCE501 Hydraulics & Fluid Mechanics 1 (Lecture) 8 DLS408 Surveying Law and Regulations 6 DCE502 Hydraulics & Fluid Mechanics 1 (Laboratory) 6 DLS405 Surveying 1 10 DLS406 Surveying Drafting 9 DLS403 Surveying Practice 10 Total CP 49 Trimester 4 DLS409 CAD for Surveyors 10 DLS407 Town and Country Planning 6 DLS509 Surveying 2 10 DLS513 Introduction to Geodetic & GPS Surveying 10 DLS519 Topographical Surveying 6 DLS511 Engineering Survey Theory 10 Total CP 52 Trimester 5 DLS514 Cadastral Survey and Survey Practice 10 DLS605 Cadastral Survey Project 9 DLS606 Engineering Survey Practice 10 DCE603 Hydraulics & Fluid Mechanics 2 (Lecture) 7 DCE604 Hydraulics & Fluid Mechanics 2 (Laboratory) 5 DLS516 Introduction to Photogrammetry and GIS 10 Total CP 51 TRADE DIPLOMA IN LAND SURVEYING (SEMESTER MODE) STAGE 1 Unit code Unit Name STAGE 2 CP Unit code CP MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics 2 10 LSY405 Surveying 1 10 OHS403 Occupational Health & Safety 3 10 CIN302 Use of Computers 10 LSY509 Surveying 2 10 LSY403 Surveying 1 Practice 12 LSY408 Survey Law and Implementation [Related Regulations] 10 LSY406 Surveying Drafting 10 LSY409 CAD for Surveyors 10 COM401 Technical Communication 2 10 CIV 412 Hydraulics & Fluid Mechanics 10 Total CP 62 Total CP STAGE 3 58 Unit Name Unit code CIV 400 Unit Name Computer Aid Drafting 60 STAGE 4 CP Unit code 10 LSY415 Unit Name GPS Survey CP 12 CIV 519 Hydraulics 10 LSY417 Valuation for Surveyors 10 LSY 407 Town and Country Planning 10 LSY511 Engineering Surveying 10 LSY 513 Geodetic Computation 10 LSY516 Introduction to Photogrammetry 12 LSY 514 Cadastral Survey and Survey Practice 12 LSY518 Cadestrial Survey Project 10 LSY519 Topographical Survey 12 ETH401 Introduction to Ethics and Governance 9 Total CP 64 Total CP 63 BACHELOR OF CIVIL ENGINEERING Year 1 SEMESTER 1 Unit code Unit Name SEMESTER 2 CP Unit code Unit Name CP LNG501 English for Academic Studies 12 BEN506 Introduction to Electrical and Electronics 12 BEN502 Engineering Computation 1 12 BEN601 Engineering Computation 2 12 BEN503 Engineering Physics 12 BEN507 Introduction to Computer Programming 12 BEN504 Engineering Graphics 12 BEN508 Engineering Mechanics 12 BEN505 Material Science 12 BEN509 Workshop Practice 12 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 Year 2 SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2 BEC602 Surveying for Engineers 12 BEC607 Engineering Analysis and Problem Solving 14 BEC603 Geomechanics 12 BEC608 Earthworks, Curves and Hydrographic Survey 16 BEC604 Hydraulics 1 12 BEC609 Hydraulics 2 16 BEC605 Structural Mechanics for Engineers 12 BEC610 Ordinary Differential Equations and Numerical Analysis 14 BEC606 Engineering Geology 12 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 Year 3 SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2 BEC701 Design and Analysis of Timber Structures 14 BEC705 Reinforced Concrete Structures 16 BEC702 Design and Analysis of Steel Structures 14 BEC706 Foundation Engineering 14 BEC703 Geotechnical Engineering 16 BEC707 Civil Measurement and Tendering 16 BEC704 Engineering Hydrology 16 BEC708 Design of Masonry Structures (Project) 14 BEC709 Airport Engineering(Elective) 14 Total CP 60 Total CP 74 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK FNU has a responsibility to the Nation, the student and to industry. The student and industry in their turn have a responsibility to their chosen profession. In these days of ever widening access to tertiary education a bachelor’s degree is rapidly becoming the minimum qualification for gaining entry to para-professional as well as to professional employment. It is therefore seen as being of vital importance to all parties to enable each student to reach the highest level of education of which he or she is capable. In practice this means that the best students should aspire to degree. This is the reason FNU offers a Bachelor of Engineering (Civil) programme, to cater the needs of the industry and to help aspiring and deserving students to fulfill their dreams. 59 Year 4 SEMESTER 1 BEC710 Water Resource Engineering SEMESTER 2 16 BEC714 Project Management 14 14 BEC711 Civil Engineering Technology 14 BEC715 Irrigation Engineering (Elective) BEC712 Highway Engineering and Design Application 16 BEC716 Structural Analysis 16 BEC713 Ports, Harbour and Basic Coastal Engineering 14 BEC717 Earthquake Engineering (Elective) 16 BEC718 Advanced Water Engineering Project 16 Total CP 60 Total CP 76 Attachment of 6 months (Students can take attachment with in four years of the degree program also) Total CP 240 270 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Job Opportunities Job opportunities are available in the construction Industry for tradesmen, technicians, technologists and professionals. Various government ministries and departments, statutory organizations, contracting companies, consultant firms, local governments, disciplined forces and teaching fraternity employ graduates from the School. Graduates may be self-employed as entrepreneurs or form a small company to get started in business. Opportunities are also available for off-shore employment in the region.There is a clear stair casing arrangement at all levels of study in the school. Students may enrol in the Certificate IV programmes and follow the path to aspire for the professional qualification. Multi-entry and exit points offer opportunities to the students with different backgrounds and abilities to pursue studies and aspire to the same goals but achieve them at different times. Unit Descriptors LNG501 English for Academic Studies The unit is designed as an integrated, activity based unit, this course aims to equip the student with the skills required to communicate ideas of a technical nature clearly and succinctly. Modes of communication addressed in this course include written, oral, graphical and symbolic forms. This unit also aims to improve the student’s study skills and to encourage independent learning. The syllabus includes communication theory, intrapersonal communication, non-verbal communication, influence of culture on communication, group processes, and strategies to manage conflict, structure and delivery of oral presentation, research and writing analytical reports. BEN502 Engineering Computation 1 The unit aims to provide the students with the mathematical knowledge and expertise required for their engineering studies. The syllabus of the unit includes review of basic principles of linear algebra and trigonometric functions, differential calculus, integral calculus and finite integration. BEN503 Engineering Physics The syllabus of the unit includes the study of laws of motion, work and energy, wave optics, nuclear physics, electromagnetism, atomic and quantum structure. 60 Total CP BEN504 Engineering Graphics The unit aims to provide students understanding and interpretations of engineering drawings. Course content includes introduction to basic sketching techniques, application of pictorial, orthographic and auxiliary projection, visualization and production of sectional representations, manual drafting techniques applied to drawing machines, introduction to AUTOCAD and solid works, standards for lettering and paper layout and requirements for both detail and assembly drawings, additional representations for surface finish, geometric tolerancing, keyways, welding and fabrication, abbreviations applied to engineering drawings, constructional techniques, for locus of a point, helix construction, intersection and development. BEN505 Material Science The syllabus of the unit includes structures and imperfections of crystalline solids , diffusion in materials, solidification of metals and alloys, deformation and strengthening, heat treatments of metals and alloys, failure and fracture toughness of materials ,structure and properties of engineering ceramics, structure and properties of polymers, cement and concrete, masonry, timbers, aggregates, paints and other surface finishing. BEN506 Introduction to Electrical & Electronics Engineering The syllabus includes Kirchoff’s laws, concept and terminology of nodal analysis to solution of simple resistive networks, The Venin’s and Norton’s theorem, the transient analysis, digital electronics, Boolean algebra, the combinational logic circuits, the flip flops and sequential circuits, Analog electronics and discrete amplifying devices and circuits. BEN507 Introduction to Computer Programming The purpose of this paper is to give the student a good understanding of computer hardware and develop the ability to formulate the logic for general problems and writing programs with syntax. The syllabus includes Computer Hardware, System Software, Linux Fundamentals, Data Types, Control Structures, Arrays and Functions, Structures and Unions and ObjectOriented Programming. BEN508 Engineering Mechanics The syllabus includes the study of the theoretical principle of analysis of forces in equilibrium of different concurrent force systems and parallel force systems, scalars and vectors, dot and cross products, force moment and couple, resultants and free body diagrams, trusses, torsion, centroids and second moment of area and friction. BEN601 Engineering Computation 2 The unit aims to introduce to the student an understanding of advanced calculus and the ability to formulate and solve models of complex engineering systems. The syllabus includes vectors and geometry of space, vector functions, partial derivatives, multiple integrals; vector Fields, Laplace Transforms and Fourier series. BEC602 Surveying for Engineers The unit introduces the elementary methods of conducting small scale land surveys and acquaints students with the surveying profession and its relationship with civil engineering. The syllabus includes: Correction in linear measurement due to sag, temperature, tension calibration, slope and curvature; Angular measurements using compass and Theodolite surveying instrument, angle distance and bearing calculations; levelling; setting out of vertical and horizontal control on the ground, principle of Tacheometry, use of planimeter; area and volume calculations; Theodolite traverse which lead to the plotting of topographic maps; Tacheometry to determine horizontal and vertical control of land survey, surveying calculations including area calculations and volume calculations of cut and fill; use of global positioning system(GPS) for control surveys, topographic surveys and staking out of control points on the ground. BEC603 Geomechanics This unit introduces the concept of total stress, pore water pressure, effective stress and its implications on the behavior of soils. The syllabus includes the analysis of two phase and three phase of soils; study of hydraulic properties of soil such as the permeability BEC604 Hydraulics 1 This unit deals with the analysis of fluid at rest, fluid in motion and the dynamic effect of forces created by the moving liquid. The syllabus of the unit are: study of total hydrostatic pressure in plane and curved surface, buoyant force, stability of floating bodies, dimensional analysis and hydraulic similitude by Buckingham Pi Theorem, application of different hydraulic model laws ( Reynolds’s Model Law, Froude Model Law, Euler Model Law, Weber Model Law, Mach model law) in analysis of water engineering structures; pipeline system including minor losses in pipes, friction losses in pipes, pipes in series, pipes in parallel, pipe network analysis by Hardy Cross method and Linearization method; Analysis of the net positive suction head (NPSH) of pump and pump selection; Steady open channel flow including analysis of best economic trapezoidal section, specific energy, critical depth of flow, rapidly varying flow, hydraulic jump , gradually varying flow, classification of surface profiles, and the analysis of backwater profile by direct step and numerical integration methods, analysis of turbo machinery. BEC605 Structural Mechanics for Engineers The unit deals with the application of elastic analysis of statically indeterminate beams and frames using moment distribution method, three moment equation, slope deflection equation. It also includes deflection analysis by double integration method, area moment method, conjugate beam method and virtual work method. This theoretical knowledge of structural analysis are mandatory for engineering student to learn being the first step in structural design of reinforced concrete, structural steel and timber structures. It also includes engineering analysis of suspended cables, arches, retaining wall, small gravity dams and simple suspension bridge. BEC606 Engineering Geology The unit aims to extend the students’ knowledge of the origin, composition, structure, and history of Earth. Also, to develop an appreciation of the importance of geology to Civil Engineering particularly with regards to the sensitive development of natural earth resources and the need to take account of ecological and environmental protection matters. Syllabus includes study of minerals and rocks; classification of rocks into igneous rocks, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks; the study of land forming process; volcanoes and volcanic activity study geothermal plant as source of renewable energy; ground water hydrology; glaciology; structural geology and plate tectonics; marine geology and geophysics. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK BEN509 Workshop Practice The syllabus includes the history and overview of manufacturing and technology, safety in the workshop and introduction to occupational health and safety (OHS) regulations, common practical’s in manufacturing processes such as milling, drilling, turning, welding (practical and theoretical) and heat treatment of ferrous metals and alloys. and seepage, Darcy Law, and Laplace equations and flow nets including sketching, critical hydraulic gradients, uplift pressures on weirs, shear strength of soil consisting of undrained and drained parameters; application of Mohr circle in the analysis of shear strength parameters of soil; conduct of shear box laboratory test, vane test and triaxial test to determine the shear strength parameters of soil. 61 BEC607 Engineering Analysis and Problem Solving The unit provides students with MATLAB knowledge and create awareness that MATLAB can be a powerful computing tool to solve many engineering problems. The syllabus includes using MATLAB for arithmetic operations, taking advantage of Math builtin- functions in programming; creating one(vector) and two(matrix) dimensional arrays ; Array addition and subtraction, array multiplication and addition, element by element operation, using arrays in MATLAB builtin-math function, two dimensional plots of given data; polynomials, curve fitting and interpolation; three dimensional plotting with special graphics; application of MATLAB in numerical analysis of engineering problem solving. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 62 BEC608 Earthworks, Curves and Hydro graphics Survey The unit introduces the basic principles and analysis of earthworks, roadway curves and the basic principle of hydro graphic surveying in order to increase the students’ depth of knowledge in the field of engineering surveying. It is a necessary knowledge for engineering students to have an in-depth theoretical knowledge of geometrical design of horizontal alignment [simple curve, horizontal compound curve, horizontal reverse curve, and the clothoid (spiral easement curve)] and vertical alignment [symmetrical vertical parabolic curve and unsymmetrical vertical parabolic curve] of roadway. It also includes the analysis of horizontal movement of earthworks such as the preparation of earthwork mass diagram. The unit further gives emphasis to the study of the basic principle of hydro graphic surveying such as measurement of discharge of river by slope area method or by using current meters or floats. BEC609 Hydraulics 2 This unit is the continuation of Hydraulics 1. It is concentrated on the analysis of unsteady flow problems, i.e., unsteady rapidly varied flow and numerical analysis of gradually varied flow in open channel using the explicit finite difference quotient method, solitary surge waves propagation [upstream positive surge wave, upstream negative surge wave, downstream positive surge wave & downstream negative surge wave due either to partial rapid closure or opening of sluice gate ], sediment transport, design of erodible and non-erodible channel using the tractive force method, pipe and pump analysis, pipe network analysis using linearization method , principle of water hammer, principle of surge tank analysis, hydraulic analysis of control regulating structures and control measurement structures. BEC610 Ordinary Differential Equations and Numerical Analysis The unit introduces the principle of Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs) & Numerical Analysis and creates awareness of its importance in solving engineering problems. The syllabus includes first and second orders ordinary differential equations; numeric in general; numeric linear algebra and numeric for ODEs and PDEs. BEC701 Design and Analysis of Timber Structures The unit deals with the importance of structural design codes in the design of timber structures and develops the students’ ability to determine the structural design loads to which an engineering timber structure will be subjected. It also includes the procedural step of designing wooden bearer, wooden post, timber floor deck, timber trusses and the connection details between each part of the different components of timber building structures. BEC702 Design and Analysis of Steel Structures The unit deals with the importance of structural design codes in the design of steel structures and develop the students’ ability to determine the structural design loads to which an engineering steel structure will be subjected. It also includes the procedural step of designing universal structural beams, structural steel stanchions, structural steel floor trim deck, different kinds of steel truss and the connection details between each part of the different components of building structures made of structural steel. BEC703 Geotechnical Engineering The syllabus of the unit are: Determination of shear strength parameters of cohesive and cohesion less soil ; Ultimate bearing capacity of shallow foundations using Terzaghi theory and Meyerhoff theory; analysis of lateral active and passive earth pressure of a retaining wall by Rankine theory and Coulomb Wedge theory; analysis of slope stability of roadway embankment by Swedish method , Bishop method or by the use of Taylor Chart ; analysis of cantilever and anchored sheet pile wall; Structural analysis of gravity retaining wall, analysis of axial capacity of pile foundations and bearing capacity of rock foundations. BEC704 Engineering Hydrology The unit aims to introduce to the students the study of the principles of hydrology and its importance in flood estimation which includes the importance meteorological data like evaporation, transpiration precipitation percolation, formation of clouds and the hydrologic cycle and ground water hydrology. It also includes the study of four different methods of flood forecasting to determine the design discharge of a river, such as: Flood Frequency Analysis (FFA), Intensity Frequency Duration (IFD) Curve, Unit Hydrograph and Runoff routing method. BEC705 Reinforced Concrete Structures Concrete is a versatile building material which is used extensively in multi-story buildings, airports, dams, roads and many other important parts of today’s modern infrastructure. Whilst it is inherently strong in compression, its weakness in tension is offset by suitable steel reinforcement which is initially either unstressed or prestressed. This results in a composite material which requires a detailed understanding of its behavior before safe and economical designs can be produced. Accordingly this course provides a detailed coverage of: The behavior of reinforced and prestressed concrete, durability and fire resistance, behavior and design for strength and serviceability of reinforced concrete beams, slabs and columns, anchorage, detailing, behavior and design for strength and serviceability of fully prestressed and partially prestressed concrete beams and sslabs. It also includes the application of the theories and principles of reinforced concrete design in design calculation of rectangular concrete beams, suspended concrete slab, concrete columns using ultimate strength design (USD). BEC707 Civil Measurement & Tendering This unit consists of two parts. The first is the study of the principles and requirements of civil measurement as applied to civil engineering works to familiarize students with the terminologies of project documentation and trade activities. The second is the study of the principles and requirement of tendering and estimating as applied to civil engineering works. It also includes study of preparation of bill of quantities and cost analysis of engineering projects for purposes of decision making whether to enter into a contract and tender in a certain project.; study of the procedure of preparation of tender documents. BEC708 Design of Masonry Structures (Project) The unit aims to check whether the student upon reaching year 3 semester 2 of the Civil Engineering Programme has sufficient structural knowledge in structural design and analysis of reinforced concrete design, foundation engineering, earthquake engineering and geotechnical engineering. The student will be required to design at least a three storey building made of reinforced concrete. The progress of the design works of the student will be closely supervised by the unit lecturer to ensure that his/her design is in accordance with existing engineering design criteria and standards. The method of teaching will be similar to a class-based unit where students will be given example of complete design of three storey building as reference and guidance on their actual design. BEC709 Airport Engineering The aim of the unit is to introduce to students the principle governing the planning and design of airports, including visual flight rules and regulations, structural method of design of airport pavements, airport capacity BEC710 Water Resource Engineering The unit aims to introduce to the student the theoretical principle of analysis and design of water supply distribution system and urban sewer design whether functioning as a separate sewer or as a combined sewer system. It also includes the study of importance of water treatment plant and sewage treatment plant. The unit further gives importance to solid waste management. Syllabus includes study of water treatment, design of water supply distribution system, waste water and sewage treatment, design of sanitary sewer line, solid waste management and environmental impact assessment. BEC711 Civil Engineering Technology The unit aims to introduce to the students the different construction method adopted in construction of engineering works. It consists of two parts; the first is engineering construction technologies and the second is building services for human convenience. Syllabus includes. Power requirements of mobile equipment, dozers, scrapers, hydraulic excavators, loaders, trucks and hauling equipment’s, pumps and compressors, explosives, drilling and blasting, aggregate production, asphalt mix production and placement, cranes, cofferdams, caissons, piling and dredging. BEC712 Highway Engineering & Design Application The unit aims to develop and strengthen the students’ knowledge in design and construction of roadways. The syllabus includes highway evaluation; planning and design of roadway; preliminary road alignment studies; Road construction materials and testing; Road drainage and erosion control; design analysis of rigid and flexible pavements. It also gives emphasis to basic design principle of airport pavement and railroad track roadway ballast pavement. BEC713 Ports, Harbor and Basic Coastal Engineering The unit aims to introduce to students the study of wave mechanics and coastal processes along with fundamentals that underline the practice of coastal engineering. The syllabus includes the study of the physical characteristics and behaviour of coastal environment; analysis of surface gravity waves by small amplitude wave theory; the formulation of finite – amplitude wave theory; wave refraction, diffraction and reflection; coastal water level fluctuations; wind generated waves; study of different coastal structures and the study of different zone processes. It also includes the study of basic principles of design and layout of ports and harbors. BEC714: Project Management The unit is of three parts. The first part is about engineering contract management; the second part deals with the quality control or quality assurance and the last part is about project planning management. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK BEC706 Foundation Engineering The unit is of two parts. The first part deals with the study of theoretical principles and procedures of designing different kinds of foundation structures such as block wall footings, square and rectangular footings, combined rectangular, trapezoidal footings, continuous footing, mat foundations and footing on piles using the principle of USD. The second part deals with the study of disastrous effect of earthquake to engineering structures; the study includes analysis and design of engineering structures subject to the combined effect of dead load and live load. and delay, airport configuration, various lighting and marking system. 63 The syllabus includes study of pre-contract procedures, normal contracting procedures, arbitration procedures, organization of quality assurance, design aspects of quality assurance, defective prevention system, network technique for project management, project unit cost schedule by S-curve the importance of Programme Evaluation and Review Technique – Critical Path Method (PERT-CPM) in construction and management of engineering projects. BEC715 Irrigation Engineering The unit aims to introduce students the theories and principles of design and analysis of conveyance structures of canal system for irrigation purposes. It also includes the study of drip irrigation, design analysis of irrigation canal structures such as inverted canal siphons, elevated flumes, pipes crossing, drops and chutes, the principles involved in design of small overflow irrigation dams. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 64 BEC716 Structural Analysis The unit aims to introduce students to the study of the basic fundamentals of structural analysis using the matrix based method of analysis (Direct stiffness method and finite element method) of analysis of trusses, beams and frame structures. It also includes the study of approximate method of analysis of lateral loads due to wind and earthquake (portal method, cantilever method, or the factor method). It further includes the review of structural analysis of statically indeterminate structures using the classical methods (method of consistent deformation, slope deflection method and moment distribution method), matrix method of analysis, stiffness method and flexibility method. BEC717 Earthquake Engineering The unit aims to introduce to students the theories and principles of engineering seismology, i.e., origin, cause and effect of earthquake , calculation of design lateral forces using static and the basic dynamic analysis, building forms for earthquake resistance, seismic design and detailing of masonry building, seismic design and detailing of Reinforced Concrete building and earthquake soil dynamics. BEC718 Advanced Water Engineering Project The aim of the unit is to check whether the student upon reaching year 4 semester 2 of the Civil Engineering Programme has sufficient hydrological knowledge in design and analysis of water engineering structure. The student will be required to design a baby ogee shape irrigation dam with a height less than 6.00 meters. The progress of the design works of the student will be closely supervised by the unit lecturer to ensure that his/her design is in accordance with existing engineering design criteria and standards. The method of teaching will be similar to a class-based unit where students will be given example of complete design of one irrigation dam as reference and guidance on their actual design. MTH405: Engineering Mathematics I This unit enables the students to understand the Engineering Mathematics which are used in engineering calculation. Examples will be related to problems encountered in current industrial practice. The assignments will be used to enable the students to work through complex problems with tutorial guidance. All assignments will be based on standard industrial procedures. Prerequisites: A pass in FSLC and MER for admission CIN302: Computing The main aim of the unit is to develop the student’s awareness of the computer as a working tool and to encourage students to integrate the use of computers into all aspects of their work. The syllabus of the unit includes general knowledge in computing, main components of the computer, elements and different parts of the computer, proficiency in the use of Microsoft explorer, Microsoft word and the Microsoft excel spreadsheet. Prerequisites: A pass in FSLC and MER for admission BCE404: Construction Science The unit is in three parts. The first covers basis chemistry and environment, the second basis statics and the third provides an introduction to basic structural analysis. The syllabus includes basic chemistry and factors affecting environment such as , conduction, convection, radiation, heat insulating properties of walls, sources of lights, intensity of sound; analysis of different kinds of force system (concurrent, non-concurrent, noncoplanar, non-parallel force system); finding center of gravity of regular and irregular figures; finding moment of inertia of regular and irregular figures; analysis of trusses by Bow notations, method of joints and method of sections; theory of forces and moments induced in a beam; and construction of shear force and bending moment diagram by shear and moment equation or by semi - graphical method. Prerequisites: A pass in FSLC and MER for admissions BCE405: Construction Technology 1 The syllabus of the unit includes : Types of site investigation methods, study of the preliminary site investigations and steps necessary to complete one engineering construction project; different types of foundation structures including standard foundation design procedures of strip, pad and raft , piled and stepped footing, introduction to the concept of bearing pressure and cut and fill excavation methods; rainfall and runoff interception and removal; parts of timber house, types of timber materials used for construction, construction of a timber house, requirements for cyclone and eart6hquake resistant structure; Types of blocks and concrete block wall construction. BCE406: Construction Drawing 1 To develop the student draughting skills, the syllabus consists of : Touring a drawing office and observation by the students of the different draughting machine, draughting equipment, stationary, engineer’s scale and measures for the care of drawing equipment and instrument; study of conventional method of representations of common construction materials, architectural fixtures and fittings , use of standard engineering symbols, scale drawing, normal scales; the syllabus also includes practical exercises of drawing locality plan ,site plan, floor plan, elevations foundation plan, roof framing plan and structural plan of one storey or two storey residential building. Prerequisites: A pass in FSLC CIV412: Hydraulics & Fluid Mechanics To introduce the student to the fluid state: To develop the students ability to conceptualise fluid flows of different types: To enable the student to apply the fundamental principles of mechanics in typical engineering situations involving fluids both at rest and in motion. BCE507: Construction Materials The syllabus of the unit includes: Materials for concrete construction, types of cement and their characteristics, types of aggregates, reinforcing steel bars for reinforcement and pre-stressing , types of admixtures, curing method of concrete; performing laboratory exercises to determine the workability of concrete( Slump test) , laboratory testing concrete cylinder cubes using the Universal Testing Machine(UTM) to determine the characteristic compressive strength of concrete at 7 , 14 , 21 and 28 days; Description of types of mortars, concrete mix design , timber as construction materials; study of metals and paints and surface finishes. Prerequisites: BCE404. BCE513: Surveying Procedures The unit aims to introduce to the students the elementary methods of conducting small scale land surveys. Syllabus of the unit includes description of surveying instrument, surveying documentations, geometrical methods of determining relative location of a point plotted in the map and transferred to the ground, methods of linear measurement,correction in linear measurement due to sag, temperature , tension calibration, slope & curvature; Angular measurements using compass and Theodolite surveying instrument, angle distance, and bearing calculations; levelling ; setting out of vertical and horizontal control on the ground. BCE516: Theory of Structures1 The unit provides the students with a basic knowledge of CIV510: Civil Engineering Technology 1 This unit enables the students to develop and strengthen the knowledge in the fields of civil engineering construction science by use of classroom teaching and visiting construction sites. It includes the study of site investigation, site organization and temporary services, earthmoving plant and machinery, heavy transport and lifting plant machinery, concrete batching plant, site drainage, excavation works, road works and the study of different types of retaining walls. CIV512: Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics 1 This unit is the study of fluid at rest or in motion. The unit is mostly concentrated in the study of effect of fluid at rest, i.e., the intensity of pressure, total hydrostatic pressure in plane and curved surface, Pascal law, the law of Archimedes on buoyancy, forces acting on dam, stability of floating bodies, venturi meter, orifices, weirs, pitot tube, steady flow, uniform flow, three kinds of energy of fluid flow, continuity of flow, application of energy theorem (Bernoulli’s equations) and simple pipeline analysis. CIV513: Engineering Surveying This unit increases the depth of knowledge in the field of engineering surveying. It exposes the student to more advanced topics involving both practice and calculation which are of particular relevance to civil engineering. Syllabus includes: Theodolite traverse which lead to the plotting of topographic maps ; Tachometry to determine horizontal and vertical control of land survey , surveying calculations including area calculations and volume calculations of cut and fill; use of global positioning system(GPS) for control surveys, topographic survey and staking out of control points on the ground. CIV514: Theory of Structures 2 The unit aims includes the following: study of classical methods of elastic analysis of statically indeterminate beams and frames (moment distribution method, three moment equation, slope deflection equation); study of beam deflection (double integration method, area moment method, conjugate beam method and virtual work method); plotting of shear force and bending moment diagrams of statically indeterminate beams and frames. CIV515: Soil Mechanics The unit aims to develop and strengthen the student’s practical soil and site investigation skills. The important components of this unit are practical experience of both laboratory and field-testing. It includes the study COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK CIV500: Computer Aided Design 1 This unit introduces students to the concepts of 2 dimensional AutoCAD Draughting and to identify the techniques to complete drawing in the most efficient way. Syllabus includes concepts and principles of computer graphics as used in CAD, Auto CAD tools, key functionalities of Auto CAD, Dimensioning Auto CAD drawings l and learning to use the Auto CAD plotter. Prerequisites: A pass in FSLC & MER kinds of force systems, moments and couples, reaction forces and applied loads in trusses and beams, shear force diagrams, bending moment diagrams, and centre of gravity of regular and irregular figures, determination of moment of inertia, stress, strain, Poisson’s ratio, horizontal shear stress in beams, composite beams, and Mohr’s circle of stress. Prerequisites: BCE404 65 of water solid air relationship in soil, permeability , capillary action of soils, soil consistency limits, soil consolidation, soil compaction, determination of ultimate bearing capacity of shallow foundations and analysis of lateral active and passive pressures of retaining wall. CIV516: Structural Design 1 Structural Design 1 pertains to structural design of timber structures. The topics include calculation of design loads (dead load, live load, wind load, moving load) in accordance with the appropriate code of practices. It is concentrated in design of timber structural elements such as design of bearer, wooden post, timber trusses and study of connection details of structural elements in a timber structures. It also includes the determination of site wind speed that affects timber structures. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 66 CIV518: Measurements of Civil Engineering Works This unit enables students to produce accurate take off of building materials required in a particular project. The student should be able to read drawings, interpret the drawing and measure the materials required. At the same time be able to cost the materials calculated. CIV519: Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics II This unit introduces the student to the fluid state; to develop the students’ ability to conceptualise fluid flows of different types; The study includes: analysis of steady flow of fluid in pipeline and open channel flow involving dimensional analysis and hydraulic similitude using the different model laws in hydraulics (Reynolds’s model law, Froude Model Law, Euler Model Law, Weber Model and Mach model law) and the application of these model laws to analysis of different hydraulic problems; rapidly varied flow and gradually varied flow in open channel, specific energy , critical depth of flow, the hydraulic jump, backwater profile , simple pipeline analysis, pump and pipeline analysis, pipe network analysis and turbo machinery. CIV520: Highway Engineering The unit aims to develop and strengthen the students’ knowledge in design and construction of roadways. It also includes the survey of existing infrastructure in the country and site investigation skills. The important elements of this unit are practical experience of laboratory and field-testing. The syllabus includes highway evaluation; planning and design of roadway; preliminary road alignment studies; Road construction materials and testing; Road drainage and erosion control; design analysis of rigid and flexible pavements CIV521: Civil Engineering Design Project The aim of this unit is to check and measure the acquired civil engineering knowledge of the student in providing solution to realistic engineering problem. He/ she will then be presented with practical engineering problems and a set of design constraints. The student then tries to come up with the best working solutions. His/her grade in the unit shall be evaluated based on the quality of research and the manner of his/her oral presentation of the engineering solution he/she had adopted on the design task given. CIV522: Structural Design II Structural Design 2 pertains to structural design of concrete and structural steel structures. This unit enables the students to learn the standard procedures for designing both concrete and steel frame structures using the Limit state method, considering serviceability, durability and strength. Analysis of the deflection requirement during service of the structure to satisfy the serviceability requirement , design of concrete beams, suspended concrete floor slabs, and concrete columns by Ultimate Strength Design principle to satisfy strength requirement using the design criteria of New Zealand Standard of Design of Concrete Structures and Design of Structural steel.. BCE414: Building Services I This unit involves learning through practical assignments. Information will be given through discussion and directed research by students. Students should become conversant with regulations and standards applied in Fiji. Where this unit is used for specialist engineering [e.g. air-conditioning, electrical information given will concentrate on new content material and rely on integration of specialist learning. Pre-requisites: BCE405 BCE500: Construction Technology II This unit is concerned to develop practical technology in response to construction problems. The topics include Site investigation, study of different types of foundations, site drainage, study of different parts of timber structures, concrete block wall construction, types of roof trusses and framing methods and installation, types and fixing details of doors and windows. Pre-requisites: BCE405 BCE506: Construction Drawing II [CAD 1] This unit involves practical learning based on a series of assignments and class works to develop the student’s understanding of construction technology. All exercises in this unit should refer to domestic construction. Pre-requisites: A pass in FSLC and MER. BCE513: Surveying Procedures The unit aims to introduce to the students the elementary methods of conducting small scale land surveys. Syllabus of the unit includes description of surveying instrument, surveying documentations, geometrical methods of determining relative location of a point plotted in the map and transferred to the ground, methods of linear measurement, ccorrection in linear measurement due to sag, temperature , tension calibration, slope & curvature; Angular measurements using compass and Theodolite surveying instrument, angle distance, and bearing calculations; levelling ; setting out of vertical and horizontal control on the ground. BCE515: Building Services II This unit is concerned with the construction engineer’s activities and responsibilities in services installations. The level of specialist knowledge should be kept to comprehensive level only, of the design requirements and installation. It is important that theory is supported with examples of current technology through site visits and input from specialist engineers. The examination must reflect the assignment work. Some input from specialists might be used as would site visits. Pre-requisites: BCE414 BCE518: Construction Drawing III (CAD 2) This unit involves practical learning based on series of assignments and class works to develop the students’ understanding of construction technology. All exercises in this unit should refer to domestic construction. Pre-requisites: BCE506 BCE523: Construction Technology III This unit focuses on the quality standards, legislative control and factors of safety that should be understood through methods of construction. Students will go through training in soil testing, foundation types, elements of construction concepts in building forms and roof structures. Training will focus on commercial and industrial buildings their construction, protection from fire, strong winds and earthquakes. Training will also look into temporary structures, stairs and maintenance. Pre-requisites: BCE500 ARC512: Design Appreciation This unit provides students with opportunities to develop skills in preparation for houses and building regulations and by law; scale drawing, abstraction of information from manufacturers’ catalogues and application data sheets. It includes studies of the evolution of architectural design and principles, i.e., basic value of architectural design, aesthetic requirements as to pattern and forms of the structure. ARC516: Environmental Science This unit enables the students to understand the technical and practical energy concerns that will complement this material. In a way that is pertinent to architecture, it will help meet the most important architectural challenge of the new millennium: to create a sustainable future through an environmental approach to design. The topics include study of climate, construction materials( cement types, concrete properties, grading, seasoning , moisture content protection of timber materials, material corrosion, design wind speed, topography and wind flow, comfort and desirable condition of engineering structures , noise and noise control of architectural structures. ARC517: Design Theory This unit provides students with opportunities to develop skills in designing and incorporating the necessary ARC519-Computer Aided Design II [3D] This unit introduces students to the concepts of 2 dimensional AutoCAD Draughting and to identify the techniques to complete drawing in the most efficient way. Syllabus includes concepts and principles of computer graphics as used in CAD, Auto CAD tools, key functionalities of Auto CAD, Dimensioning Auto CAD drawings and learning to use the Auto CAD plotter. Pre-requisites: BCE405, BCE506, BCE518. ARC521-Architectural Practice This unit enables students to understand procedures in the process of what architects do in the process of construction. This will include architects responsibilities, client’s responsibilities and contractor’s responsibilities before, during and after construction of any project. ARC524: Architectural Design Project This unit enables students to develop an understanding of the design process from environmental site analysis, historical research, conceptual stages to presentation ready for critique and the justification of design options and decisions taken. BCE509: Site Production and Supervision This unit enables students to understand the roles of a supervisor on site and to understand how hazards could be eliminated from the site. It complies with the law to ensure accidents are reduced and the different ways of performing actions. The unit also motivates the students to understand that accidents can only be reduced if things are planned from the beginning and workers are aware that accidents are caused and they just do not happen. Students will come to know different stages and methods of construction and understand that better site organization contributes to construction success. Pre-requisites: BCE500 BCE511: Building Law This module is concerned with how the laws are made and administered at an introductory level. General principles must be understood and their application in Fiji. Case studies should be used to illustrate principles only. Visits to relevant establishments and guest lecturers/speakers should be used to strengthen the understanding of current practice in Fiji. This unit enables students to understand what Law in Building is all about and also how the different categories of laws are made. It distinguishes between criminal law and civil law and so enables students to understand the different business organizations they can join/ form if they are to go into business. The unit covers the meanings of contracts, breach of contract and its remedies and understanding that other parties have and the capacities to absorb risks when things go wrong [insurance] within the organizations. It also covers liabilities and consumer protection. Pre-requisites:BCE405 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK BCE520: Contract Management The subject matter will be linked to the construction industry but will involve a broad understanding of the basis of contract law. Pre-requisites: BCE500 requirements that houses meet the required building regulations and by law; and the house is comfortable to live in. 67 BCE517: Tendering and Estimating This unit is based on developing practical skills. Learning will be concentrated on class and field exercises. Visits to local projects will form a part of the course. Industrial input will be incorporated as available. BCE522: Project Organization This unit is concerned with the identification of management theory and its application in construction projects. Current working examples in Fiji should be used where possible to form the basis of exercises and case studies. Documentation currently in use would be valuable in teaching the application of planning and control techniques. Site visits are important part of this unit, with special regard to safety and site organization. Pre-requisites: BCE500 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 68 BLG520: Building Project 4 This unit enables the students to evaluate their work individually on a project. It instills, develops and provides students with an understanding of the design process from environmental site analysis, historical research and conceptual stages to presentation ready for critique and the justification of design options and decisions taken. At the end of this unit students should able to read and interpret plans and extract whatever materials are required for the project. Prerequisites: BCE500 BLG521: Quality Assurance This unit helps students to understand what quality assurance is all about and to understand the importance of being accredited. It complies to work towards the implementation of ISO 9000 and also understand rights of consumers and duties of manufacturers QSY401: Measurement 1 This module introduces the student to the basic skills of Quantity surveying measurement procedures. Learning must focus on the application of these skills. The current acceptable local method of measurement must be adhered to. The process of measurement should be used to develop high standards of presentation, consistency, work, planning, correct application of geometrical and trigonometrically techniques/formulae. Descriptions used should stress the importance of accuracy. Prerequisites: BCE405 QSY523: Quantity Surveying Practice This unit is concerned with the technical support needed by the Quantity Surveyor, both in private practice and within a construction organization. The learning blocks have been expressed in terms of consultancy practice, but they should be suitably re-worded as necessary to reflect professional practice from within a building contracting organization. Evidence, both documentary and legal form an important element of this unit. Input from practicing professionals, including legal personnel is recommended. Prerequisites: BCE520, QSY517 QSY517: Measurement 2 This unit further develops measurement skills learnt in Measurement 1. The work must be based on current construction techniques used in Fiji and current documentation. Work must be carried out to an acceptable industrial standard. Industry should be encouraged to contribute documentation and act as visiting tutor. Prerequisites: QSY501 QSY501: Quantity Surveying Project 4 This unit enables the students to evaluate their work individually on a project. At the completion of the project they should be able to prepare bills of quantities and submit it for the preparation of tender. Prerequisites: QSY517 QSY524: Measurement 3 This unit emphasizes the understanding of services installation and integration. Because the quantity of much of the specialist measurement work is limited in Fiji, this area of the syllabus will need support through videos and current case studies. Where ever possible, local current construction works must be used to strengthen understanding. Prerequisites: QSY517 LSY403: Surveying1 Practice The unit aims to introduce the fundamentals of levelling, contour interpolation and the care and maintenance of surveying instruments. The course content includes understanding the types of levelling instrument, carry out levelling up to first order levelling work, carry out grid levelling, carry out contour interpolations and drawing of contour lines, calculations of volumes from grids and contours lines, trigonometric heighting, barometric heighting and sounding. LSY405: Surveying 1 This unit aims to introduce the basic surveying procedures and calculations. The course content includes calculation of bearings, angles, directions, understanding the use of compass and theodolite for measuring distances, angles, bearings and azimuths, setting out required angles, practical works on measuring horizontal and vertical angles, traverse calculations, traverse adjustment using Bowditch method, calculations of area by coordinates method, calculation of missing sides from given distances and bearing of a traverse LSY406: Surveying Drafting This unit enables students to set up drawing from levels produced from surveyors. The unit is focused on skills and accuracy in the use of scales in measuring and calculation of angles to what is required to enable to plot the drawing as required. LSY407: Town and Country Planning This unit enables students to understand the principles and practices of town and country planning The topics include study of the principle of town and country planning, land zoning, design of agricultural, residential, commercial and industrial subdivisions, land requirement and usage in urban areas, survey layout of roads ,junctions and car parks . LSY508: Survey Law and Implementation (Related Regulations) The unit aims is to introduce the laws governing survey work, land title and registration. The topics include land tenure and leases, land holdings and title systems, land identification and appellation, plans, indexes, and record maps, ordinances affecting lands, Land Transfer act, Land registration, ownership, easements, caveats, Right of way, Native title rights mortgages and leases. LSY511: Engineering Surveying The unit aims to introduce the principle of carrying out engineering survey and design of drainage, water and sewer reticulation for a subdivision. The course content includes survey marks, detail survey, contouring, road surveys, methods and specifications of setting centreline and cross sections, terminology, geometry and setting out of horizontal curves by chords and deflection angles, survey requirements of Bridge site and building site, layout and design of vertical curves and hydraulic calculations for engineering survey. LSY513: Geodetic Computation This unit enables students to carry out a minor Triangulation Survey and its adjustments, concept of Geodesy and obtaining azimuths from stellar and solar observations. The syllabus includes; concept of Geodesy, the geometry of spheroid, compilations of heights by reciprocal and one way observations, methods of observations and adjustment of triangulation figures, general knowledge of map projections, reduction of bearings and distances to the traverse Mercator projection, study of the geodetic datum and standard meridians, study of principle of electronic distance measurement; study of the astronomical bodies , solar system and satellites, study of the celestial sphere and its reference system, the astronomical triangle, correction to astronomical observations, relations between solar, sidereal, ephemeris, standard and clock times, the almanac, determination of azimuth, latitude, longitude and time from field observations. LSY514: Cadastral Survey and Survey Practice This unit provides students with a comprehensive knowledge to carry out surveys in relation to property boundaries. LSY415: GPS Survey This unit introduces the basic principle of GPS LSY516: Introduction to Photogrammetry This unit aims to introduce the basic principles of aerial photogrammetry, remote sensing and understanding the principle of Geographical Information System(GIS) The course content includes the types and evaluation of geometric properties of aerial photographs, calculation of scales of aerial photo , flying height and area measurement , stereo viewing , definitions of remote sensing and GIS. LSY518: Cadastral Survey Project The unit aims to check and measure the acquired surveying knowledge of student in carrying out a practical land survey project. He/she will then be presented with practical survey engineering problems and a set of design constraints. The student then tries to come up with the best working solutions. His/her grade in the unit shall be evaluated based on the quality of research and the manner of his/her oral presentation of the engineering survey solution he/she had adopted on the design task given. LSY417: Valuation of Surveyors This unit aims to introduce the understanding of the code of Ethics and the Code of Professional Conduct of Land surveying. It includes the topics ethics, professional behaviour, discipline and duty of surveyor, study of the provisions of OHS and Safety Employment Act, the importance of continuing professional development, study of the laws of Professional Indemnity Insurance and understanding of the general company policies, role of surveyor as an expert witness and the price of negligence that goes with being a professional, study of proper record keeping of survey data and proper supervision of survey field work. BCE302: Trade Calculations I This Unit is concerned with the practical applications of mathematics as a basis calculation in this program. Examples used should be on industry related problems, including excavation work, costing to timber framed buildings, reinforced concrete, concrete mixture, materials testing and quantities, conversion and estimation. BCE303: Trade Calculations II This unit is concerned with the practical application of mathematics as a basis for making many calculations. Upon the completion of this unit the student will be able to apply the law of indices to simplify algebraic equations, use logarithms with products, quotients and powers, apply formulae to calculate the area, volume and surface area of regular and irregular shapes, solve quadratic equations by different methods, solve simultaneous equations by different methods, and use COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK LSY509: Surveying 2 This unit aims to introduce advance methods of surveying calculations and principles. It includes horizontal and vertical control survey, triangulations, trilateration, traversing, trigonometric heighting, single and reciprocal rays, barometric levelling, reconnaissance, error propagation and optimal design of control networks. survey. The course content includes: basic principle of GPS survey, understanding the use of GPS survey equipment, receiver configuration, coordinate system and GPS site calibration, mission planning , real time kinematic surveying , post processing and network adjustment. 69 trigonometric functions to solve real life construction industry practical problems. More Calculation on directly related construction aspects of practical application is an impact to the Unit. BCE304: Craft Science I Experiments either individually or in group form the basis of this unit. Upon the completion the student will be able to determine the volume, density, specific gravity, porosity and granular composition of common materials, determine the influence of water on materials, demonstrate through experiment the chemical composition of water, verify the principle of moments, and show the effects of size, shape, junction and velocity on rates of flow through pipes and channels COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 70 BCE309: Craft Science II Experiments both in the laboratory and in the external environment are fundamental to this unit. Upon the completion, students will be able to demonstrate through experiments a basic knowledge of chemical terms, graphically and using calculations, illustrate through calculations and graphical means the effects of acceleration, energy transfer and friction, measure fluid pressure including atmospheric pressure, measure temperature and illustrate through graphical and numeric methods, and solve simple problems associated with the application of electricity in tools and instruments. Pre-requites: MER PSM301: Plumbing & Sheetmetal Drawing 1 This unit is practical. Learning is based on a series of assignments to progress the accuracy and drawing technique of the student. Upon the completion of this unit the student will be able to identify techniques of preparation and maintenance, produce them free hand and describe them. Produce two and three dimensional drawings, industrial standard drawings, measure elements and components to produce lists and schedules. Prerequisite: MER PSM302: Cold Water Theory A This unit aims to provide the supporting theory to workshop practice. Upon completion of this unit the student will be able to prepare annotated sketches and calculations to describe alternate methods of supplying domestic water, prepare cold water instillation, produce a schedule for cold water instillation, describe preparation of materials, storage, site, operations, fixing and commissioning, compile checklists to install cold water system to ensure standards. Prerequisite: MER PSM303: Cold Water Practice This unit aims to provide the supporting theory to workshop practice. Upon completion of this unit the student will be able to demonstrate methods of bending, cutting, forming, fixing and joining, construct simulated domestic cold water instillation, carry out connection from main connection to domestic water meter, test workmanship and materials above and below ground instillation. Prerequisite: MER PSM305: Applied Materials This unit is concerned with the practical selection, handling and use of common materials used in the craft skills. Upon the completion of this unit the student will be able, through visual and simple tests, identify materials, inspect materials, recognize and produce a list of basic defects and their possible causes, describe characteristics of common materials, be able to select materials for certain purpose, handle, store and protect material. Prerequisites: MER PSM306: Sheetmetal Practice A This unit enables the student to gain in skills in basic procedures and craftsmanship in sheet metal work. Upon the completion of this unit the student will be able to inspect, prepare and operate sheet metal machines, mark out, cut, drill and join a variety of common materials and alloys, produce detailed information of various simple shapes in sheet metal. Prerequisites: MER PSM307: Sheetmetal Theory A This unit brings together and extends the technology developed through earlier workshop practical exercises. Upon the completion of this unit, students will be able to describe with suitable sketches and specification notes the covering of a domestic roof in sheet metal, schedule the components for a sheetmetal roof, produce a schedule to describe the working process for the roof finishing, and compare, through testing and working characteristics, the use of a variety of materials. Prerequisites: MER PSM308: Sanitation and Drainage Theory A This unit is concerned with standard installations and requirements in Fiji. Upon the completion of this unit student will be able to fully describe the materials selected, storage arrangements, setting out and leveling procedures, and working method of installing underground pipe-work, describe the installation of sanitary fittings, describe the construction of a small sewage treatment plant, and produce a working checklist to inspect the complete drainage installation. Prerequisites: MER PSM310: Hot Water Practice A This unit is concerned with hot water installations as currently carried out in Fiji. Students understand how to prepare drawings, construct, install components; arranges pipe-work and controls, and test examples of direct and indirect hot water systems; prepare drawings, develop patterns, manufacture hot water cylinder, and install as an electric hot water cylinder, including commissioning and testing’ construct a solar water heating system including solar panel, storage vessel, and all pipe-work; and arrange commissions and installations. Prerequisites: MER PSM311: Hot Water Theory A This unit aims to provide the supporting theory to workshop practice. Prepare annotated sketches to describe design and construction of the key components used in hot water installation, draw up a scheme for the hot water installation, produce schedules for a proposed hot water installation, prepare work instructions to describe a hot water installation, compile a basic check list to inspect a hot water installation. PSM412: Welding and Fabrication This unit is concerned with welding and fabrication techniques applied in the construction industry. Upon the completion of this unit student will be able operate standard types of welding equipment, describing safety select filler rod and carries out welding of all types and be able to identify faults. Prerequisites: MER PSM414: Cold Water Theory B This unit aims to provide the supporting theory to workshop practice. Upon completion of this unit the student will be able to describe alternate methods of supplying domestic water, prepare a cold water installation, list materials, fittings and fixtures describe the preparation of materials, storage, site operations, fixing and concealment of a domestic cold water installation, and compile a basic check list to inspect. Prerequisite: PSM 302 PSM415: Hot Water Theory B This unit aims to provide the supporting theory to workshop practice. Upon completion of this unit the student will be able to design and construct the key elements used in hot water installations; Draw up a scheme for the hot water installation; prepare work instructions to describe a hot water installation compliance with design specification and legal requirements. Prerequisite: PSM 310 PSM416: Sheetmetal Construction This unit brings together and extends the technology developed through earlier workshop practical exercises. Upon completion of this unit the student will be able to describe with suitable sketches and specification notes the covering of a complex domestic roof, schedule the components for a sheet metal roof, describe the working process for the roof finishing, describe the weatherproofing, to compare traditional roofing materials and possible alternatives. PSM417: Sheetmetal Theory B This unit enables the student to gain skills in working with sheet metal. Upon completion of this unit the PSM418: Project - Building Services Learning will be achieved through practical assignments. Upon completion of this unit the student should be able to design from main supply to disposal system a complete plumbing/drainage system for a domestic dwelling, including all hot, cold and waste pipe work, inspect and test services, produce an electrical layout, using a checklist to inspect simple elements. Prerequisites: FSLC PSM419: Sanitation and Drainage Theory B This unit is concerned with standard installations and requirements in Fiji. Upon completion of this unit the students will be able to prepare annotated sketches to fully describe the materials selected, produce drawings and specification notes fully describe the installation of sanitary fittings, and produce a working checklist to inspect the complete drainage installation. Prerequisites: PSM 308 PSM420: Sanitation and Drainage Practice B This unit should include a wide variety of materials and components currently in used in Fiji. Upon completion of this unit the students will be able to complete the construction of above ground installation and below ground installation, demonstrate working principles of a basic sewage treatment plant, test underground drainage, and select standard tests for above ground installations. PSM421: Design and Calculations In this unit the students describe and calculate speed, velocities, accelerations, force and pressure, fluid in motion relative discharging powers, pipe flow loss of head due to friction, Thomas Formula, Chezy Formula and sizing of soak ways, heat loss through fabrics and ventilations, describe use of immersion heaters and gas heaters and solve problems relating to hot water and gas heaters. BCE 422: Elementary Surveying Lectures and demonstrations will be augmented by practical field work and draughting. In this unit the students measure and record lengths accurately using surveying bands, chains, and tapes to survey a site to record/establish boundaries, carry out grid leveling and spot height, use levels to set stepped footing, boning rods and sight rails to set out drainage systems for housing subdivision. CJY301: Applied Materials 1 This concerned with the practical selection, handling and use of common materials used in the craft skills. This module should be linked to practical workshop visits to ensure the students understand the role and importance of the materials in applied technology. Prerequisite: MER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK PSM413: Sheetmetal Practice B This unit enables the student to gain skills in basic procedures and craftsmanship in sheet metal work. Upon the completion of this unit student will be able to inspect, maintain and adjusts sheet metal machines, mark out, cuts, drills and joints a variety of common materials and alloys, solder a variety of joints using base metals, copper and copper alloys. Prerequisite: PSM 306 student will gain knowledge on the construction with Sheetmetal, drainage systems, damp proof causes and roof calculation. Prerequisite: PSM 307 71 CJY302: Trade Practice A The theory should only be used to support practical work in Carpentry and Joinery Prerequisite: MER CJY303: Trade Theory A Drawing and related calculations from essential elements in Carpentry and Joinery Prerequisite: MER CJY305: Trade Practice B Involves the application of basic mathematics. Modules can be used to simulate some of the work, but at least one full size problem must be tackled. Prerequisite: MER COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 72 CJY306: Computing & Joinery Drawing 1 This unit practically based on a series of assignments to progress the accuracy and drawing techniques of the students. Drawings should be based on methods of construction and assembly criteria. All drawings should relate to crafts drawing needs. Prerequisite: MER CJY307: Trade Theory B This unit relates to real construction problems. Drawings and related calculations form essential elements in all the learning blocks. Prerequisite: CJY303 CJY308: Trade Theory C This basically applies to the standard forms of construction with a broad understanding of new or traditional forms as alternative methods. Prerequisite: CJY303 CJY409: Construction Materials 2 This unit is primary concern with the understanding of the various tests on materials to determine their properties. Prerequisite: CJY307 CJY411: Trade Practice C The introduction of theory should only be used to support practical work. Prerequisite: CJY305 CJY412: Trade Practice D In this unit, students to set out and construct an in-situ flight open riser staircase, with simple wall fixed hand rail; sets out, marks out, produces cutting list and forms the elements of a staircase with a change of direction, including shaved treads; constructs a section of joinery staircase complete with closed strings, newels and straight hand rails; sets out, marks out, produces cutting list and constructs a shaped hand rail with balustrade and simple joinery item. Prerequisite: CJY305 CJY413: Wet Trade Theory A The aim of this unit is to provide a sound basis of knowledge to enable the students to comprehend the construction process and the relationship of practical units exercises to that process. Prerequisite: MER CJY414: Trade Practice E Mainly concerned with provision of false work and framework, including basic measurements. Prerequisite: CJY412 CJY415: Trade Practice F Concerned with specialist carpentry and joinery practice Prerequisite: CJY412 CJY416: Trade Theory D Drawings and related calculations form essential elements in all the learning blocks. Prerequisite: CJY308 CJY417: Computing & Joinery Drawing 2 The work will be based on CAD application to providing information and non-standard details information. Prerequisite: CJY306 CJY418: Wet Trade Practice A The application of processes and procedures which control quality, where theoretical input is necessary. Prerequisite: MER CJY419: Wet Trade Theory B This unit is concerned with the use of large wet construction technology in large domestic buildings. The use of brickwork in forming decorative opening and block work up to ground floor level. Prerequisite: CJY413 CJY420: Wood Machining Theory A This unit and assessments are based on series of practical project industry related information. Prerequisite: MER CJY421: Workshop Project A This unit is about workshop project. Its emphasis is on safety and safe working methods. Prerequisite: MER FLS500: Built Environment This unit is concerned with the completed building, the purpose of the building the importance of having enclosures, the different types of envelopes, the internal and external temperature, heat gain and heat loss and the importance of the orientation of the building in relation to the sun path. For More Information Contact: Mr Sateesh Pisini Head of School(Higher Education) Phone : 3381044 Ext: 1653 E-mail : HOS-SBCE@fnu.ac.fj Mr Jotame Dianimoto Head of School(TVET) Phone : 3381044 Ext: 1649 E-mail : HOS-Building@fnu.ac.fj OA – Ms. Ashmeeta (HE) Ext: 1657 E-mail: oa-bce@fnu.ac.fj Ms. Olivia (TVET) Ext: 1650 E-mail: OA-Building@fnu.c.fj COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 73 SCHOOL OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING General Information Electrical and Electronics engineering are exciting and challenging field of Engineering for anyone with a genuine interest in, and aptitude for, mathematics and applied science. For more than a century and a half now, engineers in these fields have played a significant role in the development of systems that have made a profound change in the way people live and work. Large and small industries as well as institutions of all descriptions are of no exception. So simply put, electrical engineering and the effects of electronics engineering disciplines like telecommunication, computing and e- businesses affect every aspect of a nation’s economic growth, development, wealth and health. The School of Electrical and Electronics Engineering offers its allied industries and school leavers a very dynamic and comprehensive programme to pursue a career in electrical and electronics engineering. The major areas of interest are electrical power generation, transmission, distribution and utilization; digital computer engineering; telecommunication and networking; control and instrumentation and electrical & electronics systems design. The school is planning to start a new program in biomedical technology for biomedical technicians. This is a Cert IV program to cater for the Industrial demand. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 74 The Fiji National University through the School is registered as a CISCO LOCAL ACADEMY and offers the CISCO/CCNA Computer Networking qualification through the CISCO parent company in the USA. Advanced Diploma of Engineering (Electrical and Electronics Engineering) This programme is offered after the Trade Diploma and is equivalent to year 2nd year of a normal 4-year Bachelor of Engineering degree. Bachelor of Engineering Degree Programme Since semester 1 of 2009, students with form seven pass in English, Mathematics, Physics and one other science or engineering technology subject enter the BE programme. The new crop of engineers out of this programme will be very versatile and skilled in this discipline of engineering that spans from Trade Diploma through advanced diploma and finally the normal final degree programme. Since the industrial attachment is part of the training requirement, the programme demonstrates the multi-entry and multi-exit feature which is flexible to the choices of students and employers during the course of training at the school. NOTES: 1) There are also opportunities for working people who may want some personal upgrading to enhance their careers. 2) Besides the normal programmes on offer, employers may request the design of special units or programmes for the general upgrading of their employees. 3) In general, as an electrical or electronics serviceman, or craftsman, or technician, or technologist, or engineer in the areas mentioned above, you can participate in this on-going technological evolution by improving and perhaps refining the existing systems or indeed by inventing and developing new systems to meet the everchanging needs of our society. CAMPUSES: Suva Ba Labasa programs. - all programmes - Certificate classes, Electrical and Electronics; Serviceman’s courses normal or after hours - Certificate Classes, Electrical and Electronics and Serviceman’s Courses & Trade Diploma Staff Profile Dip.Electrical Eng. Licensed Wireman HIGHER EDUCATION STAFF HEAD OF SCHOOL DR. ARIF KHAN PhD (Electrical), M.Tech, B.Tech, Dip/(Elect.Eng) ANANAIASA WAQA SOVAKI Diploma in Applied Computing, Cert IV in Training & Assessment, CCNA PROFESSOR DR. VISAGAPERUMAN RAMACHANDRAN PhD (Electrical/Electronics), MSc(Opto Elect.), BSc(Physics) PATERESIO LALIQAVOKA(Part-Time) Broadcast Technician Cert.; Telecommunication Technician Cert. C Level, (City and Guilds of London Inst.); Ordinary Technician Dip. (Mechanical and Electrical Eng.), (City and Guilds) VISITING ASSISTANT PROFESSOR PRASANNA WAICHAL MSc, BSc(Electronics Engineering) TETEKA PILITATI(Part-Time) Diploma in Electrical Engineering ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DR. MD SHAHIDUL ISLAM PhD (Wireless Communication) LECTURER I ULAIASI GUDRU Adv Dip. Electro Tech; Dip. EE; IDTT; Trade Cert Electronics Eng; Cert. Marine Electronics, (Aust) EREMASI CAMA TAMANISAU BE (Hon) Electrical and Computing, BSc. Math and Phy, Cert. (Copyright and Related Rights) SAMUELA ROKOCAKAU MSc(Dig.Syst.), BSc(Mths/Phy)(USP), BEd(Mths/Sc.) LECTURER VISHAL CHARAN BETech (Electrical/Electronics) EDWIN RAJ VANS PGDip.(Electronics), BETech (Elect./Electronics) SHIU KUMAR MSc (Engineering), PGDEE, BTech (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) OFFICE ADMINISTRATOR Varsha Devi B. com (Management & Public Administration) TVET STAFF HEAD OF SCHOOL JIULIASI VEIWILI ULUIBUROTU BEng. Electronics and Computers (Eng); HND; Dip. Telecommunications Eng; Cert. (Diesel Eng.) SENIOR LECTURER SHASHANK UPADHYAY MSc (Telecommunications & Networking) SAIMONI MATAWALU Adv. Dip (Eng.); Dip. (Elect.Eng.); Dip (Ter.Teach); Cert.IV (Work.Asess./Training), (APTC); Licensed Electrical Wireman LECTURER MORITEKEI RAVULALA AMAN ATISH CHAND DTT; Adv. Dip Elect. Electronics; Dip. Elect; Trade Cert. Electrical Eng. SURENDRA LAL Dip. Electrical Eng; Trade Cert. (Elect.) SITIVENI DAUNA KAMAKAWA B.Eng(Electrical) LECTURER II ANIEL V JAGGESSAR B.Eng (Electrical & Electronics) Dip. Electrical Eng; Licensed Wireman (FEA) ASHLESH KUMAR Dip. Electronics Eng ww PAULA TUIVANUYALEWA Dip. Electronic Eng., Trade Cert.Elect; Higher Tech. Cert. of Telecom. (TTC); Cert. IV in Workplace Training and Assessment; Broad.Tech.Cert; SEBIUTA UTONI Dip. Electrical Eng; Cert. AutoCad JALE CURUKI BSc (Telecom.Eng.), Dip.(Telecom.Eng.)(TTC) SUMENDRA KUMAR, Dip. (Electrical Eng.); Trade Cert. (Electrical Eng.); Licensed Wireman COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK SENIOR LECTURER DR. SACHIN SHARMA PhD (Electronics) SANDIP KUMAR BETech (Electrical and Electronics) SONEL M GOUNDAR Dip. (Electrical Eng.), Licensed Wireman KALIVATI UQE Adv. Diploma Electro Technology ROPATE SILA 75 Diploma in Electrical & Electronics Eng RONESH SHARMA MSc (Electronics Engineering) OLIVA NAQURA Cisco Certified Instructor ASSISTANT LECTURER NAUNEET MENON Dip. Electronics Eng. RONEEL MAHARAJ Adv. Dip.Eng (Electrical and Electronics); Dip.(Elect. Eng.) NIRAJ ASHWIN CHAND, Dip. (Electrical) Trade Cert. Electrical Eng; Licensed Wireman COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 76 RAMIT SINGH Adv. Dip. Electrical Eng. LAB DEMOSTRATOR ELENOA V BALE (Study Leave) Trade Cert. Electrical Eng; Licensed Wireman PRANID REDDY(Electrical) Adv. Dip (Electrical & Electronics) RAVNEEL NARAYAN Adv. Dip (Electrical & Electronics) SENIOR TECHNICIAN TEVITA QATAIGAU Dip. Electronics Eng; Trade Cert. Electronics Eng; Cert. Marine Electronics, (Aust) LAB TECHNICIAN VINAY MAHARAJ Dip(Electrical) RONEET PRASAD Dip. Electronics Eng RAVNEEL ASRE Trade Certificate OFFICE ADMINISTRATOR MEREISI LILy MATATOLU Dip.(IT) Programme Details and Duration SHORT CERTIFICATE TRADE IV DIPLOMA COURSES - CERTIFICATE Total number of units to PENSTER (2016) SEMESTER TRIMESTER ENGINEERING DIPLOMA (4 AWARDS) (2016) 35 units (4 25 units 19 units 45 units 25 units 12 units 5 3 5 4 2 semesters 5 units 7 units 7 - 9 units 6 - 9 units 5 units 3 – 7 units 8 weeks 15 weeks 15 weeks 18 weeks 18 weeks 18 weeks 12 Months 12 months 12 months 6 months 6 months - - Minimum period to complete ¾ academic 2 academic 2 academic 2 academic 2 academic 1 academic 4 academic the whole programme Year years years years years year years complete the programme 6 units TRIMESTER BACHELOR OF ADVANCED Number of Pensters/ trimesters/semesters to 3 pensters years) 8 Semesters (4 years) complete all units Number of units to complete each penster/trimesters/ 2 units semester Number of weeks per penster/trimesters/semester Minimum period required for industrial attachment 8 weeks The College is offering Certificate IV and Trade diploma in Trimester Mode from 2014 onwards. For any enquiry on the trimester mode programmes for 2016 please contact the Head of School. Entry Qualifications Certificate IV Programmes Pass in Form 6 with 200 out of 400 marks with 50% minimum marks in English and Mathematics, and any 2 subjects OR Preliminary Science with GPA of 2.00 or more Trade Diploma Programmes Pass in Form 6 with 200 out of 400 marks with 50% minimum marks in English, Mathematics, Physics, and any other 1 relevant subject. Advanced Diploma in Engineering (Electrical and Electronics) Holder of the FIT/FNU Trade Diploma in Electrical Engineering Bachelor of Engineering (4 majors) Pass in Form 7 with 280 out of 400 marks with pass (50% or more) in English, Mathematics, Physics and any other 1 Science or Technology subject OR Foundation Science with GPA of 3.00 or more. Programme Stages and Units: Certificate IV in Electrical Engineering(Penster Mode) STAGE 1 Unit code EEE321 Unit Name Basic Craft Skill 1A (Fitting) Basic Craft Skill 1A (Fitting) STAGE 2 CP Unit code Unit Name CP 8 EEE326 Basic Craft Skill 2 (Welding and Fabrication) 8 EEE326 Basic Craft Skill 2 (Welding and Fabrication) 8 8 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Trimester Mode Programmes for 2016 77 EEE322 Basic Craft Skill 1B (Electrical Builders) 8 EEE327 Craft Calculations 2 8 EEE301 Mathematics for Trade 8 EEE328 Engineering Drawing 2 8 EEE324 Engineering Drawing 1 8 EEE329 Electrical Principles (Trade) 1 8 EEE325 Craft Science for Electrician 8 COM201 Technical Communications 1 4 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 1 10 Total CP 50 Total CP STAGE 3 36 STAGE 4 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK EEE391 Electrical Principles (Trade) 2 8 EEE344 Electrical Principles (Trade) 3 8 EEE392 Electronics for Electricians 1 8 EEE445 Electrical Installation Technology B 8 EEE395 Electrical Installation Technology A 8 EEE446 Electrical Installation Practical B 8 EEE396 Electrical Installation Practical A 8 EEE447 Electrical Machines 1 8 EEE394 Electrical Testing 8 EEE448 Electronics for Electricians 2 8 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethics 5 Total CP 45 Total CP 40 STAGE 5 EEE449 Electrical Installation Technology C 8 EEE452 Electrical Machines Practical (Winding) 8 EEE450 Electrical Installation Practical C 8 EEE520 Programmable Logic Controller (PLC)2 8 EEE451 Electrical Measurements and Machines 8 Total CP 40 CERTIFICATE IV ELETRICAL ENGINEERING(TRIMESTER MODE) Trimester 1 Unit code Unit Name CP MTH301 Preliminary Mathematics I 5 EEE321 Electrical Workshop Practice 7 EEE324 Engineering Drawing 7 EEE325 Material Science For Electricians 7 EEE329 Electrical & Electronic Principles & Testing Equipment 7 COM301 Communication Skills and Studies 7 Total CP 40 Trimester 2 EEE392 Electronics For Electricians 7 EEE395 Electrical Installations Technology - 1 7 EEE396 Electrical Installations Pract -1 9 EEE447 Electrical Machines 7 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethical Practices 5 OHS403 Occupational Health and Safety III 10 Total CP 45 Trimester 3 78 EEE449 Electrical Installation Technoligy - 2 7 EEE450 Electrical Installation Practical -2 7 EEE451 Electrical Measurements & Testing 7 EEE452 Electrical Machines Pract (Winding) 7 EEE439 Programmable Logic Controller + Scada 7 EEE448 Electrical Project 7 Total CP 42 CERTIFICATE IV IN ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING (PENSTER MODE) STAGE 1 Unit code Unit Name STAGE 2 CP Unit code Unit Name CP EEE301 Mathematics for Trade 8 EEE307 Electrical Principles 1B 8 EEE302 Electrical Principles 1A 8 EEE308 Workshop Practice 2 8 EEE303 Workshop Practice 1A 8 EEE309 Electronics Fundamentals 8 EEE304 Workshop Practice 1B 8 EEE310 Components and Measurements 8 EEE305 Electrical Measurements 8 COM201 Technical Communications 1 4 EEE404 Engineering Drawing 8 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 1 10 Total CP 48 Total CP 46 STAGE 3 STAGE 4 Electrical Principles 1C 8 EEE416 Workshop Practice 3 8 EEE412 Digital Electronics 1A 8 EEE417 Digital Electronics 1B 8 EEE413 Analog Electronics 1A 8 EEE418 Analog Electronics 1B 8 EEE414 Computer Applications 8 EEE419 Computer Systems 1 8 EEE415 Electronic Communications System 8 EEE420 Electronic Communication System 2 8 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethical Practices 5 Total CP 48 Total CP 40 STAGE 5 EEE421 Electronics Project 8 EEE422 Television Systems 8 EEE424 Radio Receivers and Transmitters 8 EEE426 Computer and Data Communication 8 EEEXXX Elective 8 Total CP 40 STAGE 5 ELECTIVES - Select one unit from the following electives depending on the area of specialisation * Computer Technology Electives * Communication Electives EEE427 Computer Technology 8 EEE423 Video Recorders 8 EEE428 Computer Peripherals 8 EEE425 Audio Equipment and System 8 EEE429 Computer Systems 2 8 EEE430 PC Servicing 8 EEE438 Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) 8 CERTIFICATE IV ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING (TRIMESTER MODE) Trimester 1 Unit code Unit Name CP MTH301 Preliminary Mathematics I 5 EEE302 Electrical Principles 7 EEE303 Electronics Workshop Practice 1 7 EEE305 Electrical Measurement and Component 7 EEE414 Computer Application & Systems 7 COM301 Communication Skills and Studies 7 Total CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK EEE411 40 Trimester 2 EEE412 Digital Electronics 7 79 EEE413 Analog Electronics 7 EEE415 Electronic Communication (1 & 2) 7 EEE416 Electronic Workshop Practice 2 9 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethical Practices 5 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety I 10 Total CP 45 Trimester 3 EEE421 Electronic Project 7 EEE422 Television System 7 EEE424 Radio Receiver and Transmitter 7 EEE426 Computer & Data Communication 7 EEE439 Programmable Logic Controller & SCADA 7 Optional Unit (Select only 1) EEE429 Computer Programming 7 EEE430 PC Maintenance & Repair 7 Total CP 42 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK CERTIFICATE IV IN BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING Trimester 1 MTH304 Mathematics for Trade 9 EEE312 Electrical Principles 9 EEE313 Electrical, Electronics & Gas Safety w/shop 9 BMT342 Anatomy, Physiology & Infection Control 9 EEE315 Electrical Components & Measurements 9 COM301 Technical Communication 5 Total CP 50 Trimester 2 EEE412 Digital Electronics 7 EEE413 Analog Electronics 7 EEE493 Computer Systems 9 BMT471 Biomedical Materials & Devices 9 MEC379 Pneumatics, Hydraulics & Refrigeration 9 OHS401 Occupational Health & Safety 5 Total CP 46 Trimester 3 EEE421 Electronic Project 7 BMT474 Medical Imaging Systems 9 BMT451 Introduction to Bioinformatics 9 BMT472 Biomedical Instrumentation 9 EEE436 Microcontroller Applications 9 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethical Practices 5 Total CP 48 CERTIFICATE IV IN BROADCAST ENGINEERING Trimester 1 MTH304 Mathematics for Trade 9 EEE302 Electrical Principles 9 EEE303 Electrical, Electronics & Gas Safety w/shop 9 EEE305 Anatomy, Physiology & Infection Control 9 EEE414 Electrical Components & Measurements 9 COM301 Technical Communication 5 Total CP 80 50 Trimester 2 EEE412 Digital Electronics 7 EEE413 Analog Electronics 7 EEE415 Computer Systems 9 EEE416 Biomedical Materials & Devices 9 ETH301 Pneumatics, Hydraulics & Refrigeration 9 OHS401 Occupational Health & Safety 5 Total CP 46 Trimester 3 EEB301 First Aid & Tower Safety 3 EEB400 Broadcast Engineering Fundamentals 6 EEB401 Audio/Video Equipment & Systems 6 EEB402 Broadcast Studios & Master Control Rooms 6 EEB403 Broadcast Chain & Auxiliary Services 6 EEB404 Digital Broadcasting Systems & Networking 7 EEB405 Transmitters, Antennas & Coupling Units; 7 Total CP 41 Trimester 1 COM401 Technical Communication II 10 MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 MEC450 Engineering Graphics 4 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 MEC470 Engineering Graphics Laboratory 6 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory / Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP 55 Trimester 2 MEC451 Engineering Mechanics 8 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics II 10 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics/Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming /Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 MEC452 Engineering Workshop Practice 5 MEC472 Engineering Mechanics Laboratory 2 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Lab / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP Laboratory / Electrical and Electronics COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK TRADE DIPLOMA IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (TRIMESTER MODE) 50 Trimester 3 EEE464 Electronic Measurement & Component 8 EEE465 Electrical and Mechanical Workshop 8 EEE466 Circuit Analysis 7 EEE467 Electrical Principles 7 EEE468 Engineering Computing 8 81 MEC557 Fundamentals of Mechanical Engineering. 6 EEE471 Circuit Analysis Laboratory 3 EEE472 Electrical Principles Laboratory 3 MEC570 Fundamentals of Mechanical Engineering Laborator 3 Total CP 53 Trimester 4 EEE585 Engineering Management 6 EEE542 Project I - Electrical 9 EEE543 Digital & Analog Electronic Engineering 7 EEE544 Renewable Energy Technologies 7 EEE545 Electrical Machines 7 EEE554 Computer System 7 EEE547 Electrical Machine Laboratory 7 EEE548 Electrical Machine Laboratory 3 EEE558 Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) & SCADA Laboratory 3 Total CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 82 56 Trimester 5 EEE570 Final Project II - Electrical 8 EEE571 Electrical Power Networks & Theorems 6 EEE572 Electrical Power Generation 6 EEE573 Electrical Power Transmission & Distribution 6 EEE574 Power Control Electronics 6 EEE575 Electrical Power Utilization & Design 6 EEE576 Electrical Circuit Design and Application 6 EEE577 Electrical Power Generation Laboratory 3 EEE578 Power Controls Electronic Laboratory 3 Total CP 50 TRADE DIPLOMA IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (SEMESTER MODE) SEMESTER 1 Unit code Unit Name SEMESTER 2 CP Unit code Unit Name CP EEE401 Engineering Mathematics 1 10 EEE407 Electrical and Mechanical Workshop 10 EEE402 Electrical Principles 2A 10 EEE408 Circuit Analysis 1 10 EEE403 Electrical Measurements and Components 8 EEE409 Engineering Computing 10 EEE404 Engineering Drawing 8 EEE410 Engineering Mathematics 2 10 EEE405 Engineering Science 10 EEE431 Electrical Principles 2B 8 COM401 Technical Communications 8 EEE433 Mechanical Principles 8 OHS403 Occupational Health and Safety 6 ETH401 Introduction to Ethics Values and Governance 9 Total CP 60 Total CP SEMESTER 3 65 SEMESTER 4 MGT402 Supervisory Studies 8 EEE506 Final Project 10 EEE437 Introduction to Electronics 10 EEE535 Electro Technology 10 EEE533 Electrical Machines 10 EEE536 Electrical Power Generation 10 EEE438 Renewable Energy Technology 10 EEE537 Electrical Power Transmission and Distribution 10 EEE505 Computer Systems 10 Electives - Select Two (2) elective depending on the area of specialisation. EEEXXX Elective 10 Total CP Electives - Select One (1) elective depending on the area of specialisation. 58 10 10 Total CP EEE517 60 Micro Controller Applications 10 EEE534 Electrical Applications 10 EEE519 Control Systems Engineering 10 EEE520 Programmable Logic Control 10 EEE534 Electrical Applications 10 EEE538 Electrical Power Utilization 10 EEE520 Programmable Logic Control 10 EEE509 Power Control Electronics 10 EEE539 Electrical Power Services 10 EEE510 Electronic Instrumentation 10 TRADE DIPLOMA IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (ELECTRONICS INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL (TRIMESTER MODE) Trimester 1 Technical Communication II 10 MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 MEC450 Engineering Graphics 4 PHY416/CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445 ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 MEC470 Engineering Graphics Laboratory 6 PHY470/CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory / Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP 55 Trimester 2 MEC451 Engineering Mechanics 8 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics II 10 MEC452 Workshop Practice 5 PHY416/CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 MEC472 Engineering Mechanic Laboratory 2 PHY470/CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory / Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP 50 Trimester 3 EEE463 Workshop Practice for Electronic Technician 6 EEE475 Digital Electronic I 7 EEE476 Analog Electronic I 7 EEE466 Circuit Analysis 7 EEE468 Engineering Computing 7 EEE467 Electrical Principles 7 EEE471 Circuit Analysis Laboratory 3 EEE472 Electrical Principles Laboratory 3 EEE478 Analog and Digital Electronics Laboratory 3 Total CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK COM401 50 Trimester 4 EEE550 Final Project I - Electronics 8 EEE551 Digital Electronics II 7 EEE552 Analog Electronics II 7 EEE583 Control System Engineering 7 83 EEE554 Computer System 6 EEE555 Computer Technology 6 EEE556 Analog II and Digital II Electronics Laboratory 3 EEE558 Computer Technology Laboratory 3 EEE558 Control System Engineering Laboratory 3 Total CP 50 Trimester 5 EEE560 Final Project II - Electronic 8 EEE585 Engineering Management 6 EEE559 Power Control Electronics 6 EEE580 Electronics Instrumentation 7 EEE581 Microcontrollers Application 8 EEE547 Programmable Logic Controllers(PLC) and SCADA 6 EEE578 Power Control Electronics Laboratory 3 EEE582 Electronic Instrumentation Laboratory. 3 EEE549 PLC and SCADA Laboratory 3 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Total CP TRADE DIPLOMA IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (ELECTRONICS INSTRUMENTATION AND CONTROL) (SEMESTER MODE) SEMESTER 1 Unit code SEMESTER 2 CP Unit code EEE401 Engineering Mathematics 1 10 EEE406 Workshop Practice 8 EEE402 Electrical Principles 2A 10 EEE408 Circuit Analysis 1 10 EEE403 Electrical Measurements and Components 8 EEE434 Digital Electronics 2A 10 EEE404 Engineering Drawing 8 EEE435 Analog Electronics 2A 10 EEE405 Engineering Science 10 EEE409 Engineering Computing 10 COM401 Technical Communications 8 EEE410 Engineering Mathematics 2 10 OHS403 Occupational Health and Safety 6 ETH401 Introduction to Ethics ,Values and Governance 9 Unit Name Total CP 60 Unit Name Total CP SEMESTER 3 CP 67 SEMESTER 4 COMPULSORY EEE540 Power Systems and Machines 10 MGT402 Supervisory Studies 8 EEE502 Digital Electronics 2B 10 EEE508 Final Project 10 EEE503 Analogue Electronics 2B 10 EEE509 Power Control Electronics 10 EEE504 Electronic Communication Systems 10 EEE510 Electronic Instrumentation. 10 EEE505 Computer Systems 10 ECI501 Certified Cisco Networking Associate 1 10 EEE507 Computer Technology 10 EEEXXX Electives 10 EEEXXX Electives 10 Total CP 60 Total CP 68 Choose 2 electives from EEE511 Electronic Communications Technology 10 EEE528 Microcontroller Applications 10 EEE521 Communications Measurements 10 EEE529 Control Systems Engineering 10 EEE523 Computer and Data Communications 10 EEE520 Programmable Logic Controller 10 EEE524 Television System 10 EEE525 Engineering Software 10 EEE526 84 50 Total CP PC Maintenance and Repair 10 60 Total CP 30 TRADE DIPLOMA IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (TELECOMMUNICATION AND NETWORKING) (TRIMESTER MODE) Trimester 1 Unit code Unit Name CP MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 MEC450 Engineering Graphics 4 CHM406/PHY416 Engineering Chemistry/Engineering Physics 8 CIN445/EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming/Introduction to Electrical and Electronic Engineering 8 OHS402/ETH401 Occupational Health & Safety/Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 COM401 Technical Communication 10 MEC470 Engineering Graphic Laboratory 6 CHM470/PHY470 Engineering Chemistry Laboratory/Engineering Physics Laboratory 2 CIN470/EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory/Introduction to Electrical and Electronic Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP 50 Trimester 2 Engineering Mathematics II 10 MEC451 Engineering Mechanics 8 MEC452 Engineering Workshop Practice 5 PHY416/CHM406 Engineering Physics/Engineering Chemistry 8 EEE460/CIN445 Introduction to Electrical and Electronic Engineering/Introduction to Computer Programming 8 ETH401/OHS402 Introduction to Ethics and Governance/Occupational Health & Safety 5 MEC472 Engineering Mechanic Laboratory 2 PHY470/CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory/Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 EEE470/CIN470 Introduction to Electrical and Electronic Laboratory/Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory 2 Total CP 50 Trimester 3 EEE463 Workshop Practice for Electronic Technician 7 EEE475 Digital Electronic I 7 EEE476 Analog Electronic I 7 EEE466 Circuit Analysis 7 EEE468 Engineering Computing 6 EEE467 Electrical Principles 7 EEE471 Circuit Analysis Laboratory 3 EEE472 Electrical Principles Laboratory 3 EEE478 Analog and Digital Electronics Laboratory 3 Total CP 50 Trimester 4 EEE550 Final Project I - Electronics 8 EEE551 Digital Electronic II 7 EEE552 Analog Electronic II 7 EEE553 Electronic Communication System I 7 EEE554 Computer System 6 EEE555 Computer Technology 6 EEE556 Analog and Digital Electronic Laboratory 3 EEE557 Electronic Communication System Laboratory 3 EEE558 Computer Technology Laboratory 3 Total CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK MTH504 50 Trimester 5 EEE560 Project II - Electronics 8 EEE585 Engineering Management 6 85 EEE559 Electronic Communication System Technology 6 EEE561 Computer and Data Communication 6 ECI501 Networking Fundamentals 6 EEE562 Engineering Software 6 EEE563 Radar and Microwave 6 EEE564 Electronic Communication System Laboratory 3 EEE565 Computer and Data Laboratory 3 Total CP 50 TRADE DIPLOMA IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (TELECOMUNICATION AND NETWORKING) (SEMESTER MODE) SEMESTER 1 Unit code Unit Name SEMESTER 2 CP Unit code CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK EEE401 Mathematics for Technicians 1 10 EEE406 Workshop Practice 8 EEE402 Electrical Principles 2A 10 EEE408 Circuit Analysis 1 10 EEE403 Electrical Measurements and Components 8 EEE434 Digital Electronics 1 10 EEE404 Engineering Drawing 8 EEE435 Analog Electronics 1 10 EEE405 Engineering Science 10 EEE409 Engineering Computing 10 COM401 Technical Communications 10 EEE410 Mathematics for Technicians 2 10 OHS403 Occupational Health and Safety 10 ETH401 Introduction to Ethics, Values and Governance 9 Total CP 66 Total CP SEMESTER 3 67 SEMESTER 4 COMPULSORY EEE540 Power Systems and Machines 8 MGT402 Supervisory Studies 8 EEE502 Digital Electronics 2 10 EEE508 Final Project 10 EEE503 Analog Electronics 2 10 EEE511 Electronic Communications Technology 10 EEE504 Electronic Communication Systems 10 EEE523 Computer and Data Communications 10 EEE505 Computer Systems 10 EEEXXX Elective 10 EEE507 Computer Technology EEEXXX Elective 10 Total CP 8 56 Total CP 58 SEMESTER 4 ELECTIVES - SELECT TWO UNITS FROM THE FOLLOWING ELECTIVES, DEPENDING ON THE AREA OF SPECIALISATION EEE521 Communications Measurements 10 EEE529 Control Systems Engineering 10 EEE524 Television System 10 EEE520 Programmable Logic Controller 10 EEE525 Engineering Software 10 EEE509 Power Control Electronics 10 EEE531 PC Maintenance and Repair 10 EEE510 Electronic Instrumentation 15 EEE528 Micro-controller Application 10 EEE532 Radar and Microwave 10 TRADE DIPLOMA IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (COMPUTING AND CONTROL) (SEMESTER MODE) SEMESTER 1 Unit code 86 Unit Name Unit Name SEMESTER 2 CP Unit code Unit Name CP EEE401 Mathematics for Technician 1 10 EEE406 Workshop Practice 8 EEE402 Electrical Principles 2A 10 EEE408 Circuit Analysis 1 10 EEE403 Electrical Measurements and Components 8 EEE434 Digital Electronics 2A 10 EEE404 Engineering Drawing 8 EEE435 Analog Electronics 2A 10 EEE405 Engineering Science 10 EEE409 Engineering Computing 10 COM401 Technical Communication 10 EEE410 Mathematics for Technician 2 10 OHS403 Occupational Health and Safety Total CP 10 66 ETH401 Introduction to Ethics, Values and Governance Total CP SEMESTER 3 9 67 SEMESTER 4 COMPULSORY EEE540 Power Systems and Machines 8 MGT402 Supervisory Skills 10 EEE502 Digital Electronics 2B 10 EEE508 Final Project 10 EEE503 Analogue Electronics 2B 10 EEE529 Control Systems Engineering 10 EEE504 Electronic Communication Systems 10 EEE528 Micro-Controller Applications 10 EEE505 Computer Systems 10 EEE509 Power Control Electronics 10 EEE507 Computer Technology 8 EEEXXX Elective 10 EEEXXX Elective 10 Total CP 56 Total CP 70 SEMESTER 4 ELECTIVES - SELECT ANY TWO FROM THE FOLLOWING ELECTIVES DEPENDING ON THE AREA OF SPECIALISATION Electronic Communications Technology 10 EEE520 Programmable Logical Controller 10 EEE521 Communication Measurements 10 EEE509 Power Control Electronics 10 EEE524 Television System 10 EEE510 Electronics Instrumentation 10 EEE523 Computer and Data Communications 10 EEE525 Engineering Software 10 EEE531 PC Maintenance and Repair 10 ADVANCED DIPLOMA IN ENGINEERING (ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS) (SEMESTER MODE) SEMESTER 1 Unit code Unit Name SEMESTER 2 CP Unit code Unit Name CP EEE601 Engineering Planning 10 EEE607 Electronic Technology (Telecommunication) 10 EEE602 Electrical Technology (Power Engineering and Control) 10 EEE608 Engineering Computations II 10 EEE604 Electronic Technology (Electronics) 10 EEE609 Engineering Technology Studies 10 EEE605 Engineering Mathematics 10 EEE610 Electrical Engineering Modeling 10 EEE606 Circuits and Signals 10 EEE611 Engineering Project 10 ETH501 Intermediate Ethics and Governance 11 EEE612 Electronic Technology (Microcontroller) 10 Total CP 61 Total CP 60 ELECTIVES – At least one (1) and not more than two (2) units may be selected from the following electives relevant to the area of specialization. *ELECTRONICS/TELECOMMUNICATION/ COMPUTER/CONTROL/ INSTRUMENTATION *ELECTRICAL EEE511 Electronics Communication Technology 10 EEE505 Computer Systems 10 EEE521 Communication Measurement 10 EEE529 Control Systems Engineering 10 EEE523 Computer and Data Communication 10 EEE536 Electrical Power Generation 10 EEE524 Television System 10 EEE537 Electrical Power Transmission and Distribution 10 EEE525 Engineering Software 10 EEE534 Electrical Applications 10 EEE531 PC Maintenance and Repair 10 EEE538 Electrical Power Utilization 10 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK EEE511 87 EEE529 Control Systems Engineering 10 EEE520 Programmable Logic Controller 10 EEE520 Programmable Logic Controller 10 EEE509 Power Control Electronics 10 EEE510 Electronic Instrumentation 10 EEE539 Electrical Power Services 10 10 EEE510 Electronic Instrumentation 10 Bachelor of Engineering Awards: • Bachelor of Engineering (Electrical & Renewable Energy) • Bachelor of Engineering (Telecommunication and Networking) • Bachelor of Engineering (Computer and Control) • Bachelor of Engineering (Electronics and Instrumentation) BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING (ELECTRICAL AND RENEWABLE ENERGY) Year 1 SEMESTER 1 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Unit code Unit Name SEMESTER 2 CP Unit code Unit Name CP LNG501 English for Academic Purposes 12 BEN506 Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering 12 BEN502 Engineering Computation I 12 BEN601 Engineering Computation II 12 BEN503 Engineering Physics 12 BEN507 Introduction to Computer Programming 12 BEN504 Engineering Graphics 12 BEN508 Engineering Mechanics 12 BEN505 Material Science 12 BEN509 Workshop Practice 12 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 Year 2 SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2 EEE601 Engineering Planning 12 EEE600 Design Project 12 EEE627 Logic Design 12 EEE603 Electrical Engineering Modeling 12 EEE681 Electro-technology 12 EEE661 Introduction to C++ Programming 12 EEE662 Engineering Software 12 EEE618 Mechatronics 12 EEE694 Engineering Mathematics III 12 EEE695 Engineering Mathematics IV 12 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 Year 3 SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2 EEE701 Fields & Waves 12 EEE707 Group Project 42 EEE761 PLC & SCADA Systems 12 EEE766 Microcontroller-Based System Design 9 EEE782 Electrical Machines 12 EEE706 Engineering & Society 9 EEE743 Control Systems Engineering 12 EEE784 Power Generation 12 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 Year 4 SEMESTER 1 Unit code 88 Unit Name SEMESTER 2 CP Unit code Unit Name CP EEE787 Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing 24 EEE786 Project II 24 EEE788 Power Transmission & Distribution 12 EEE791 Renewable Energy & New Technologies 18 EEE789 Power Utilization & Services 12 EEE790 Innovation Management & New Product Development 18 EEE785 Project 1 12 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING (TELECOMMUNICATIONS & NETWORKING) Year 1 SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2 LNG501 English for Academic Purposes 12 BEN506 Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering BEN502 Engineering Computation I 12 BEN601 Engineering Computation II 12 BEN503 Engineering Physics 12 BEN507 Introduction to Computer Programming 12 BEN504 Engineering Graphics 12 BEN508 Engineering Mechanics 12 BEN505 Material Science 12 BEN509 Workshop Practice 12 Total CP 60 Total CP 12 60 Year 2 SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2 Engineering Planning 12 EEE600 Design Project 12 EEE627 Logic Design 12 EEE603 Electrical Engineering Modeling 12 EEE681 Electro Technology 12 EEE618 Mechatronics 12 EEE662 Engineering Software 12 EEE661 Introduction to C++ Programming 12 EEE694 Engineering Mathematics III 12 EEE695 Engineering Mathematics IV 12 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 Year 3 SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2 EEE701 Fields & Waves 12 EEE707 Group Projects 42 EEE748 Telecommunication Systems 12 EEE745 Introduction To Computer Networking 9 EEE747 Radio Frequency (RF) Principles 12 EEE706 Engineering & Society 9 EEE743 Control Systems Engineering 12 EEE750 Digital Communication 12 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 Year 4 SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2 EEE787 Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing 24 EEE786 Project II 24 EEE793 Communication Theory 12 EEE794 Mobile & Personal Communication Systems 18 EEE790 Innovation Management and New Product Development 18 EEE792 Antennas and Propagation 12 EEE785 Project I 12 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING (COMPUTER & CONTROL) Year 1 SEMESTER 1 Unit code LNG501 Unit Name English for Academic Purposes SEMESTER 2 CP 12 Unit code Unit Name CP BEN506 Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering 12 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK EEE601 89 BEN502 Engineering Computation 1 12 BEN601 Engineering Computation II 12 BEN503 Engineering Physics 12 BEN507 Introduction to Computer Programming 12 BEN504 Engineering Graphics 12 BEN508 Engineering Mechanics 12 BEN505 Material Science 12 BEN509 Workshop Practice 12 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 Year 2 SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2 EEE601 Engineering Planning 12 EEE600 Design Project 12 EEE627 Logic Design 12 EEE603 Electrical Engineering Modeling 12 EEE681 Electro Technology 12 EEE618 Mechatronics 12 EEE662 Engineering Software 12 EEE661 Introduction to C++ Programming 12 EEE694 Engineering Mathematics III 12 EEE695 Engineering Mathematics IV 12 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Year 3 SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2 EEE701 Fields & Waves 12 EEE707 Group Project 42 EEE767 Computer Architecture 12 EEE745 Introduction To Computer Networking 9 EEE743 Control Systems Engineering 12 EEE706 Engineering & Society 9 EEE768 System Programming & System Control 12 EEE769 Advanced Programming Language 12 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 Year 4 SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2 EEE787 Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing 12 EEE786 Project II 24 EEE795 Artificial Intelligence & Robotics 12 EEE797 Microprocessor Systems & Embedded Systems 18 EEE796 VHDL and Logic Synthesis 12 EEE790 Innovation Management & New Product Development 18 EEE785 Project - Industry 24 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING (ELECTRONICS & INSTRUMENTATION) Year 1 SEMESTER 1 Unit code SEMESTER 2 Unit Name CP Unit code Unit Name CP LNG501 English for Academic Studies 12 BEN506 Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering 12 BEN502 Engineering Computation I 12 BEN601 Engineering Computation II 12 BEN503 Engineering Physics 12 BEN507 Introduction to Computer Programming 12 BEN504 Engineering Graphics 12 BEN508 Engineering Mechanics 12 BEN505 Material Science 12 BEN509 Workshop Practice 12 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 Year 2 SEMESTER 1 EEE601 90 Engineering Planning SEMESTER 2 12 EEE600 Design Project 12 EEE627 Logic Design 12 EEE603 Electrical Engineering Modeling 12 EEE681 Electro Technology 12 EEE618 Mechatronics 12 EEE662 Engineering Software 12 EEE661 Introduction to C++ Programming 12 EEE694 Engineering Mathematics III 12 EEE695 Engineering Mathematics IV 12 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 Year 3 SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2 EEE701 Fields & Waves 12 EEE707 Group Project 42 EEE761 PLC & SCADA Systems 12 EEE714 Industrial Instrumentation 9 EEE713 Principles of Measurement & Instrumentation I 12 EEE706 Engineering & Society 9 EEE743 Control Systems Engineering 12 EEE723 Industrial Electronics 12 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 SEMESTER 2 EEE787 Fundamentals of Digital Signal Processing 12 EEE786 Project II 24 EEE796 VHDL and Logic Synthesis 12 EEE797 Microprocessor Systems & Embedded Systems 18 EEE798 Industrial Measurement & Instrumentation II 12 EEE790 Innovation Management & New Product Development 18 EEE785 Project I 24 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 SHORT PROGRAMME IN ELECTRICAL SERVICEMAN’S COURSE (ESC) General Guidelines The prerequisite units must be completed before enrolment is allowed in the dependent unit. E.g. EEE211 Applied Electricity 1 must be passed before enrolment in EEE121 Applied Electricity 2. STAGE 1 Unit Code EEE211 EEE212 Unit Name Applied Electricity 1 Electrical Wiring 1 (Practical) STAGE 2 CP Unit Code Unit Name 4 EEE221 Applied Electricity 2 4 EEE222 Electrical Wiring 2 (Practical) STAGE 3 CP Unit Code 4 EEE330 4 EEE331 Unit Name Stator Winding (Theory and Practical) Armature Winding (Theory and Practical) CP 4 4 SHORT PROGRAMME IN RADIO, ELECTRONICS AND TELEVISION SERVICEMAN’S COURSE General Guidelines The Prerequisite units must be completed before enrolment is allowed in the dependent unit. E.g. EEE201 Basic Electronics must be passed before enrolment in EEE282 Radio and TV Servicing. STAGE 1 STAGE 2 STAGE 3 Unit Code Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name CP Unit Code EEE201 Basic Electronics 4 EEE282 Radio and TV Servicing 4 EEE332 4 EEE285 4 EEE333 EEE202 Workshop Practice (optional) Radio and TV Workshop Unit Name Colour TV and VCR Servicing Colour TV and VCR Workshop COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Year 4 SEMESTER 1 CP 4 4 Alternative Pattern Other patterns of attendance are possible, subject to student demand, staff availability and compliance with specified Prerequisites. 91 NOTE: For full time students, the normal pattern of attendance allows the programme to be completed over three, 8 weeks pensters, on a part -time basis. Students are recommended to obtain work experience between stages, but may proceed directly to the next stage, subject to the requirements specified for industrial attachment. Sponsored students normally attend on a ‘stage release’ basis and obtain work experience between stages. CISCO Local Academy CISCO Certified Network Associate Cisco Networking Academy provides online courses, interactive tools, and lab activities to help individuals develop the skills needed to fill ICT positions in virtually every type of industry. The Cisco CCNA® Discovery curriculum provides foundational networking knowledge, practical experience, opportunities for career exploration, and softskills development to help students prepare for entry-level careers in IT and networking. Students who enroll in CCNA Discovery are not expected to have any previous technical skills or knowledge, aside from basic PC skills. The Students who have completed Form-4 study (FJC, Fiji Junior Certificate) are encouraged to attend the CCNA Discovery course for further IT & ICT career opportunities. The certificate is issued by the Cisco Networking Academy, USA. The certificate is internationally recognized by both local and overseas employers & institutions. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK CCNA There is, of course, the four (4) module course for Certified Cisco Networking Associate (CCNA) for school leavers at year 12 and working people who have interest in a career in IT or ICT industries. CISCO Certification in Semester Mode Unit Code Unit Name CP Stage 1 ECI503 Introduction to Network 10 Routing & Switching Essential 10 Scaling Network 10 Connecting Network 10 Stage 2 ECI504 Stage 3 ECI603 Stage 4 ECI604 LOCATIONS: Derrick Campus Namaka Campus Ba Campus Labasa Campus Job Opportunities Job opportunities for Electrical and Electronic Engineering Certificate, Certificate IV, and Trade Diploma, Advanced Diploma or Bachelor of Engineering holders are available both locally and abroad since these qualifications are recognised all over the World. A number of places of work that can readily provide opportunities for employment are the local electrical and electronics contractors and repair shops, hotel industries, government departments, sugar industries, food processing industries, biomedical engineering in hospitals, garment industries, Fiji Electricity Authority, telephone communication, switching and networking with Telecom Fiji, satellite communications links like in FINTEL, computer industries, airline industries including aircrafts and air terminal services, marine and land transport industries and other information and communication technology and/or allied industries, broadcasting systems, IT industry, in radio stations or audio visual engineering in television or film industry. The opportunities have quite a wide spectrum. Besides, FNU’s electrical and electronic graduates enjoy performing tasks and carrying out responsibilities and challenges from workshop level to above middle level management. This speaks about the credibility, recognition and acceptance of the school’s qualification. 92 NOTE: All the certificate IV and Trade Diploma Programmes are also offered in Trimester mode from 2014 onwards. For Further information, kindly contact the HOS/SEEE. Unit Descriptors BMT451: Introduction to Bio-Informatics This is an interdisciplinary field which this unit provides so that students make effective use of biomedical data and information for scientific inquiry, problem solving, and decision making to improve human health. It also provides an introduction to biomedical informatics. A variety of data and text mining techniques are introduced and applied to study practical problems in biological sciences, clinical medicine and public health. The unit introduces also the students to data and computer communication technology. BMT472: Biomedical Instrumentation This is unit intended for those specialising in biomedical engineering systems – with particular emphasis on the subject matter that will enable the students to learn the basic principles of different instruments/equipment used in the health care industry. The practical work done in this area will impart skills in the use, servicing and maintenance of this instruments/equipment. EEB301: First Aid & Tower Safety This unit will empower the student with necessary knowledge skills and attitude to be able to identify hazards, take preventice actions and perform first aid when needed. EEB400: Broadcast Engineering Fundamentals This unit will introduce the student to the standards and pracitices used in radio and television broadcasting EEB401: Audio/Video Equipment & Systems This unit will introduce the student to the technology used in the audio & video industry and the principles in which they operate. EEB402: Broadcast Studios & Master Control Room (MCR)This unit will introduce the student to the standards and practices used in radio and television studios & master control rooms (MCR) and associated equipment. EEB403: The Broadcast Chain & Auxiliary Services This unit will introduce the student to the technology and methods used in transferring the broadcast signal from the studio to the transmission station and from outside venues to the broadcast studios for live feeds or ingestion. EEB404: Digital Broadcasting Systems & Networking This unit will introduce the student EEB405: Transmitters, Antennas & Coupling Units This unit will empower the student with the required knowledge, attitude and skills to be able to work safely and efficiently in a broadcast transmission facilities. EEE201: Basic Electronics The purpose of this unit is to provide a basic knowledge and understanding of electricity and electronics in general. This knowledge shall be reinforced during practical sessions for clearer understanding. Thus through this unit there can be an understanding of basic concepts involved in electricity and electronics phenomena. EEE202: Workshop Practice (Optional) The overall purpose of this unit is to develop the manual and tool based skills which are required for the installation, servicing and maintenance of electronic equipments. This unit is mainly concerned with tools and techniques associated with wiring and circuit. EEE211: Applied Electricity 1 The purpose of this unit is to introduce students to safety, theoretical aspects of the fundamentals of Electrical principles, components and circuits. EE212: Electrical Wiring 1 (Practical) The purpose of this unit is to introduce students to the practical aspects of the fundamentals of Electrical wiring and circuits and wiring diagrams. EEE221: Applied Electricity 2 The overall purpose of this unit is to provide students some knowledge of machines and transformers. EEE222: Electrical Wiring 2 (Practical) This unit is to provide knowledge of electrical wiring and installation and be more familiar with standards and by laws of supply authorities like Fiji Electricity Authority (FEA). EEE282: Radio and TV Servicing The purpose of this unit is to provide students an understanding of the principles involved in radio and television circuitry. EEE285: Radio and TV Workshop This unit is primarily concerned with the practical training and exposure to relevant equipment’s. The students will be exposed to servicing radio and television and acquire workshop skills. EEE301: Mathematics for Trade The purpose of this unit is to develop skills in performing calculations of the type required for electrical trade work. This is primarily concerned with reinforcing the basic mathematical principles taught in high school and developing skills in applying this mathematical to COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK BMT471: Biomedical Materials and Devices This is a unit which is intended for those who need to develop knowledge and application skills in biomedical engineering materials and devices. In the delivery of this unit, emphasis will be placed on integrating the ‘theoretical’ and ‘practical’ aspects of materials and devices. In particular, this will involve the extensive ‘hands-on’ use of materials and devices, for programme composition in medical and biomedical application for biocompatibility. to digital broadcasting, High Definition systems, streaming session and broadcast computer networking and interconnections. 93 problems of the type found in the electrical trade. EEE302: Electrical Principles 1A This is the first of three units, the overall purpose of which is to provide the foundation in Electro technology required by all electronics trade personnel, irrespective of their area of specialization. This unit covers the basic principles of electrodynamics, electrostatics, magnetism and electromagnetism. EEE303: Workshop Practice 1A This is one of a set of units, the overall purpose of which is to develop the manual and tool based skills which are required for the construction, installation and maintenance of electronic equipment. This unit is mainly concerned with the fabrication and maintenance of sheet metal and plastic enclosures and fittings COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 94 EEE304: Workshop Practice 1B This is one of a set of units, the overall purpose of which is to develop the manual and tool based skills which are required for the construction, installation and maintenance of electronic equipment. This unit is mainly concerned with tools and techniques associated with wiring and circuit construction. EEE305: Electrical Measurements The main purpose of this unit is to develop basic skills in the use of electrical instruments and measurement techniques. It is also intended to assist students in understanding the concepts covered in the unit, Electrical Principles 1, through the use of instruments to demonstrate basic electrical and electromagnetic phenomena and laws. EEE306: Engineering Drawing The purpose of this unit is to develop basic skills in the preparation and interpretation of engineering drawings relevant to electronics trade personnel. EEE307: Electrical Principles 1B The overall purpose of this unit is to provide the foundation in electro technology required by all electronics trade personnel, irrespective of their area of specialization. This unit provides students with an understanding of the sources of electromotive force (emf) and develops skills in the analysis of simple single phase alternating current circuits. EEE308: Workshop Practice 2 This is one of a set of units, the overall purpose of which is to develop the manual and tool based skills which are required for the construction, installation and maintenance of electronic equipment. This unit is mainly concerned with the construction, testing and maintenance of printed circuit boards. EEE309: Electronics Fundamentals The purpose of this unit is to provide an understanding of electronic fundamentals and to develop basic skills in the prototype construction and testing of simple electronic circuits EEE310: Components and Measurements The purpose of the MEASUREMENTS section of this unit is to further develop skills in the use of electrical instruments and measurement techniques, with particular emphasis on the testing of ac circuits. The purpose of the COMPONENT section of the unit is to develop an understanding of the construction, characteristics and applications of the basic passive components used in electronics. This unit is also intended to support the unit, Electrical Principles 2, through laboratory assignments which involve the evaluation of ac circuits. EEE321: Basic Craft Skills 1A (Fitting) This is one of a set of units, the overall purpose of which is to develop the manual and tool based skills which are required for the construction, installation and maintenance of electrical equipment and services. This unit is mainly concerned with the development of skills in the use of hand and machine tools for fabrication and fitting. EEE322: Basic Craft Skill 1B (Electrical Builders) The purpose of this unit is to develop the manual and tool based skills which are required for the construction, installation and maintenance of electrical equipment and services. This unit is mainly concerned with the development of skills in the use of hand and machine tools for the installation of electrical services and equipment’s in buildings. EEE324: Engineering Drawing 1 The overall purpose of this unit is to develop skills in the preparation and interpretation of engineering drawings relevant to electrical trade personnel. EEE325: Craft Science for Electricians The purpose of this unit is to provide an understanding of the non-electrical areas of engineering science required by electrical trade personnel. EEE326: Basic Craft Skills 2 (Welding and Fabrication) The overall purpose of this unit is to develop the manual and tool based skills which are required for the construction, installation and maintenance of electrical equipment and services. This unit is mainly concerned with the development of skills related to welding and fabrication EEE327: Craft Calculations 2 This is the second of two units, the overall purpose of which is to develop skills in performing calculations of the type required for electrical trade work. EEE328: Engineering Drawing 2 The overall purpose of this unit is to develop skills in the preparation and interpretation of engineering drawings relevant to electrical trade personnel. EEE329: Electrical Principles (Trade) 1 The overall purpose of this unit is to provide the foundation in electro-technology required by electrical trade personnel. This unit covers the basic principles of electrodynamics, electrostatics, magnetism and electromagnetism. EEE330: Stator Winding (Theory and Practical) The purpose of this unit is to provide students the knowledge and skills of stator windings, tests and methods of finding faults and remedies. EEE331: Armature Winding (Theory and Practical) The purpose of this unit is to provide students the knowledge and skills of Armature windings, tests and methods of finding faults and remedies. EEE333: Color TV and VCR Workshop This unit is primarily concerned with the practical training and exposure to relevant equipment. The students will be exposed to servicing color TV and VCR and acquire workshop skills EEE344: Electrical Principles (Trade) 3 The overall purpose of this is to provide the foundation in electro-technology required by electrical trade personnel. This unit is primarily concerned with three phase circuits and basic power control electronics. EEE391: Electrical Principles (Trade) 2 The overall purpose of this unit is to provide the foundation in electro-technology required by electrical trade personnel. This unit provides students with an understanding of the performance of basic passive components in ac circuits and develops skills in ac circuit analysis. EEE392: Electronics for Electricians 1 The purpose of this unit is to develop skills required by electricians for the installation and maintenance of electronic systems and equipment’s. EEE394: Electrical Testing The purpose of this unit is to develop skills in the use of electrical instruments and measurement techniques for the testing of electrical installations and equipment. EEE395: Electrical Installation Technology A The overall purpose of this unit is to develop an understanding of the basic principles, characteristics and application of the technology used in electrical installations. EEE396: Electrical Installation Practical A The overall purpose of this unit is to develop skills in the installation, testing and maintenance of electrical services and equipment. EEE401: Engineering Mathematics 1 EEE402: Electrical Principles 2A The overall purpose of this unit is to provide the foundation Electro technology required by all electrical engineering paraprofessional irrespective of their area of specialization. This unit reviews and extends the coverage of the basic principles electrodynamics, electrostatics, magnetism and electromagnetism which taught in High School and develops skills in the application of these principles in an engineering context. EEE403: Electrical Measurements and Components The overall purpose of the measurements section of this unit is to develop those basic skills, in the use of electrical instruments and measurement techniques, which are required by all electrical engineering paraprofessional and the Components section of the unit is to develop an understanding of the construction, characteristics and applications of the basic electrical. EEE404: Engineering Drawing This unit develops basic skills in the preparation and interpretation of engineering drawings, required by all electrical engineering paraprofessionals, irrespective of their area of specialization. The areas of the drawing include Principles of Orthogonal and Pictorial Projection, 3D free hand sketches, interpretation of circuit and wiring diagrams with standards and Basic features of CAD. EEE405: Engineering Science This unit provides the foundation in the non-electrical areas of engineering science required by all electrical engineering paraprofessionals, irrespective of their area of specialization. This unit develops skills in the application of these principles in an engineering context. EEE406: Workshop Practice The purpose of this unit is to develop the manual and tool based skills. This unit deals with safety rules, codes and laws relevant to electrical/electronic workshop practice, mechanical operations and methods to produce printed circuit boards. EEE407: Electrical and Mechanical Workshop The purpose of this unit is to develop the manual and tool based skills required by those specializing in units leading to the Diploma in Electrical Engineering (Electrical) award. It prepares student for workshop safety, size and shape ferrous/nonferrous metals, lathe turning, craft skills, welding, TPS cables installations for lightings and GPO’s, and wiring motor control circuits. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK EEE332: Color TV and VCR Servicing The purpose of this unit is to provide the students with a good understanding of the basic principles involved in radio and television and supported by an elaborate and relevant workshop with industrial exposure and practical experience. The overall purpose of this unit is to provide the foundation in applied mathematics required by all electrical engineering paraprofessionals, irrespective of their area of specialization. This unit is primarily concerned with reinforcing the basic mathematical principles taught in High School and developing skills in applying this mathematics to problems of the type found in electrical engineering. 95 EEE408: Circuit Analysis 1 The purpose of this unit is to provide the foundation in dc and ac circuit analysis required by all electrical engineering paraprofessionals, irrespective of their area of specialization. EEE409: Engineering Computing This unit provides an understanding of how computers are used in the solution of engineering problems and to develop skills in the use of computer based simulation software for the analysis of circuits and systems relevant to all areas of electrical engineering and also designed to develop skills which can be used to facilitate the analysis and understanding of circuits and systems in other units, by reducing the human component of the computational process. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 96 EEE410: Engineering Mathematics 2 The purpose of this unit is to provide students with a broader range of mathematical tools, relevant to all areas of electrical engineering and to further develop skills in applying this mathematics in an engineering context In the delivery of this unit, emphasis will be place on teaching mathematical principles at a level of abstraction which ensures an understanding of their universality, while also ensuring that students are able to apply mathematics to specific problems which are relevant to engineering. EEE411: Electrical Principles 1C This is the third of three units, the overall purpose of which is to provide the foundation in electro technology required by all electronics trade personnel, irrespective of their area of specialization. This unit provides students with an understanding of frequency response, resonance, transmission lines, transformers and machine fundamentals. It also further develops skills in measuring circuit and device performance. EEE412: Digital Electronics 1A The overall purpose of this unit is to provide students with an understanding of the basic principles of digital electronics and to develop skills in the use of instruments and measurement techniques to evaluate the performance of digital devices and circuits. This unit is mainly concerned with basic logic functions and gates, flip flops and simple combinational logic and sequential circuits.Prerequisites: Successful completion of Stage 2 EEE413: Analog Electronics 1A The overall purpose of this unit is to provide students with an understanding of the basic principles of analog electronics and to develop skills in the use of instruments and measurement techniques to evaluate the performance of analog devices and circuits. This unit is mainly concerned with basic linear amplifying devices and circuits. EEE414: Computer Applications The purpose of this unit is to provide an understanding of how computers are used in the solution of engineering problems and to develop skills in the use of computer software for the analysis of circuits and systems relevant to electronics. This unit is also designed to develop skills which can be used to facilitate the analysis and understanding of circuits and systems in other units, by reducing the human component of the computational process and allowing students to concentrate on problem formulation and the interpretation of results. EEE415: Electronic Communication Systems 1 The overall purpose of which is to provide students with a broad overview of the main types of electronic communications systems and to develop skills in using Instruments and measurement techniques to evaluate the performance of these systems. This unit is primarily concerned with analog communication systems. EEE416: Workshop Practice 3 This is one of a set of units, the overall purpose of which is to develop the manual and tool based skills which are required for the construction, installation and maintenance of electronic equipment. This unit further develops skills in the construction, testing and maintenance of printed circuit boards. EEE417: Digital Electronics 1B This is the second of two units, the overall purpose of which is to provide students with an understanding of the basic principles of digital electronics and to develop skills in the use of instruments and measurement techniques to evaluate the performance of digital devices and circuits. This unit is mainly concerned with device families, MSI devices, A/D and D/A conversion and display devices. EEE418: Analog Electronics 1B The overall purpose of this unit is to provide students with an understanding of the basic principles of analog electronics and to develop skills in the use of instruments and measurement techniques to evaluate the performance of analog devices and circuits. This unit further develops knowledge and skills related to amplifying devices and circuits and cover the basic principles of waveform generators and optoelectronic and power control devices and circuits. EEE419: Computer Systems 1 The COMPUTER APPLICATIONS unit is primarily concerned with the use of specific applications software. This unit is designed to provide a more detailed understanding of the operation of computer systems, with particular emphasis on the role and use of system software. EEE420: Electronic Communication Systems 2 The overall purpose of this unit is to provide students with a broad overview of the main types of electronic communications systems and to develop skills in using instruments and measurement techniques to evaluate the performance of these systems. This unit covers digital communication systems, multiplexing, satellite communications, cellular phone systems, optical fiber communication and antennas. Prerequisites: Successful completion of Stage 3 EEE421: Electronics Project This is a compulsory unit which is intended to provide students with the opportunity to undertake largely selfdirected work, which involves the analysis, construction and testing of an electronic circuit or system and the oral and written reporting of results. EEE422: Television Systems This is an elective unit intended for those specializing in video communication technology – with particular emphasis on developing understanding and skills related to the operation, testing, installation and maintenance of television receivers. EEE424: Radio Receivers and Transmitters This is an elective unit intended for those specializing in electronic communication technology with particular emphasis on developing understanding and skills related to the construction, testing, installation and maintenance of radio receivers and transmitters. EEE425: Audio Equipment and Systems This is an elective unit intended for those specializing in electronic audio Technology – with particular emphasis on developing understanding and skills related to the operation, testing, installation and maintenance of audio equipment and systems. EEE426: Computer and Data Communication This is an elective unit intended for those specializing in computer and data communication technology – with particular emphasis on developing understanding and skills related to the operation, testing, installation and maintenance of computer and data communication systems EEE427: Computer Technology This is an elective unit intended for those specializing in computer technology – with particular emphasis on developing an understanding of the basic principles of computer architecture and the characteristics, functions and performance of microprocessors. EEE428: Computer Peripherals This is an elective unit intended for those specializing in computer technology – with particular emphasis on developing understanding and skills required for the installation, testing and servicing of the peripheral devices associated with personal computer systems. EEE429: Computer Systems 2 EEE430: PC Servicing This is an elective unit intended for those specializing in computer technology – with particular emphasis on developing understanding and skills required for the installation testing and servicing of personal computer systems. EEE431: Electrical Principles 2B This unit develops understanding and skills related to the operation and performance of basic electrical equipment and circuits. It includes Operation Principles of AC/DC Generators, Single and 3 phase AC current circuits and waveforms, Self and Mutual Inductances, Transformer operation Principles and Construction and Uses of appropriate instruments and techniques for circuit testing. EEE432: Computer and Information The purpose of this unit is o provide an understanding of how computers are used in solutions of engineering problems and to develop skills in the use of computer for the analysis of circuits and systems relevant to hospitality engineering. This unit is also designed to develop skills which can be used to facilitate the analysis and understanding of circuits and systems in other units, by reducing the human component of the computational process and allowing students to concentrate on problem formulation and the interpretation of results. EEE433: Mechanical Principles The purpose of this unit is to develop an understanding of the principles and technology which govern the operation and performance of the electromechanical equipment. It includes problems related Gas Laws, Energy Cycles, Gas & Steam turbine operation Principle, Functions of control for Prime Movers and equipment’s tests within the scope of this unit. EEE438: Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) This unit is intended to prepare students for control technology and systems, with particular emphasis on developing understanding and skills required for the analysis, testing, installation and maintenance of programmable logic control equipment. Prerequisites: Successful completion of Stage 4 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK EEE423: Video Recorders This is an elective unit intended for those specializing in video communication technology – with particular emphasis on developing understanding and skills related to the operation, testing, installation and maintenance of video recorders. This is an elective unit intended for those specializing in computer technology – with particular emphasis on developing understanding and skills related to the operation, testing and maintenance of microprocessors based systems. EEE445: Electrical Installation Technology B The overall purpose of this unit is to develop an understanding of the basic principles, characteristics and application of the technology used in electrical installations. EEE446: Electrical Installation Practical B The overall purpose of this unit is to develop skills in the installation, testing and maintenance of electrical services and equipment’s. 97 EEE447: Electrical Machines The overall purpose of this unit is to develop understanding and skills related to the construction, operation and performance of electrical machines. This unit is mainly concerned with DC machines and induction motors. understanding of the operation of computer systems, with particular emphasis on the role and use of system software. This unit is also designed to develop basic skills in computer programming, using a structured high level language.Prerequisites: Successful Completion of Semester 2 EEE448: Electronics for Electricians 2 The purpose of this unit is to develop skills required by electricians for the installation, testing and maintenance of electronics systems and equipment’s. EEE507: Computer Technology The purpose of this unit is to develop an understanding of the basic principles of computer architecture and the characteristics, functions and performance of microprocessors and to develop skills in programming at assembly level. EEE449: Electrical Installation Technology C The overall purpose of this unit is to develop an understanding of the basic principles, characteristics and application of the technology used in electrical installations. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK EEE450: Electrical Installation Practical C The overall purpose of which is to develop skills in the installation, testing and maintenance of electrical services and equipment’s. EEE451: Electrical Measurements and Machines The purpose of this unit is to develop understanding and skills related to the construction, operation and performance of electrical machines. This unit is mainly concerned with transformers and synchronous machines and also further develops skills in the use of instruments for power circuit measurements. EEE452: Electrical Machines Practical (Winding) The purpose of this unit is to develop skills in the installation, testing, maintenance and repair of electrical machines and associated equipment’s. EEE502: Digital Electronics 2B The purpose of this unit is to provide a more detailed and extensive coverage of digital electronics. This unit further develops skills in the use of analytical techniques and instrument based measurements to evaluate the performance of digital electronic circuits – with an emphasis on the integration of the `theoretical` and `practical` aspects of the unit. EEE503: Analog Electronics 2B The purpose of the unit is to provide a more detailed and extensive coverage of analog electronics, for those specializing in electronics based units. This unit further develops skills in the use of analytical techniques and instruments to evaluate the performance of analog electronic circuits – with an emphasis on the integration of the ‘theoretical’ and ‘practical’ aspects of the unit. EEE504: Electronic Communication Systems The purpose of this unit is to provide students with a broader overview of the main types of electronic communication systems and to develop skills in using instruments to evaluate the performance of these systems. 98 EEE505: Computer Systems This unit is designed to provide a more detailed EEE508: Final Project In this unit students are required to undertake largely self-directed work, which involves the analysis, construction and testing of a circuit, system or piece of equipment and requires the oral and written reporting of results. EEE509: Power Control Electronics This unit is primarily concerned with those specializing in the application of electronics to the control of power systems. Topics include power control devices, control circuits, rectifiers, inverters, process control, AC motors and DC motors. EEE510: Electronics Instrumentation This is an elective unit intended for those specialising in control technology and systems, with particular emphasis on the electronic instrumentation used in control systems. EEE511: Electronic Communications Technology This particular unit emphasis on developing understanding and skills required for the analysis, testing, installation and maintenance of devices and circuits used in communication systems. EEE520: Programmable Logic Controller This is an elective unit intended for those specialising in control technology and systems, with particular emphasis on developing understanding and skills required for the analysis, testing, installation and maintenance of programmable logic control equipment. EEE521: Communications Measurement This particular unit emphasis on developing understanding and skills related to the instruments and measurement techniques used for testing communication systems and equipment. EEE523: Computer and Data Communications The purpose of this unit is to develop understanding and skills required for the analysis, testing, installation and maintenance of data communication equipment and systems. EEE524: Television System This unit is designed to develop understanding and skills related to the operation, testing installation and maintenance of video transmitting, receiving and recording equipment. EEE525: Engineering Software The purpose of this unit is to develop more advanced skills in computer programming. This unit involves the extensive ‘hands-on’ use of computer facilities, for program composition and execution. EEE528: Microcontroller Applications This is an elective unit which is intended for those who need to develop application skills in microcontroller projects. In the delivery of this unit, emphasis will be placed on integrating the ‘theoretical’ and ‘practical’ aspects of microcontroller. In particular, this will involve the extensive ‘hands-on’ use of microcontroller facilities, for program composition and electronic/ electrical circuit extension. EEE531: PC Maintenance and Repair The purpose of this unit is to develop understanding and skills required for the installation, testing and servicing of computer systems and associated equipment. EEE532: Radar and Microwave This is an elective unit intended for those specializing in radar and microwave communication technology – with particular emphasis on basic knowledge to develop an understanding of the principles and acquired skills and techniques used for this communication systems and equipment. EEE533: Electrical Machines This unit is designed to develop understanding and skills related to the operation and performance of electrical machines, for those specializing in units leading to the award of the Diploma in Electrical Engineering (Electrical). Topic includes motors, transformers and synchronous machines. EEE534: Electrical Applications The purpose of this unit is to prepare those students who want to study major in electrical and allied services in the electrical industry and to give exposure towards public supply systems and its security. EEE535: Electro Technology This unit further develops analytical skills and the understanding of circuit operation, with particular emphasis on circuits and components relevant to power system technology. EEE536: Electrical Power Generation This is an elective unit intended for those specializing in electrical power systems, with particular emphasis on developing understanding and skills required for EEE537: Electrical Power Transmission and Distribution This is an elective unit intended for those requiring an understanding of the equipment and techniques used in the transmission and distribution of electrical power. EEE538: Electrical Power Utilization This is an elective unit intended for those requiring expertise in the utilization of electrical energy. It includes tariffs, Lighting design, and Refrigeration plant, Air Conditioning, Electric Process heating and Energy Management. EEE539: Electrical Power Services This is an elective unit intended for those requiring expertise in the selection of systems and equipment used in the provision of a range of electrical services. This introduces Prediction of energy requirements, lighting, distribution and drive equipment’s and alarm systems for industrial applications. EEE540: Power Systems and Machines This unit is designed to develop understanding of the basic principles of electric power systems and machines for those specializing in electronics. Particular attention is given to the characteristics and applications of the low power machines commonly found in electronic systems which involve an integrated approach to the analytical and experimental evaluation of machine performances and the development of skills in testing and fault diagnosis. EEE600: Design Project In this unit, students working as a group are required to undertake largely self-directed work, which involves the analysis, construction and testing of a circuit, system or piece of equipment and requires the oral and written reporting of results. EEE601: Engineering Planning This unit is intended to give students an appreciation of the principles of project planning and management, and how to apply this knowledge to a wide range of engineering projects. EEE602: Electrical Technology (Power Engineering and Control) The purposes of this unit are two folds. These are: Power engineering in which it provides students with grounding in the chief components of the electrical theory that underlies the discipline of Electrical Power Engineering. These include the principles of power electronics, power transformers, harmonics, and public utility systems and unbalance three phase loads. Control in the unit will provide a fundamental knowledge of control and instrumentation. EEE603: Electrical Engineering Modeling The purpose of this unit is for the use of a “problem COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK EEE529: Control Systems Engineering This unit is intended for those specialising in electrical/ electronic control technology and systems. Topics include performance term, control system, signal conditioning and controllers and correction unit. the design, operation and maintenance of generating stations. 99 knowledge of the complex world of engineering. In this unit the students will build on the problem-solving skills developed in earlier units while acquiring, mastering and assimilating new knowledge and techniques into the area of study. EEE604: Electronic Technology (Electronics) This module introduces the major analog and digital electronic devices and equipment. There will be an involvement of the design, examination, analysis and evaluation of these systems on the basis of their characteristics parameters. This unit involves the use of suitable software packages for design and evaluation and analysis. It will embrace also their application in power engineering, instrumentation and control. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK EEE605: Engineering Mathematics The purpose of this unit is to further develop skills in the use of mathematical tools to solve problems relevant to electrical engineering. Topics include complex numbers, Laplace transform, matrix, integration and Fourier analysis. EEE606: Circuits and Signals This unit develops the background of circuit theory to enable students to have an understanding of the fundamental principles which underlie the more applied modules. The unit also covers the basic elements of discrete signal analysis, the importance of Fourier analysis, and the underlying concepts of radio communications. EEE607: Electronic Technology (Telecommunications) This module deals with the major areas of electronics in communication engineering: It gives an overview of how data communications take place by understanding the concepts of information theory. It covers topics such as transmission media, modulation techniques, communication networks and error performance of both analog and digital communication systems. EEE608: Engineering Computations II The purpose of this module is to continue the process of equipping students with mathematical skills and methods appropriate to engineering; and to provide students with a sound mathematical base necessary to pursue an understanding of advanced calculus, and the ability to formulate and solve models of complex engineering systems. EEE609: Engineering Technology Studies This module gives students an appreciation of the principles and practice of management and how to apply this knowledge to a wide range of engineering situations. Also gives an awareness of the structures and functions of engineering organizations. 100 EEE610: Electrical Engineering Modelling The purpose of this module is for the use of a ‘problem based learning approach’ to extend the students knowledge of the complex world of engineering. In this unit the students will build on the problem solving skills developed in earlier units while acquiring, mastering and assimilating new knowledge and techniques into the area of study. Students will be required to develop skills in programming using MATLAB. EEE611: Engineering Project This module provides an introduction to the process of a technical project including time management, cooperative working, documentation, reporting and presentation skills as well as the technical skills required to complete the project. EEE612: Electronic Technology (Microcontroller) This module touches on microcontrollers and their related onboard devices. The principles of program design and structured design programming are included. A high level language is used to program the control and status registers of these onboard devices, to implement control programs. This includes programming the ADC, serial, timers and interrupt systems. EEE618: Mechatronics The purpose of this unit is to provide a foundation for those specializing in electronics and instrumentation (and control) the principles, modeling, interfacing and signal conditioning of motion sensors and actuators; hardware-in-the-loop simulation and rapid prototyping of real-time closed-loop computer control electro mechanically systems. It also deals with modeling, analysis and identification of discrete-time or samples-data dynamic systems and commonly used digital controller design methods. It provides also an introduction to non-line effects and their compensation in mechatronic systems. EEE627: Logic Design I The purpose of these units is to further develop skills in the use of mathematical tools to solve problems relevant to electrical engineering EEE661: Introduction to C++ Programming The purpose of this unit is to further provide a foundation in programming for those specializing in computer engineering–with particular emphasis on developing programming skills through the use of the C++ language. Here the students will learn procedural programming, object based programming and objectoriented programming and relate to a variety of real applications EEE662: Engineering Software This is the unit which is intended for the student to show the need to develop more advanced skills in computer programming because of the nature of their work that is mostly computer based. In the delivery of this unit, emphasis will be placed on rating the ‘theoretical’ and ‘practical’. Aspects of computing in particular, this will involve the extensive ‘hands-on’ use of computer facilities, for program composition and execution. There will be also an introduction to the use of SCADA software and its application in control. EEE681: Electro-technology The purpose of this unit is to further develop analytical skills and the understanding of circuit operation,with particular emphasis on circuits and components relevant to power system technology. The students should be able to analyze circuits using techniques like Laplace transforms and its inverse EEE706: Engineering & Society The purpose of this unit is to give students an appreciation of the principles and practice of management and how to apply this knowledge to a wide range of engineering situations. It also provides an awareness of the structures and functions of engineering organizations and their operations and control from a managerial and financial perspective. Students will also have a notion of the economics overview EEE707: Group Project In this unit the students will be working in groups of two only and are required to undertake largely self-directed work, which involves the analysis, construction and testing of a circuit, system or piece of equipment and requires the oral and written reporting of results. EEE713: Principles of Measurement & Instrumentation This unit is intended for those specializing in electronics and instrumentation engineering. It introduces them to the concept of measurement and the related instrumentation requirement as a vital ingredient of a vast area of engineering including the electronics and communication engineering. This unit prepares the students to be able to control and manage systems under their charge. It should also provide the basis EEE714: Industrial Instrumentation This unit is intended for those specializing in electronics and instrumentation engineering. It introduces them to the concept of measurement and the related instrumentation requirement as a vital ingredient of avast area of engineering including the electronics and communication engineering. This unit prepares the students to be able to control and management of systems under their charge. It should all so the basis for further studies and development of this area of engineering. EEE723: Industrial Electronics This is intended for those specializing in the application of electronics to the control of power systems and other similar systems. It introduces students to feedback and non-feedback system and the conditions or stability. It should also the basis for further studies and development to this area of engineering under their charge. It should also form the basis for further studies and development to this area of engineering. EEE743: Control Systems Engineering This unit is intended for those specializing in electrical/ electronic control technology and systems and to prepare them for control and management of systems under their charge. It should also provide the basis for further studies and development of this area of engineering. EEE745: Introduction to Computer Networking In this unit the students will be working in groups of two only and are required to undertake largelyself-directed work, which involves the analysis, construction and testing of a circuit, system or piece of equipment and requires the oral and written reporting of results. EEE747: Radio Frequency (RF) Principles The objectives of the course are to introduce students to the basic RFcomponents, sub-systems, and their applications in the design of modern wireless communications. During the course, examples from real RF systems are presented and discussed. EEE748: Telecommunication Systems This course aims to explain and analyze the communication systems used in analogue and digital communication systems. To do this, a survey of linear analogue and digital modulation is given. Comparisons are made between practical modulation schemes in the presence of noise in terms of bandwidth, signalto-noise ratio and complexity. The course then looks state principles and practice of coding for reliable and efficient communication over noisy channels. EEE750: Digital Communication The purpose of this unit is to provide a good understanding of digital transmission techniques, emphasizing important concepts and features of digital radio systems. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK EEE694: Engineering Mathematics III The purpose of this unit is to continue the process of developing the concepts and techniques of calculus and line algebra appropriate to engineering; and to provide students with a sound mathematical base necessary to pursue higher studies in mathematics. EEE695: Engineering Mathematics IV The purpose of this module is for the use of a “problem based learning approach’ to extend the students’ knowledge of the complex world of engineering. In this unit, the students will build on the problem solving skills developed in earlier units while acquiring, mastering and assimilating new knowledge and techniques in to the area of study. EEE701: Fields and Waves This unit intends to cover the fundamental principles of the physics of electricity and magnetism. It begins with the fundamental physics of Maxwell’ equations and how the Ohms Law and Kirchoff’s current and voltage laws are a natural result. The mathematical concepts of electrostatics, magneto statics, and vector calculations underpin the more complex electrical engineering topics in later units. Transmission lines are included as a practical application of the non-trivial issues that arise in the design and application of high frequency circuits and systems for further studies and development of this area of engineering. 101 EEE761: PLC&SCADA Systems This is a unit intended for those specializing in control and instrumentation technology and systems, with particul are emphasis on developing understanding and skills required for the analysis, testing, installation and maintenance of programmable logic control equipment. This is also for larger systems control and monitoring to even extra-large capacity. SCADA is introduced as the data acquisition system for local and extended vicinities. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 102 EEE766: Microcontroller Based System Design This purpose of this unit is to teach students design and interfacing of microcontrollerBased embedded systems In particular, this will involve the extensive ‘hands-on’ use of microcontroller facilities, for program composition and electronic/electrical circuit extension. High-level languages are used to interface the microcontrollers to various applications. Further the internal structure and operation of microcontrollers will be studied and the design methodology for software and hardware applications will be developed through the labs and design projects. There are extensive hands-on labs/projects. Embedded system for sensor applications will be introduced. GUI using C# will be introduced. There will be additional projects for students. Students will be expected to develop independence and learn much of the material on their own. EEE767: Computer Architecture The purpose of this unit is to develop an understanding of the basic principles of computer architecture and their characteristics, functions and performance. A parallel studies against the current computer architecture and performance shall be studied in some detail. It is also to provide the foundation to develop skills in programming application software with computer controls. EEE768: System Programming and System Control The purpose of this unit is to show students the principles and methodologies a computer tool that is able to today’s society of operating system, as the name tells the uniqueness of this special kind of programming systems is related to the latest development. For details about such uniqueness, we have an entire semester to elaborate. EEE769: Advanced Programming Language The purpose of this unit is to further provide an in depth study of programming concepts and programming for those specializing in computer engineering–with particular emphasis on developing programming skills through the use of the C++ language. Here the students will learn more procedural programming, object- based programming and object-oriented programming and relation variety of real time applications EEE782: Electrical Machines This unit is designed to develop understanding and skills related to the operation and performance of electrical machines, for those specializing in units leading to the award of the Bachelor of Electrical Engineering (Electrical & Renewable Energy).This should prepare the students for a good understanding of machines types, function principles and application. EEE784: Power Generation This unit is intended for those specializing in electrical power systems, with particular emphasis on developing understanding and skills required for the design, operation and maintenance of generating stations. Acquaint engineering students with power generation systems, their operation in an economic mode, and their control. It also introduces students to the important “terminal” characteristics for thermal and hydroelectric power generation systems. EEE785: Project I & EEE786: Project II In this unit students are required to undertake selfdirected work, which involves the analysis, construction and testing of a circuit, system or piece of equipment and require the oral and written reporting of results. This major project in the final year of study takes several forms ranging from design oriented work to investigative work. The project title and topic are chosen to provide intellectual challenge appropriate to final year honors study and the student is expected to firstly identify and elucidate the problems, then plan and execute a relevant programme of work. Assessment is ongoing through the project via an individual supervisor or group of supervisors , culminating with a comprehensive report of work done in the form of thesis. EEE787: Fundamentals of Digital signal processing This unit is to prepare trainee engineers for digital signal processing (DSP) that is concerned with their presentation of signal by a sequence of numbers or symbols and the processing of these signals. Digital signal processing analog signal processing are subfields of signal processing. DSP includes subfields like: audio and speech signal processing on radar signal processing, sensor array processing, spectral estimation, statistical signal processing, digital image processing, signal processing for communications, biomedical signal processing, seismic data processing, etc.. EEE788: Power Transmission &Distribution This unit is intended for electrical engineering major students who require an understanding of the equipment and techniques used in the transmission and distribution electrical power. Thus the students shall be familiar with the function of different components used in Transmission and Distribution levels of power systems, and modeling of these components. EEE789: Power Utilization and Services This unit is intended to provide the students with the expertise in the utilization and application of electrical energy in a variety of situations whether domestics or industrial. It shall provide them with skills and knowhow of load demands from consumers and how to provide the appropriate electrical service they desire with safety protection in mind. The students shall also have an in-depth knowledge of tariffs. EEE790: Innovation Management & New Product Development The purpose of this unit is to give students the background products and innovation management and how to apply this knowledge to a wide range of engineering situations particularly in search of solution to the present problem. Prerequisites: Successful completion of Semester 1 of Y4 EEE792: Antennas and Propagation The purpose of this unit is to introduce the fundamentals of propagation and antennas with primary applications to the field of mobile telecommunication. It will include modeling aspects of the wireless communication channel and design principles of antenna rays utilized in communications. EEE793: Communication Theory The purpose of this unit is to introduce the basic concepts behind the advanced communication systems including widely used equalizers, multi-carrier transceivers for data transmission channels with moderate/severe inter-symbol interference (ISI) EEE794: Mobile and Personal Communication Systems The unit is intended for students of communication engineering to extend their theoretical knowledge and understanding to the field of mobile radio communication design. It prepares students in the theory that supports the practical design and development of mobile radio For More Information Contact: EEE795: Artificial Intelligence & Robotics This unit is to prepare trainee engineers to develop a computer application, which encompasses perception, reasoning and learning and to provide an in-depth understanding of major techniques used to simulate intelligence. Further, it is to introduce the students to basics of modeling, design, planning, and control of robot systems. In essence, the material treated in this course is a brief survey of relevant results from geometry, kinematics, statics, dynamics, and control. EEE796: VHDL & Logic Synthesis The purpose of this unit is to train students to describe a digital system at the structural or the behavior al level. It provides an understanding that behaves or at level can be further divided into data flow and algorithmic whereas the structural level mimics the actual physical level. The unit is also provided and insight into what is typically done in terms of data flow between registers (Register Transfer level). EEE797: Microprocessor Systems and Embedded Systems The purpose of this unit is for students to write programs for low power embedded devices that communicate with other computers or devices to solve practical problems. The course will cover the relevant theoretical knowledge required for writing such applications, and provide practical experience in writing C programs for Atmel microprocessors. The unit will also give students an appreciation for some of their search issues in low power embedded systems. EEE798: Industrial Measurement & Instrumentation 2 The unit is intended for those specializing in electronics and instrumentation engineering. It introduces them to the concept of measurement and the related instrumentation as a vital ingredient to a vast area of engineering including electronics and communication engineering. It should also provide the basis for further studies and development in this area of engineering. Dr. Arif Khan Head of School (HE) Phone: 3381 044, Ext :1149 E-mail: HOS-SEEE@fnu.ac.fj COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK EEE791: Renewable Energy and New Technologies The purpose of this unit is to give students the background of some conventional renewable energy methodologies and examine how they can be improved through innovation for efficiency and improvements. Though ambitious, the ultimate intention is the development of these technologies at commercial level. It is also intended through this unit to apply a wide range of engineering situation or opportunities for the purpose of generating clean energy for household to start with. transmitters, receivers and antenna systems in VHF and UHF ranges which are configured for high capacity mobile telephone communication in the commercial and noncommercial environment. Mr. Jiuliasi V Uluiburotu Head of School (TVET) E-mail:HOS-Electrical@fnu.ac.fj Phone: 3381044 Ext : 1976 OA- Ms. Varsha Ext: 1148 E-mail:oa-seee@fnu.ac.fj OA- Ms. Mereisi Ext: 1501 E-mail:OA-Electrical@fnu.ac.fj 103 School of Mechanical Engineering General Information Mechanical Engineering is a diverse field and one of the broadest engineering disciplines. It is diverse in a sense that it involves from tiny measuring instruments to huge aircraft carriers or power plants. It plays a role in manufacturing, environmental control, transportation, renewable energy, and much more. Mechanical Engineering and its allied fields COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK are involved in multifaceted functions such as testing, evaluation, distributing and marketing the devices they create and manufacture. They are working on power equipment, refrigeration and air conditioning, machine tools, material handling systems and industrial production equipment. In addition, mechanical engineers work in manufacturing or agriculture production, maintenance and technical sales; many become administrators or managers The School of Mechanical Engineering offers exciting engineering programmes from Certificate IV to Trade Diploma and Bachelor level to employers, employees and forms 6 and 7 school leavers who wish to pursue their career in the engineering field. Staff Profile HIGHER EDUCATION STAFF HEAD OF SCHOOL JOJI MARAU MISAELE MSc. Mechanical Engineering, B.E. Mechanical, Diploma Mechanical Engineering. Ordinary Diploma in Mechanical Engineering. DR ANIL RANA Ex-Commander (Indian Navy, Retd.); Ph.D. Reliability Engineering), M Tech (Industrial Tribology);MDBA (Finance); B Tech (Mechanical Engineering) PROFESSOR SIDDH NATH SINGH Ph.D.(Mech.Eng.), MSc(Mech.Eng.), BSc(Mech.Eng.) SENIOR LECTURER MR. RAJESH KANTHI GOUD Masters in Mechanical Engineering (Spl. Structural Mechanics)Blekinge Institute of Technology Sweden, B.Tech in Production Engineering (D.V.R College of Engg. & Technology) LECTURER II DR DELLENA GLORIA ALAGCAN PhD Communities Development; MSc in Agro Business; BSc Agriculture Eng; Registered Professional Agricultural Engineer MOHAMMED NIZAM KHAN B. E Tech (GCED) 104 TUTOR ALVIN AJNESH LAL OFFICE ADMINISTRATOR LAVENIA MAUREEN DOMINIKO Bachelors in Management, Dip. in Business (Office Admin); Dip. in Business (Management); Cert. Junior Secretarial Studies; Certificate in Shorthand Speed. TVET STAFF HEAD OF SCHOOL RATU TOUTOU B Mech Eg. (Hons); Advance Dip Mech Eng; Dip Mech Eng;TCert Fab/Weld);Cert 3D Modelling using Solid Works Software HEAD OF DEPARTMENT RUDRA NAND BEd; IDTT, Adv Trade Cert. (Shipbuilding); Trade Cert. (Shipbuilding); Trade Cert. (Fabrication and Welding). Welder Class 1 FNTC. LECTURER I BASDEO LAL BE (Agriculture); Dip. (Trop. Agri.); Voc.Teach.Cert LECTURER II TAOBA VOLA BERA Diploma in Agriculture Engineering LAGI CAMA BAILEY B.Ed; Cert IV (Assessment and Workplace Training) (Tundra AU); Trade Cert. (Fitting and Machining), IDTT. WILLIAM BENJAMIN BROWN Cert. (Agricultural Eng.); IDTT; Int.Dip. (Educational Management) KITIONE SUMASAFU FESAITU Dip. (Mechanical Eng.); Trade Cert. (Fitting and Machining); IDTT ALIPATE KAU GONEROGO Trade Cert. (Refrigeration and Air-conditioning) VAFOOU KAMEA Adv. Dip.(Mechanical Eng.); Trade Cert. (Fitting and Machining) RONIL RAVINESH NADAN Trade Cert. (Refrigeration and Air-conditioning) KAYLESH CHANDRA B.Ed. (TVET): New Zealand Cert. (Engineering/ Production)International Diploma in Tertiary Teaching VASENAI KERENI DANIAL ABHILAKH MAHARAJ Dip. Mech Eng.; Dip Plant Eng ; T/Cert. In Ref &AIrcon; Cert. in Training of Trainers; Class 2 Trade Test Engineer; Best Apprentice – Gold Medalist (FNTC) KELEPI NABANIVALU Ordinary Dip in Mechanical Engineering;Teaching Cert. (Adult Education), ; Trade Cert. (Fitting and Machining) PENAIA ROGOIMURI BE (Mechanical), University of Auckland; MechEng CERT; Associate. Dip. (Electronics Eng.); IDTT MELTON BRIDGE STEVEN SIMMONS M(Ed); PGD (TVET) ; BEd (TVET); Cert. IV (Workplace Training and Assessment (TUNDRA AU); International Diploma in Tertiary Teaching; Adv.Dip. (Mechanical Eng.); Dip. (Mechanical Eng.); Ordinary Dip.(Mechanical Eng.); Trade Cert. ILIESA CAMA TADULALA Dip.(Mech.Eng.), Trade Cert. (Fabrication and Welding) USAIA SOTUTU TAGI MSc (Industrial Design); BSc(Hon’s)(Computer Aided Product Design); International Dip. Ed; Trade Cert. (Weld and Fabrication); Cert. (Infor. / Tech) ACA STANLEY ULUIVITI Trade Cert. (Refrigeration and Air-conditioning) TUTORIAL ASSISTANT JIALE COLATANAKADAVU LITIDAMU Trade Certificate (Fabrication and Welding) TECHNICIAN JEFFERY AUGUSTUS MATTHIAS, Dip (Mechanical Eng); Trade Certificate (Automotive) FAZIL BEGG, Advance Diploma Mechanical Engineering; Diploma Mechanical Engineering Diploma Plant Engineering TANIELA TOKALAU RATUKANIA, Trade Certificate (Fitting & Machining); Cert. of Apprentice (Craft Apprenticeship); Trade Course Certificate (Course of Instruction); Certificate in Computer Training (NZ PTC); Diploma in Education (Industrial Arts); Training of Trainers Module 1 AMINIASI QALIVUTU Trade Cert. (Fitting and Machining) NAVNEEL NILESHWARA NAND OFFICE ADMINISTRATOR SUNITA SHARMA BA (Accounting & Information Systems) COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK PATRICK MICHAEL Trade certificate in Fitting & Machining (Apprenticeship);Ordinary Diploma in Mechanical engineering; Diploma in Mechanical Engineering; Certificate IV in Workplace Assessment TUTOR ATUNAISA LEWENILOVO Dip. (Mechanical Eng.) Tech. Apprentice, Cert Tertiary Teaching, Cert III TIG. Welding, Cert Firefighting AKANISI TEVULU VARANI Trade Cert. (Refrigeration and Air-conditioning) ASSISTANT LECTURER RAJNEEL CHANDRA Trade Cert. (Fabrication and Welding) DEWENDRA DEO Trade Cert. (Refrigeration and Airconditioning) 105 Programme Details and Duration Certificate IV level Trade Diploma level Bachelor of Engineering (Semester) Penster Trimester Semester Trimester 27 units 20 units 25 units 40 units 8 5 pensters 3 trimesters 4 semesters 5 trimesters 8 semesters 5 5-7 6 6-9 4 Number of weeks per period 8 weeks 15 weeks 18 weeks 15 weeks 18 weeks Minimum period required for industrial attachment 12 months 12 months 12 months 6 months 3 - 6 months Minimum period of time to complete the whole programme 2 ½ years 2 years 2 years 2 years 4 years Total Number of units to complete the programme Number of period to complete all units Number of units to complete in each period COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Trimester Mode Programmes for 2016 The College is offering Certificate IV and Trade diploma in Trimester Mode from 2014 onwards. For any enquiry on the trimester mode programmes for 2016 please contact the Head of School. Entry Qualifications Certificate IV Programmes 200 out of 400 marks in Form 6 with minimum of 50% in any 4 subjects. Trade Diploma Programmes Pass in Form 6 with 200 out of 400 marks with 50% minimum marks in English, Mathematics, Physics, and any other 1 relevant subject. Bachelor of Engineering (4 majors) Pass in Form 7 with 280 out of 400 marks with pass (50% or more) in English, Mathematics, Physics and any other 1 Science or Technology subject OR Foundation Science with GPA of 3.00 or more. Programmes CERTIFICATE IV PLANT MAINTENANCE (PENSTER MODE) PENSTER 1 Unit Code Unit Name PENSTER 2 CP Unit Code Unit Name CP PLM301 Basic Machining Processes 5 PLM303 Bearing and Lubrication 5 MEN305 Workshop Science 4 MEN304 Workshop Calculations 4 CIN301 Computer Use and Applications 12 MEN303 Trade Drawing A 4 COM201 Technical Communication 1 7 MEN302 Welding Process 4 PLM304 Basic Machining Practice 5 PLM302 Installation Practice 5 OHS401 Occupational, Health and Safety 1 10 Fundamentals of Ethics 5 Total CP 43 Total CP PENSTER 3 PLM406 Heat Engines 27 PENSTER 4 6 PLM409 Hydraulics and Pneumatics 5 PLM411 Heat Engine Practice 6 PLM408 Power Transmission 5 MEN306 Applied Materials 4 PLM407 Lifting and Mechanical Handling 4 MEN418 Computer Aided Design(CAD) 4 ACR228 Building Services 5 MEN308 Electrical Principle 4 PLM401 PM Practice A 5 Total CP 24 Total CP 24 PENSTER 5 106 PLM404 Maintenance Technology 6 PLM405 Steam Plant A 6 PLM403 Plant Technology 5 PLM402 PM Practice B 5 PLM411 Heat Engine Practice 6 PLM408 Power Transmission 5 MEN306 Applied Materials 4 PLM407 Lifting and Mechanical Handling 4 MEN418 Computer Aided Design(CAD) 4 ACR228 Building Services 5 MEN308 Electrical Principle 4 PLM401 PM Practice A 5 Total CP 24 Total CP 24 PENSTER 5 PLM404 Maintenance Technology 6 PLM405 Steam Plant A 6 PLM403 Plant Technology 5 PLM402 PM Practice B 5 PLM410 Industrial Automation 4 Total CP 24 CERTIFICATE IV PLANT MAINTENANCE (TRIMESTER MODE) Trimester 1 Unit Code Unit Name CP Basic Machining Processes 5 MEN305 Workshop Science 4 CIN301 Computer Use and Applications 12 COM201 Technical Communication 1 7 PLM304 Basic Machining Practice 5 OHS401 Occupational, Health and Safety 1 10 Total CP 43 Trimester 2 Unit code Unit Name CP PLM421 Fundamentals of Heat Practices 9 PLM422 Electro Hydrolics and Pneumetics 9 ACR325 Engineering Building Sevices 4 MEN315 Introduction to Mechanics 5 PLM423 Industrial Instrumentation and PLC Control 9 MEN428 AutoCAD and Introduction to Solid Works 8 FWG316 Welding Processes and Practice 6 Total CP 50 Trimester 3 PLM424 Plant Preventive Maintenance and Management 9 PLM425 Plant Engineering Technology 9 PLM426 Steam Power Plant 10 PLM427 Mechanical Power Transmission 9 EEE312 Electrical and Electronic Principle and Testing Equipment 5 MEN429 3D-CAD Using Solid Works 8 Total CP 50 CERTIFICATE IV AGRICULTURAL ENGINEERING Trimester 1 Unit Code Unit Name COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK PLM301 CP FMG317 Basic Machining Processes and Practice 8 MEN315 Introduction to Mechanics 5 MEN316 Engineering Drawing 6 COM301 Technical Communication 4 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 1 3 MEN318 Engineering Workshop Calculation 4 AGE350 Integrated Farming Systems and Practice 9 AGE351 Agricultural Farm Surveying & Leveling 8 107 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethical Practices 5 Total CP 52 Trimester 2 AGE450 Farm Irrigation Drainage & Practice 10 AGE451 Farm Power and Mechanization Systems 10 AGE452 Tractor Operation & Management 10 AGE453 Farm Environment & Agri-ecosystems 9 EEE312 Electrical and Electronic Principle and Testing Equipment 5 FWG316 Welding Processes and Practice 6 Total CP 50 Trimester 3 AGE461 Farm Management & Rural Enterprise Development 10 AGE462 Farm Structures, Buildings and Construction Practices 10 AGE463 Farm Implements, Cultivation and Maintenance Practice 10 AGE470 Engineering Project 1 10 AGE464 Post-Harvest Process and Practice 10 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Total CP 50 CERTIFICATE IV IN FABRICATION AND WELDING (PENSTER MODE) STAGE 1 Unit Code Unit Name STAGE 2 CP Unit Code Unit Name CP FWG315 Fabrication Drawing A 4 COM201 Technical Communication 4 FWG311 Fabrication Technology A 4 FWG321 Fabrication Technology B 5 FWG313 Welding Technology A 4 FWG322 Fabrication Practice B 5 FWG312 Fabrication Practice A 4 CIN301 Use of Computers 12 FWG314 Welding Practice A 4 FWG323 Trade Calculations 4 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 10 Total CP 30 Total CP 30 STAGE 3 STAGE 4 MEN306 Applied Materials A 4 FWG441 Fabrication Technology C 4 FWG431 Welding Technology B 4 FWG442 Fabrication Practice C 4 FWG433 Fabrication Drawing B 4 FWG443 Welding Technology C 5 FWG432 Welding Practice B 4 FWG444 Welding Practice C 4 MEN308 Electrical Principle 4 FWG445 Trade Science 5 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethics 5 Total CP 25 Total CP 22 STAGE 5 FWG453 Fabrication Drawing C 5 MEN418 Computer Aided Design (CAD) 4 FWG451 Fabrication Technology D 4 FWG454 Fabrication and welding Project 5 FWG452 Welding Technology D 4 Total CP 22 CERTIFICATE IV IN FABRICATION AND WELDING (TRIMESTER MODE) Trimester 1 108 COM301 Technical Communication 5 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 1 3 FWG332 Welding Technology 1 13 FWG331 Fabrication Technology 1 13 FWG333 Fabrication Drawing 1 8 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethical Practices 5 FWG334 Fabrication and Welding Calculations 6 Total CP 53 Trimester 2 FWG411 Fabrication Drawing 2 5 FWG335 Welding Engineering Materials and Application 6 FWG412 Welding Technology 2 13 FWG414 Welding Science 8 FWG413 Fabrication Technology 2 13 EEE312 Electrical and Electronic Principles and Testing Equipment 5 Total CP 50 Trimester 3 Fabrication Technology 3 6 FWG422 Welding Technology 3 6 FWG424 Fabrication and Welding Project 16 FMG 317 Basic Machining Processes and Practice 8 FWG421 Fabrication Drawing 3 6 MEN428 AutoCAD and Introduction to Solid Works 8 Total CP 50 CERTIFICATE IV IN FITTING AND MACHINING (TRIMESTER MODE) Trimester 1 Unit Code Unit Name CP FMG321 Fitting and Machining Process 1 8 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 1 3 MEN316 Engineering Drawing 6 FWG316 Welding Process & Practice 6 FMG322 Fitting and Machining Practice 1 11 FMG323 Sheetmetal Fitting Practice 1 8 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethical Practice 5 MEN318 Engineering Workshop Calculation 4 Total CP 51 Trimester 2 FMG324 Fitting and Machining Process 2 8 FMG423 Applied Engineering Drawing 8 COM301 Technical Communication 4 PLM421 Fundamentals of Heat Engines 9 EEE312 Electrical and Electronic Principles and Testing Equipment 5 FMG325 Machining Practice 2 11 MEN315 Introduction to Mechanics 5 Total CP 50 Trimester 3 FMG426 Specialized Machining Processes including CNC. 7 FMG419 Applied Engineering Material Process 10 FMG425 Applied Measurement and Inspection 4 FMG428 Diagnostics and Maintenance 11 FMG427 Specialized Machining Practice 10 MEN428 AutoCAD and Introduction to Solid Works 8 Total CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK FWG423 50 TRADE DIPLOMA IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING (TRIMESTER MODE) Trimester 1 Unit Code COM401 Unit Name Technical Communication CP 10 109 MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 MEC450 Engineering Graphics 4 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/ EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 MEC470 Engineering Graphics Laboratory 6 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/ EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory / Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP 55 Trimester 2 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK MEC451 Engineering Mechanics 8 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics II 10 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/ EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming /Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 EWP452 Engineering Workshop Practice 5 MEC472 Engineering Mechanics Laboratory 2 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Lab / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/ EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory / Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP 50 Trimester 3 MEC551 Engineering Analysis with MATLAB 6 MEC552 Strength of Materials 7 MEC554 Production Technology 7 MEC555 Engineering Thermodynamics 7 MEC558 Mechanics of Fluid and Machinery 8 MEC559 Engineering Materials 8 MEC578 Mechanics of Fluid and Machinery Laboratory 2 MEC571 Engineering Materials Laboratory 2 MEC573 Workshop Practices I 3 Total CP 50 Trimester 4 MEC561 Manufacturing Technology 7 MEC562 Plant Machinery Technology 7 MEC563 Thermal Engineering 7 MEC564 Machine Design 7 MEC565 Introduction to Solid Works 7 MEC560 Engineering Management 7 MEC575 Computer Numerical Control Lab 3 MEC576 Heat Power Engineering Laboratory 2 MEC577 Workshop Practices II 3 Total CP 50 Trimester 5 110 MEC680 Engineering Project 10 MEC566 Instrumentation and Controls 8 MEC567 Power Plant Engineering 8 EEE 547 Programmable Logic Controller 8 MEC569 Maintenance Management 8 MEC581 Instrumentation and Controls - Laboratory 2 EEE558 Programmable Logic Controller - Laboratory 3 MEC583 Power Plant Engineering Laboratory 3 Total CP 50 TRADE DIPLOMA IN MEHANICAL ENGINEERING (DME) (SEMESTER MODE) STAGE 1 Unit Code Unit Name STAGE 2 CP Unit Code Unit Name CP Technical Communication II 10 CIN410 Micro Computers Application 8 PEN401 Mechanical Science A 10 PEN405 Material Science 10 PEN402 Engineering Drawing 10 PEN501 Mechanical Science B 10 PEN403 Thermodynamics A 10 PEN417 Production Technology B (DME) 10 MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics II 10 PEN407 Production Technology A (DME) 10 PEN406 Workshop Practice 10 Total CP 60 Total CP STAGE 3 PEN502 Computer Aided Design 2 (CAD) 58 STAGE 4 14 PEN409 Power Plant 5 10 PEN504 Plant Engineering 10 PEN500 Mechanical Engineering Project PEN410 Fluid Mechanics A 10 PEN506 Fluid Mechanics B 10 PEN503 Thermodynamics B 10 PEN508 Instrumentation and Control 10 PEN511 Electrical Electronics for Mechanical Engineering 10 PEN509 Manufacturing Technology (DME) 10 PEN510 Machine Design 10 ETH401 Introduction to Ethics and Governance 10 64 Total CP Total CP 55 Electives MGT402 Supervisory Studies 10 PEN513 Engineering Economics 10 PEN516 Accounting for Engineers 10 PEN514 Logic Controls 10 PEN512 Refrigeration and Air-conditioning Engineering 10 PEN515 Quality Assurance 10 Total CP 60 TRADE DIPLOMA IN PLANT ENGINEERING (SEMESTER MODE) STAGE 1 Unit Code Unit Name STAGE 2 CP Unit Code Unit Name CP COM401 Technical Communication 2 10 CIN410 Micro Computers Application 14 PEN401 Mechanical Science A 10 PEN405 Material Science 10 PEN402 Engineering Drawing 10 PEN501 Mechanical Science B 10 PEN403 Thermodynamics A 10 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics II 10 MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 PEN406 Workshop Practice 10 PEN404 Plant Technology (DPE) 10 PEN408 Plant Technology B 10 Total CP PEN502 60 Computer Aided Design 2 (CAD) 14 Total CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK COM401 64 PEN409 Power Plant 5 10 10 PEN504 Plant Engineering 10 PEN500 Mechanical Engineering Project PEN410 Fluid Mechanics A 10 PEN506 Fluid Mechanics B 111 PEN503 Thermodynamics B 10 PEN508 Instrumentation and Control 10 PEN511 Electrical Electronics for Mechanical Engineering 10 PEN509 Manufacturing Technology (DME) 10 PEN510 Machine Design 10 ETH401 Introduction to Ethics and Governance 9 PEN505 Plant Management (DPE) 10 Total CP 60 Total CP 64 Electives MGT402 Supervisory Studies 10 PEN513 Engineering Economics 10 PEN516 Accounting for Engineers 10 PEN514 Logic Controls 10 PEN512 Refrigeration and Air-conditioning Engineering 10 PEN515 Quality Assurance 10 TRADE DIPLOMA IN AGRICULTURAL ENGINEERING Trimester 1 Unit Code CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK MEC551 Engineering Analysis with MATLAB 6 MEC552 Strength of Materials 7 MEC554 Production Technology 7 MEC555 Engineering Thermodynamics 7 MEC558 Mechanics of Fluid and Machinery 8 MEC559 Engineering Materials 8 MEC578 Mechanics of Fluid and Machinery Laboratory 2 MEC571 Engineering Materials Laboratory 2 MEC573 Workshop Practices I 3 Total CP 55 Trimester 2 MEC451 Engineering Mechanics 8 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics II 10 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/ EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming /Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 EWP452 Engineering Workshop Practice 5 MEC472 Engineering Mechanics Laboratory 2 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory/Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/ EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory / Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory Total CP 2 50 Trimester 3 AGE520 Agriculture for Engineers 8 AGE521 Farm Surveying and Levelling 8 MEC558 Fluid Mechanics and Machinery 8 AGE523 Engineering Statistics 6 AGE524 Basic Manufacturing Technology 6 MEC559 Engineering Materials 8 MEC571 Engineering Materials Laboratory 2 AGE575 Basic Manufacturing Technology Laboratory 2 MEC578 Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Laboratory 2 Total CP 112 Unit Name 50 Trimester 4 AGE500 Agricultural Engineering Project I 7 AGE531 Agricultural Structures & Buildings 7 AGE532 Soil & Water Resources Engineering 8 AGE533 Agribusiness Management & Entrepreneurship 7 AGE534 Farm Machinery & Power 8 AGE535 Post Harvest Engineering 7 AGE580 Soil & Water Resources Lab 2 AGE581 Post Harvest Engineering Lab 2 AGE582 Farm Machinery & Power Lab 2 Total CP 50 Trimester 5 Tractor Systems & Controls 8 AGE620 Drainage and Irrigation Engineering 6 AGE541 Rural Development, Extension & Technology Transfer 6 AGE542 Bio-Energy Engineering 6 AGE543 Precision Agriculture 6 AGE590 Agricultural Engineering Project II 10 AGE591 Tractor Maintenance and practice Lab 4 AGE592 Drainage and Irrigation Laboratory 2 AGE593 Bio-Energy Lab 2 Total CP 50 TRADE DIPLOMA IN AGRICULTURAL ENGINEERING (SEMESTER MODE) STAGE 1 Unit Code Unit Name STAGE 2 CP Unit Code Unit Name CP MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics II 10 AGE402 Engineering Science1 10 COM402 Technical & Development Communication 7 AGE415 Engineering Drawing and Surveying 10 AGE502 Engineering Science 2 12 AGE416 Integrated Rural Development and Extension 10 AGE 407 Engineering Design and Manufacturing 10 AGE417 Agricultural Science1 10 AGE414 Eng. Stats. and Research Methods 10 AGE418 Agricultural Engineering Economics & Entrepreneurship 10 AGE419 Agricultural Science2 10 Total CP 60 Total CP STAGE 3 AGE501 Agricultural Resources Engineering and Management 59 STAGE 4 10 AGE421 Agricultural Meteorology and Hydrology 10 10 AGE420 Agricultural Power and Mechanical Systems 10 AGE422 Agricultural Ecosystems Engineering and Management Ecosystems Engineering and Management AGE503 Agri. Industry Process Engineering 10 AGE509 Engineering Thesis .Field Practice Seminar 10 AGE504 Agricultural Infrastructure. Development and Management 10 ETH401 Introduction to Ethics and Governance 10 AGE406 Engineering Mechanical and Hydraulics 10 AGE506 Agricultural Engineering Project 10 OHS403 60 TOTAL CP TOTAL CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK AGE610 1 Elective Occupational Health and Safety III 10 50 113 Electives AGE511 AGE512 Agri. Ecological Eng Tourism Renewable Energy Development and Management 10 AGE513 Bio-Organic Engineering Agriculture 10 10 AGE514 Agri-Environmental Management Engineering 10 AGE510 Peri Urban Engineering Agriculture 10 TOTAL CP 50 TRADE DIPLOMA IN RENEWABLE ENERGY (TRIMESTER MODE) Trimester 1 Unit Code Unit Name CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK COM401 Technical Communication II 10 MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 MEC450 Engineering Graphics 4 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/ EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 MEC470 Engineering Graphics Laboratory 6 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/ EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory / Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP 55 Trimester 2 MEC451 Engineering Mechanics 8 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics II 10 PHY416/ CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445/ EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming /Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445/ ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety/Introduction to Ethics and Governance 5 EWP452 Engineering Workshop Practice 5 MEC472 Engineering Mechanics Laboratory 2 PHY470/ CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory/Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/ EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory / Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP 50 Trimester 3 114 MEC558 Fluid Mechanics and Machinery 8 REE554 Thermal Engineering 10 REE506 Biomass Energy System 10 REE400 Renewable Energy Project 1 8 MEC559 Engineering Materials 8 MEC578 Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Laboratory 2 REE570 Biomass and Thermal Engineering Laboratory 2 MEC572 Materials Engineering Laboratory 2 Trimester 4 REE510 Solar Energy System 8 REE511 Wind Energy System 8 REE500 Renewable Energy Project 2 8 EEE566 Electrical Machines Drives and Controls 8 MEC560 Engineering Management 9 REE574 Solar Energy Laboratory 3 REE575 Wind Turbine Laboratory 3 EEE580 Electrical Machines Drive and Controls Laboratory 3 Total CP 50 Trimester 5 REE590 Energy Conversation Technology 10 REE591 Energy Audit, Security, Policy and Planning 10 REE592 Hydro-Electric Power System 10 REE593 Renewable Energy Project 3 16 REE594 Hydro-Electric Laboratory 4 Total CP 50 YEAR 1 SEMESTER 1 Unit Code Unit Name SEMESTER 2 CP Unit Code Unit Name CP BEN503 Engineering Physics 12 BEN506 Introduction to Electrical and Electronics 12 LNG501 English for Academic Studies 12 BEN601 Engineering Computation 2 12 BEN505 Material Science 12 BEN507 Introduction to Computer Programming 12 BEN504 Engineering Graphics 12 BEN508 Engineering Mechanics 12 BEN502 Engineering Computation 1 12 BEN509 Workshop Practice 12 AGE418 Agricultural Engineering Economics & Entrepreneurship 10 AGE419 Agricultural Science2 10 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 YEAR 2 SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2 MEC602 Project (Mechanical) 15 MEC702 Engineering Computation 3 15 MEC603 Engineering Planning 15 MEC605 Manufacturing Technology 15 MEC604 Engineering Management 15 MEC606 Solid Mechanics 15 MEC701 Computer Aided Design and Analysis 15 MEC607 Dynamics 15 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 YEAR 3 SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2 MEC703 Design Project (Mechanical) 15 MEC705 Renewable Energy 15 MEC709 Quantitative Techniques 15 MEC710 Advanced Industrial Computing 15 MEC704 Mechanics and Dynamics of Machinery 15 MEC707 Thermodynamics 15 MEC706 Mechatronics 15 MEC708 Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer 15 Total CP 60 Total CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK BACHELOR IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING (SEMESTER MODE) 60 YEAR 4 SEMESTER 1 SEMESTER 2 MEC711 Engineering Studies 15 MEC714 Mechanical Design and Analysis MEC713 Industrial Project (Mechanical) A 15 MEC715 Advanced Operations Management 15 15 115 MEC713 Industrial Project (Mechanical) A 15 MEC715 Advanced Operations Management 15 MEC718 Mechanical Behavior of Materials 15 MEC717 Industrial Project (Mechanical) B 15 MEC719 Internal Combustion Engines 15 Electives (Choose 1 unit) MEC712 Advanced Manufacturing Technology 15 MEC716 Automation Systems 15 Total CP 60 Total CP 60 Job Opportunities Our graduates are already in employment in large and small engineering organizations. It ranges from Designing, Manufacturing, Power Generation, farming activities, maintenance of pumps to Aircrafts. They are absorbed into all types of Industries in Fiji from backyard workshops to managerial positions. The graduates with Trade Diploma and Certificate IV levels have secured employment as middle management supervisors as well as craft skill mechanics at shop floor operations. Our graduates are also geared towards entrepreneurship. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 116 The local engineering firms are demanding high quality trade and technician level graduates, for employment. Graduates in the Certificate, Trade Diploma provided with the opportunities to further upgrade their qualifications to degree level at FNU. The FNU graduates also have the advantage to specialize on specific units of their choice should they wish to venture out and begin their own businesses. Unit Descriptors: ACR301: Refrigeration Fundamentals This unit enables the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for the refrigeration trade. Topics include, heat, pressure, temperature and their relationships, absolute and gauge pressure and its major applications. ACR302: Refrigeration Procedures This unit enables the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for refrigeration maintenance work. Topics include tube, tube joining, job preparation, service gauges and gaskets. As this module deals with basic principles of refrigeration and knowledge of industry there are a variety of delivery strategies that could be used. ACR304: Refrigerants This unit enables development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for handling refrigerants. Topics include refrigerant properties, safe handling of refrigerants, reclaim and evacuation, precautions and leak detecting. Students are to undertake the project wok, assignments and class exercises for the competency for refrigeration and air conditioning. ACR305: Refrigeration Components This unit provides an introduction to the scope of development of the elementary knowledge of refrigeration and air conditioning controls. The topics basically include functions of compressor, condenser, evaporator and flow control. This module deals with basic principles of refrigeration and knowledge of industry there are a variety of delivery strategies that could be used. Prerequisite: ACR301 ACR306: Refrigeration Operations This unit aims to provide the students with the knowledge and skills in the operation of the refrigeration system. The topics include pressure enthalpy chart, refrigerant oil properties, compressor calculations and types of motor drivers. Unit includes integrated theory and practical lessons. Students are to undertake projects, seminars and assignments in order to complete unit. Prerequisite: ACR302 ACR307: Refrigerant Flow Controls This unit enables the development of the elementary knowledge required for refrigerant controls. The topics include liquid flow controls, vapor flow controls, safety procedures and selection criteria. The unit deals with creating models based on real situations as a means of imparting the information. Delivery strategies should integrate theory with demonstration and student practical as much as possible. Prerequisite: ACR301 ACR311: Test Equipment The unit serves to prepare the students in the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for testing refrigeration systems. As this module deals with basic of test equipment (Electrical) and knowledge of industry, there are a variety of delivery strategies that could be used. ACR312: Electrical Fundamentals This unit provides a broad introduction to electrical science. Topics include components and basic physics. This introductory unit should emphasis practical application of topics with concepts reinforced by laboratory experiment. Students are to undertake projects and assignments in order to complete unit. ACR313 Refrigerants Air-conditioning DC Principles The unit serves to prepare the students in the development of DC electrical theory. Topics include electrical power, series and parallel resistant circuits, electromagnetism, electromagnetic induction, inductance and RL circuits. Students are to undertake projects and assignments in order to complete unit. ACR400: Electrical Drawing This unit enables the development of the knowledge and skills required for Electrical Drawing. The content includes connecting various switching circuits using panels and leads and develops number of switching charts for various types of light switches. Draw a wiring light circuit using TPS cables and the appropriate accessories. Prerequisite: ACR312 ACR402: Cool Room and Freezers This unit aims to provide the students with the knowledge and skills of Cool Rooms/Freezer Rooms. The content includes food spoilage, types and construction, layouts and installations, components and features, system and defrosts controls, commission, service and maintenance. ACR403: Merchandising and Display Cabinets This unit is to provide the students with the knowledge and skills to install service and maintain merchandising and display cabinets. The topics include types and construction, components and features, layouts and installations, system and defrost controls, multiple systems, commission, service and maintenance. ACR405: Fault Finding and Diagnostics This unit enables the development of intermediate knowledge and skills of students to perform systematic fault isolation through the application of diagnostic techniques. Students are to undertake the project wok, assignments and class exercises for the competency for refrigeration and air conditioning. ACR406: Ventilation This unit aims to provide the students with the knowledge and skills of Ventilation. Topics cover ventilation systems and its requirements. Students are to undertake the project wok, assignments and class exercises for the competency for refrigeration and air conditioning. ACR408: Refrigeration System Controls This unit aims to provide the students with the knowledge and skills of Electrical controls. Topics include symbols in electrical circuit, basic control circuit, 3 phase motors, operating of refrigeration and air conditioning plants, use/ applications of timers and on-the-job controls. Prerequisite: ACR304 ACR410: Domestic Refrigerators and Freezers This unit enables the development of knowledge and skills for servicing and repairing domestic refrigerators and freezers. Topics include dangers and safety procedures, refrigerators/ freezers and components, electrical and refrigeration faults, use of manufacturer’s catalogues and procedures for installations, consuming and service dockets. Students are to undertake projects and assignments in order to complete unit. ACR411: Introduction to Air Conditioning This unit provides a broad introduction to air conditioning maintenance. Topics include introduction, psychometrics and load estimation. As a result of successfully completing this unit the student will be able to: describe the scope and application of air conditioning, comfort conditions and the SAA codes applicable, Plot and determine the properties of air on the psychometric chart. Determine estimated heat load quantities using the chart. Identify and interpret the different air conditioning processes. Determine the temperatures of air using a sling hygrometer. Students are to undertake the project wok, assignments and class exercises for the competency for refrigeration and air conditioning. Prerequisite: ACR301 ACR412: Cooling Tower Operation This unit enables to develop skills required for competency in handling large air conditioning equipment. The topics include cooling towers, evaporators, health requirements and statutory requirements. As a result of successfully completing this unit the student will be able to: Start and stop a cooling tower in accordance with safety and manufacturer’s instructions. Determine the correct operation of the cooling tower. Identify responsibility under the legislation. Maintain records. ACR413: Refrigeration and Air-conditioning Installations This unit aims to provide the students with the knowledge and skills to install refrigeration piping and COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK ACR314: Refrigerants Air-conditioning AC Principles The unit serves to prepare the students in the development of AC electrical theory. Topics include trigonometry, AC waveform, measuring instruments, phases and resistive AC circuits. Students are to undertake the project wok, assignments and class exercises for the competency for refrigeration and air conditioning. ACR407: Air Conditioning Controls This unit aims to provide the students with the knowledge and skills of air conditioning controls. Topics include control system fundamentals, circuit diagrams, and types of control systems, fluid flow control, energy management principles and commissioning procedures. Students are to undertake the project wok, assignments and class exercises for the competency for refrigeration and air conditioning. 117 Topics include dangers and safe working practices, site drawings and specifications, piping installations, pipe sizing, pressure testing and refrigerant piping accessories. Students are to undertake the project wok, assignments and class exercises for the competency for refrigeration and air conditioning. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 118 ACR416: Appliance Motor Circuits This unit enables to develop the knowledge and skills required for competency in Appliance Motor Circuits. Topics include identifying dangers and observe safety procedures. Describe the construction, operation and application of typical appliance motors. Identify state application and test typical single phase starters and overload devices Use circuit diagrams and appropriate test equipment to connect/disconnect, test and fault find typical appliance motors and associated circuits. Students are to undertake the project wok, assignments and class exercises for the competency for refrigeration and air conditioning. AGE300: Integrated Farming Systems This unit provides the students the fundamental knowledge and approaches on agriculture and natural resources production and management in an integrated and holistic way for sustainable agricultural productivity that will develop their skills to apply these gained knowledge in the development of agribusinesses and farm enterprises. AGE301: Farm Management and Entrepreneurship This unit enables the students to acquire fundamental knowledge and skills in the development, establishment and management of sustainable farm businesses and related enterprises through the application of appropriate agricultural engineering technologies and strategies. AGE302: Workshop Technology A To enable the students to develop the elementary and basic knowledge and skills required for efficient workshop safety and practice. AGE305: Farm Machinery Development his unit provides an introduction to the scope of development of the elementary knowledge of refrigeration and air conditioning controls. The topics basically include functions of compressor, condenser, evaporator and flow control. This module deals with basic principles of refrigeration and knowledge of industry there are a variety of delivery strategies that could be used. Prerequisite: ACR301 AGE400: Farm Resources Management Engineering This unit enables the students to acquire fundamental knowledge and skills in understanding the dynamics of the farm environment and its natural resources (soil, water, energy, climate, biodiversity) as a system and how these various components of the system are interrelated with each other, and how these components can be harnessed efficiently for a sustainable and profitable production. AGE401: Farm Meteorology and Phonology To enable the students to have basic and adequate knowledge and skills on the fundamental concepts, theories and applications of farm meteorology and crop phonology to support sustainable agriculture and natural resources production and management. AGE402: Engineering Science 1 This unit enables student develop the basic knowledge, concepts and principles of Applied Physics and Chemistry as applied to the practice of agricultural science and engineering works. AGE403: Farm Shop Practice 1 This unit is intended to enable the graduates to develop basic and appropriate knowledge and skills required for understanding metals and plastics fabrication as well as fitting and machining techniques and theory as part of services necessary to the practice of agricultural engineering. AGE404: Engineering Project and Entrepreneurial Practice 1 To enable the students to apply the basic knowledge, concepts and principles they learnt and acquired to practice agricultural engineering through establishment of farm businesses or enterprises based on technologies or products developed. AGE405: Farm Surveying and Mapping This unit is to enable students to develop basic knowledge, skills and competency in engineering drawing practice, and surveying for mapping and leveling including introduction to the potential applications of Geographic Information System (GIS), and the subsequent interpretation of engineering drawings and survey maps relative to agriculture and natural resources management. AGE406: Engineering Mechanics and Hydraulics This unit is to provide the students the basic knowledge, concepts and principles of Engineering Mechanics and Hydraulics as applied to the practice of agricultural engineering and related fields. Theory and practical applications are appropriately and adequately delivered through lectures, practical exercises, assignments, seminar-presentations, practical projects and case studies. Students are to undertake project work, assignments and class activities in competent to the unit. AGE407: Engineering Design and Manufacturing This unit is to provide the students the basic knowledge, concepts and principles of Engineering Design and Manufacturing System and enable them to acquire skills and capacity to apply these knowledge and skills to the practice of agricultural engineering through the development of relevant engineering technologies and systems to enhance and sustain agriculture and natural resources production, utilization and productivity. AGE408: Farm Environment and Waste Management To provide the students the basic knowledge, concepts and principles of Environmental Science and Management as applied to the practice of agricultural engineering and the development of relevant technologies and systems to improve farm resource management and productivity. Prerequisite: Stage 4 Completed AGE409: Farm Electricity and Processing This unit provides the agricultural engineering graduates the necessary knowledge and skills in transforming farm produce into high value products that will improve farm income and productivity as well as utilize farm wastes, by-products and other indigenous and renewable energy resources for farm electrification and power generation. AGE411: Engineering Project and Entrepreneurial Practice 3 To enable the students to apply the basic knowledge, concepts and principles they learnt and acquired in stages 1, 2, 3 and 4 as proposed and carried out in Entrepreneurial Practices 1 and 2 and present their project results in a seminar. AGE412: Engineering Project and Entrepreneurial Practice 2 To enable the students to apply the basic knowledge, concepts and principles they learnt and acquired to understand and carry out in Entrepreneurial Practice. AGE413: Farm Shop Practice 2 This unit is intended to enable the graduates to develop the intermediate and appropriate knowledge and skills in the management and operation required for construction services including carpentry and masonry as applied to the practice of agricultural engineering. AGE414: Engineering Statistics and Research Methods This unit provide the students the basic knowledge, concepts and principles of Applied Statistics and Basic Research Methods as applied to the practice of agricultural engineering particularly on research and development (R and D) to generate/improve relevant engineering technologies and systems to enhance and sustain agriculture and natural resources production, utilization and productivity. Students are to undertake the project wok, assignments and class exercises for the competency for the unit. AGE416: Integrated Rural Development and AGE417: Agricultural Science 1 This unit provides the students the fundamental knowledge and approaches on agriculture and natural resources production and management for sustainable agricultural productivity that will develop their skills to apply these gained knowledge in the development of efficient and integrated production systems that will increase and sustain productivity and growth in the agriculture and natural resources sectors of the Fiji economy. AGE420: Agricultural Power and Mechanization Systems This unit provides the basic and enhanced knowledge and skills for the students to understand and apply the principles and concepts of agricultural mechanization, and use and management of various sources of power and machinery for the production of various agricultural, forestry and fishery products that will increase and sustain productivity of the agri-industries as a vital contribution to the growth and development of the Fiji economy as a whole. Students are to undertake a variety of assignments, projects and tests to achieve the desired outcome. AGE421: Agricultural Meteorology and Hydrology This unit is to enable the students to have adequate indepth knowledge and skills on the fundamental concepts, theories and principles in agricultural meteorology and hydrology, and their functions and applications to support sustainable agriculture and natural resources production and management. Theory and practical are appropriately delivered through lectures, seminarspresentations, field observations, laboratory and actual field works, and project development. Students are to undertake a variety of assignments, projects and tests to achieve the desired outcome. Prerequisite:AGE501, AGE504 AGE422: Agro-ecosystems Engineering and Management This unit is to enable students to know and acquire knowledge and skills in the fundamentals of environment, ecology, ecosystems management, and agro-ecosystems engineering approaches to conserve and manage the ecosystems for sustainable agriculture and natural resources production and productivity. Students are to undertake the formative and summative assessments; project/ field work and class activities in competent to the unit. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK AGE410: Farm Structures and Construction This unit is intended to equip agricultural engineering graduates the adequate and enhanced knowledge and skills in the construction of necessary farm infrastructures and their components, and related facilities in the practice of agricultural engineering works. Extension This unit is to provide the students the basic knowledge, concepts and principles of Rural Development and Extension, and enable them to apply these learning in the practice of agricultural engineering, especially in promoting, delivering and extending relevant engineering technologies and systems to farmers and other stakeholders helping them to enhance and sustain agriculture and natural resources sectors’ production and productivity. Students are to undertake the project wok, assignments and class exercises for the competency for the unit. 119 Prerequisite: stage 3 completed AGE500: Agricultural Science 2 This unit is a sequel to Agricultural Science 1 that will enable the students to apply the knowledge and skills gained from the previous unit in conducting in-depth analysis and assessment of the various components of the agriculture and natural resources production systems and be able to integrate them into a more cohesive, appropriate and efficient system that will increase and sustain productivity and growth in the agriculture and natural resources sectors of the Fiji economy. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 120 AGE501: Agricultural Resources Engineering and Management This unit enables the students to acquire fundamental knowledge and skills in understanding the dynamics of the environment and its natural resources (soil, water, energy, climate, biodiversity) as a system and how these various components of the system are interrelated with each other, and how these components can be harnessed efficiently for a sustainable agricultural production that will ensure and vital for a stable and enduring socio-economic development in the country. AGE502: Engineering Science 2 The unit enables the development of the knowledge and skills required for competency in the intermediate science of mechanical engineering. Topics include machines, eccentric masses, and practice of graphical and analytical techniques, shearing forces and bending moments in randomly loaded simply supported beam. AGE503: Agricultural -Industrial Process Engineering This unit provides the agricultural engineering graduates the necessary knowledge and skills in transforming agricultural produce into innovative high value products that will form the foundations for a thriving and productive Fiji agri-industries contributing to a large extent and sustainable manner in the growing and developing Fiji economy. Students are to undertake the formative and summative assessments; project/ field work and class activities in competent to the unit. AGE504: Agricultural Infrastructures Development and Management This unit is intended to equip agricultural engineering graduates the adequate and enhanced knowledge and skills in the development of agricultural infrastructures and their components, and related facilities necessary and vital in supporting agricultural and natural resources production and utilization in sustainable manner, as well as providing the graduates the basic and appropriate knowledge and skills in the management and operation of these infrastructures/facilities, and with adequate provision of advancing knowledge and innovations in the practice of agricultural engineering in this aspect. AGE505: Agricultural Engineering Economics and Entrepreneurship This unit enables the students to acquire fundamental knowledge and skills in the applications of basic economic principles and techniques for the development and establishment of sustainable agribusinesses and related enterprises mainly propelled by the application of appropriate agricultural engineering technologies and strategies. AGE506: Agricultural Engineering Projects This unit is to enable the students to consolidate and apply the knowledge and skills they learned and acquired by packaging a conceptual proposal for a relevant agricultural engineering project, either a research, an extension delivery system, or an agribusiness/ enterprise that will showcase the practice of agricultural engineering and the application/development of agricultural engineering technologies and techniques for major priority agricultural commodities/industries of Fiji leading towards improved productivity, efficiency and sustainability of the agriculture and natural resources sectors of the economy. Students are to undertake project work, assignments and class activities and presentations in competent to the unit. AGE509: Agriculture Engineering Thesis/ Field Practice Seminar This unit is to enable students to apply the basic knowledge, concepts and principles they learnt and acquired in the practice of agricultural engineering through establishment of agribusinesses or enterprises, conduct of applied research to develop new products or pilot test existing technologies for improvement, or develop and pilot test extension delivery systems to promote and encourage the use of agricultural engineering technologies to farmers, industry players and other stakeholders. Students are to undertake project work, assignments and class activities in competent to the unit. AGE510: Peri – Urban Engineering Agriculture This unit is to enable the students to learn and acquire the basic knowledge, concepts and principles of Peri-Urban Agriculture and Management as applied and enhanced with the practice of agricultural engineering, and the development of relevant engineering technologies and systems for food security and improved productivity of urban areas and the agriculture and natural resources sectors as a whole. Students are to undertake the project work, assignments and class exercises for the competency for the unit. AGE511: Agricultural-Ecological Engineering Tourism This unit is to enable students to know and acquire knowledge and skills in the fundamentals of environment, ecology, ecosystems management, and agro ecosystems engineering approaches to develop technologies/innovations that conserve and manage the ecosystems, not only for sustainable agriculture and natural resources production, but also adding aesthetic and panoramic value that attract and encourage tourism development contributing to the productivity of the industry. AGE512: Renewable Energy Development and Management This unit familiarizes as conventional energy resources are almost exhausted and their consumption cost is increasing, the need to explore and develop renewable energy resources is presently of paramount importance worldwide. Hence, the application of engineering knowledge and skills is vital to the development and management of these potential resources. This unit, therefore, provides the students the basic knowledge, concepts and principles in agricultural engineering that can be applied in the development of relevant engineering technologies and systems to utilize these renewable energy resources to address the current concerns and increasing cost of using conventional energy sources, particularly for agriculture and natural resources production. Students are to undertake the project wok, assignments and class exercises for the competency for the unit. This unit enables the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required mainly for gear drive construction. AGE513: Bio-organic Engineering Agriculture This unit is to provide the students the basic knowledge, concepts and principles of Biological and Organic Agriculture combined with the applications of agricultural engineering techniques and strategies to develop relevant engineering technologies and systems for improved organic agriculture management that will enhance and sustain agriculture and natural resources production and productivity. FMG406: Engineering Material Process The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of the knowledge and skills required for engineering material processing and testing. AGE514: Agricultural-Environmental Management Engineering This unit is to provide the students with basic knowledge, concepts and principles of Environmental Science and Management as applied to the practice of agricultural engineering and the development of relevant engineering technologies and systems to improve resource management and balance utilization with conservation and protection vital in enhancing and sustaining agriculture and natural resources production and productivity. FMG408: Maintenance & Diagnostics The purpose of this unit is to provide the basic knowledge and skills for the installation and maintenance of plants and machines. FMG311: FM Process A The purpose of this unit is to develop knowledge required for efficient workshop safety and use of basic turning and measurement practice. FMG415: FM Practice D The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of the elementary knowledge required mainly for the operation of more advance machine tools, and helical and worm gear cutting. FMG313: FM Process B This unit enables the development of the knowledge and skills required for competency in communicating engineering information using technical graphics FMG314: FM Practice B This unit enables the development of intermediate knowledge and skills required for workshop machining practice. FMG315: FM Process C FMG404: Measurements and Inspection This unit enables the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for accurate metrological measurement and Inspection. FMG405: Advanced Measurement The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of intermediate knowledge and skills required for precise measurement and quality control procedures. FMG407: I C Engines This unit enables the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for handling heat engines related to plant installations. FMG414: FM Process D The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of the elementary knowledge required mainly for the operation of more advance machine tools, and helical and worm gear cutting Prerequisite: FMG315 FMG416: FM Practice C This unit enables the development of intermediate knowledge and skills required for workshop machining practice. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK FMG312: FM Practice A The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of basic skills required for use of hand tools, lathes and measuring tools FMG403: Trade Drawing B The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of the knowledge and skills required for competency in communicating engineering information using technical graphics. FMG417: FM Practice E This unit enables the development of intermediate knowledge of aspiring Fitter and Machinist where they will be able to integrate other facets of skills necessary to be competent in the production and assembly of component parts. FMG418: FM Process E This unit enables the development of the advance knowledge and skills required for machining technology. 121 FWG311: Fabrication Technology A This unit enables to develop the knowledge and skills required for competency in fabrication. Students carry out a number of assignments, projects, and practicing numerous examples fabrication practice. FWG441: Fabrication Technology C This unit enables the development of intermediate knowledge required for the fabrication trade. Students carry out a number of assignments, projects and practicing numerous laboratory experiments FWG312: Fabrication Practice A The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for practical metal fabrication. FWG442: Fabrication Practice C This unit enables the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for Fabrication work. Students carry out a number of assignments, projects and practicing laboratory experiments. FWG313: Welding Technology A This unit is intended to enable the graduates to develop basic and appropriate knowledge and skills required for understanding welding theory as part of services necessary to support the practice of agricultural engineering. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK FWG314: Welding Practice A This unit enables the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for practical metal fabrication. Students carry out a number of assignments, projects and practicing laboratory experiments. FWG315: Fabrication Drawing A The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of the knowledge and skills required for competency in communicating engineering information using technical graphics. FWG444: Welding Practice C This unit enables the development of intermediate welding knowledge and skills required for the trade. Students carry out a number of assignments, projects and practicing numerous laboratory experiments. FWG445: Trade Science The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of basic knowledge and skills in Design and basic analysis. FWG321: Fabrication Technology B This unit enables the development of the extended knowledge and skills required for fabrication theory. Students carry out a number of assignments, projects and practicing laboratory experiments. FWG451: Fabrication Technology D This unit enables the development of advanced knowledge and skills of the steel fabrication trade. Students carry out a variety of assignments, and projects and test to meet the objectives. FWG322: Fabrication Practice B This unit enables the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for practical metal fabrication. FWG452: Welding Technology D This unit enables the development of advanced knowledge and skills of the welding trade. Students carry out a number of assignments, projects and practicing laboratory. FWG323: Trade Calculations The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of analytic knowledge and skills required for competency in learning Fabrication and Welding trade. FWG431: Welding Technology B This unit enables the development of extended knowledge and skills required for practicing the welding trade. Students carry out a number of assignments, projects and practicing numerous laboratory experiments. FWG432: Welding Practice B This unit enables the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for the welding trade. Students carry out a number of assignments, projects and practicing numerous workshop exercises. 122 FWG443: Welding Technology C This unit enables the development of the advanced knowledge and skills required for the welding trade. Students carry out a number of assignments, projects and practicing numerous laboratory experiments. Prerequisite: FWG413 FWG433: Fabrication Drawing B The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of intermediate knowledge and skills for drawing competency for mechanical trade people. FWG453: Fabrication Drawing C This enables the development of the advanced skills required for fabrication drawing. Students carry out a number of assignments, projects and practicing laboratory. Prerequisite: FWG433 FWG454: Fabrication & Welding Project This unit consolidates the knowledge and skills learned during the program and to apply them in practical and creative manner. Students carry out a number of assignments, projects and careful design study including financial and commercial considerations. MEN302: Welding Process The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of intermediate knowledge and skills required for workshop fitting and machining MEN303: Trade Drawing A To enable the students to develop elementary and basic knowledge and skills in science required for trades training and engineering works. MEN304: Workshop Calculation To enable the students to develop the basic knowledge and skills in arithmetic and mathematics required to do the practice of engineering works and other vocational units. Through this unit the students learn of algebra, geometry and trigonometry, basic S.I Units calculate angles Triangles and trigonometric functions formulae, and apply these formulae to determine and calculate areas, masses and volumes. MEN305: Workshop Science To enable the students the development of intermediate scientific knowledge and skills for engineering trades trainees relevant and applicable to the practice of agricultural engineering. MEN308: Electrical Principles This unit is to provide the basic knowledge and skills of the science of electricity for engineering trades trainees. Students carry out a number of assignments, projects and practicing laboratory experiments. MEN309: Building Services for Agriculture This unit is intended to enable the graduates to develop the intermediate and appropriate knowledge and skills in the management and operation required for building services installation and maintenance as applied to the practice of agricultural engineering. MEN403: Trade Drawing B The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of intermediate knowledge and skills for drawing competency for mechanical trade’s people. Prerequisites:MEN303 MEN418: Computer Aided Design CAD This unit enables the development of the knowledge and skills required for computer aided drafting. Students carry out a variety of assignments and projects to create a folio of work. PEN401: Mechanical Science A This unit expands the development of elementary knowledge and skills required competency and understanding the physics of mechanics. Topics include application of appropriate SI unit for engineering quantities, using of graphical techniques in statistic equilibrium, principle of moments, coefficients of drying friction; relations of a moving mass, issues relating to the motion of bodies with finite mass and fracture and metal specimen. Students are to undertake the project wok, assignments and class exercises for the competency for physics of mechanics. PEN403: Thermodynamics A This unit enables to develop basic knowledge and skills in the physics of heat and its uses in engineering. The basic topics include the following along with major projects and assignments in parallelism to the class activities: temperature and heat, gases, processes (non-flow), heat transfer and vapors. Students are required to complete projects and assignments to supplement the theory. PEN404: Plant Technology A This unit enables the student to be well grounded in fundamentals of knowledge and practical experience to adapt him/her to rapid technological changes in the plant and equipment for which he/she will be responsible. The unit requires the students to carry out projects and assignments to supplement the theory. PEN405: Material Science This unit is as a sequel to Engineering Science 1, this unit introduces and provides the students the basic knowledge, concepts and principles in Materials Science, including the use of biological and organic Materials through the application of Organic Chemistry and Biotechnology, and their relevance to the practice of agricultural engineering. Topics include fundamentals, strength and properties of materials, chemical processes in the environment affecting material properties, biological processes and biotechnology in material science, bio-chemical processes and operational systems management. Students are to undertake the project wok, assignments and class exercises for the competency for physics of mechanics. PEN406: Workshop Practice The unit enables to develop the intermediate knowledge and hands on skills of students that can only be attained through experience in the workshop. Topics include the practices of safety procedures, art of hand skills, skills required in the electric arc welding, use of brazing equipments and uses of machine tools. Students are required to carry out projects and workshops. PEN407: Production Technology A The unit tends to cover the knowledge and skills required for competency in learning engineering related units. Topics include safety precautions and hazards in the workshop environment, familiarization of hand, powered and machine tools, using of appropriate precision measuring instruments and using of appropriate tools to perform metal removing COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK MEN306: Applied Materials This unit enables the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for using materials in engineering. Students carry out a number of assignments, projects and practicing numerous laboratory experiments. PEN402: Engineering Drawing This unit is a broad introduction to drawing practice and in interpreting engineering drawings. The topics basically include drawing practice, plane and 3D constructions, developments, engineering drawing, mechanisms and assembly drawings. Students are to apply logical analytical reasoning to a variety of drafting problems within the scope of this descriptor. Undertaking a variety of assignments projects and tests to objective material. And icing numerous examples in drawing practice. 123 operations. Project work and assignments are required in this unit in parallelism with class activity. PEN408 Plant Technology B The purpose of this unit s enable the student to be well grounded in fundamentals of knowledge and practical experience to adapt him/herself to rapid technological changes in the plant and equipment for which he/she will responsible. Prerequisite: PEN404 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 124 PEN409: Power Plant This unit deals with the development of the basic knowledge and skills required for the installation, running and maintenance of power plant. The topics being covered are quality and quantity of steam generated by various fuels, illustration of a conventional steam plant, boiler maintenance, principles of various power generating turbines and pipeline installations. Students are required to relate theory to practical applications of power engineering under taking projects and assignments. Prerequisite: PEN504 PEN410: Fluids Mechanics A The purpose of this module is to enable the development of elementary knowledge and skills required for competency and understanding in the physics of fluids. PEN417: Production Technology B This unit aims to produce precise and efficient skills in production technology in each course participant, so there is an emphasis on practical work in the laboratory/workshop. Much of this can be carried out in groups. Site visits to factories are an important aspect of practical experience in this course. The topic covered; measurement, plant layout, quality, work study techniques, casting and molding, testing of materials and production. Students are required to undertake a variety of assignments, projects and tests to make subjective and objective decisions. PEN500: Engineering Project This unit consolidates the knowledge and skills learned during the program and to apply them in practical and creative manner. The units include team work and group participation. Relevant communication skills used to illustrate outline details, technical solutions of group projects, co-operation as member of a team, formal presentation and justification of technical proposal. Under minimal guidance students must use their own initiative to conceive a project idea, design it and construct it. Prerequisite: Completed stage 3 PEN501: Mechanical Science B The unit enables the development of the knowledge and skills required for competency in the intermediate science of mechanical engineering. Topics include machines, eccentric masses, and practice of graphical and analytical techniques, shearing forces and bending moments in randomly loaded simply supported beam and knowledge of deflection of rectangular beams with regards to rigidity. Students are required to apply logical analytical reasoning to a variety of problems within the scope of this descriptor. Undertaking a variety of assignments projects and tests to objective material. Practicing numerous laboratory experiments. Prerequisites:PEN401 PEN502: Computer Aided Design 2 (CAD) This unit enables the development of the knowledge and skills required for computer aided drafting. Topics include the introduction to PCs, CAD commands, text and dimensioning and students are required to carry out projects and assignments to supplement the theory. PEN503: Thermodynamics B This unit enables the development of elementary knowledge and skills required for competency in performing thermodynamic and Heat transfer principles to a variety of engineering problems. The topics include second law of thermodynamics, chemistry of combustions, vapor cycles and vapors. Students are recommended to apply logical analytical reasoning to a variety of problems within the scope of this descriptor. Undertaking a variety of assignments, projects and tests to make subjective and objective decisions. Prerequisites: PEN403 PEN504: Plant Engineering This unit enables the development of the knowledge and skills required for competency learning plant engineering related units. Topics include; heat engines, uses of compressed air, rot dynamics and reciprocating pumps, types of bearings, installation of mechanical plant, installation and distribution of gas and water systems and designing of a hydraulic power transmission system. Students are required to complete projects and assignments to apply the theory. PEN505: Plant Management This unit enables the development of moderate knowledge and skills required for competency in plant management and maintenance. The major topics include plant engineering and management, planning, planned maintenance, maintenance workshops. Students would be encouraged to apply logical analytical reasoning to a variety of problems within the scope of this descriptor. Students are to carry out projects and assignments along with the class activity. PEN506: Fluid Mechanics B This unit’s objective is to enhance the knowledge in designing fluid systems. The topics included in this unit are flow processes, pipe friction, flow in channels, fluid power and pumping systems. Students are to undertake the following in competency for the unit by applying logical analytical reasoning to a variety of problems within the scope of this descriptor. Undertaking a variety of assignments, projects and tests to make subjective and objective decisions. Practicing numerous laboratory experiments, Prerequisites: PEN408 PEN508: Instrumentation and Controls The unit aims to give the student an introductory grasp of digital control principles through the use of logic circuits and PLCs. Analogue principles are reinforced in practice through the use of operational amplifiers and measuring instruments. Students are required to undertake a variety of assignments, projects and tests to make subjective and objective decisions. Prerequisites: PEN511 PEN510: Machine Design This unit is concerned to develop student’s concepts of the design process and the production of standard components. The role of standards, tolerances. Materials selection, specification and production techniques should be clearly understood in the process of successful design. Students should be encouraged to analyze and discuss current and traditional engineering design solutions to expand their understanding of design restraint and product demand. Prerequisite: PEN501 PEN511: Electrical Electronics for Mechanical Engineers This unit enables development of the knowledge and skills required for competency in electrical engineering science as a complement to mechanical oriented studies. The topics basically include physics revision, simple circuits, electromagnetism, instruments, power systems, pharos analysis, AC induction, DC motors and generators. Topics basically include electrical principles revision, DC and AC circuits, semi – conductors, detectors and output devices technology and telemetry technology Students are required to complete projects and assignments to supplement the theory. PLM301: Basic Machining Process The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for efficient workshop safety and practice. PLM302: Installation Practice The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for simple mechanical maintenance. PLM304: Basic Machining Practice The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of intermediate knowledge and skills required for workshop fitting and machining PLM401: PM Practice A The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of elementary knowledge and skills for practicing plant maintenance. PLM402: PM Practice B The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of the intermediate knowledge and skills required for plant maintenance. PLM403: Plant Technology The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of intermediate knowledge and skills for studying related units in plant engineering PLM404: Maintenance Technology The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of the intermediate knowledge and skills required for plant maintenance management. PLM405: Steam Plant The purpose of this unit is to enable the participant to develop the basic knowledge and skills to operate and carry basic maintenance on a small steam power plant PLM406: Heat Engines Pressure, systems and its boundary, cycle. Ideal and non-ideal gas. Boyle’s and Charles’s laws. Steam: properties, principle of generation. Principle of operation of internal combustion engines. Fuel: type, calorific values and combustion principles. Dynamometers. PLM407: Lifting and Mechanical Handling The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of knowledge and skills required for plant installation and mechanical handling. PLM408: Power Transmission The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for assembling power trains. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK PEN509: Manufacturing Technology This unit enables the development of the advanced knowledge required for competency in manufacturing engineering. The basic topics include processes, measurements, method study, and work measurement, machining and testing of materials. This unit should be approached in such a way that the student develops an understanding of the technological processes involved in mechanical and production engineering so that an analytical approach is developed to some of the problems associated with the processes. Industrial visits are an important aspect of this unit. Prerequisite: PEN507 PLM303: Bearings and lubrication The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for elementary maintenance of plant machineries. PLM409: Hydraulics and Pneumatics The purpose of this unit is to enables the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for efficient handling of hydraulics & pneumatics devices. PLM410: Industrial Automation The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of intermediate knowledge and skills for industrial automation. PLM411: Heat Engines Practice 125 The purpose of this unit is to enable the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for maintenance of engines. Bachelor of Engineering (Mechanical) COM501 Communication Literacy Introduces students to the importance of communication in an engineering context. A real life engineering conceptual design problem is used as the vehicle through which to establish the necessity for accurate and efficient communication. The paper will also allow students to begin developing a reflective practice approach to their work through the preparation of a weekly journal. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK BEN502 Engineering Computation 1 Gives the student an understanding of differential and integral calculus, and develops the ability to formulate and solve models of simple engineering and scientific systems BEN503 Engineering Physics Engineering Physics program will have a strong grounding in engineering design, science, practice and the application of physics to engineering. BEN504 Engineering Graphics The operation of producing engineering working drawings to recognized national drawing standards, manually and on computer. BEN505 Material Science This unit explores crystal structure and mechanical properties of materials. Various types of materials and their applications will be taught in this unit. BEN506 Introduction to Electrical and Electronics engineering The purpose of this unit is to provide the foundation in dc and ac circuit function and analysis required by all electrical engineering paraprofessionals, irrespective of their area of specialization. This unit extends the skills in basic ac/dc circuit analysis in Electrical Principles and provides a foundation in dc and ac circuit analysis. BEN507 Introduction to Computer Programming An introduction to computer programming for engineering applications using the C and C++ programming languages, including program design, input/output, data types, flow control, functions, arrays, strings, pointers, disk file input/output, classes and objects. BEN508 Engineering Mechanics Covers fundamental knowledge of engineering mechanics statics. Introduces principles, theories and problems of static engineering systems in terms of force relationships. 126 BEN509 Workshop Practice Basic manufacturing technology and processes. An introduction to material properties and their applications. Practical workshop sessions include lathe, bench and welding/fabrication. Safety in manufacturing is an important aspect. BEN601 Engineering Computation 2 Develops an understanding of advanced calculus and the ability to formulate and solve models of complex engineering systems. MEC602 Project (Mechanical) An introduction to some aspects of the process of producing a technical project: time management, cooperative working, documentation, reporting, presentation skills and technical skills. MEC603 Engineering Planning Focuses on techniques and principles of project planning applicable to a wide range of engineering projects. Topics include project scheduling, resource management, project budgets, risk management, project and product costing. Management of individuals, teams and companies. MEC604 Engineering Management An awareness of the functions and structures of organizations and the principles of management and leadership as they relate to engineers and engineering functions. MEC605 Manufacturing Technology This course introduces a broad spectrum of manufacturing techniques and is designed to give an understanding of the working principles of the machinery and processes as used in manufacturing products. The importance of efficiency and costing is emphasized. MEC606 Solid Mechanics The behavior of solid bodies subjected to external loading. External loads are identified with their transmission into internal stresses and accompanied strains. The main objectives will be to implement these relationships into the mechanical design procedure in order to determine the appropriate material and geometry for the structural or machine member. MEC607 Dynamics The study of motion of matter including concepts such as force and acceleration relationships, inertia, work and energy, impulse and momentum and the interaction of bodies as a result of their motion. MEC701 Computer Aided Design and Analysis Computer systems management and computer applications: solid modeling and extension into computer aided manufacturing; dynamic mathematics processing; simulation for experimentation. MEC702 Engineering Computation 3 The main purpose of this paper is to equip the student with a variety of different analytical and mathematical approaches and techniques for modeling electrical and mechanical components and systems. MEC703 Design Project (Mechanical) Provides students with the opportunity to carry out a real engineering project the success of which depends largely on their own initiative. MEC704 Mechanisms and Dynamics of Machinery Mechanisms and Dynamics of Machinery (Theory of Machines) is a branch of applied mechanics that is concerned with understanding the relationships between the geometry and motions of the parts of a machine or mechanism and the forces, which produce these motions. The main objectives will be to implement these relationships in the mechanical design procedure and develop the ability of students to formulate and solve problems in the kinematics and dynamics of machinery. MEC706 Mechatronics Mechatronics is the synergistic integration of mechanism, electronics, and computer control to achieve a functional system. This paper will introduce technologies involved in mechatronics (Intelligent Electro-Mechanical Systems), operational principles and the techniques necessary to apply this technology to mechatronic system design. Topics covered include sensors, actuators, modeling using building block and state space methods, model-based control, stability criteria and programming of PLCs. MEC707 Thermodynamics This paper builds on the knowledge of fundamental engineering principles in the area of thermodynamics. It covers the application of the First and Second Laws of Thermodynamics to open systems, closed systems and to a range of engineering devices. This section builds on the knowledge of the First and Second Laws of thermodynamics. The understanding and skills in thermodynamics are extended to the practical applications including: Brayton and Rankine Power Cycles, Vapour Compression Refrigeration Cycles, Psychometric, Air Conditioning and Combustion. MEC708 Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer This paper builds on the basic knowledge of engineering principles in the areas of fluid mechanics and fluid dynamics. This paper is concerned with the static and MEC709 Quantitative Techniques Recognition of solvable problems and the selection of appropriate techniques to solve these problems. Measurement of industrial processes including QA and QC systems; formulations of Operations Research (OR) Models; mathematical programming of replacement and maintenance problems, schedules; implementation and maintenance of OR solutions; simulation, linear programming and optimization. MEC710 Advanced Industrial Computing This unit discusses and identifies the complex issues involved in the implementation of integrated computer aided design and manufacturing (CIM) systems. The various system elements are discussed, investigated and evaluated. Selected system elements are linked and analyzed. In conveying the technology of efficient computer integrated systems, their applications and implementation in a fast changing industrial environment, emphasis is placed on collaborative group work, and a high level of professional documentation and presentation. MEC711 Engineering Studies The role of the engineer and the engineering profession in society is taught to the students. Current thinking in the areas of professional ethics in engineering together with environmental and sustainability considerations will be covered in this unit. MEC712 Advanced Manufacturing Technology The purpose of this paper is to apply earlier principles and knowledge to analysis manufacturing techniques at an advanced level and thereby gain an understanding of the manner in which the BE undergraduate programme will be used in the manufacturing industry. The intention of this paper is for the student to learn the ability to use existing skills (e.g.: maths/modeling, mechanics, thermodynamics, engineering materials) to delve deeply into a topic at an advanced level. MEC713 Industrial Project (Mechanical) A The students should take up an industrial project either from the Industry or within the University. A supervised programme of real life industrial experience, relevant industrial education in production processes, management techniques, research applications, design and other activities in a working environment will be covered in this project. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK MEC705 Renewable Energy This unit presents an introduction to energy systems and renewable energy resources, with a scientific examination of the energy field and an emphasis on alternate energy sources and their technology and application. The class will explore society’s present needs and future energy demands, examine conventional energy sources and systems, including fossil fuels and nuclear energy and then focus on alternate, renewable energy sources such as solar, biomass (conversions), wind power, geothermal and hydro. Energy conservation methods will be emphasized. dynamic behavior of incompressible fluids. The focus is on the ability to understand and use the mathematical descriptions of fluid systems. This unit also builds on the knowledge of fundamental engineering principles in the area of heat transfer. It covers the physical and theoretical description of the three modes of heat transfer: conduction, convection and radiation and the application of fundamental heat transfer equations to engineering heat flow situations. The thermal design of heat exchangers is covered as a specific practical application of heat transfer theory. 127 MEC714 Mechanical Design and Analysis This unit covers an understanding of the mechanical design process as applied to complex engineering systems: problem solving, decision making, creation and optimization; good practice and standard methods in engineering design; preliminary and detail design involving engineering systems, processes and components using appropriate design tools; function, cost, material properties, standards compliance, ethics, safety and risk management; design review and redevelopment, design reporting and communication. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 128 MEC715 Advanced Operations Management A holistic view of the total operations of the competitive production environment involving a detailed study of the individual elements of the organisation and the way they interface. Better solutions are always encouraged, so much so that the subject material has changed dramatically over the past few years. This course is designed to give the student a fundamental understanding of the techniques used in modern manufacturing and operations management. MEC716 Automation Systems Automation systems: robotics, high volume systems, flexible manufacturing systems, computer numerical control and relevant software; application to an appropriate project. MEC717 Industrial Project (Mechanical) B. The students should take up an industrial project either from the Industry or within the University. A supervised programme of real life industrial experience, relevant industrial education in production processes, management techniques, research applications, design and other activities in a working environment will be covered in this project. MEC718 Mechanical Behavior Materials This paper explores the relationship between structure and properties of materials under various mechanical loadings and manufacturing environments. Understanding this relationship enables appropriate selection of materials and cost effective manufacturing processes to deliver products to required specifications. MEC719 Internal Combustion Engines This paper builds and integrates previous studies in the fields of mechanics, thermodynamics and heat transfer. The following topics in the field of Sparkand Compression- Ignition Engines will be covered: Aspects of design, normal combustion, abnormal combustion, combustion chamber effects, fuel and ignition systems, testing and performance maps, fuels and fuel properties, emissions and their control. For More Information Contact: Mr. Joji Marau Head of School(HE) Phone: 3381 044 Ext: 1728 E-mail: HOS-Mechanical@fnu.ac.fj Mr. Toutou Head of School(TVET) Phone: 3381 044 Ext: 1720 E-mail: HOS-SME@fnu.ac.fj OA – Ms. Lavenia Ext: 1713 Email:OA-Mechanical@fnu.ac.fj – Ms. Sunita Sharma Ext: 1713 Email:oa-sme@fnu.ac.fj Department of Printing Technology General information The Department of Printing Technology is one of the oldest departments in the College. The Department is situated at the Narere Campus. The department had been offering programme in the Certificate IV level and currently developing units for the Trade Diploma in Printing Technology. LECTURER MESAKE KOLOIKEIRASEA, Trade Diploma in Graphic Reproduction (UK); Trade Cert in Printing (FIT); Cert. IV in Training and Assessment (FIT); IDTT (FIT); Cert. in Graphic Reproduction (Japan); Class 1 Certificate in Graphic Reproduction (Supervisor level) (FNTC) TECHNICIAN SANJAY VIJAY KUMAR, Prepress (FIT); Lithographic III and II Certificate (FNTC); III and II Certificate (FNTC); Proficiency (APTECH) Certificate in Graphic Offset Machinist Class Photomechanical Class Certificate in Computer OFFICE ADMINISTRATOR JOYCE NAICKER, Diploma (Business Studies & Management Accounting) Programme Details and Duration PROGRAMME CERTIFICATE IV IN PRINTING TECHNOLOGY Total number of units to complete the programme 18 Number of trimesters to complete the programme 3 Number of units to complete in each trimester 6 Minimum period required for industrial attachment 1 year Minimum period to complete the whole programme 2 years Entry Qualification Certificate IV in Printing Technology 200 out of 400 marks in Form 6 with minimum of 50% in any 4 subjects. Programmes, Stages and Units COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK STAFF PROFILE HEAD OF DEPARTMENT NEMANI NABALARUA, B.Ed. (TVET), University of Newcastle, Aust.; IDTT, (FIT);Certificate IV in Workshop Training and Assessment (TUNRA , University of Newcastle); Graduate Certificate in Tertiary Teaching (USP), Trade Cert in Printing (FIT); Certificate in Desktop Publishing (FIT); Certificate in Graphic Design (FIT) , Certificate of Supervision (FNTC), Certificate in Printmaking (USP). Certificate IV in Printing Technology This programme has been designed whereby a single area, Printing Technology, is taught in a wider encompassing approach. It has been developed to provide its graduates with skills, knowledge and creativity to address the needs of the local printing industry. The programme covers a wide range of topics in Pre-press, operation of different types of printing machines, and also the bookbinding and print finishing methods. 129 TRIMESTER 1 TRIMESTER 2 Unit Code Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name CP GAD416 Layout & Design 1 11 GAD418 Layout & Design 2 11 PRT303 Graphic Pre-Press 1 10 PRT304 Graphic Pre-Press 2 10 PRT305 Print Finishing 1 10 PRT306 Print Finishing 2 10 PRT307 Trade Calculation 1 5 PRT308 Trade Calculation 2 5 PRT309 Printing Science 1 6 PRT310 Printing Science 2 6 COM301 Technical Communication 6 OHS403 Occupational Health & Safety 10 TRIMESTER 3 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 130 PRT405 Screen Printing 10 PRT401 Graphic Pre-press 3 10 PRT402 Press & Print Finish. 3 10 PRT403 Trade Calculation 3 5 ETH401 Introduction to Ethics and Governance 9 PRT404 Printing Science 3 6 Industrial Attachment - 6 months Job Opportunities Certificate IV in Printing Technology graduates are employed in any Printing Industry which includes Newspaper companies and the Packaging industry. Graduates may also gain entry qualifications for Trade Testing at the Training and Productivity Authority of Fiji, as well as overseas job markets. Unit Descriptors GAD 416: Layout and Design 1 This unit is designed to develop an appreciation for the aesthetics of basic graphic design using traditional techniques and modern computer technology. The unit covers basic Layout styles, color theory, visual weighting of the page elements and principles of graphic design as applied in the printing industry. GAD 418: Layout and Design 2 This unit is designed to develop an appreciation for the aesthetics of advance graphic design using traditional techniques and modern computer technology. The unit covers advance layout styles, color theory, visual weighting of the page elements and principles of graphic design as applied in the printing industry. GAD 418: Layout and Design 2 This unit is the continuation of Layout & Design 1.It aims to develop an appreciation for the aesthetics of graphic design using traditional techniques and modern computer equipment. It will teach students about basic Layout styles applied in graphic design, color theory, visual weighting of the page elements and principles of graphic design. PRT303: Graphic Pre-press 1 This unit aims to develop an appreciation for basic plate-making in the print industry. It is focused on prepress techniques and how the images are prepared for printing using the Letterpress and Offset printing process. It also encompasses the traditional method of “Hot Metal Composition” and the photographic process of image preparation. PRT304: Graphic Pre-press 2 This unit encompasses the Graphic prepress section and its aims to develop an appreciation for Pre-press techniques in theory and practical. This level which is one step up from the PRT 303 covers a wide range of skill and technique in darkroom work and image preparation. PRT401: Graphic Pre-press 3 This is an advanced level of training which enables students to identify chemicals and use them accordingly with minimum supervision. The unit covers an indepth study of all chemicals, inks, powder and other substance and solutions used in the printing process. PRESS AND PRINT FINISHING PRT305: Press and Print Finishing 1 This unit covers the printing and finishing components of what is expected of them to perform in the industry after completing the training programme. Students are trained to acquire skills in, machine maintenance, operation and troubleshooting techniques in the press and finishing areas. They undergo theory and practical training with strict supervision at this preliminary stage. PRT306: Press and Print Finishing 2 In this Unit students are trained theoretically and practically with advance techniques of Press and Print Finishing which enables them to work with moderate supervision in the teaching and learning environment. The unit covers intermediate skills and techniques in machine maintenance, press operation and trouble shooting at a higher level than PRT 305. PRT402: Press and Print Finishing 3 This unit covers the maintenance and operation of all printing duplicators and presses. It is an advanced level of training compared to PRT 305 and PRT 306, where students are required to work with minimum supervision in machine maintenance, press operation and troubleshooting. PRT307: Trade Calculations 1 This unit aims to develop a competency for students wishing to advance into Costing and Estimation in the print industry. It helps the student work out costs of materials, labor and the overall cost of a print job. PRT308: Trade Calculations 2 This unit covers estimating and costing technique which students should acquire at the end of the programme. This enables students to be competent in estimating and costing any given job. PRT309: Printing Science 1 This unit is designed for learners to develop their skills and understanding in the science of the “latent image” in image preparation and how different chemicals affect image transfer. It also covers the chemical makeup, printing inks and ink drying actions in the various printing processes. PRT310: Printing Science 2 This is an intermediate level of what is learned in PRT 309. It is more in depth into the study of chemical components their usage and safety precautions in their handling. After the completion of the unit learners should acquire relevant skills is handling chemicals, their usage and relevant safety measures in their handling. PRT404: Printing Science 3 This unit aims to develop an advance competency for PRT405: Screen Printing This unit aims to develop student’s competency in the screen printing field about the basic screen printing techniques of image transfer from paper, Green Film stencil, and photographic emulsion to material. It also covers frame making, mesh starching, color mixing and printing techniques in the Screen printing process. COMM 301: Communication skills and studies This course offers the student the opportunities to increase proficiency in both written and verbal communication that can be adapted to a variety of situations at the Certificate level. This is to be achieved by developing the skills of listening which then leads to making notes, enhancing those notes through research of written materials culminating in adapting those skills for specific contexts. Simultaneously, speaking skills are developed that would allow the student to make basic seminar presentations which are well researched, structured and executed. All these skills are then practiced in specialized context. OHS 403 OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY This unit is designed to develop students’ knowledge and understanding in the fundamentals of Occupational Health and Safety Laws with Associated Regulations. To enable students to acquire the necessary skills to be able to identify hazards and assess risk in their workplaces and also develop control measures that are effective to eliminate or reduce the risk to an acceptable level. ETH 401 ETHICS VALUES AND GOVERNANCE The unit provides students with a broad understanding of ethics, ethical behaviour and practice and equips them with skills and guidelines for making ethical judgments and decisions. It provides an overview of values, norms and laws governing human behaviour in different historical/social contexts, considers a range of ethics philosophies and theories, examines some key ethical controversies, and looks at the application of ethics in relevant contemporary contexts, including commerce and industry, professions and trades, and COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK PRT403: Trade Calculations 3 This unit is developed for students to be able to estimate and cost any given job with minimum supervision. This is the final stage for the Trade Calculation unit in the Certificate IV level and a student is expected to be able to provide a quote whenever needed. This unit covers the calculation of all printing materials, labor, and mark up costs for any printing job. students in the science of the “latent image” in prepress plates and how different chemicals affect image transfer. It also looks at the chemical make-up in printing inks and “wash-up” chemicals on the machines. For More Information Contact: Mr. Nemani Nabalarua Department of Printing Technology Phone: 3392000/3385813 Ext: 4990 E-mail: enquiry-engineering@fnu.ac.fj / HOD-PT@fnu.ac.fj OA – Ms. Joyce Naicker Email: oa-pt@fnu.ac.fj Ext: 4751 131 FACULTY OF TRANSPORT SCHOOL OF AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING & ROAD TRANSPORT General Information The customers of today demand more from the vehicle manufacturers to meet their likes and needs, such as ride ability, comfortability, navigation of routes or Global Position System, ease of application or voice communication with machines/car, to do work as delegated and etc. These demands have therefore obliged training providers such as FNU’s to prepare and equip the Automotive Engineers/ Technicians well with knowledge and skills to service, repair and maintain these new age technologies in all the automobiles and vehicles of today and tomorrow. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK There is also the demand on the designers and manufacturers to produce new and modern vehicles to higher levels that meet the customer’s needs. The installations of new gadgets, sensors and other new technologies in these new modern vehicles has challenged the School to continue to keep abreast with new knowledge and skills to prepare students for the market needs of today. The School of Automotive Engineering and Road Transport offers a wide variety of programmes in the field of Automotive Engineering and Road Transport and a comprehensive range of programmes that provides opportunities for students (employers and employees to be), vehicle drivers and vehicle owners to take specific units within a programme or to be specialised in any of the full- time programmes offered by the school. Staff Profile HEAD OF SCHOOL (TVET) APISAI DOVITANA B, Eng. (Hons) (Automobile and Manufact); HNDEngineering (Automobile Eng.); Ordinary Dip. (Automobile Eng.); Adv. TradeCert.(Diesel and Electrical); Trade Cert. (Automotive Mechanics); Adv. Cert. (Vehicle inspection)(Japan); Cert. Ed.; Int. Dip. Ed. Mgt SENIOR LECTURERS FOTUWAIKA YAVALA Cert. (Voc.Edu.Mgt); HND Engineering; Ordinary Dip. (Automotive Engineering), Trade Cert. (Automotive Mechanic). JOSAIA VUNITALI PGDip (Edu); Post Trade Automotive; International Dip. Tertiary Teaching B.Ed. (TVET); Trade Cert. (Automotive Mechanics). SUDHIR SHARMA Dip. Tech (Auto.Eng); Dip (Auto.Eng); Cert. in Road Transport;Int. Dip.(Ter.Teach) SARATH SASIDHARAN PG (Master of Engineering),BE(Automotive Engineering) 132 LECTURER I SACHIN MAHARAJ Dip. Automotive Eng, Trade Cert. Light Motor Vehicle Dip. Tertiary Teaching; Cert. Motor Vehicle Mechanics Class III ETUATE KOROI BSc Eng. (Hons), Dip Eng. (HITEC), C.M CILT , MITA LECTURER II ACHIELLES RAJ KUMAR Ord. Dip. (Auto.Eng); Trade Cert. (Auto. Mech.); Int. Dip. (Tert.Teach.). AMENTAVE VUATALEVU International Dip. Tertiary Teaching; Dip. (Automotive Eng.); Cert. of Apprenticeship (Craft Apprentice); Trade Cert. (Automotive Mechanics). ATISH R SHARMA Dip. (Automotive Eng.); Trade Cert. (Heavy Commercial Vehicles); Cert. Motor Vehicle Mechanic Cert. Class II andIII; Cert. Motor Vehicle Electrical/Electronics JOSEFA WAKOL Dip. (Automotive Eng.); International Dip. Tertiary Teaching; Trade Cert. (Automotive Eng); Cert. IV – Training and Assessment. JOSEVA BUADROMO Trade Cert. (Automotive Mechanics)Dip. Tertiary Teaching . KITE LAGICERE(Study Leave) Dip.(Automotive Engineering.);InternationalDip. Tertiary Teaching; Trade Cert. (Motor vehicle Electrical/ Electronics); Cert. IV Training and Assessment. Dip. (AutomotiveEng.); Dip. (Education); Trade Cert. (Automotive Eng). PRANEEL DUTT Dip Automotive Engineering); Trade Cert. Automotive Engineering.); Trade Cert. (Light motor Vehicle) . PRAVIN R Int.Dip. Tertiary Teaching; BTech – Mechanical / Manufacturing Eng; Trade Cert. Motor Vehicle Electrical/Electronics;Cert. IV in Assessment& Workshop Training. SITERI RASOUSOU Dip. Automobile Eng, Trade Cert. Heavy Mobile Plant Cert; Dip.Tertiary Teaching . ASSISTANT LECTURERS JEREMAIA TUWAI NAQIRI Int. Dip. Tertiary Teaching; Dip. (Mechanical Eng); Cert. of Apprenticeship (Craft Apprentice); Trade Course Cert. (Course of Instruction); Trade Cert. (Automotive Mechanics); Adv Cert/Diploma (Automotive Engineering) (Japan); AutoCAD Cert. (NHCC); Advance Dip. (Mechanical Eng) PAULO MEKEMEKE Dip. (Automotive Eng); Trade Cert. Heavy; Cert. in Fiji Secondary Teacher Training (Advance College). AMINIO WAIWAI Trade Cert. (Panel Beating) CHRISTOFFER CHAND Dip. (Automotive Eng.)Trade Cert. (Light Motor Vehicle) SUNIL KUMAR Dip. (Automotive Eng); Trade Cert. (Automotive Eng.) Trade Cert. (Heavy Mobile Plant). TUTORIAL ASSISTANT BIMLESH CHAND, Trade Cert. (Panel Beating);Dip. Tertiary Teaching SUSHEEL DUTT Dip. Auto Eng; Trade Cert. Light Motor Vehicles;Dip. Tertiary Teaching OSEA KASAMI Ordinary Dip. (Automotive Engineering); Trade Cert. (Light Motor Vehicle) ;Dip. Tertiary Teaching VIKASH REDDY PGDip. (Physics); BSc (Phy/Maths); International Dip. Tertiary Teaching; Cert IV in Training and Assessment; Fiji Secondary Teacher Training Certificate. LAB DEMOSTRATOR SAMUELA VURUNA, Cert. (Information Technology) ; Trade Cert. (Light Motor Vehicle) ALFRED KAITU SEFETI Dip. (Automobile Eng.); Cert. Basic Arc Welding; Trade Cert. (Automotive Engineering); Cert. IV (Training and Assessment) ATISH R SHARMA Dip. (Automotive Eng); Trade Cert. (Heavy Commercial Vehicles); Cert. Motor Vehicle Electrical/ Electronics;Cert. (Motor Vehicle Mechanics Class II and III);Dip. Tertiary Teaching SHAMAL NARAYAN Dip. (Automotive Eng.);Cert. (Motor Vehicle Mechanics TECHNICIANS JONETANI BABA, Trade Certificate (Automotive Mechanics) MUSUDROKA SOKIVETA, Dip. (Automotive Eng.); Trade Cert (Motor Vehicle and Electrical), Cert. IV (Training and Assessment) NARDEEP P KUMAR Dip. (Automotive Eng.); Trade Cert. (Automotive Eng) OFFICE ADMINISTRATOR ALISI TAKAYAWA KASAMI Dip. (Business Office Administration) Programme Details and Duration CERTIFICATE IV Total number of units to complete the programme Number of pensters/trimesters/semesters to complete all units Number of units to complete each penster/ trimesters/semester Number of weeks per penster/trimesters/ semester COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK RUSILA CAGI Dip. (Automobile Eng.); Trade Cert. (Motor Vehicle Electrical/Electronics);Dip. Tertiary Teaching Class II and III); Trade Cert. (Automotive Light Motor Vehicle); Dip. Tertiary Teaching TRADE DIPLOMA PENSTER TRIMESTER SEMESTER TRIMESTER 25-28 17 units 20-24 37 - 40 5 pensters 3 trimesters 4 semesters 5 trimesters 6-7 5-6 6-8 6-9 8 weeks 15 weeks 18 weeks 15 weeks 133 Minimum period required for industrial attachment 6 months 6 months 6 months 6 months Minimum period to complete the whole programme 1½ years 2 years 2 ½ years 2 years Trimester Mode Programmes for 2016 For any enquiry on the trimester mode programmes for 2016 please contact the Head of School. Entry Qualifications Certificate III Completion of Form 5 (Year 11) level of studies OR Certificate II Certificate IV 200 out of 400 marks in Form 6 with minimum of 50% in any 4 subjects. Trade Diploma in Automotive Engineering Pass in Form 6 with 200 out of 400 marks with 50% minimum marks in English and any other 3 subjects. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 134 Trade Diploma in Road Transport Technology and Management Pass in Form 6 with 200 out of 400 marks with 50% minimum marks in English and any other 3 subjects. Common Units in the first three Stages (The following 15 units in the first three stages are common to the following 4 programmes) CERTIFICATE III IN AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING (TRIMESTER MODE) STAGE 1 (Automotive Fundamentals) STAGE 2 [Automotive Fundamentals) Unit Code Unit Name CP Unit Code AUT321 Basic Vehicle Mechanical Systems 7 AUT326 Basic Automotive Calculation 8 AUT322 Vehicle Mechanical Systems 9 AUT327 Spark Ignition Engine 10 AUT323 Vehicle Mechanical Systems Workshop 7 AUT328 Spark Ignition Engine and Fuel System 8 AUT324 Vehicle Electrical/Electronics System Workshop 9 AUT329 Technical Communication 1 10 AUT325 Occupational Health and Safety 8 COM301 Fundamentals of Ethics 5 Total CP 40 Unit Name Total CP CP 41 STAGE 3 AUT330 Fundamentals of Engine Technology & Fuel System 8 ETH301 Basic Automotive Calculation 5 AUT331 Fundamentals of Engine Technology & Fuel System Workshop 11 CIN301 Computer Use and Application 4 AUT332 Basic Engineering Drawing 8 Total CP CERTIFICATE IV IN AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING (PENSTER MODE) 36 CERTIFICATE IV IN AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING [MAJOR IN LIGHT MOTOR VEHICLE] STAGE 1 (Automotive Fundamentals) Unit Code Unit Name STAGE 2 [Automotive Fundamentals) CP Unit Code Unit Name CP AUT303 Workshop Safety Procedures 8 AUT301 Basic Automotive Calculation 8 AUT304 Vehicle Mechanical Systems 8 AEN301 Spark Ignition Engine 8 AUT305 Vehicle Mechanical Systems Workshop 10 AEN302 Spark Ignition Engine and Fuel System 8 AUT306 Vehicle Electrical/Electronics System 8 AEN303 Spark Ignition Engine Workshop 8 AUT307 Vehicle Electrical/Electronics System Workshop 8 COM201 Technical Communication 1 4 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 10 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethics 5 Total CP 52 Total CP 41 STAGE 3 (Major in Diesel Engine Maintenances, Services and Repairs) AEN304 Compression Ignition Engines 8 AEN307 Automotive Engine project 10 AEN305 Compression Ignition Engine and Fuel System 8 AUT308 Craft Science 8 AEN306 Compression Ignition Engines Workshop 10 Total CP 44 STAGE 4 (Major in Light Motor Vehicles) Unit Code Unit Name STAGE 5 (Major in Light Motor Vehicles) CP Unit Code Unit Name CP Technical Drawing 8 AEN309 Vehicle Mechanical Science 2 8 AEN308 Vehicle Mechanical Science 1 8 AEN310 Automotive Commercial Procedures 8 LMV401 Motor Vehicle Technology 1 8 LMV403 Motor Vehicle Technology 2 8 LMV402 Motor Vehicle Technology Workshop 1 10 LMV404 Motor Vehicle Technology Workshop 2 10 CIN301 Computer Use and Applications 12 LMV405 Motor Vehicle Project 10 Total CP 46 Total CP 44 CERTIFICATE IV IN AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING [MAJOR IN HEAVY COMMERCIAL VEHICLE] STAGE 1 (Automotive Fundamentals) STAGE 2 [Automotive Fundamentals) AUT303 Workshop Safety Procedures 8 AUT301 Basic Automotive Calculation 8 AUT304 Vehicle Mechanical Systems 8 AEN301 Spark Ignition Engine 8 AUT305 Vehicle Mechanical Systems Workshop 10 AEN302 Spark Ignition Engine and Fuel System 8 AUT306 Vehicle Electrical/Electronics System 8 AEN303 Spark Ignition Engine Workshop 8 AUT307 Vehicle Electrical/Electronics System Workshop 8 COM201 Technical Communication 1 4 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 10 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethics 5 Total CP 52 Total CP 41 STAGE 3 (Major in Diesel Engine Maintenances, Services and Repairs Unit Code Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name CP AEN304 Compression Ignition Engines 8 AEN307 Automotive Engine project 10 AEN305 Compression Ignition Engine and Fuel System 8 AUT308 Craft Science 8 AEN306 Compression Ignition Engines Workshop 10 Total CP 44 STAGE 4 (Major in Light Motor Vehicles) Unit Code Unit Name STAGE 5 (Major in Light Motor Vehicles) CP Unit Code Unit Name CP AUT302 Technical Drawing 8 AEN309 Vehicle Mechanical Science 2 8 CIN301 Computer Use and Applications 12 AEN310 Automotive Commercial Procedures 8 AEN308 Vehicle Mechanical Science 1 8 HCV403 Heavy Commercial Vehicle Technology 2 8 HCV401 Heavy Commercial Vehicle Technology 1 8 HCV404 Heavy Commercial Vehicle Workshop 2 10 HCV402 Heavy Commercial Vehicle Workshop 1 10 HCV405 Heavy Commercial Vehicle Project 10 Total CP 46 Total CP 44 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK AUT302 135 CERTIFICATE IV IN AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING [MAJOR IN HEAVY MOBILE PLANT] STAGE 1 (Automotive Fundamentals) STAGE 2 [Automotive Fundamentals) AUT303 Workshop Safety Procedures 8 AUT301 Basic Automotive Calculation 8 AUT304 Vehicle Mechanical Systems 8 AEN301 Spark Ignition Engine 8 AUT305 Vehicle Mechanical Systems Workshop 10 AEN302 Spark Ignition Engine and Fuel System 8 AUT306 Vehicle Electrical/Electronics System 8 AEN303 Spark Ignition Engine Workshop 8 AUT307 Vehicle Electrical/Electronics System Workshop 8 COM201 Technical Communication 1 4 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 10 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethics 5 52 Total CP Total CP 41 STAGE 3 (Major in Diesel Engine Maintenances, Services and Repairs) COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK AEN304 Compression Ignition Engines 8 AEN307 Automotive Engine project 10 AEN305 Compression Ignition Engine and Fuel System 8 AUT308 Craft Science 8 AEN306 Compression Ignition Engines Workshop 10 Total CP 44 STAGE 4 (Major in Heavy Mobile Plants) STAGE 5 (Major in Heavy Mobile Plants) CIN301 Computer Use and Applications 12 AEN309 Vehicle Mechanical Science 2 8 AUT302 Technical Drawing 8 AEN310 Automotive Commercial Procedures 8 AEN308 Vehicle Mechanical Science 1 8 HMP403 Heavy Mobile Plant Technology 2 8 HMP401 Heavy Mobile Plant Technology 1 8 HMP404 Heavy Mobile Plant Workshop 2 8 HMP402 Heavy Mobile Plant Workshop 1 10 HMP405 Heavy Mobile Plant Project 10 46 Total CP Total CP 42 CERTIFICATE IV IN AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING [MAJOR IN MOTOR VEHICLE ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS] STAGE 1 (Automotive Fundamentals) STAGE 2 [Automotive Fundamentals) AUT303 Workshop Safety Procedures 8 AUT301 Basic Automotive Calculation 8 AUT304 Vehicle Mechanical Systems 8 AEN301 Spark Ignition Engine 8 AUT305 Vehicle Mechanical Systems Workshop 10 AEN302 Spark Ignition Engine and Fuel System 8 AUT306 Vehicle Electrical/Electronics System 8 AEN303 Spark Ignition Engine Workshop 8 AUT307 Vehicle Electrical/Electronics System Workshop 8 COM201 Technical Communication 1 4 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 10 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethics 5 STAGE 3 (Major in Diesel Engine Maintenances, Services and Repairs AEN304 Compression Ignition Engines 8 AEN307 Automotive Engine project 10 AEN305 Compression Ignition Engine and Fuel System 8 AUT308 Craft Science 8 AEN306 Compression Ignition Engines Workshop 10 Total CP 44 STAGE 4 (Major in Motor Vehicle Electrical and Electronics) 136 CIN301 Computer Use and Application 12 STAGE 5 (Major in Motor Vehicle Electrical and Electronics) AEN310 Automotive Commercial Procedures 8 AUT302 Technical Drawing 8 AEE403 Automotive Electronics and Auxiliary Systems 8 AEN308 Vehicle Mechanical Science 1 8 AEE404 Automotive Electronics and Auxiliary Workshop 8 AEE401 Automotive Electrics 8 AEE405 Automotive Electrical/ Electronics Project 8 AEE402 Automotive Electrical Workshop 10 AEE301 Automotive Electrical Science 10 Total CP 46 Total CP 42 CERTIFICATE IV IN AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING [MAJOR IN LIGHT MACHINERY] STAGE 1 (Automotive Fundamentals) STAGE 2 [Automotive Fundamentals) Workshop Safety Procedures 8 AUT301 Basic Automotive Calculation 8 AUT304 Vehicle Mechanical Systems 8 AEN301 Spark Ignition Engine 8 AUT305 Vehicle Mechanical Systems Workshop 10 AEN302 Spark Ignition Engine and Fuel System 8 AUT306 Vehicle Electrical/Electronics System 8 AEN303 Spark Ignition Engine Workshop 8 AUT307 Vehicle Electrical/Electronics System Workshop 8 COM201 Technical Communication 1 4 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 10 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethics 5 Total CP 52 Total CP 41 STAGE 3 (Major in Diesel Engine Maintenances, Services and Repairs) AEN304 Compression Ignition Engines 8 AEN307 Automotive Engine project 10 AEN305 Compression Ignition Engine and Fuel System 8 AUT308 Craft Science 8 AEN306 Compression Ignition Engines Workshop 10 Total CP 44 STAGE 4 (Major in Heavy Mobile Plants) STAGE 5 (Major in Heavy Mobile Plants) CIN301 Computer Use and Application 12 AEN309 Vehicle Mechanical Science 2 8 AUT302 Technical Drawing 8 AEN310 Automotive Commercial Procedure 8 AEN308 Vehicle Mechanical Science 1 8 ALM404 Power Transmission Technology 8 ALM402 Hydraulic & Pneumatics & Elect Power Generation 8 ALM405 Power Transmission Technology Workshop 10 ALM403 Hydraulic & Pneumatics & Elect Power Generation Workshop 10 ALM401 Light Machinery Project 10 Total CP 46 Total CP 44 CERTIFICATE IV IN AUTOMOBILE ENGINEERING [MALOR IN BODY WORKS] STAGE 1 [Automotive Fundamentals) STAGE 2 [Automotive Fundamentals) AUT303 Workshop Safety Procedures 8 AUT301 Automotive Calculation 8 PBS301 Hand Forming Theory 8 PBS303 Welding Technology 8 PBS302 Hand Forming Workshop 10 PBS304 Body Maintenance Theory 8 AUT306 Vehicle Electrical/Electronic System 8 PBS305 Body Maintenance Workshop 10 AUT307 Vehicle Electrical/Electronics System Workshop 10 COM201 Technical Communication 1 4 OHS401 OHS 10 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethics 5 Total CP 54 Total CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK AUT303 43 137 STAGE 3 (Major in Body Works) AUT308 Craft Science 8 PBS308 Auto Body Project 10 PBS306 Corrosion Treatment Theory 8 PBS309 Auto Body Design 10 PBS307 Corrosion Treatment Workshop 8 Total CP 44 STAGE 4 (Major in Body Works) COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 138 STAGE 5 AUT302 Technical Drawing 8 AEN309 Vehicle Mechanical Science 2 8 AEN308 Vehicle Mechanical Science 1 8 AEN310 Automotive Commercial Procedures 2 8 CIN301 Computer Use and Application 12 PBS403 Realignment Technology 8 PBS401 Vehicle Accident Repair 8 PBS404 Realignment Technology Workshop 10 PBS402 Vehicle Accident Repair Workshop 10 PBS405 Realignment Technology Project 10 46 Total CP Total CP 44 CERTIFICATE IV IN AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING(TRIMESTER MODE) CERTIFICATE IV IN AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING [MAJOR IN LIGHT MOTOR VEHICLE] TRIMESTER 1 TRIMESTER 2 AUT310 Vehicle Mechanical Systems 8 AEE310 Vehicle Management Systems 8 AUT311 Vehicle Mechanical Systems Workshop 8 AEE311 Vehicle Management Systems Workshop 8 AUT312 Vehicle Electronics and Fuel System 8 MTH301 Preliminary Mathematics I 10 AUT313 Vehicle Electronics and Fuel Systems Workshop 8 COM301 Communication Skills and Studies 7 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 10 ALM410 ALM Technology I 8 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethical Practices 5 ALM411 ALM Technology I Workshop 8 47 Total CP Total CP 49 TIMESTER 3 AUT314 Vehicle Mechanical Science 8 AUT315 Auto. Commercial Procedures 8 ALM412 ALM Technology II Workshop 8 ALM413 ALM Technology II Workshop 8 ALM414 Light Machinery Project 8 Total CP 40 CERTIFICATE IV IN AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING [MAJOR IN HEAVY COMMERCIAL VEHICLE] TRIMESTER 1 TRIMESTER 2 AUT310 Vehicle Mechanical Systems 8 AEE310 Vehicle Management Systems 8 AUT311 Vehicle Mechanical Systems Workshop 8 AEE311 Vehicle Management Systems Workshop 8 AUT312 Vehicle Electronics and Fuel Systems 8 MTH301 Preliminary Mathematics I 5 AUT313 Vehicle Electronics and Fuel Systems Workshop 8 COM301 Communication Skills and Studies 7 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 10 HCV410 HCV Technology 1 8 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethical Practices 5 HCV411 HCV Workshop 1 Total CP 47 Total CP TIMESTER 3 8 44 AUT314 Vehicle Mechanical Science 8 AUT315 Automotive Commercial Procedures 8 HCV412 HCV Technology 2 8 HCV413 HCV Workshop 2 8 HCV414 HCV Project 8 TOTAL CP 40 CERTIFICATE IV IN AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING [MAJOR IN HEAVY MOBILE PLANT] TRIMESTER 1 TRIMESTER 2 Vehicle Mechanical Systems 8 AEE310 Vehicle Management Systems 8 AUT311 Vehicle Mechanical Systems Workshop 8 AEE311 Vehicle Management Systems Workshop 8 AUT312 Vehicle Electronics and Fuel Systems 8 MTH301 Preliminary Mathematics I 5 AUT313 Vehicle Electronics and Fuel Systems Workshop 8 COM301 Communication Skills and Studies 7 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 10 HMP410 HMP Technology 1 8 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethical Practices HMP411 HMP Workshop 1 5 Total CP 47 Total CP 8 44 TIMESTER 3 AUT314 Vehicle Electrical Science 8 AUT315 Automotive Commercial Procedures 8 HMP412 HMP Technology 2 8 HMP413 HMP Workshop 2 8 HMP414 HMP Project 8 Total CP 40 CERTIFICATE IV IN AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING [MAJOR IN MOTOR VEHICLE ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS] TRIMESTER 1 TRIMESTER 2 AUT310 Vehicle Mechanical Systems 8 AEE310 Vehicle Management Systems 8 AUT311 Vehicle Mechanical Systems Workshop 8 AEE311 Vehicle Management Systems Workshop 8 AUT312 Vehicle Electronics and Fuel System 8 MTH301 Preliminary Mathematics I 5 AUT313 Vehicle Electronics and Fuel Systems Workshop 8 COM301 Communication Skills and Studies 7 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 10 AEE410 Automotive Electrics 8 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethical Practices 5 AEE411 Automotive Electrics Workshop 8 Total CP 47 Total CP 44 TIMESTER 3 AEE312 Automotive Electrical Science 8 AUT315 Auto. Commercial Procedures 8 AEE412 Automotive Electronic and Aux. Systems 8 AEE413 Auto. Electronic and Aux. Systems W/S 8 AEE414 Automotive Electrical and Electronic Project 8 Total CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK AUT310 40 CERTIFICATE IV IN AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING [MAJOR IN LIGHT MACHINERY] TRIMESTER 1 Unit Code Unit Name TRIMESTER 2 CP Unit Code Unit Name CP 139 AUT310 Vehicle Mechanical Systems 8 AEE310 Vehicle Management Systems 8 AUT311 Vehicle Mechanical Systems Workshop 8 AEE311 Vehicle Management Systems Workshop 8 AUT312 Vehicle Electronics and Fuel System 8 MTH301 Preliminary Mathematics I 5 AUT313 Vehicle Electronics and Fuel Systems Workshop 8 COM301 Communication Skills and Studies 7 OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 10 ALM410 ALM Technology I 8 ALM411 ALM Technology I Workshop 8 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethical Practices 5 Total CP 47 Total CP 44 TIMESTER 3 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 140 AUT314 Vehicle Mechanical Science 8 AUT315 Auto. Commercial Procedures 8 ALM412 Engineering Graphics 8 ALM413 Light Motor Vehicle Technology 2 8 ALM414 Light Machinery Project 8 Total CP 40 CERTIFICATE IV IN AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING [MAJOR IN BODY WORKS] TRIMESTER 1 ABW301 TRIMESTER 2 Minor Repair Theory 8 MTH301 Preliminary Mathematics I 5 7 ABW302 Minor Repair Workshop 8 COM301 Communication Skills and Studies ABW303 Automotive System 8 ABW305 Welding Technology 8 8 ABW303 Automotive System Workshop 8 ABW306 Welding Technology Workshop OHS401 Occupational Health and Safety 10 ABW410 Major Body Frame Repair Theory 8 ETH301 Fundamentals of Ethics 5 ABW411 Major Body Frame Repair Workshop 8 47 Total CP Total CP 44 TRIMESTER 3 AUT314 Vehicle Mechanical Science 8 AUT315 Automotive Commercial Procedures 8 ABW412 Collision Repair Technology 8 ABW413 Collision Repair Workshop 8 ABW414 Collision RepairProject 8 Total CP 40 TRADE DIPLOMA IN AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING (SEMESTER MODE) STAGE 1 STAGE 2 Unit Code Unit Name Unit Code Unit Name CP MTH405 Engineering Mathematics 1 CP 10 DAE408 AutoCAD 10 DAE402 Vehicle Engineering Science 1 10 DAE407 Automotive Sensory System 10 DAE403 Automotive Electrical & Electronic Principles 10 DAE409 Vehicle Technology 10 DAE404 Automotive Engineering Drawing 7 DAE410 Engineering Design 10 DAE405 Workshop Administration and Customer Service 7 DAE411 Engineering Materials 10 DAE401 Automotive Laboratory Workshop 1 6 COM401 Technical Communication 10 DAE406 Engine Technology 10 DAE413 Automotive Laboratory Workshop 2 6 Total CP 60 Total CP 66 STAGE 3 STAGE 4 DAT407 Transport & Environment 9 DAE504 Auto Project 9 DAE502 Mechanics of Road Vehicle 2 9 DAE507 Manufacturing Technology 10 DAE503 Vehicle Engineering Science 2 9 DAE506 Automotive Engineering Management 9 DAE505 Auto Measurements & Instrument Control 9 DAE508 Automobile Thermodynamics 10 DAE412 Automobile Quality Assurance and Reliability 9 CIN410 Micro Computer Applications 9 DAE504 Engineering Mathematics 8 ETH401 Introduction to Ethics and Governance 9 OHS403 OHS 10 Total CP 53 Total CP 66 TRADE DIPLOMA IN TRANSPORT TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT(SEMESTER MODE) STAGE 1 CP Unit Code ATM501 Transport System 1 Unit Name 10 ATM503 Transport Systems 2 10 ATM502 Mechanics of Transport System 1 10 ATM504 Mechanics of Transport System 2 10 OHS403 Occupational Health and Safety 10 ATM505 Transport Legislation 1 10 AEN511 Workshop Administration and Organisation 10 AEN512 Quality Assurance 10 COM401 Technical Communication 10 ACC401 Accounting Environment 15 ACC301 Introduction to Accounting 15 ETH401 Introduction to Ethics and Governance 9 65 Total CP Total CP Unit Name CP 64 STAGE 3 STAGE 4 ATM506 Transport Accident Investigation 10 ATM510 Transport and Environment 10 ATM508 Vehicle Noise and Vibration 10 ATM511 Transport Contract Services 10 ATM507 Project 30 ATM601 Transport Management 10 ATM509 Logistic Supply Management 10 ATM512 Distribution and Business Planning 10 CIN406 Computer Applications 14 ATM602 Fleet Control and Logistics 10 AEN510 Engineering Design 10 ATM603 Transport Legislation 2 10 Total CP 65 Total CP 64 TRADE DIPLOMA IN AUTOMOTIVE ENGINEERING (TRIMESTER MODE) TRIMESTER 1 Unit Code TRIMESTER 2 Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name CP COM401 Technical Communication II 10 MEC451 Engineering Mechanics 8 MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics II 10 MEC450 Engineering Graphics 4 PHY416 / CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 PHY416 / CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445 / EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 Introduction to Computer Programming / Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445 / ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety / Introduction to Ethics Governance 5 5 EWP 452 Engineering Workshop Practice 5 CIN445 / EEE460 OHS445 / ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety / Introduction to Ethics Governance COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Unit Code STAGE 2 141 CIN445 / EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering OHS445 / ETH401 8 OHS445 / ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety / Introduction to Ethics Governance 5 Occupational Health and Safety / Introduction to Ethics Governance 5 EWP 452 Engineering Workshop Practice 5 MEC470 Engineering Graphics Laboratory 6 MEC 472 Engineering Mechanics Laboratory 2 PHY470 / CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 PHY470 / CHM 470 Engineering Physics Lab / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/ EEE 470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory / Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 CIN470/ EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory / Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP 55 Total CP 50 TRIMESTER 3 TRIMESTER 4 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK MEC 551 Engineering Analysis with MATLAB 6 AUE 503 Principles of Automobile Manufacturing 7 MEC 552 Strength of Materials 7 AUE 504 Mechanics of Road Vehicles 7 AUE 501 Automotive Electrical/Electronic Systems 7 AUE 505 Automotive Engineering I 7 AUE 502 Applied Thermodynamics 7 MEC 564 Machine Element Design 7 MEC 558 Fluid Mechanics and Machinery 8 MEC 565 Introduction to Solid Works 7 MEC 559 Engineering Materials 8 AUE 571 Automobile Manufacturing Laboratory 3 MEC 571 Engineering Materials Laboratory 2 AUE 572 Mechanics of Road Vehicles Laboratory 2 MEC 578 Mechanics of Fluid and Machinery Laboratory 2 AUE 573 Automotive Workshop Practice I 3 AUE 570 Automotive Electrical/Electronic Systems Workshop 3 Total CP 50 Total CP 43 TIMESTER 5 AUE 506 Automotive Engineering Project 8 AUE 507 Automotive Engineering II 7 AUE 508 Introduction to Mechatronics and Sensor Technology 7 AUE 509 Quality Assurance & Reliability Engineering 7 AUE 510 Instrumentation and Measurement in Automotive Engineering 7 ATM 510 Transport and Environment 8 AUE 574 Introduction to Mechatronics Laboratory 2 AUE 575 Instrumentation and Measurement Laboratory 2 AUE 576 Automotive Workshop Practice II 3 Total CP 51 TRADE DIPLOMA IN ROAD TRANSPORT TECHNOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT (TRIMESTER MODE) TRIMESTER 1 Unit Code CP Unit Code Unit Name CP COM401 Technical Communication II 10 MEC451 Engineering Mechanics 8 MTH405 Engineering Mathematics I 10 MTH504 Engineering Mathematics II 10 4 PHY416 / CHM406 Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445 / EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 MEC450 142 Unit Name TRIMESTER 2 PHY416 / CHM406 Engineering Graphics Engineering Physics / Engineering Chemistry 8 CIN445 / EEE460 Introduction to Computer Programming / Introduction to Electrical and Electronics Engineering 8 OHS445 / ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety / Introduction to Ethics Governance 5 OHS445 / ETH401 Occupational Health and Safety / Introduction to Ethics Governance 5 EWP 452 Engineering Workshop Practice 5 MEC470 Engineering Graphics Laboratory 6 MEC 472 Engineering Mechanics Laboratory 2 PHY470 / CHM470 Engineering Physics Laboratory / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 PHY470 / CHM 470 Engineering Physics Lab / Engineering Chemistry Laboratory 2 CIN470/ EEE 470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory / Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 CIN470/ EEE470 Introduction to Computer Programming Laboratory / Electrical and Electronics Engineering Laboratory 2 Total CP 55 Total CP TRIMESTER 3 50 TRIMESTER 4 Transport Geography I 8 AUT405 Vehicle Dynamics 7 ACC401 Accounting Environment 14 AUT407 Transport Geography II 10 AUT402 Road Traffic Law 8 AUT408 Transport Policy and Environment 10 AUT403 Automotive Technology 7 AUT409 Transport Economics 10 MTH411 Probability and Statistics 10 AUE509 Quality Assurance and Reliability Engineering 7 AUT404 Automotive Technology Laboratory 4 AUT406 Vehicle Dynamics Laboratory 3 51 Total CP Total CP 47 TIMESTER 5 AUT501 Vehicle Noise and Vibration 7 AUT503 Traffic Collision and Investigation 7 AUT504 Logistic and Supply Management 7 AUT505 Traffic Control and Planning 7 AUT506 Management for Engineers 7 AUT507 Transport Project 12 AUT502 Vehicle Noise and Vibration Laboratory Total CP 4 51 Job Opportunities There is a great demand for safe and comfortable means of road transport. This in turn demands qualified / skilled Automotive Mechanics, Technicians and Automotive Engineers to repair and service vehicles to meet the Fiji standard. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK AUT401 Numerous job opportunities are offered to graduates in private firms and government departments. As a qualified Certificate IV or Trade Diploma holders, graduates are employed as Senior Mechanics, Leading Hands, Supervisors, Vehicle Inspectors and in middle management as well as lecturers and secondary school teachers in Technical and Vocational, Education and Training Centers. The qualifications also enable students to pursue further education to degree level. The knowledge and skill acquired also equip entrepreneur’s to venture into starting their own business or selfemployment ventures. 143 Unit Descriptors AEN301: Spark Ignition Engine This unit will enable students to competently service, adjust and check spark ignition engines by repairs or modifications. Prerequisites: AUT301, AUT 305, AUT306, AUT307 AEN302: Spark Ignition Engine and Fuel Systems This unit provides the students an understanding of the concept of spark ignition engine fuel systems and electrical/ electronics components. It also allows students to explain service requirements for various engine management systems and procedures required for fuel and electrical/electronics systems. Prerequisites: AUT 304, AUT306 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 144 AEN303: Spark Ignition Engine Workshop This units enable students to acquire an in depth knowledge of spark ignition engine system workshop components, operating principles and understanding of the concept of the spark ignition engine. Prerequisites: AUT 305, AUT 307 AEN304: Compression Ignition Engine This unit allows students to understand the concept of compression ignition engine components, describe the service and repair procedures for top and bottom end of compression ignition. Prerequisites: AUT304, AUT305, AEN 402, AEN403 AEN305: Compression Ignition Engine and Fuel System This unit deals with the concept of compression ignition engines, and fuel systems. It also includes fuel supply system components and its function. Prerequisites: AUT304, AUT305 AEN306: Compression Ignition Engine Workshop This unit provides students with an understanding of the concept of compression ignition engines. It also allows students to demonstrate the standard service routine in accordance with workshop repair manuals on lubrication system, repair and tests turbo and supercharging units. Prerequisites: AEN402, AEN403, AEN404, AEN405 AEN307: Automotive Engine Project This unit deals mainly with concept of automotive engine project. This includes identifying customer’s complaints on various diesel and petrol engines, preparing a detailed documented report on all projects undertaken. Prerequisites: AUT305, AUT307, AEN 403, AEN406 AEN308: Vehicle Mechanical Science 1 This unit allows students to understand various science concepts and appreciate how they are being applied in Automotive engineering related problems. This includes concepts of heat, gas properties, heat cycles and combustion process. Prerequisite: AUT401 AEN309: Vehicle Mechanical Science 2 This unit enables students to understand various scientific concepts and their application to motor vehicle components and also concepts in real workshop situations and scientific concepts being applied by the engineer’s design and the manufacture various motor vehicle components. Prerequisite: AEN408 AEN310: Automotive Commercial Procedure This unit deals mainly at the concept of workshop management, decision making, self-control and leadership. Also included is a requirement according to OHS regulations. Prerequisite: COM201 DAE507: Engine Technology The unit provides the students significant knowledge on the importance of engine design and how to differentiate features in relation to vehicle performance and to identify and differentiate the features of conventional and electronic fuel systems. Through this course students get an understanding of the selection of engineering material for vehicle components for improved performances. Prerequisite: Certificate IV in Automobile Engineering DAE503: Vehicle Engineering Science 1 The unit provides students fundamental knowledge on the engineering mechanics and how to solve industryrelated problems in regard to using engineering materials for better vehicle performance. Prerequisite: Cert. Automobile Engineering DAE504: Automotive Electrical and Electronic Principles The unit provides students the ability to understand the basics of electrical and electronics principles and to do calculations on electric and magnetic circuits. Students will become versed in electric symbols and understand more about electronics and semi-conductor devices, as well as gaining skills to recognize and identify AC and DC circuits and usage. Prerequisite: Cert. Automobile Engineering DAE505: Engineering Drawing The unit is designed for the students to have a better understanding of engineering drawing in order for them to master engineering design concepts. Students will learn to draw using 3rd angle and 1st angle drawing to conform to standards, drawing with scales or interpreting a scale drawings, carrying out assembly drawing with components not assembled, drawing an isometric object from given plan view, front or end view, and learn to construct objects using drawing skills. Prerequisite: Cert. Automobile DAE512: Engineering Materials The unit enables the student to determine various types of material properties through laboratory investigation, demonstrates the effects of combining materials to improve performance characteristics in relation to Automobile and to have thorough knowledge of composite material and there uses and advantages Prerequisite: Cert. Automobile experience of engineering applications and develop their sense of responsibility and self-assurance to be able to work in a team environment DAE509: Auto-Cad The unit is designed to assist the students in the development of their elementary knowledge and skill. Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to evaluate the features of the design process which are of importance to the engineering industry, assess and appreciate how computer software can assist in the design and analysis of an engineering component and how to use a modern computer. DAE602: Mechanics of Road Vehicle 2 The unit provides the students an understanding of vehicle test methods and the concept of vehicles in motion. It provides knowledge on the fundamental control of vehicles into advance levels also on performance prediction and design analysis. Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to analyze simple vehicle aerodynamic problems, solve problems analytically in a vehicle laboratory and be able to carry out tests on vehicles and compare practical results to theoretical results. DAE508: Automotive Sensory System The unit provides the students an understanding of the concept of vehicle electronic systems to provide a background on vehicle sensors and their uses on an advance level; to analyse simple vehicle electronics; to identify the different types of sensors used in modern vehicles; to diagnose faults in vehicle electronic circuits; and to carry out tests on vehicles and compare practical results to the theoretical findings. Prerequisite: DAE403 DAE603: Vehicle Engineering Science 2 The unit is designed for the students to understand the strength of materials, familiarize with the principle of motion, torque, and energy release and absorb on moving bodies, to extend the students’ basic knowledge of mechanical science principles and their applications to engineering problems and to perform experimental investigations and reinforce theoretical concepts. Prerequisite: DAE402 DAE502: Mechanics of Road Vehicle 1 This unit is intended to develop the students’ understanding of vehicle engineering dynamics and its applications to automotive engineering problems, apply the technology of vehicle engineering and the science of vehicle dynamics to the solution of automotive engineering problems, and to perform experimental investigation and relate this to theoretical analysis. DAE604: Auto Project The unit is designed for students to increase their ability to plan, organize and communicate the solution to a brief project and solve a realistic engineering problem, which requires the application and integration of other units within the program. Furthermore, upon completion of this unit, students will be able to synthesize the content of other units of the program, broaden their DAE606: Engineering Management The unit intends to provide a good understanding of the management functions of any engineering company and the concept of good management. Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to identify the need for good management, identify the role of managers, recognize and apply important marketing strategies, communicate effectively on middle management levels, communicate and solve industrial disputes and apply business plans in a practical environment. DAE605: Measurement and Instrumental Control The unit provides the students an understanding of the principles and use of measurement and instrumentation as used in the mechanical, automotive and manufacturing industry. In addition, it gives a sound knowledge of mechanical and electrical instrumentation appropriate to automotive and mechanical engineering. DAE607: Manufacturing Technology The unit enables students to gain skills and evaluate basic Manufacturing Technology including the selection of techniques and processes, specify appropriate manufacturing techniques taking into account quality, quantity and cost, and appreciate application of developing technology and appropriate techniques. Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to select appropriate equipment and plan the manufacture of a range of simple parts using basic fabrication techniques; where appropriate conduct practical investigation; and identify, analyse and select the correct information leading to manufacturing decisions in regard to operations for the production of a simple product. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK DAE510: Vehicle Technology The unit is formulated to illustrate to the students the importance of vehicle system requirements, driveline and steering systems, design requirements for transmission and final drive, to provide an overall view of vehicle performance through the vehicle system operations and to highlight the importance of vehicle structure and safety requirements in vehicles. Prerequisite: DAE501 DAT503: Transport Legislation 1 The unit is designed for the development of students’ knowledge and understanding of vehicle legislation such as those stipulated in the Fiji’s Land Transport Act and those observed internationally. Upon completion of this unit, the students will be able to understand the main component of vehicle legislation and demonstrate the standard inspection procedures and legislation on road vehicles. DAE608: Thermodynamics The unit is designed to assist the students in the 145 development of their elementary knowledge and skills in the physics of heat and its uses in engineering. The other main purpose is to provide sufficient knowledge in the elementary principles of thermodynamics and fluid mechanics. Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to determine a wide range of engine operating temperatures through calculation, determine engine maximum torque, power, and maximum fuel consumption of different gear ratios or engine speed by laboratory tests on engines, determine the mechanical equivalent of heat by allowing mechanical work to agitate a liquid enclosed in an insulated calorimeter, determine basic fluid properties, components and their selection and be able to calculate static fluid pressure and forces. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK DAE511: Engineering Design The unit is drawn to enhance the students understanding of the basic principles of design and the use of engineering components; to apply a systematic approach on any engineering design work, analyze, calculate and determine proper specifications and needs of a given engineering design component; and to apply costing on assigned projects. DAE506: Workshop Administration and Customer Service The unit provides the students the understanding of the principles of workshop administration. It gives a sound base knowledge on customer service approaches and applications, applying the theory of workshop supervision on real situation problems and acquiring the skills and knowledge on how to develop good customer relationships. DAE513: Quality Assurance The unit provides an understanding of the concepts, principles and implementation of quality assessment in engineering. Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to apply the quality principles of quality assurance in an organization, illustrate information flow in defect prevention, use and understand the application of statistical appraisal tools to enhance meaningful gains and to use product appraisal equipment and gain meaningful knowledge from the exercises. AUT303: Workshop Safety Procedure This unit provide the students an understanding of the concepts of workshop safety procedures and enables students to acquire an in depth knowledge of workshop safety procedures. Prerequisite: FSLC or equivalent AUT402: Technical Drawing This unit provides the students an understanding of the concepts of technical and engineering related drawings of mechanical components, also to understand their functions and operating principles. Prerequisite: FSLC or equivalent 146 ALM401: Mechanical Aid Project This unit enables students to undertake on-job training under minimum supervision, and carry out report writing upon successful completion of tasks. ALM402: Hydraulic, Pneumatics and Electrical Power Generation This unit enables students to understand the concepts of operations of various components related to hydraulic and compressed air systems and electrical power generation and also to acquire practical knowledge of fault diagnostic and rectification procedures. ALM403: Hydraulic, Pneumatics and Electrical Power Generation Workshop This unit enables students to understand the concepts of operations of various components related to hydraulic and compressed air systems and electrical power generation and also to acquire practical knowledge of fault diagnostic and rectification procedures. ALM404: Power Transmission This unit enables students to understand the concepts of operations of various components related to hydraulic and compressed air systems and electrical power generation and also to acquire practical knowledge of fault diagnostic and rectification procedures. ALM405: Power Transmission Workshop This unit enables students to understand the concepts of operations of various components related to hydraulic and compressed air systems and electrical power generation and also to acquire practical knowledge of fault diagnostic and rectification procedures DAT501: Transport Systems 1 The unit intends to develop knowledge and skills required in the development of strategic initiatives as well as personal responsibilities in performing complex technical operations, planning and evaluating in a variety of contexts in relation to road transport. Prerequisite: Cert. Automobile Engineering DAT502: Mechanics of Transport System 1 The unit is designed to develop the student’s ability to apply the technology of vehicle engineering and the science of vehicle dynamics to the solution of automotive engineering problems and to perform experimental investigation and relate this to theoretical analysis. Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to apply the knowledge and theory of vehicle engineering in a real work situation, develop and analyze problems involving bending theory, simple mechanism vibrations and balances and be able to understand vehicle engineering dynamics and their application to automotive engineering problems. Prerequisite: Cert. Automobile Engineering DAT602: Mechanics of Transport System 2 The unit is designed to help students understand the strength of materials and familiarize themselves with the principle of motion, torque, and energy release and absorb on moving bodies. Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to extend the basic knowledge of mechanical science principles and their applications to engineering problems and to perform experimental investigations and reinforce theoretical concepts. Prerequisite : DAT502 DAT403: Transport Legislation 1 The unit is designed to develop knowledge and understanding of vehicle legislation such as those stipulated in the Fiji’s Land Transport Act and those observed internationally. Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to describe the main component of vehicle legislation and demonstrate the standard inspection procedures and legislation on road vehicles. Prerequisite: DAT502 DAT607: Transport Project The unit enables students to undertake independent research analysis to a specific topic related to road transportation. Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to develop a project proposal after consultation with a supervisor, analyze the problem to be solved and state the specific objectives, prepare a group chronological plan and prepare a formal written report on the project. Prerequisite: DAT501/DAE510 DAT505: Vehicle Noise and Vibration The unit is formulated for the students to gain the skills and knowledge to understand the nature of sound and its relationship to vibration and methods of reducing its sources. Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to locate sources of noise and vibration with respect to engine, exhaust, wind noise and other rotational imbalances, explain the relationship between noise and vibration, differentiate between structureborne and air-borne sources, analyse and describe methods of noise reduction in areas concerned and utilize the instrumentation that is used to document human non-linear response to sounds. Prerequisite: DAT501 DAT506: Logistic Supply Management The unit provides students with the required theoretical and practical knowledge on situational analysis and develops appropriate strategies in accordance with the organizational environment. It also develops the necessary skills to create and formulate a business plan for an organization at different operating categories. Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to mobilize resources, coordinate multi-modal DAT507: Transport and Environment The unit enables students to look at the relationship between transport fuel and environment with the objective of examining fuel efficiency whilst reducing pollution through the exhaust system. Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to understand energy generation, energy conservation, and energy aspects of transport and environment. Prerequisites: DAT501 DAT606: Transport Contract Services The unit is designed to promote an awareness which will provide students the knowledge and skills about negotiating transport contacts services with contractors and the ability to define, evaluate and formulate a contract. Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to negotiate contracts with contractors, complete contract negotiation and complete enterprise contract requirement. Prerequisite: COM302 DAT508: Distribution and Business Planning The unit is designed to equip students with situations, market analysis skills, evaluation of resource distribution with the capability to developing strategies on proper distribution of resources. It also provides an awareness to develop, implement and evaluate a workable business plan. Prerequisite: COM302 DAT605: Transport Management The unit helps students to develop an understanding of different technical operational transport solutions and proactively plan and manage transport contracts, formulate appropriate methods of asset inventories and contribute to the development of corporate transport policies.Prerequisite: COM302 DAT604: Fleet Control and Logistics The unit provides students with the underpinning knowledge that equips them to make informed decisions about the transport fleet and its operations in support of the business. It also develops their awareness of the commercial implications of effective asset utilization. Prerequisite: COM302 DAT603: Transport Legislation 2 The unit enables students to have a thorough knowledge of the acts and regulations of the governing authority overseeing the transportation requirements of Fiji and recommend appropriate changes to the government as necessary in accordance with the mode of transportation available and corresponding access routes. Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to describe defective type pursuant to LTA Regulation, explain the importance of steering and suspension components, vehicle braking system, seating and safety of drivers and determine maximum loads on a vehicle. Prerequisite: DAT505 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK DAT504: Transport Accident Investigation This unit is designed for those who have a responsibility for, or have interest in the safety of road transport operations. It will enable students to identify the causes of collisions and other transport incidents and apply the lessons learned for preventative strategies required on Fiji roads. Upon completion of this unit, students will be able to describe the background to, and cause of, road traffic collisions and incidents, explain the methodology of gathering and assessing available data resulting from an incident, monitor and reduce risks to these incidents and use basic tools to assess the information gathered and come up with the appropriate course of action.Prerequisite: Cert. Automobile Engineering transport activities, monitor consignment(s) tracking and implement contingency management strategy Prerequisite: COM302 147 AUT304: Vehicle Mechanical System This unit introduces the concept of vehicle mechanical systems, components, functions and their operating principles. Prerequisite: FSLC or equivalent AUT305: Vehicle Mechanical System Workshop This unit deals with safety inspection on vehicles. It also includes distinguishing of vehicle body types, components and reassembly. Prerequisite: FSLC or equivalent AUT306: Vehicle Electrical/Electronic System This unit enables the students to understand the concepts of vehicle electrical/electronic systems. Topics included are the testing/replacing electrical/ electronic units and components, fundamentals and circuits. Prerequisite: FSLC or equivalent COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK AUT307: Vehicle Electrical/Electronic System Workshop This unit enables students to acquire vehicle electrical/ electronic systems knowledge, appropriate industrial ability and practical skills, connect circuits and carry out measurements. Prerequisite: FSLC or equivalent AUT308: Craft Science This unit allows students to understand the real applications of scientific knowledge gained from high schools in the world of technology or engineering, with emphasis on automotive engineering. This includes understanding basic molecular structures of materials, corrosion, mass, volume and quantities, behavior of fluids, linear motion and dynamics. Prerequisite: FSLC – Physics and Chemistry HMP401: Heavy Mobile Plant Technology 1 This unit provides a broad based theoretical knowledge and skill of design features, operation, and maintenance, overhaul and fault diagnosis of heavy mobile plant, components and systems. Prerequisite: AUT304 HMP402: Heavy Mobile Plant Workshop 1 This unit provides a broad based knowledge and skills of the repair, maintenance and overhaul of the crawler and wheeled tractors components and systems. Prerequisite: AUT305 HMP403: Heavy Mobile Plant Technology 2 This unit provides a broad based theoretical knowledge and skills of design features, operation, maintenance, overhaul and fault diagnosis of heavy mobile plant, components and systems. Prerequisite: AUT304 148 HMP404: Heavy Mobile Plant Workshop 2 This unit provides a broad based practical knowledge and skills of the repair, maintenance and overhaul of the crawler and wheeled tractors components and systems. Prerequisite: AUT305 HMP405: Heavy Mobile Plant Project This unit provides the students wide range of knowledge and understanding of heavy mobile plants. To allow students to be self-confidence in research work providing their own ideas and motivation towards their projects. LMV401: Motor Vehicle Technology 1 This unit provides students with an understanding of the concepts of operation of components on suspension, chassis and brakes. It also enables students to describe the function and basic services of air conditioning systems and preventative service maintenance. Prerequisite: AUT304 LMV402: Motor Vehicle Technology Workshop 2 This unit enables students to carry out inspection and repairs on road wheels and suspension. It also includes repairs in anti-skid and braking systems. Prerequisite: AUT305 LMV403: Motor Vehicle Technology 2 This unit provides an understanding to the students of the concepts of operation of various components related to light vehicle power transmission. To enable the students to acquire an in depth theoretical knowledge of fault diagnostic and rectification procedures and also the importance of the preventive maintenance schedules. Prerequisite: AUT304 LMV404: Motor Vehicle Technology Workshop 2 This unit provides the students with practical expertise on components associated to light vehicle transmission. To enable students acquire an in depth knowledge in diagnostic and rectification procedures with minimum supervision. Prerequisite: A405 LMV405: Motor Vehicle Project This unit provides the students wide range of knowledge and understanding of light motor vehicle. To allow students self-confidence in research providing their own ideas and motivation towards their projects. AEE401 Automotive Electrics This unit provides the students with an understanding of the concepts of vehicle electrical/electronic systems. It also enables students to acquire an in-depth knowledge of vehicle electrical/electronic components, their functions and their operating principles. Prerequisite: AUT406, AUT407 AEE402 –Automotive Electrical Workshop This unit provides students an understanding of the concepts of vehicle electrical/electronic systems. It includes tests and services for the vehicle’s airconditioning system, faults diagnosis and preventative maintenance of the ignition system and how to carry out fault diagnosis and preventative maintenance of the starting system. Prerequisite: MVE401 AEE403-Automotive Electronics and Auxiliary System This unit provides students with an understanding of the concepts of vehicle electrical/electronic systems; especially lighting, charging, EFI and other vehicle auxiliaries systems. It also enables students to acquire knowledge of vehicle electrical/electronic components, their functions and their operating principles. Prerequisite: MVE401, MVE402 AEE406- Automotive Electrical Science This unit illustrates student’s knowledge of engineering mechanics to solve industry related problems and understanding of the engineering materials that are used in automobiles today. It also includes mass, volume, densities, relative densities and their units. Prerequisite: A pass in FSLC or equivalent PBS308- Auto Body Project This unit develops ability to diagnoses the problems and attend to customer’s requests, and be able to prepare quotations, material lists and a report of work done at completion of tasks. Prerequisite: A pass in FSLC or equivalent PBS301- Hand Foaming Theory This unit promotes the safe and healthy work environment. It investigates the history of the manufacture of the first automobile and improvement work carried out till today. Prerequisites: A Pass in FSLC or equivalent PBS302- Hand Foaming Workshop This unit basically imparts to the students how to be a safe worker and the art and skills of panel fabrications; to know the importance and the purpose of shape in a panel; panel parts identification and inner structure modeling and strength. Prerequisite: A Pass in FSLC or equivalent PBS303 - Welding Technology This unit instills the importance of a safe working environment and a safe working method and also provides the students with the knowledge to understand welding principles and procedure. Prerequisite: A Pass in FSLC or equivalent PBS304 – Body Maintenance Theory This unit provides the students with the operational functions of body jack and alignment equipment and a spray gun tool/correct surface preparation procedures ready for filler application and to know the importance PBS305 - Body Maintenance Workshop This unit provides the students with practical experience on components and equipment that is associated with the development of high level of knowledge in realignment technology and develops a sense of confidence. Prerequisites: A pass in FSLC or equivalent PBS306 – Corrosive Treatment Theory This unit provides the understanding of steps and the purpose to carry out repairs by sectioning and be well versed with the wheel alignment angles and repair procedures in the case of a major frontal accident. Prerequisite: A pass in FSLC or equivalent PBS307- Corrosion Treatment Workshop This unit develops the student’s ability to diagnose problems and attend to customer requests; and to prepare quotations, material lists and prepare reports of the work done at completion of tasks. Prerequisite: A pass in FSLC or equivalent PBS309- Auto Body Design This unit is to enhance the students understanding of the basic principles of computer design and the advantage of hand drawing over CAD. Prerequisite: A pass in FSLC or equivalent PBS402- Vehicle Accident Workshop This unit provides the student with practical experience of components and equipment associated with minor accident repairs, with minimum supervision to be confident and produce the best. Prerequisite: A pass in FSLC or equivalent PBS403- Realignment Technology This unit provides the students with capability in major repair techniques and alignment of vehicles. Prerequisite: A pass in FSLC or equivalent PBS404 - Realignment Technology Workshop This unit provides the students with practical experience on components and equipment that are associated with the development of high level of knowledge in realignment technology and helps them develop a sense of confidence. Prerequisite: A pass in FSLC or equivalent COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK AEE404-Automotive Electronics and Auxiliary Workshop This unit provides the students with an understanding of overhauling and testing components of charging, lighting, EFI systems and other vehicle auxiliary faults. It also provide the students with skills to carry out logical test procedures for diagnosing and rectifying faults in charging circuits, lighting circuits, EFI and other vehicle auxiliaries Prerequisite: MVE402 of having a strong sub-frame structural member and its effect on weight share. Prerequisites: A pass in FSLC or equivalent PBS405 - Realignment Technology Project This unit provides the students a wide range of knowledge and understanding of major accident realignment and restriction work and allows students to build self-confidence and be self-motivated in research work and project writing. Prerequisite: A pass in FSLC or equivalent 149 For More Information Contact: Mr. Pravin Chand Acting Head of School Phone: 3381044/ Ext: 1971 E-mail: pravin.chand@fnu.ac.fj OA – Ms. Alisi Ext: 1601 Email: OA-Automobile@fnu.ac.fj COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 150 General Information The Fiji Maritime Academy (FMA), previously known as the School of Maritime Studies, was established in 1975 by the Government of Fiji to increase the number of qualified Mariners and Seafarers in Fiji and the Pacific region. It shifted to its current location at Laucala Bay in 1982. In 2007, the School included the Fisheries Programme in its curriculum and was renamed the School of Maritime and Fisheries. In January 2014, the Academy handed over its Management to CINEC, (Colombo International Nautical and Engineering College) Sir Lanka, and has been re-branded the Fiji Maritime Academy. All programmes offered as approved by the Maritime Safety Authority of Fiji (MSAF). The Academy has been conducting courses in compliance with Standards of Training, Certification and Watchkeeping for Seafarers (STCW) 78 code as amended in 2010. All operational and management level Certificate of Competency (COC) are issued by MSAF. Staff Profile CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICER CAPTAIN ANURA B. HERATH HEAD OF ACADEMY/HEAD OF NAUTICAL SCIENCE CAPTAIN VOI GARISAU Master Class 1 (Foreign Going), (NZ),1ST Mate (Foreign Going), (UK), 2ND Mate (Foreign Going), (UK) Class 2 Pilots License(Suva); Graduate Deck Cadet of Southampton School of Navigation (UK) (Now War sash Maritime Academy)ONC (Nautical Science), (UK); B App Sc (Nautical Studies), (AMC, AUST);Examiner Master & Mates Certificate (Singapore), JP (Fiji) ADJUSTMENT LECTURER TOMASI CAMA KETE, MSc. [Marine Management] [WMU, Sweden]; Master class 1, Australia LECTURER II RUSIATE LOMANI, Class 3 Masters and Watch Keeper (FIT), Dip. Nautical Science (FIT), Adv. Certificate in Ship Operation (FIT) MACUI MUA Diploma in Nautical Science, Adv. Cert. in Ships operations, Class 3 Master Watch keeper MSAF, ToT1 JOSEFA BALEINUKULALA Master Class 5 Certificate-FIT HOD-SAFETY AND SURVIVAL/ PRINCIPLE LECTURER TEVITA ROBANAKADAVU,M.N.I , Adv. Dip inApp.Sc (Shipmaster), (Aust); Master Mariner Class 1 FG.,(NZ); IDTT, (FIT); Craft Cert. Shipbuilding, (FIT); Adv Cert. Shipbuilding, (FIT) LECTURER II TOKA WAQABACA, Class 3 master/ Deck Watch Keeper CoC, Fiji] Dip. (Nautical Science) (FIT); Adv. Cert. (Ships Operations), (AMC, AUST); Adv. Instructors Cert., (FMF,NZ) SHERYN LUTUNI Class 3 WatchKeeper TUTORIAL ASSISTANT MOSESE DIGITAKI, Dip (Marine Seafood), (USP); Adv. Cert. (Ships Operations), (FIT). PART -TIME LECTURER TANIELA BAYA, Cert. Deck Apprenticeship; Cert of Competency Deck Watch keeper Class III Master SATINI TATAU- Class 3 Watch Keeper COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Fiji Maritime Academy has been providing service like Maritime Training to the Seafarers of Fiji as well as nationals from the South Pacific region. We offer courses that enable high school graduates the pathway to obtaining certification to work as navigation or engineering officers on local and international ships. HOD- MARINE ENGINEERING SUNIA BIU LAVAKI, 3rd Class Motor, (FIT); 2nd Class Motor, (FIT); Higher National Dip. Eng., (UK) LECTURER II GEORGE RUDOLPH FONMOA, TC (Fitting and Machining), (FIT); Cert. (Mechanical Engineering) (Part 1) City and Guilds; (FIT); Cert. Tertiary Teaching (FIT); Cert. Basic Welding (FIT). 151 OSEA WAQANISAU, B.Tech (Mechanical & Manufacturing), [USP] TIMOCI TURAGA-Diploma in Applied Computing CCNA- FIT JOSEVATA WILIKIBAU, Class 3 (Marine Eng) (Watch keeper), (FIT); Dip. (Marine Engineering), (FIT); Class3/Watch-Keeper (Marine Engineering), (Manukau, NZ). HEAD OF DEPARTMENT -QUALITY MR. MAHESA ABEYNAYAKE Marine Engineer Class 1 TECHNICIAN VANI TUNABA. Trade Certificate in Machining, Mechanical engineering technician Part I (City & Guilds), Mechanical engineering technician Part II (City & Guilds) PROGRAM ASSISTANT (MARINE ENGINEERING/ QUALITY DEPT/SIMULATOR) PRIYA PRITIKA DAYAL, BCom-Management and Public Administration and Economics- USP PROGRAM ASSISTANT (NAUTICAL SCIENCE/ SAFETY AND SURVIVAL AND SHIP BUILDING) FAWIZA KHANAM, Diploma in Business Administration, FNU HOD-SHIPBUILDING WAISALE SOVALAWA, Cert. (Shipbuilding),(FIT); Cert. (Course of Instruction), (FNTC); TC (Shipbuilding), (FIT); Adv. Trade Cert (Shipbuilding), (FIT); Dip. (Tertiary Teaching)(FNU). COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK OFFICE ADMINISTRATOR MOHAMMED TASLIM, BSc. (Marine Science), USP ASSISTANT LECTURER ISIRELI VAKURUIVALU, Adv TC (Shipbuilding), (FIT); TC (Shipbuilding), (FIT); Cert. (Teaching), (AMC, Aust.) ACADEMIC OFFICER SONAL SHARMA, PGD-Management and Public Administration, USP TECHNICIAN TUIMASI MASITABUA, TC (Shipbuilding), (FIT). FINANCE OFFICER PRIYA SINGH, PGD-Accounting, FNU HOD-SIMULATOR Vacant PERSONAL ASSISTANT TO CEO IVA MAGARET CHAND, BSc. (Pre Professional Biology) SIMULATOR INSTRCTOR/ SENIOR LECTURER REBEKAH SOKOC–COC, Deck Watch Keeper (FIMSA), ToT 1 MAINTENANCE SUPERVISOR KISHORI NAND RAJ, (Marine OHS) (FNU), (Survival Technique) (FNU), (First Aid) (St. John) TECHNICIAN RAVINESH CHAND- Trade Diploma Industrial Electronics and Avionics, CCNA- FIT LIBRARIAN GEETA NARAYAN, Cert (Library Studies) Programme Details and Duration for Nautical Science CERTIFICATE II CERTIFICATE III CERTIFICATE IV TRADE DIPLOMA LEVEL LEVEL LEVEL LEVEL Total Number of Units to complete 19 15 14 48 2 Trimesters 2 Trimesters 2 Trimesters 6 Trimesters 9 8 7 7 12 weeks 12 weeks 12 weeks 12 weeks 9 months 9 months 9 months 12 months 2 year 2 years 2 years 4 years the programme Number of Trimester to complete all units Number of units to complete each Trimester Number of weeks per trimester Minimum period required for industrial attachment Minimum period of time to complete the whole programme Programme Details and Duration for Marine Engineering 152 Total Number of Units to complete the programme CERTIFICATE II CERTIFICATE III CERTIFICATE IV TRADE DIPLOMA LEVEL LEVEL LEVEL LEVEL 16 9 14 39 Number of Trimester to complete all units Number of units to complete each Trimester Number of weeks per trimester Minimum period required for industrial attachment Minimum period of time to complete the whole programme 2 Trimesters 1 Trimester 2 Trimesters 5 Trimesters 8 9 7 8 12 weeks 12 weeks 12 weeks 12 weeks 12 months sea time 12 months sea time 1 1/2 years 2 years 4 years 6 workshop/12 months sea time 2 year 6 months 6 months workshop 12 months sea time Programme Details and Duration for Ship Building Total Number of Units to complete the programme Number of Trimester to complete Number of units to complete each Trimester Number of weeks per trimester Minimum period required for industrial attachment Minimum period of time to complete the whole programme STAGE 2 STAGE 3 STAGE 4 9 8 9 8 1 Trimester 1 Trimester 1 Trimester 1 Trimester 9 8 9 8 12 weeks 12 weeks 12 weeks 12 weeks 6 months 6 months 6 months 6 months 1 year 1 years 1 years 1 years Trimester Mode Programmes for 2015 For any enquiry on the trimester mode programmes for 2016 please contact the Head of Academy or Academic Officer-FMA. Entry Qualification Cadet Officer Training Trade Diploma in Nautical Science and Trade Diploma in Marine Engineering a. Fiji Seventh Form Examination (FSFE) pass mark of 240/400 or equivalent b. Fiji School Leaving Certificate(FSLC) pass mark of 240/400 or equivalent For both (a) (b), 60% pass mark in Maths, Physics and English is essential • Pass in Aptitude Test Conducted by FMA Certificate II in Ship Operations (Class 5 Master) Prerequisite Certificate: Safety Certificate. Required Sea Service: Either (a) 36 months approved seagoing service whilst holding a Certificate of Competency not lower than a Safety Certificate; or (b) 24 months approved seagoing service on ships of 80 gross tonnage or more whilst holding a Certificate of Competency as Master/Engineer Class 6; or (c) 24 months approved seagoing service on ships of 80 gross tonnage or more whilst holding a Certificate of Competency as Deck Watch Rating; (d) 6 months approved seagoing service on ships of 80 gross tonnage or more whilst holding a Certificate of Competency as Able Seafarer Deck. And MSAF approval letter Certificate III in Ships Operations (Class 4 Master) Prerequisite Certificate: Master Class 5. Required Sea Service: 12 months approved seagoing service as a watchkeeping officer holding a Certificate of Competency not lower COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK all units STAGE 1 153 And MSAF approval letter Certificate IV in Ships Operations (Class 3 Master) Prerequisite Certificate: Master Class 4. Required Sea Service: (a) 12 months approved seagoing service as a watchkeeping officer whilst holding a Certificate of Competency not lower than a Master Class 4 on a ship of more than 500 gross tonnage; or (b) 36 months of approved education (approved cadet training program) including18 months sea service served on ships of more than 500 gross tonnage; or (c) 12 months of approved sea service as watchkeeping officer whilst holding a Deck Watchkeeper near coastal Certificate on ships of more than 500 gross tonnages. And MSAF approval letter Department of Marine Engineering COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 154 Certificate II in Marine Engineering (Class 5 Engineer) Prerequisite Certificate: Safety Certificate Required Sea Service: Either: (a) not less than a 24 months of approved sea service on ships of 100 kW or more18 months of the 24 months must be served on duties associated with engine Operation and 6 months of approved workshop; or (b) have completed approved education and training of at least 24 months which includes 12 months of onboard training (on ships of more than 100 kW main propulsion power) documented in an approved training record book; (c) not less than 12 months approved seagoing service on ships of greater than 100 Kw engine power whilst holding a Certificate of Competency as Master/ Engineer Class 6 and completed not less than six months of approved workshop training; or (d) not less than 12 months approved seagoing service on ships of greater than 100kW engine power whilst holding a Certificate of Competency as Engine Watch Rating and completed not less than six months of approved workshop training; (e) Not less than 6 months approved workshop whilst holding a Certificate of Competency as Able Seafarer Engine served on duties associated with engine operation Course And MSAF approval letter Certificate III in Marine Engineering (Class 4 Engineer) Prerequisite Certificate: Safety Certificate. Required Sea Service: Either: (a) Not less than 12 months approved seagoing service on ships of 250 kW or more as a watchkeeping engineer whilst holding a Certificate of Competency as an Engineer Class 5; (b) Have completed approved education and training of at least 36 months which includes 6 months onboard training (on ships more than 250 kW propulsion power machinery) which include on-board training documented in an approved training record book. And MSAF approval letter Certificate IV in Marine Engineering (Class 3 Engineer) Prerequisite Certificate: Engineer Class 4. Required Sea Service: Either: (a) Not less than 12 months approved seagoing service as a Watchkeeping Engineer whilst holding a Certificate of Competency as an Engineer Class 4; or (b) Have completed approved education and training of at least 36 months which includes 6 months onboard training on ships of more than 500 kW main propulsion power machinery. Onboard training must be documented in an approved training record book; or (c) Have completed 24 months approved shore based (slipways, dockyards, marine engineering workshops or boiler workshops) education and training documented in an approved training record book; and (d) have served 12 months of approved sea going service in an engineering capacity on ships of more than 500 kW main propulsion power machinery. And MSAF approval letter Department of Ship Building: Certificate IV– Shipbuilding •Form 6 pass in Technical Drawing, Math and English. •Experience in Woodwork or Metal work will be considered. Programmes, Stages and Units All Certificate programmes from I to IV are worth a minimum of 60 credit points each. The credit points are made up of 3 elements as follows: (i) A Safety Certificate at least 10 credit points; (ii) 12 months approved sea service attachment (requirement by MSAF) which makes up between 30 to 40 credit points; (iii) Formal courses at level 2 and 3 worth from 10 - 20 credit points. MARINE ENGINEERING PROGRAMMES Certificate II in Marine Engineering (Class 5) Unit Name CP DME302 Marine Engineering Drawing and Design Unit Code Unit Name 2 DME 304 Enabling Computer 2 DME303 Marine Basic Mathematics 3 DME405 Applied Mechanical Science 3 DME406 Marine Basic Thermodynamics 2 DME402 Marine Basic Fitting and Practice 9 COM 301 Communication skills 5 DME 420 Social Education 1 DME404 Marine Engineering Knowledge - Motor 5 DME 201 Maritime Law 1 DME407 Marine Engineering Knowledge General 5 DME 300 Naval Architect and Ship construction 2 DME408 Marine basic Electrical knowledge 5 DME409 Marine Basic Machining 9 DME 305 ISO 9000 & 14000 awareness course 1 DME 403 Engine Simulator training 3 TOTAL CP CP 62 Note: Pre-requisite: Basic Safety Certificate and MSAF Approval Letter Student have to Complete 6 months workshop and 12 months sea time : Certificate III in Marine Engineering (Class 4) DME 411 Marine Basic Applied Mechanics 2 3 DME 416 Marine Basic Electro Technology and Electronics 4 DME 412 Marine Basic Thermodynamics 2 2 DME 417 Marine Engineering Knowledge- General 2 6 DME 413 Marine Engineering Drawing 3 DME 418 Basic Naval Architecture and Ship Construction 4 DME 414 Marine Basic Applied Mathematics 3 DME 419 Engine Simulator Training 2 DME415 Marine Engineering knowledgeMotor 2 5 TOTAL CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Unit Code 32 Note: Pre-requisite: Class 5 Engineer and MSAF Approval Letter Students have to complete 12 Month sea time Certificate IV in Marine Engineering (Class 3) Unit Code Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name CP DME 510 Marine Applied Mathematics 3 3 ACR 450 Principles of Marine Refrigeration 4 DME 503 Marine Applied Mechanics 4 WKE 513 Vessel Management and Maritime Law 4 155 DME 504 Marine Thermodynamics 3 EVG301 Ethics Values and Governance 4 DME 502 Marine Engineering Drawing and Design 3 3 DME 505 Marine Engineering Knowledge-General III 10 WKE511 Marine Control System 4 DME 506 Marine Engineering Knowledge- Motor III 10 DME 508 Naval Architecture and Ship Construction 5 DME 512 Marine Electronics Principles 4 DME 516 Marine Room Simulation 2 2 TOTAL CP 64 Note: Pre-requisite: Class 4 Engineer and MSAF Approval Letter Students have to complete 12 months Sea time Trade Diploma in Marine Engineering (EA1) COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Unit Code Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name CP DME 302 Marine Engineering Drawing and Design 2 DME 404 Marine Engineering Knowledge-Motor 5 DME 303 Marine Basic Mathematics 3 DME 407 Marine Engineering Knowledge-General 5 DME 304 Enabling Computer 2 DME 201 Maritime Law 2 2 DME 405 Applied Mechanical Science 3 DME 300 Naval Architect and Ship Construction DME 406 Marine Basic Thermodynamics 3 DME 408 Marine Basic Electrical Knowledge 5 DME 402 Marine Basic Fitting and Practice 9 DME 409 Marine Basic Machining 9 1 3 COM 301 Communication Skills 5 DME 305 ISO 9000 &140000 awareness course DME 420 Social Education 4 DME 403 Engine Simulator Training MSC112 Elementary First Aid MNS 204 Personal Safety and Social Responsibility MSC110 Basic Fire Fighting MSC106 Seafarer Designated Security Duties MNS101 Survival Technics TOTAL CP 68 Note: EA2 The students are required to do 6 months Workshop and 12 months sea time and the relevant assignment to be completed prior to entry into EA3 Trade Diploma in Marine Engineering (EA3) Unit Code Unit Name CP DME 411 Marine Basic Applied Mechanics 2 3 DME 412 Marine Basic Thermodynamics 2 DME 413 Unit Code Unit Name CP DME 416 Marine Basic Electro Technology and Electronics 4 2 DME 417 Marine Engineering Knowledge- General 2 6 Marine Engineering Drawing 3 DME 418 Basic Naval Architecture and Ship Construction 4 DME 414 Marine Basic Applied Mathematics 3 DME 419 Engine Simulator Training 2 DME 415 Marine Engineering KnowledgeMotor 2 5 TOTAL CP 32 Note: EA 4:The students are required to do 12 months of sea time and the relevant assignment to be completed prior to entry to EA5. Trade Diploma in Marine Engineering (EA5) Unit Code 156 Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name CP DME 510 Marine Applied Mathematics 3 3 EVG 401 Ethics, Values and Governance 4 DME 503 Marine Applied Mechanics 4 DME 505 Marine Engineering Knowledge- General III 10 DME 504 Marine Thermodynamics 3 DME 506 Marine Engineering Knowledge- Motor III 10 DME502 Marine Engineering Drawing and Design 3 3 DME 508 Naval Architecture and Ship Construction 5 DME 507 Marine Electrical Knowledge 4 DME 512 Marine Electronics Principles 4 WKE 511 Marine Control System 4 DME 509 Engine Room Simulation 2 2 ACR 450 Principles of Marine Refrigeration 4 WKR513 Vessel Management and Maritime Law 4 TOTAL CP 64 Trade Diploma in Marine Engineering (Watch Keeper) Unit Code Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name CP Marine Applied Mathematics 3 3 EVG 401 Ethics, Values and Governance 4 DME 503 Marine Applied Mechanics 4 DME 507 Marine Electro Technology II 6 DME 504 Marine Thermodynamics 3 DME 508 Naval Architecture & Ships 5 DME502 Marine Engineering Drawing and Design 3 3 WKE 514 Marine Engineering knowledge Motor IV 6 DME 507 Marine Electrical Knowledge 4 WKE 515 Marine Engineering Knowledge General III 6 WKE 511 Marine Control System 4 WKE 516 Engine Room Simulation 2 4 ACR 450 Principles of Marine Refrigeration 4 WKR513 Vessel Management and Maritime Law 4 TOTAL CP 60 NAUTICAL SCIENCE PROGRAMME Certificate II in Ships Operation (Class 5) Unit Code Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name CP CSO 200 Mathematics 3 CSO210 Navigation-Terrestrial 3 CSO201 Applied Science 3 CSO211 Meteorology 3 CSO202 Seamanship Theory 3 CSO212 Visual Communication 3 CSO203 Seamanship Practical 5 CSO213 General Ships Knowledge 4 CSO204 Communication Skills 5 CSO207 Operational Safety 5 CSO206 Enabling Computer 3 CSO215 Bridge Equipment 3 CSO205 Deck Workshop Practice 3 CSO216 ROR/Watch keeping/Oral 3 1 CSO208 Social Education 4 CSO218 ISO9000 & 14000 awareness course CSO209 Navigation-Celestial 3 CSO253 Maritime law 3 CSO252 Simulator Training 3 TOTAL CP 63 Note: Prerequisite : Safety Certificate and MSAF approval Letter Students has to complete 9 months Sea time COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK DME 510 Certificate III in Ships Operation (Class 4 Master) CSO 300 Mathematics 4 CSO305 General Ships Knowledge 5 CSO 301 Applied Science 3 CSO314 Maritime Law 5 CSO 311 Ocean & Offshore Navigation 4 CSO302 Coastal Navigation 5 CSO313 Principles of Navigation 4 CSO352 Simulator Training 3 CSO303 Meteorology 5 CSO317 ROR/Watch keeping/Orals 5 CSO316 Bridge Equipment 4 CSO319 Engineering Knowledge for deck Officers 5 157 CSO304 Operational Safety 5 CSO306 Visual Communication 3 CSO320 ISO 9000 & 14000 awareness course TOTAL CP 1 61 Prerequisite:9 months approved sea service while holding Class 5 Master Certificate of Competency and MSAF Approval Letter Certificate IV in Ships Operation (Class 3 Master) Unit Code Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name CP CSO500 Mathematics 5 CSO505 Coastal Navigation 5 CSO501 Applied Science 5 CSO506 Meteorology 5 CSO502 Principles of Navigation 5 CSO508 General Ships Knowledge 5 CSO503 Bridge Equipment 5 CSO509 Visual Communication 3 CSO504 Ocean & Offshore Navigation 5 CSO507 Operational Safety 5 EVG401 Ethics, Values & Governance 4 CSO520 ROR/Watch Keeping/ Orals 5 CSO521 ISO 9000 & 14000 awareness course 1 CSO511 Maritime Law 3 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK TOTAL CP 61 Prerequisite: 9 months approved sea service while holding Class 4 Master Certificate of Competency and MSAF Approval Letter Trade Diploma in Nautical Science (Deck Watch keeper) Unit Code Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name CP DNS500 Mathematics 5 DNS505 Coastal Navigation 5 DNS501 Applied Science 5 DNS506 Meteorology 5 DNS502 Principles of Navigation 5 DNS508 General Ships Knowledge 5 DNS503 Bridge Equipment 5 DNS509 Visual Communication 3 DNS504 Ocean & Offshore Navigation 5 DNS507 Operational Safety 5 EVG401 Ethics, Values & Governance 4 DNS520 ROR/Watch Keeping/ Orals 5 DNS521 ISO 9000 & 14000 awareness course 1 DNS511 Maritime Law 3 TOTAL CP 61 Prerequisite: 9 months approved sea service with completion of assignment book. Trade Diploma in Nautical Science (DA1) Unit Code Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name CP DNS200 Mathematics 3 DNS210 Navigation-Terrestrial 3 DNS201 Applied Science 3 DNS211 Meteorology 3 DNS202 Seamanship Theory 3 DNS212 Visual Communication 3 DNS203 Seamanship Practical 5 DNS213 General Ships Knowledge 5 DNS204 Communication Skills 5 DNS207 Operational Safety 5 DNS206 Enabling Computer 3 DNS215 Bridge Equipment 3 DNS205 Deck Workshop Practice 3 DNS216 ROR/Watch keeping/Oral 3 DNS208 Social Education 4 DNS218 ISO9000 & 14000 awareness course 1 DNS209 Navigation-Celestial 3 DNS253 Maritime law 3 MSC112 Elementary First Aid MNS204 Personal Safety and Social Responsibility MSC110 Basic Fire Fighting MNS101 Personal Survival Technics MSC106 Seafarer Designated Security Duties TOTAL CP 67 Prerequisite: Pass in FSLC /FSFE (English, Math and Physics). 9 months Sea Service (DA2) Trade Diploma in Nautical Science (DA3) 158 Unit Code DNS 300 Unit Name Mathematics CP 4 Unit Code DNS305 Unit Name General Ships Knowledge CP 5 DNS 301 Applied Science 3 DNS314 Maritime Law 5 DNS 311 Ocean & Offshore Navigation 4 DNS302 Coastal Navigation 5 DNS313 Principles of Navigation 4 DNS352 Simulator Training 3 DNS303 Meteorology 5 DNS317 ROR/Watch keeping/Orals 5 DNS316 Bridge Equipment 4 DNS319 Engineering Knowledge for deck Officers 5 DNS304 Operational Safety 5 DNS320 ISO 9000 & 14000 awareness course 1 DNS306 Visual Communication 3 TOTAL CP 61 Prerequisite: completion of DA2 (9 months Sea Time) and completion of assignment DA4-9 months Sea Time Trade Diploma in Nautical Science (DA5) Unit Code Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name CP Mathematics 5 DNS505 Coastal Navigation 5 DNS501 Applied Science 5 DNS506 Meteorology 5 DNS502 Principles of Navigation 5 DNS508 General Ships Knowledge 5 DNS503 Bridge Equipment 5 DNS509 Visual Communication 3 DNS504 Ocean & Offshore Navigation 5 DNS507 Operational Safety 5 EVG401 Ethics, Values & Governance 4 DNS520 ROR/Watch Keeping/ Orals 5 DNS521 ISO 9000 & 14000 awareness course 1 DNS511 Maritime Law 3 TOTAL CP 61 Note: 9 months Sea Time and completion of assignment DEPARTMENT OF SAFETY AND SURVIVAL Supplementary Courses Unit Code Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name MNS 101 Proficiency in Personal Survival Techniques 5 MNS 105 Proficiency in Survival Craft and Rescue Boats other than Fast Rescue Boats MNS 204 Personal Safety and Social responsibility 5 MSC 113 Proficiency in Medical First Aid MSC 112 Proficiency in Elementary First Aid 5 MSC 111 Proficiency in Advance Fire Fighting MSC 110 Proficiency in Fire Prevention and Fire Fighting 5 MSC 107 Basic Training for Oil and Chemical Tanker Cargo Operations MSC 108 Basic Training for Liquefied Gas Tanker Cargo Operations 5 MSC109 Crowd Management MSC 105 Proficiency in Security Awareness 4 MSC 106 Proficiency in Security Training for seafarers with designated security duties MNS 207 Proficiency as Ship Security Officer 1 CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK DNS500 DEPARTMENT OF MARINE SIMULATION Unit Code Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name DMS 401 Electronic Chart Display and Information system (ECDIS) DMS 408 Ship Handling and Maneuvering DMS 402 Radar Observation and Plotting DMS 409 Navigational Watch keeping Simulator DMS 410 Global Maritime Distress Safety System- General Operator certificate DMS 403 Automatic Radar Plotting Aids CP 159 DMS 404 Radar Simulator DMS 411 Global Maritime Distress Safety System- Restricted Operators Certificate DMS 405 Bridge Resource Management for Operational Level DMS 451 Engine Room Simulator Training For Operational Level DMS 406 Bridge Resource Management For Management Level DMS 452 Bridge and Engine Room for Operational DMS 407 Bridge Team Management (BTM) DMS 453 Bridge and Engine Room for Management DEPARTMENT OF SHIPBUILDING Certificate IV in Shipbuilding Stage 1 Unit Code Stage 2 Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Boat Technology 1 4 TCS310 Boat Technology 2 3 TCS302 Applied Drawing 1 4 TCS311 Applied Drawing 2 4 TCS303 Applied Mathematics 1 4 TCS312 Applied Mathematics 2 3 TCS304 Applied Lofting 1 4 TCS313 Applied Lofting 2 4 TCS305 Shipyard Practice 1 5 TCS314 Shipyard Practice 2 6 TCS306 Seamanship 1 2 TCS315 Applied Ship Stability 1 3 COM301 Technical Communication 2 TCS316 Electrical Principle 2 2 TCS308 Material and Measurement 3 TCS317 Introduction to Welding Technology 5 TCS309 Electrical Principle 1 2 TOTAL CP 30 TOTAL CP 30 Stage 3 Unit Code Stage 4 Unit Name CP Unit Code Unit Name CP TCS401 Applied Boat Technology 4 TCS410 Applied Ship Technology 4 TCS402 Applied Drawing 3 3 TCS411 Applied Drawing 4 4 TCS403 Applied Mathematics 3 3 TCS412 Applied Lofting 4 4 TCS404 Applied Lofting 3 3 TCS413 Shipyard Practice 4 4 TCS405 Shipyard Practice 3 4 TCS414 Applied Ships Stability 3 5 TCS406 Welding and Fabrication 1 4 TCS415 Applied Mechanics 4 TCS407 Computer Techniques 2 TCS416 Welding and Fabrication 2 3 TCS408 Applied Ship Stability 2 4 TCS417 Ships Plumbing and Joinery 3 TCS409 Introduction to Ships Plumbing 3 TOTAL CP 30 TOTAL CP Job Opportunities The job opportunities are offered on government, local cargo and passenger vessels, tourist Industry boats, regional island shipping agencies and on foreign-going vessels. Graduates have a strong basis to venture out towards starting their own boatbuilding business and to be captains or engineers on their own fishing or passenger boats. Programmes Offered DURATION: 12 WEEKS VENUE: LAUCALA BAY, SUVA TRIMESTER 1 TRIMESTER 2 NAUTICAL SCIENCE DEPARTMENT Trade Diploma in Ships Operations (Deck Watch keeper) 160 CP TCS301 Trade Diploma in Nautical Science (DA3) 31 Trade Diploma in Nautical Science (DA1) Trade Diploma in Nautical Science (DA5) Trade Diploma in Nautical Science (DA3) Trade Diploma in Nautical Science (DA5) MARINE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT Trade Diploma in Marine Engineering (EA5) Trade Diploma in Marine Engineering (EA1) Trade Diploma in Marine Engineering (EA1) Trade Diploma in Marine Engineering (EA3) Trade Diploma in Marine Engineering (Watch keeper) SHIPBUILDING DEPARTMENT Certificate IV in Shipbuilding (Stage 1) Certificate IV in Shipbuilding (Stage 2) Certificate IV in Shipbuilding (Stage 4) Certificate IV in Shipbuilding (Stage 3) For More Information Contact: Academic Officer: Sonal Sharma Phone: 3315979 Ext: 5700 Email: AO-FMA@fnu.ac.fj COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Head of Academy: Captain Voi Garisau Phone: 331 5979 Ext : 5750 E-mail: HOA-FMA@fnu.ac.fj 161 SCHOOL OF AVIATION STUDIES The programmes offered are: a) Certificate IV in Aircraft Maintenance Engineering - (Mechanical) This programme duration is 3 years and consists of 6 Units @ I Unit per trimester. The first three units are taught consecutively before the students are released for 1 year of practical attachment to the various airlines in Fiji for the local students and regional airlines for the overseas students. Unit 6 is then taught in trimester 3 of year 3. Graduation should follow when all the components are satisfactorily completed. COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK b) Certificate IV in Aircraft Maintenance Engineering - (Avionics) This programme duration is 3 years and consists of 6 Units @ I Unit per trimester. The first two units are taught consecutively before the students are released for 1 trimester of practical attachment to the various airlines in Fiji for the local students and regional airlines for the overseas students. Units 3, 4 and 5 are taught after the practical attachment followed by another 2 trimesters of practical. Unit 6 is then taught in trimester 3 of year 3. Graduation should follow when all the components are satisfactorily completed. c) Other programmes and short courses can be developed and delivered as per the needs of the aviation industry. All programmes are offered at the Nadi campus. We thank you for choosing the Fiji National University as your tertiary education provider and wish you well in your studies. Staff Profile HEAD OF SCHOOL SAKARAIA CAUCAU Cert. (Training Officers and Instructors Course) USP; Cert. (License Without Type Rating Electrical DC and AC Power) Luton, UK; Cert. (License Without Type Rating General Aircraft Instruments and Flight Path and Air Data Computations) Luton, UK; Cert. (Advance Avionics) Jakarta, Indonesia; Cert. (B737 – 200 Airframe Systems); Cert. (‘X’ Non Radio and Radio Coupled Auto Pilot); Cert. (B767 – 200/300 Full Type Course); Cert. (ATR – 42 Full Type Course); Cert. (B737 – 300/400/500/600/700/800 Avionics Systems) Seattle, Washington, USA; Cert. (B767 Ramp Course); Cert. (B767 – 200/300 Avionics, Extended Range Operations); Cert. (B747 Ramp Course); Cert. (Pratt and Whitney Engine Condition Trend Monitoring) Brisbane Australia; Cert. (Safety Management Systems) Singapore. LECTURER JOSEVA TURAGANIVALU Licensed Aircraft Maintenance Engineer; Full Aircraft Types: Heron DH114, Islander BN2A, BN2B, HS748, BAC 1-11, Bandeirante EMB110, Twin Otter DHC-6. Rotary Wings: Ecureil AS355F2, Dauphin AS365N2, Robinson R22, Bell206; Cert. (HRM); Cert. (Executive .Management); Cert. (Boeing’s Structure Awareness); Cert. Safety and Lead Audit); Cert. (Safety Management Systems) 162 KEVERIELI NAITINI Licensed Aircraft Maintenance Engineer (Avionics), Trade Certificate in Electrical and Electronics FIT; Certificate IV in Aeroskills (Avionics) TAFE NSW. SHAVNEEL KARAN Bachelor of Engineering Technology (Mechanical and Manufacturing) USP; Aircraft Maintenance Certificate, (CASA of Australia) VINEET DUTT Bachelor of Engineering with Honors in Aircraft Engineering University of Highlands and Islands, (Scotland) TUTOR SHONAL SRANEET CHAND Trade Certificate in Aircraft Maintenance (Mechanical) WORKSHOP TECHNICIAN SULIASI VULAONO Certificate in Human Factors Training, Ramp Training, Limited Approved Certifying Engineer, Aircraft Type SHORTS SD3-30 OFFICE ADMINISTRATOR ARIETA KEDRAIKA, Diploma in Office MINIMUM ENTRY REQUIREMENT Certificate IV Programmes(Quota-Based) : 280 out of 400 marks in Form 6 with minimum of 50% in English, Mathematics, Physics and any other 1 Science or Technology subjects. Trimester Mode Programmes for 201 For any enquiry on the trimester mode programmes for 2016 please contact the Head of School. Programmes, Units and Modules CERTIFICATE IV IN AIRCRAFT MAINTENANCE ENGINEERING (AVIONICS) Unit 1 Unit 2 Module Name CP Module Code Module Name CP COM201 Technical Communication 4 AMA321 Aircraft Servicing and Handling 6 OHS403 Occupation Health and Safety 10 AMA322 Maintenance Practices Avionics 1 6 AMA311 Introduction to Aviation and OHS 6 AMA323 Maintenance Practices Avionics 2 6 AMA312 Aircraft Maintenance Practices (General) 6 AMA324 Electrical Fundamentals DC Theory 2 6 AMA313 Aircraft Materials and Processes 6 AMA325 Electrical Fundamentals DC Theory 3 6 AMA314 Electrical Fundamentals DC Theory 1 6 AMA326 AC Theory and Power Systems 1 6 Total CP 38 Total CP Unit 3 36 Unit 4 AMA331 AC Theory and Power Systems 2 6 AMA441 Analogue Fundamentals 2 6 AMA332 AC Theory and Power Systems 3 6 AMA442 Aircraft Electrical Systems 2 6 AMA333 Aircraft Electrical Systems 1 6 AMA443 Aircraft Electrical Systems 3 6 AMA334 Aircraft Instrument Systems 1 6 AMA444 Aircraft Instrument Systems 3 6 AMA335 Aircraft Instrument ¬¬¬Systems 2 6 AMA445 Analogue Fundamentals 3 6 AMA336 Analogue Fundamentals 1 6 AMA446 Digital Techniques 1 6 Total CP 36 Total CP Unit 5 36 Unit 6 AMA451 Digital Techniques 2 6 AMA461 Pulse Systems 6 AMA452 Radio Principles 1 6 AMA462 Radio Navigation Systems 6 AMA453 Radio Principles 2 6 AMA463 Flight Controls and Flight Director Systems 6 AMA454 Radio Principles 3 6 AMA464 Automatic Flight Control Systems 6 AMA455 Aircraft Environmental Systems 6 AMA465 Inertial Navigation and Inertial Reference Systems 6 AMA456 Digital Techniques 3 6 AMA466 Aircraft Oxygen Systems 6 Total CP 36 Total CP COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Module Code 36 * Please note that the Aviation programme is taught on a modular basis, which means that, a module is completed before the commencement of the next. 163 CERTIFICATE IV IN AIRCRAFT MAINTENANCE ENGINEERING (MECHANICAL) Unit 1 Unit 2 Module Code Module Name CP Module Code Module Name CP COM301 Technical Communication (Aero) 5 AMM312 Basic Electricity A 6 OHS403 Occupational Health and Safety (Fiji) 10 AMM313 Basic Electricity B 6 AMM311 Occupational Health and Safety (Aero) 6 AMM321 Aircraft Electrical Systems 6 AMM314 Trade Technology and Practices 6 AMM328 Theory of Flight 6 AMM315 Aircraft Basic Science 6 AMM325 Aircraft Maintenance Practices A 6 AMM316 Fabrication and Metallurgy 6 AMM326 Introduction To Aircraft Maintenance 6 Total CP 39 Total CP Unit 3 Unit 4 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK Introduction to Ethics Value & Governance 6 AMM431 AMM322 Aircraft Metalwork A 6 AMM323 Aircraft Metalwork B 6 AMM324 Aircraft Metalwork C AMM327 AMM435 ETH401 36 Piston Engine Theory and Construction 6 AMM432 Piston Engine Systems 6 AMM433 Piston Engine Maintenance 6 6 AMM434 Aircraft Propellers 6 Composites 6 AMM436 Aircraft Engine Instrument Systems 6 Aircraft Instrument Systems 6 Total CP 36 Total CP Unit 5 30 Unit 6 Gas Turbine Principles and Construction 6 AMM442 Fluid Power Systems 6 AMM438 Gas Turbine Systems 6 AMM444 Auxiliary Systems 6 AMM439 Gas Turbine Maintenance 6 AMM446 Helicopters 6 AMM441 Aircraft Structures and Systems 6 AMM447 Aircraft Environmental Systems 6 AMM443 Aircraft Flight Controls 6 AMM448 Mobile Air-conditioning Systems 6 AMM445 Aircraft Maintenance Practices B 6 ACR 304 Refrigerants 6 AMM437 Total CP 36 Total CP 36 Please note that the Aviation programme is taught on a modular basis, which means that, a module is completed before the commencement of the next. General Guidelines The Prerequisite unit must be completed before enrolment is allowed in the dependent unit eg. AMM312 Basic Electricity A must be passed before enrolment in AMM313 Basic Electricity B. Job Opportunities: Successful holders of Certificates IV in Aircraft Maintenance Engineering would become Tradesman, AMEs, LAMEs, Maintenance Planners, Workshop Technicians, Quality Assurance Inspector, Supervisors, Managers and Directors of the vibrant aviation industry. Graduates from these programmes will also have opportunities to be employed in other industries apart from Aviation because of the range of subjects studied which include Electrical, Electronics, Instrumentation and Radio. 164 Unit Descriptors: AMA311: Introduction to Aviation and OHS This module introduces the students to the general facets of the aviation industry and familiarises them with the basic construction of aircraft, basic theory of flight, aircraft propulsion systems and flight control systems. Also, this module provides students with an overview of the Occupational Health and Safety (OHandS) requirements associated with the aircraft engineering environment. Prerequisites: Nil AMA312: Aircraft Maintenance Practices (General) This module introduces the students to general maintenance information on tools, tooling and documentation involving aircraft servicing, design and repair. Prerequisites: Nil AMA314: Electrical Fundamentals DC Theory 1 This module provides an introduction to the principles and applications of electricity. The module also introduces the student to basic meters and their applications. Prerequisites: Nil AMA321: Aircraft Servicing and Handling This module introduces students to the fundamental requirements of servicing and handling an aircraft whilst on the ground in a manner to ensure safety and ongoing serviceability for flight. Prerequisites: AMA311 AMA322: Maintenance Practices Avionics 1 This module provides students with the knowledge and skills necessary to solder and de-solder electronic components, connectors and terminate electrical cables using soldering techniques. It also provides the student with the knowledge and understanding of the application of circuit protection and electrical control devices. Prerequisites: AMA311, AMA312 AMA323: Maintenance Practices Avionics 2 This module develops students with the skills and knowledge needed to terminate aircraft electrical hardware and carry out repairs and minor manufacturing tasks on electrical looms and harnesses. Prerequisites: AMA322 AMA324: Electrical Fundamentals DC Theory 2 This module introduces the students to the fundamental concepts of Inductance and Capacitance. Prerequisites: AMM314 AMA326: AC Theory and Power Systems 1 This module provides students with a thorough understanding of single phase alternating current principles, concepts and laws. Also, this module develops in the students the required electrical knowledge needed to inspect, test and troubleshoot aircraft avionics systems. Prerequisites: AMA325 AMA331: AC Theory and Power Systems This module provides students with a thorough understanding of polyphase alternating current principles, concepts and laws. Also this module will familiarise the student with polyphase generation and AC machines. Prerequisites: AMA326 AMA332: AC Theory and Power Systems 3 This module familiarises the student with single and polyphase motors and also to provide the student with an introduction to Error Detection Devices, Synchro Devices, and Servomechanisms. Prerequisites: AMA331 AMA333: Aircraft Electrical Systems 1 This module familiarizes students with the operation of aircraft electrical systems and components associated with power distribution, engine starting and ignition. Prerequisites: AMA325, AMA332 AMA334: Aircraft Instrument Systems 1 This module introduces the student to the fundamental concepts of instrumentation with a sound understanding of the basic aircraft instruments and pilot static systems. Prerequisites: Nil AMA335: Aircraft Instrument Systems 2 This module provides students with a sound understanding of the operating principles and applications of engine and associated instruments. Also, this module gives the student a sound understanding of the operating principles and applications of the various aircraft instrument systems. Prerequisites: AMA334 AMA336: Analogue Fundamentals 1 This module familiarizes student with the characteristics of the fundamental building blocks of electronic circuits and systems. It is not the purpose of this module to teach students to in-depth component level of complex circuits, but rather to treat the functional blocks as COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK AMA313: Aircraft Materials and Processes This module provides the student with basic theory, practice, associated terms and processes which will enable them to identify, handle, inspect and work with a range of metals and other materials. Prerequisites: AMA311 AMA325: Electrical Fundamentals DC Theory 3 This module provides a framework for the evaluation, validation and recording of workplace evidence to support the assessment of the following Module of Competence: Maintain and/or Repair Aircraft Mechanical Components or Parts Also, this module should be undertaken in conjunction with other modules, which provide related skills and knowledge. Prerequisites: AMA324 165 components of larger over-all systems. This will provide the student with the underpinning knowledge necessary to carry out safe maintenance, servicing, testing and fault diagnosis of analogue circuitry on a wide range of aircraft systems. Prerequisites: AMA 314 AMA441: Analogue Fundamentals 2 This module familiarizes students with the characteristics of the fundamental building blocks of electronic circuits and systems. It is not the purpose of this module to teach students to in-depth component level of complex circuits, but rather to treat the functional blocks as components of larger over-all systems. This will provide the student with the underpinning knowledge necessary to carry out safe maintenance, servicing, testing and fault diagnosis of analogue circuitry on a wide range of aircraft systems Prerequisites: AMA 336 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 166 AMA442: Aircraft Electrical Systems 2 This module familiarizes students with the operation of aircraft electrical systems and components associated with aircraft lighting, warning and protection systems. This module also introduces the landing gear and antiskid systems. Prerequisites: AMA325, AMA333 AMA443: Aircraft Electrical Systems 3 This module familiarises students with the operation of aircraft electrical systems and components associated with aircraft batteries and fuel systems. Prerequisites: AMA442 AMA444: Aircraft Instrument Systems 3 This module provides the student with a sound understanding of gyroscopic principles, gyro flight instruments vacuum systems, and advanced instruments used to process and/or display attitudes. The module also includes the operating principles and applications of magnetic compasses, compass systems as well as an understanding of Ground Proximity Warning and Flight Data Recorders. Prerequisites: AMA335 AMA445: Analogue Fundamentals 3 This module familiarizes students with the characteristics of the fundamental building blocks of electronic circuits and systems. It is not the purpose of this module to teach students to in-depth component level of complex circuits, but rather to treat the functional blocks as components of larger over-all systems. This will provide the student with the underpinning knowledge necessary to carry out safe maintenance, servicing, testing and fault diagnosis of analogue circuitry on a wide range of aircraft systems. Prerequisites: AMA441 AMA446: Digital Techniques 1 This module familiarizes students with the characteristics of the fundamental building blocks of digital electronic circuits and systems. This module will provide the student with the underpinning knowledge necessary carry out safe maintenance, servicing, testing and fault diagnosis on a wide range of aircraft digital systems. Prerequisites: AMA404e AMA451: Digital Technique 2 This module familiarizes students with the characteristics of the fundamental building blocks of digital electronic circuits and systems. This will provide the student with the underpinning knowledge necessary carry out safe maintenance, servicing, testing and fault diagnosis on a wide range of aircraft digital systems Prerequisites: AMA446 AMA452: Radio Principles 1 This module familiarizes the student with basic radio principles. This is a module that introduces concepts and applications only. This module is a Prerequisite for the more in depth modules. Prerequisites: AMA332, AMA445 AMA453: Radio Principles 2 This module familiarizes students with the principles of radio receivers. Prerequisites: AMA 452 Radio Principles 1 AMA454: Radio Principles 3 This module familiarizes the student with the principles of Single Sideband Suppressed Carrier and Frequency Modulation radio transmissions. It is also intended to introduce the student to HF, VHF UHF and SATCOM radio transceivers. Prerequisites: AMA453 AMA455: Aircraft Environmental Systems This module familiarizes the student with the operation of aircraft environmental systems and components. This module will also provide the student with the underpinning knowledge necessary to carry out maintenance, servicing, testing and fault finding on such systems. Prerequisites: AMA336 AMA456 : Digital Techniques 3 This module provides the student with the knowledge to carry out safe maintenance, testing and fault diagnosis of digital circuitry. Prerequisites: AMA451 AMA461: Pulse Systems This module familiarizes the student with radio pulse systems. Prerequisites: AMA454 AMA462: Radio Navigation System This module familiarizes the student with radio navigation principles. Prerequisites: AMA454, AMA461 AMA463: Flight Controls and Flight Director Systems This module familiarizes the student with the operation of flight control and flight director systems applicable to fixed wing aircraft. This module will also provide the student with the underpinning knowledge necessary to carry out maintenance, servicing, testing and fault finding on flight control and flight director systems on fixed wing aircraft. Prerequisites: AMA444, AMA445, AMA456 AMA464: Automatic Flight Control Systems This module familiarizes the student with the operation of automatic flight control systems applicable to fixed wing aircraft. This module will also provide the student with the underpinning knowledge necessary to carry out maintenance, servicing, testing and fault finding on automatic flight control systems on fixed wing aircraft. Prerequisites: AMA463 AMA466: Aircraft Oxygen Systems This module provides the student with an understanding of the operation, line maintenance procedures and requirements of gaseous dry breathing oxygen systems. AMM311: Occupational Health and Safety (Aero) This module provides students with knowledge and skills related to workplace health and safety legislation and practices, basic workshop safety practices, basic aircraft and system maintenance, documentation and airworthiness requirements. AMM312: Basic Electricity A This module introduces students to basic electrical principles, laws and concepts. Prerequisites: AMM 311 AMM313: Basic Electricity B This module enables the students in the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for understanding electrical technology. Prerequisites: AMM312 AMM 314: Trade Technology and Practices This module provides the student with knowledge and skills relevant to the theories and practices of precision hand fitting. AMM315: Aircraft Basic Science This module provides students with trade level knowledge and skills relevant to physical science principles. Prerequisites: Nil AMM316: Fabrication and Metallurgy AMM321: Aircraft Electrical Systems This module enables the students in the development of intermediate knowledge and skills of aircraft electrical systems. Prerequisites: AMM312, AMM313 AMM322: Aircraft Metalwork A This module provides the student with knowledge and skills relevant to aircraft structural loads and structural repair requirements. Prerequisites: AMM311 AMM323: Aircraft Metalwork B This module extends students’ knowledge and skills developed in module AMM201b towards a trade level ability to evaluate aircraft damage. Prerequisites: AMM322 AMM324: Aircraft Metalwork C This module extends students’ knowledge and skills developed in module AMM201c towards a trade level ability to evaluate aircraft damage, and devise and incorporate suitable repair schemes. Prerequisites: AMM323 AMM325: Aircraft Maintenance Practices A This module introduces students to components parts, materials, and accepted inspection and maintenance. AMM326: Introduction to Aircraft Maintenance This module provides students with knowledge and skills relevant to fundamental aircraft maintenance practices, workplace health and safety requirements and documentation and airworthiness requirements. AMM327: Composites This module extends students’ knowledge and skills related to non-metallic structural elements of aircraft structures, non-metallic structural materials in use, their construction and repair practices. Prerequisites: AMM316 AMM328: Theory of Flight This module introduces the aircraft maintenance engineer/mechanic to the principles of aerodynamics. Prerequisites: AMM315 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK AMA465: Inertial Navy and Inertial Reference Systems This module familiarizes the student with the operation of inertial navigation systems (INS) and inertial reference systems (IRS). This module will also provide the student with the underpinning knowledge necessary to carry out workshop maintenance, servicing, testing and fault finding on INS and IRS. Prerequisites: AMA444, AMA445 This module introduces students to basic ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy, basic soldering and welding techniques and practices, and basic non-destructive inspection techniques. AMM431: Piston Engine Theory and Construction This module provides students with knowledge and skills relating to the construction and operating principles of four stroke spark ignition aircraft engines. Prerequisites: AMM325 AMM432: Piston Engine Systems This module provides students with knowledge and skills relevant to the systems required for the operation of four strokes spark ignition aircraft engines.Prerequisites: AMM431 167 AMM433: Piston Engine Maintenance This module extends piston engine training, including installation, maintenance and operation of engines installed in fixed-wing and rotary-wing aircraft. Prerequisites: AMM432 AMA434: Aircraft Propellers This module provides students with knowledge and skills relating to propellers and systems. Prerequisite: AMM433 AMM435: Aircraft Instrument Systems This module provides students with knowledge and skills necessary to maintain aircraft instruments systems. Prerequisite: AMM315 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK AMM436: Aircraft Engine Instrument Systems This module provides students with knowledge and skills necessary to maintain aircraft engine instruments systems. Prerequisites: AMM435 AMM437: Gas Turbine Principles and Construction This module provides students with knowledge and skills relating to gas turbine engine operation and construction. Prerequisites: AMM436 AMM438: Gas Turbine Systems This module provides students with knowledge and skills relating to gas turbine engine systems. Prerequisites: AMM437 AMM439: Gas Turbine Maintenance This module extends the practical aspects of gas turbine engine operation and maintenance. Prerequisites: AMM438 AMM441: Aircraft Structures and Systems This module extends students’ knowledge and skills related to aircraft structures, systems and components, and their maintenance. Prerequisites: AMM315 AMM442: Fluid Power Systems This module provides student with knowledge and skills relevant to hydraulic systems and components principles and maintenance, pneumatic systems and components and high pressure air systems. Prerequisites: AMA441 AMM443: Aircraft Flight Controls This module introduces the aircraft maintenance engineer/mechanic the principles of aerodynamics. Prerequisites: AMM328 AMM444: Auxiliary Systems This module extends the students’ knowledge and skills related to aircraft structures, systems and components, and their maintenance. Prerequisites: AMM443 AMM445: Aircraft Maintenance Practices B This module provides the student with knowledge and skills relevant to general aircraft maintenance practices. Prerequisites: AMM325 AMM446: Helicopters This module provides the student with knowledge and skills relevant to helicopter aerodynamics, structures, controls and systems. Prerequisites: AMM328 AMM447: Aircraft Environmental Systems This module provides students with knowledge and skills relevant to pressurization systems air and vapour cycle machines, and cabin temperature control systems. Prerequisites: AMM444 AMM448: Mobile Air-conditioning Systems This module enables the student in the development of the elementary knowledge and skills required for the Aircraft trade. Prerequisites: AMM447 For More Information Contact: Head of School Phone: 6280574 Ext: 6700 E-mail: enquiry-engineering@fnu.ac.fj HOS-Aviation@fnu.ac.fj OA – Ms. Arieta Kedraika Ext: 6704 Email:OA-Aviation@fnu.ac.fj 168 COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 169 2016 OF ENGINEERING, AND TECHNOLOGY COLLEGECOLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, SCIENCE SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY HANDBOOK 170 HANDBOOK